NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics in English and Hindi Medium PDF file format is for free download updated for new session 2024-25 based on latest NCERT Books. As per the new textbooks issued for academic year 2024-25, the additional exercises are not included in curriculum for exams.
Class 12 Physics Solutions in English Medium
Chapter 1. Electric Charges and Fields
Chapter 2. Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Chapter 3. Current Electricity
Chapter 4. Moving Charges and Magnetism
Chapter 5. Magnetism and Matter
Chapter 6. Electromagnetic Induction
Chapter 7. Alternating Current
Chapter 8. Electromagnetic Waves
Chapter 9. Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Chapter 10. Wave Optics
Chapter 11. Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Chapter 12. Atoms
Chapter 13. Nuclei
Chapter 14. Semiconductor Electronics
Class 12 Physics Solutions in Hindi Medium
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics (Weightage for 2024-25)
| Chapters | Marks |
|---|---|
| 1. Electric Charges and Fields, 2. Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance, 3. Current Electricity | 16 |
| 4. Moving Charges and Magnetism, 5. Magnetism and Matter, 6. Electromagnetic Induction, 7. Alternating Current | 17 |
| 8. Electromagnetic Waves, 9. Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, 10. Wave Optics | 18 |
| 11. Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter, 12. Atoms, 13. Nuclei | 12 |
| 14. Semiconductor Electronics | 07 |
| Two experiments one from each section | 14 |
| Practical record [experiments and activities] | 05 |
| One activity from any section | 03 |
| Investigatory Project | 03 |
| Viva on experiments, activities and project | 05 |
| Total | 100 |
UP Board Students for Class 12 Physics can also download from here. Visit to discussion forum to ask your doubts. CBSE Solutions Apps as well as NCERT Solutions and their answers, solutions of additional exercises, intext questions, back exercises questions with assignments from popular books like S L Arora, Concepts of Physics by H C Verma, Pradeep’s fundamental physics, A B C Physics, Arihant publications books, Full Marks question bank etc.
| Class: 12 | Physics |
| Contents: | NCERT Solutions and Study Material |
| Medium: | Hindi and English Medium |
| Session: | CBSE 2024-25 |
| Content Type: | PDF and Video Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics in English
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics in PDF format is given below to free download for new academic session 2024-25 based on latest CBSE Syllabus. For the regular preparation for CBSE, IIT – JEE Mains and Advance, NEET, BITSAT, GGSIPU use latest NCERT books available in the market. A few questions related to these books are given below. Ask your doubts through Discussion Forum about CBSE or NIOS boards.
Previous Years Questions
Chapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields
1. Does the charge given to a metallic sphere depend on whether it is hollow or solid? Give reason for your answer. [Delhi 2017]
Chapter 2: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
1. A 12 pF capacitor is connected to a 50 v battery. How much electrostatic energy is stored in the capacitor? If another capacitor of 6 pf is connected in series with it with the same battery connected across the combination, find the charge stored and potential difference across each capacitor. [Delhi 2017]
2. Derive the expression for the electric potential due to an electric dipole at a point on its axial line. Depict the equipotential surfaces due to an electric dipole. [Delhi 2017]
Chapter 3: Current Electricity
1. Derive an expression for drift velocity of electrons in a conductor. Hence deduce Ohm’s law. A wire whose cross sectional area is increasing linearly from its one end to the other, is connected across a battery of V volts. Which of the following quantities remain constant in the wire? (a) drift velocity (b) current density (c) electric current (d) electric field. Justify your answer. [Delhi 2017]
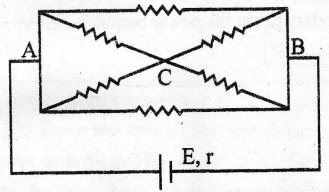
2. State the two Kirchhoff’s laws. Explain briefly how these rules are justified. The current is drawn from a cell of emf E and internal resistance r connected to the network of resistors each of resistance r as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for (i) the current draw from the cell and (ii) the power consumed in the network. [Delhi 2017]
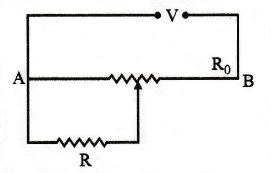
3. A resistance of R draws current from a potentiometer. The potentiometer wire, AB, has a total resistance of R0. A voltage V is supplied to the potentiometer. Derive an expression for the voltage across R when the sliding contact is in the middle of potentiometer wire. [Delhi 2017]
Questions From Board Papers
Chapter 4: Moving Charges and Magnetism
1. Describe the working principle of a moving coil galvanometer. Why is it necessary to use (i) a radial magnetic field and (ii) a cylindrical soft iron core in a galvanometer? Write the expression for current sensitivity of the galvanometer. Can a galvanometer as such be used for measuring the current? Explain. [Delhi 2017]
2. An electron of mass m revolves around a nucleus of charge +Ze. Show that it behaves like a tiny magnetic dipole. Hence prove that the magnetic moment associated with it is expressed as µ = (e/2m)L, where L is the orbital angular momentum of the electron. Give the significance of negative sign. [Delhi 2017]
CHAPTER 5: MAGNETISM AND MATTER
1. At a place, the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field is B and angle of dip is 60. What is the value of horizontal component of the Earth’s magnetic field at equator? [Delhi 2017]
Chapter 6: Electromagnetic Induction
1. A long straight current carrying wire passed normally through the centre of circular loop. If the current through the wire increases, will there be an increase induced emf in the loop? Justify. [Delhi 2017]
2. Define the term ‘Self Inductance’ and write its S.I. unit. Obtain the expression for the mutual inductance of two long co-axial solenoids S1 and S2 wound one over the other, each of length L and radii r1 and r2 and n1 and n2 number of terns per unit length, when a current I is set up in the outer solenoid S2. [Delhi 2017]
3. Draw a labelled diagram of AC generator. Derive the expression for the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the coil. A circular coil of cross-sectional area 200 sq. cm and 20 terns is rotated about the vertical diameter with angular speed of 50 rad/s in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 3.0 × 10^-2 T. Calculate the maximum value of the current in the coil. [Delhi 2017]
Questions From CBSE Board 2017
Chapter 7: Alternating Current
1. Draw a labelled diagram of a step-up transformer. Obtain the ratio of secondary to primary voltage in terms of number of turns and currents in the two coils. A power transmission line feeds input power at 2200 V to a step-down transformer with its primary windings having 3000 turns. Find the number of turns in the secondary to get the power output at 220 V. [Delhi 2017]
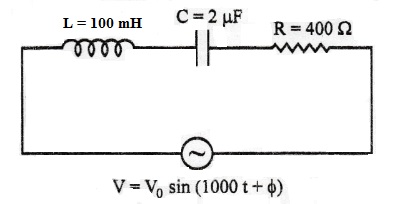
2. Find the value of the phase difference between the current and the voltage in the series LCR circuit shown below. Which one leads in phase: current or voltage? Without making any other change, find the value of the additional capacitor C1, to be connected in parallel with the capacitor C, in order to make the power factor of the circuit unity. [Delhi 2017]
Chapter 8: Electromagnetic Waves
1. How is the speed of em-waves in vacuum determined by the electric and magnetic fields? [Delhi 2017]
2. How does Ampere-Maxwell law explain the flow of current through a capacitor when it is being charged by a battery? Write the expression for the displacement current in terms of the rate of change of electric flux. [Delhi 2017]
Chapter 9: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
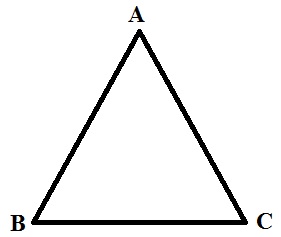
1. A ray of light incident on face AB of an equilateral glass prism, shows minimum deviation of 30. Calculate the speed of light through the prism. Find the angle of incident at face AB so that the emergent ray grazes along the face AC. [Delhi 2017]
2. Mrs. Rashmi Singh broke her reading glasses. When she went to the shopkeeper to order new spects, he suggested that she should get spectacles with plastic lenses instead of glass lenses. On getting the new spectacles, she found that the new ones could not offer satisfactory explanation for this. At home, Mrs. Singh raised the same question to her daughter Anuja who explained why plastic lenses were thicker. (a) Write the two qualities displayed each by Anuja and her mother. (b) How do you explain this fact using lens maker’s formula? [Delhi 2017]
Chapter 10: Wave Optics
1. Why should the objective of a telescope have large focal length and large aperture? Justify your answer. [Delhi 2017]
2. Distinguish between unpolarised light and linearly polarised light. How does one get linearly polarised light with the help of a Polaroid? A narrow beam of unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on a Polaroid P1. The light transmitted by it is then incident on a second Polaroid P2 with its pass axis making angle of 60 relative to the pass axis of P1. Find the intensity of the light transmitted by P2. [Delhi 2017]
3. Explain two features to distinguish between the interference patterns in Young’s double slit experiment with the diffraction pattern obtained due to a single slit. A monochromatic light of wavelength 500 nm is incident normally on a single slit of width 0.2 mm to produce a diffraction pattern. Find the angular width of the central maximum obtained on the screen. Estimate the number of fringes obtained in Young’s double slit experiment with fringe width 0.5 mm, which can be accommodated within the region of total angular spread of the central maximum due to single slit. [Delhi 2017]
Chapter 11: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
1. In the study of photoelectric effect the graph between the stopping potential V and frequency v of the incident radiation on two different metals P and Q is shown below:
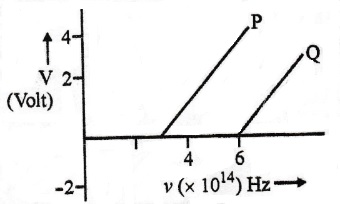
(i) Which one of the two metals has higher threshold frequency?
(ii) Determine the work function of the metal which has greater value.
(iii) Find the maximum kinetic energy of electron emitted by light of frequency 8 × 10^14 Hz for this metal. [Delhi 2017]
Atoms and Nuclei
Chapter 12: Atoms
1. Find the wavelength of the electron orbiting in the first exited state in hydrogen atom. [Delhi 2017]
2. Define the distance of closest approach. An α-particle of kinetic energy ‘K’ is bombarded on a thin gold foil. The distance of the closest approach is ‘r’. What will be the distance of closest approach for an α-particle of double the kinetic energy? [Delhi 2017]
3. Write two important limitations of Rutherford nuclear model of the atom. [Delhi 2017]
Chapter 13: Nuclei
1. A radioactive nucleus ‘A’ undergoes a series of decays as given below:
The mass number and atomic number of A2 are 176 and 71 respectively. Determine the mass and atomic number of A4 and A. Write the basic nuclear processes underlying β+ and β- decays. [Delhi 2017]
Semiconductor & Communication System
Chapter 14: Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devises Simple Circuits
1. Name the junction diode whose I-V characteristics are drawn below:
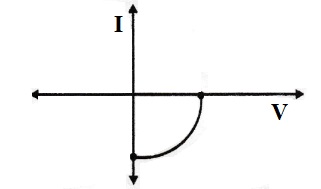
For a CE-transistor amplifier, the audio signal voltage across the collector resistance of 2 kΩ is 2V. Given the current amplification factor of the transistor is 100, find the input signal voltage and base current, if the base resistance is 1 kΩ. [Delhi 2017]
2. Zener diode is fabricated by heavily doping both p- and n- sides of the junction. Explain, why? Briefly explain the use of Zener diode as a dc voltage regulator with the help of a circuit diagram. [Delhi 2017]
Chapter 15: Communication System
1. Distinguish between a transducer and a repeater. [Delhi 2017]
Define the term ‘amplitude modulation’. Explain any two factors which justify the need for modulating a low frequency base-band signal. [Delhi 2017]




