NCERT Solutions for Class 5 EVS Our Wondrous World Chapter 7 Energy – How Things Work updated for Session 2025-26. Class 5 EVS Chapter 7 explains how energy helps things move, work and change. The chapter helps students understand different forms of energy like heat, light, sound and electrical energy. It shows the importance of the Sun as a natural source of energy and explains the use of electricity in daily life. Simple activities and examples help students learn how energy is stored, used and conserved in an easy way.
Class 5 EVS all Chapters Answers
Energy – How Things Work: Class 5 Our Wondrous World Chapter 7 Solutions
Page 114
What is Energy?
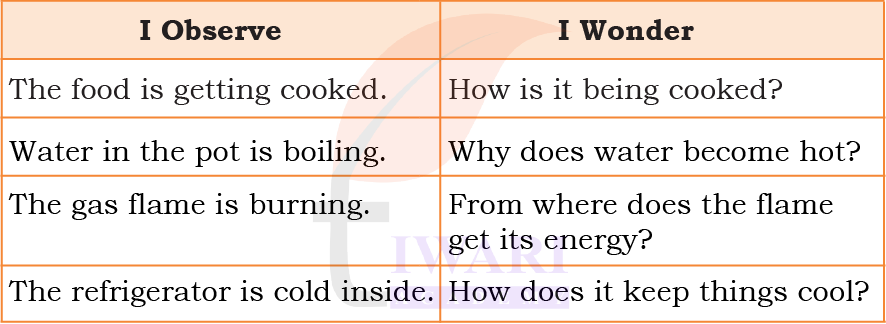
See AnswerEnergy is what makes things move, shine, make sound or become hot or cold.
For example:
► A fan moves because of electric energy.
► A bulb glows because of light energy.
► We run and play because food gives us energy.
So, without energy nothing can happen around us.
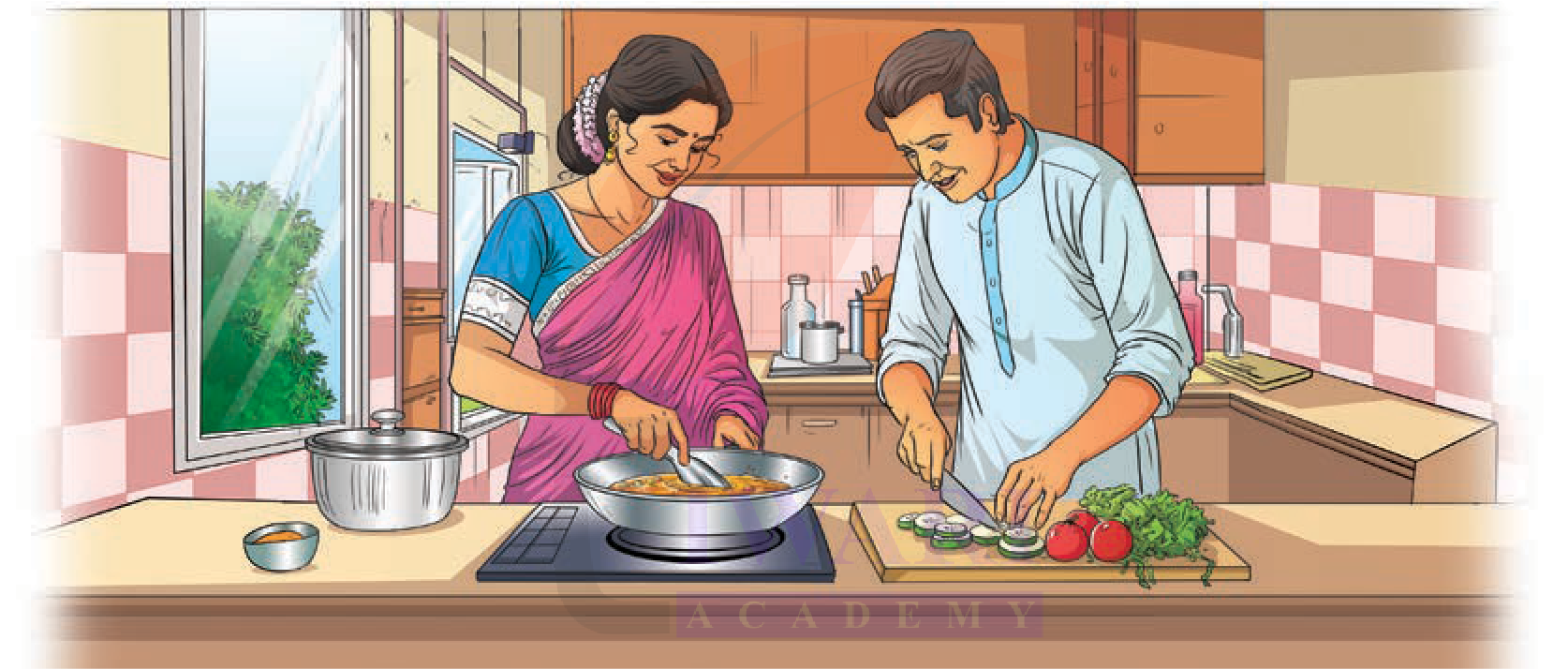

Let us observe a kitchen for some time. Write your observations and the questions that come to your mind in the table given below.

Answer:
Page 115
Similarly, we observe different kinds of activities in nature and society.
From your observation write down at least three things that you have noticed:
• Moving
• Providing light
• Making a sound
• Making things cool
• Making things hot
See Answer• Things that are Moving
Leaves moving when the wind blows.
A bird flying in the sky.
A bicycle moving on the road.
• Things that are Providing Light
The Sun shining during the day.
A bulb glowing in the room.
A candle burning during a power cut.
• Things that are Making a Sound
Birds chirping early in the morning.
A school bell ringing.
A pressure cooker whistling in the kitchen.
• Things that are Making Things Cool
A fan blowing cool air.
A refrigerator keeping food cold.
An air conditioner cooling a room.
• Things that are Making Things Hot
Gas stove heating a pot.
The Sun warming the ground.
An iron rod getting hot in fire.
Class 5 Our Wondrous World Chapter 7 Discussion based Questions
Discuss
What makes these things move, shine, make a sound or get warm and cold?
See AnswerThese things move, shine, make sound or get warm and cold because of energy.
Energy helps everything around us to work.
► Fans move because of electric energy
► Bulbs shine because of light energy
► Drums make sound because of sound energy
► The Sun makes things warm because of heat energy
► Fridges make things cold using electrical energy
So, energy is needed for everything to happen.
Page 116
Think
What would you change in the activity to make the toy move faster or slower?
See Answer► To make the toy (balloon) move faster, I will blow more air into the balloon. This will make the balloon bigger and more air will rush out, so it will move faster.
► To make the toy move slower, I will blow less air into the balloon. With less air inside, it will come out slowly, so the balloon will move slower.
So the speed changes depending on how much air we fill inside the balloon.
Class 5 Our Wondrous World Chapter 7 Thinking Based Questions
Page 117
Think
What happens if you use thinner or thicker rubber bands? Do they sound different?
See Answer► If we use thinner rubber bands, the sound becomes sharp and high.
► If we use thicker rubber bands, the sound becomes deep and low.
Yes, they sound different because thin and thick rubber bands vibrate in different ways.
Page 119
Think
What do cars and scooters need to keep running?
See AnswerCars and scooters need fuel like petrol and diesel to keep running. Vehicles move when they get energy from fuel. So, cars and scooters work because they get energy from petrol and diesel.
Class 5 Our Wondrous World Chapter 7 Writing Based Questions
Write
1. How is food cooked in your house?
See Answer► In my house, we use cooking gas (LPG) to cook food on the gas stove.
► My grandmother sometimes uses a wood-burning chulha to cook rotis.
► We have an electric induction cooktop for making dal and rice.
► During power cuts, we use kerosene stove for cooking.
Page 120
Discuss
1. What kind of fuel do you use at home for cooking?
See Answer• LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) cylinders
• Cooking gas from pipeline
• Wood and coal (in some rural areas)
• Kerosene stoves
• Electric stoves/induction cooktops
2. What are the problems using too much wood or coal?
See Answer• Creates lot of smoke that pollutes air
• Causes breathing problems and cough
• Makes kitchen walls black with soot
• Contributes to deforestation
• Produces harmful gases
• Can cause fires if not handled properly
Page 121
Activity 5
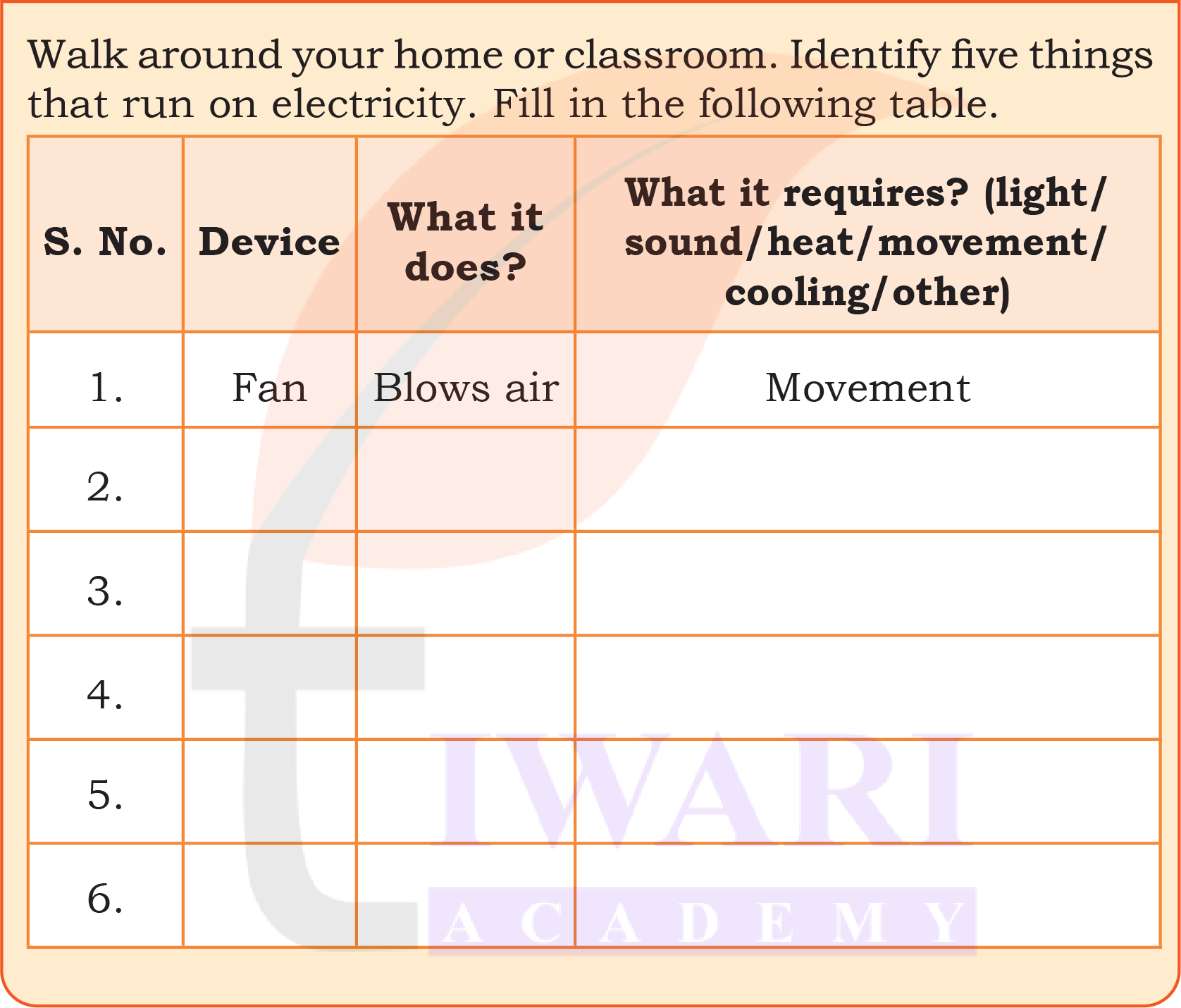
Answer:
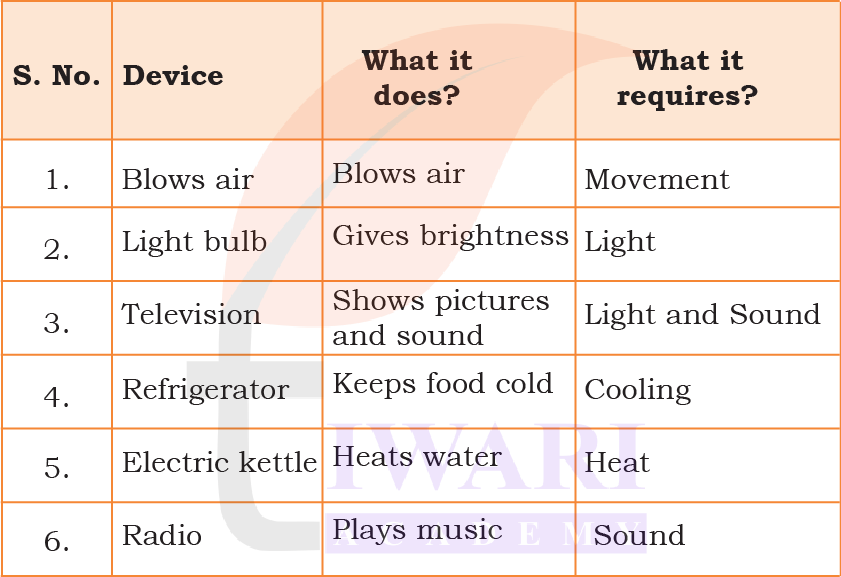
Page 122
Think
What would your day be like if there was no electricity at all?
See AnswerIf there was no electricity at all, my day would be very difficult. I would wake up without an alarm clock. There would be no lights in the house, so it would be dark at night. I would not be able to watch television or use a fan in summer.
My parents could not use the computer or charge their mobile phones. At school, we would not be able to use smart boards or fans. Food in the refrigerator would spoil. Doing homework at night would be hard because there would be less light. Life without electricity would be slow and uncomfortable.
Page 123
Think
Place a small damp cloth in the Sun. Keep another damp cloth in the shade. Which one do you think will dry first? Why?
See AnswerThe damp cloth kept in the Sun will dry first. This is because the Sun gives heat energy. The heat from the Sun helps the water in the cloth to evaporate faster.
The cloth kept in the shade gets less heat, so it will take more time to dry.
Page 125
Think
Have you even seen papads being dried in the sunlight and clothes hung out to dry?
See AnswerYes, I have seen papads being dried in the sunlight and clothes hung out to dry. My grandmother spreads papads on the terrace in sunlight to make them crisp. We hang wet clothes on clotheslines where the sun’s heat energy evaporates the water and dries them completely. This shows how we use clean solar energy in our daily lives without electricity.
Write
Can you think of more examples where we use the Sun, the wind or the flowing water?
See AnswerExamples where we use Sun, wind or flowing water:
Sun energy:
• Drying clothes on clothesline
• Drying grains and vegetables
• Solar water heaters
Wind energy:
• Flying kites
• Sailing boats
• Winnowing grains
• Windmills for grinding flour
Flowing Water energy:
• Water mills for grinding grains
• Washing clothes in flowing river
• Hydroelectric power plants
• Water wheels for irrigation
Page 127
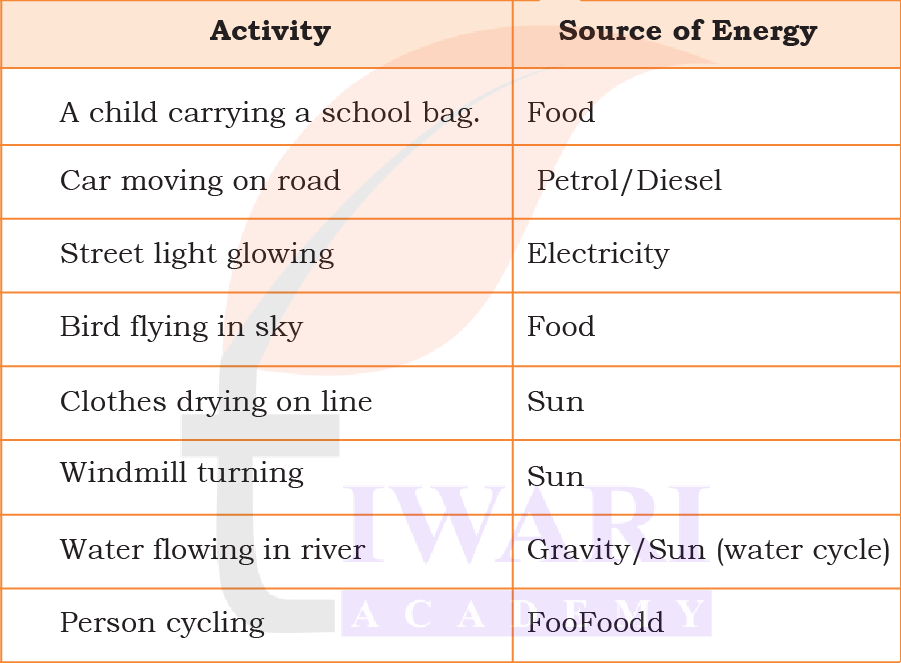
Energy All Around Us
List actions that you see in the picture above and fill in the following table.
Answer:
Class 5 Our Wondrous World Chapter 7 Let Us Reflect
Page 130
1. What will happen if there is no electricity in your house for a day?
See AnswerIf there is no electricity in my house for a day, there will be
• Lights will not work, so the house will be dark at night.
• Fans and coolers will not work, making it very hot.
• Television and computer cannot be used.
• Mobile phones will not get charged.
• Refrigerator will not work and food may spoil.
• Studying at night will be difficult.
• Daily work will become slow and uncomfortable.
2. Why is it better to use solar or wind energy instead of coal?
See Answer• Solar and wind energy do not cause pollution.
• They do not produce smoke or harmful gases.
• Coal causes air pollution when it is burned.
• Solar and wind energy will not get exhausted.
• Coal is limited and can finish one day.
• Using solar and wind energy helps protect the environment.
3. Give two examples where you have seen energy being stored.
See Answer• Energy is stored in a battery and is used to run a torch or remote control.
• Energy is stored in food, which gives us energy to work, play and study.
4. What is the one thing you can do at home to save energy?
See Answer• Switch off lights and fans when not needed
• Use LED bulbs instead of regular bulbs
• Don’t keep refrigerator door open for long
• Use stairs instead of lift when possible
• Dry clothes in sun instead of electric dryer
• Unplug chargers when not in use.
5. Find out how many kilometres a vehicle travels per litre of petrol or diesel. Ask about different vehicles. How will you compare them?
See Answer• Motorcycle: 40-60 km per litre
• Small car: 15-25 km per litre
• Bus: 3-6 km per litre
• Truck: 2-4 km per litre
Comparison:
Heavy vehicles like trucks and buses use more fuel per kilometre. Lighter vehicles with smaller engines travel more distance using less petrol/diesel, making them more economical and better for the environment.
6. Look around you home or classroom. List three objects that use energy and mention their source of energy. For example: Object; Energy Source: Electricity
See Answer• Fan → Electricity
• Bicycle → Food (human energy)
• Gas stove → LPG/Natural Gas
• Solar calculator → Sun energy
• Car → Petrol/Diesel.
7. Create and Share:
(a) Draw or make a simple plan of a ‘clean energy home’ that use solar, wind or any such source of energy.
See AnswerClean Energy Home Plan:
Draw a house with:
• Solar panels on roof for electricity
• Solar water heater for hot water
• Windows placed to get natural light
• Wind chimes or small windmill in garden
• Rainwater harvesting system
• Energy-efficient appliances
(b) Make ‘my energy diary’ for one day, record the number of times you have used the electricity fuel and so on.
See AnswerMy Energy Diary :
Morning:
• Used electricity: 3 times (lights, fan, phone charging)
• Used gas: 1 time (cooking breakfast)
• Used sun energy: 1 time (drying clothes)
Afternoon:
• Used electricity: 4 times (fan, TV, mixer, lights)
• Used fuel: 1 time (car for going to market)
Evening:
• Used electricity: 5 times (lights, fan, TV, phone charging, electric kettle)
• Used gas: 1 time (cooking dinner)
• Total: Electricity – 12 times, Gas – 2 times, Fuel – 1 time, Sun – 1 time

