NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter in Hindi and English Medium updated for new session 2024-25. The solutions of chapter 11 class 12th Physics is modified according to new textbooks issued for academic year 2024-25 exams. Now the additional exercises are not the part of syllabus.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 11
Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Solutions
- Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 Exercises Solutions
- 12th Physics Chapter 11 Additional Exercises (Not in Syllabus)
- Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 Solutions in Hindi
- Class 12 Physics NCERT Book Chapter 11
- Class 12 Physics Revision Book Chapter 11
- Revision Book Answers
- Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 Revision Notes 1
- Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 Revision Notes 2
- Visit to 12th Physics Main Page
Get the modified format of Exercises Solutions and Additional Exercises Solutions to study online without downloading for new academic session 2024-25. These solutions are useful for UP Board students also. Download Offline Apps and Solutions based on updated NCERT Books for 2024-25.
| Class: 12 | Physics |
| Chapter 11: | Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter |
| Content: | Exercises and Extra Question Answers |
| Type of Content: | PDF, Images, Text and Video Explanation |
| Academic Session: | Year 2024-25 |
| Medium used: | Hindi and English |
Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 Solutions in English
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 in PDF form free download is given below. NCERT Books and NCERT Solutions can be viewed online also without downloading. Join the discussion forum to ask your queries related to NIOS and CBSE Boards. Download offline apps based on latest CBSE Syllabus 2024-25.
Important Questions for practice
1. The work function of the following metal is given Na = 2.75 eV, K = 2.3 eV, Mo = 4.14 eV, Ni = 5.15 eV which of these metal will not give a photoelectric emission for radiation of wave length 3300 A0 from a laser
source placed at 1m away from the metal. What happens if the laser is brought nearer and placed 50 cm away.
2. Why photo-electrons ejected from a metal surface have different kinetic energies although the frequency of incident photons are same?
3. Define distance of the closest approach. An alpha-particle of kinetic energy ‘K’ is bombarded on a thin gold foil. The distance of the closet approach is ‘r’. What will be the distance of closest approach for an alpha-particle of double the kinetic energy?
4. If the total number of neutrons and protons in a nuclear reaction is conserved how then is the energy absorbed or evolved in the reaction?
5. Particle of mass M at rest decays into two particles of masses m1 and m2 having velocities V1 and V2 respectively. Find the ratio of de-Broglie Wavelengths of the two particles.
Questions from Board Papers
1. What is the stopping potential applied to a photocell, in which electrons with a maximum kinetic energy of 5.6 eV are emitted.
2. If the amount of a radioactive substance is increased four times then how many times will the number of atoms disintegrating per unit time be increased?
3. Why does only a slow neutron (.03eV energy) cause the fission in the uranium nucleus and not the fast one?
4. In Bohr’s atomic model, the potential energy is negative and has a magnitude greater than the kinetic energy, what does this imply?
5. The half life of a radioactive element A is same as the mean life time of another radioactive element B. Initially, both have same number of atoms. B decay faster than A. Why?
Important Questions on 12th Physics Chapter 11
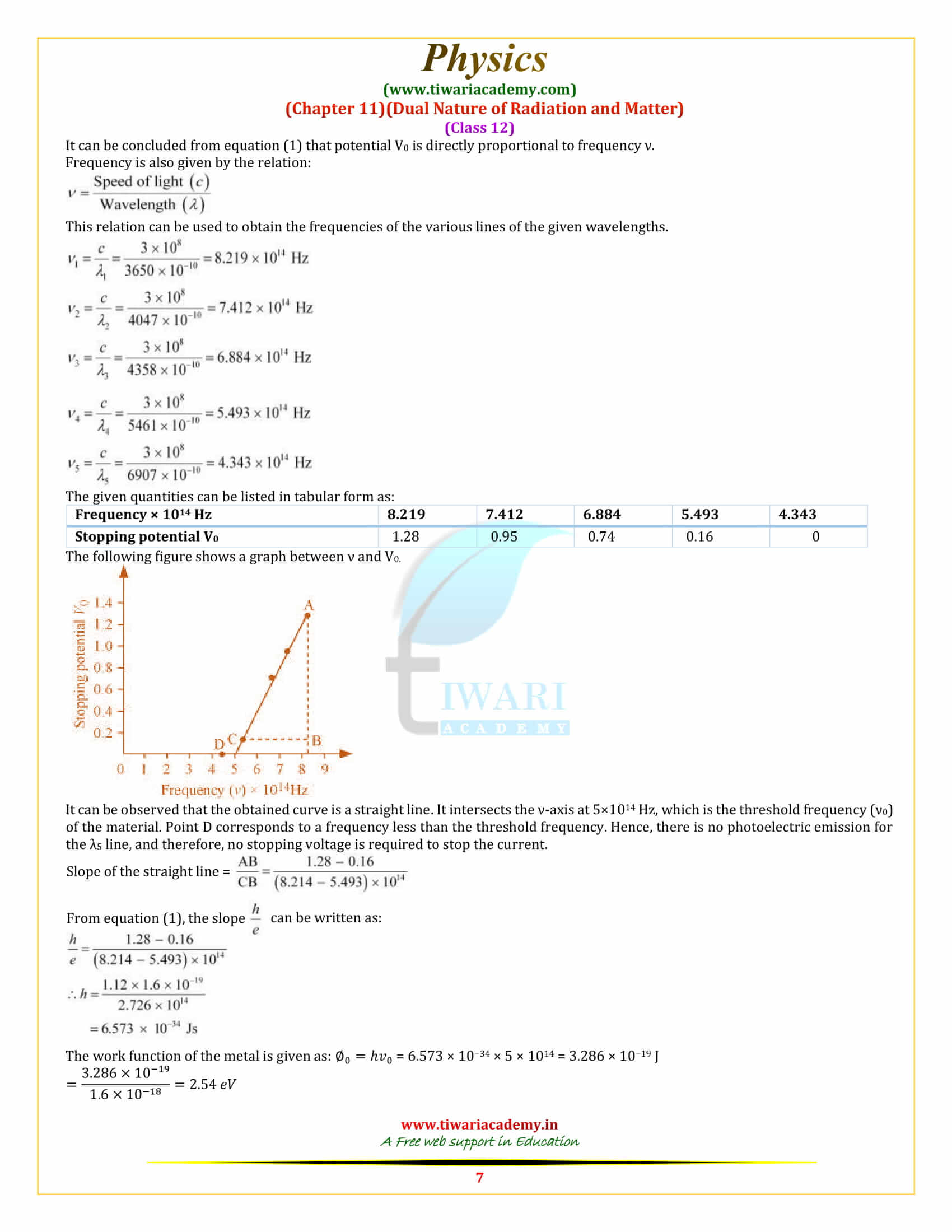
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, the slope of the cut-off voltage versus frequency of incident light is found to be 4.12 × 10⁻¹⁵ V s. Calculate the value of Planck’s constant.
The slope of the cut-off voltage (V) versus frequency (ν) of an incident light is given as: V/v = 4.12× 10⁻¹⁵ Vs V is related to frequency by the equation hv = eV Where, e = Charge on an electron = 1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ C and h = Planck’s constant Therefore, h = e × V/v = 1.6× 10⁻¹⁹ × 4.12 × 10⁻¹⁵ = 6.592 × 10⁻³⁴ Js Hence, the value of Plank’s constant is 6.592 × 10⁻³⁴ Js.
Show that the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation is equal to the de Broglie wavelength of its quantum (photon).
The momentum of a photon having energy (hν) is given as: p = hv/c = h/λ ⇒ λ = h/p … (i) Where, λ = Wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation c = Speed of light h = Planck’s constant De Broglie wavelength of the photon is given as: λ = h/mv But p = mv, therefore λ = h/p … (ii) Where, m = Mass of the photon v = Velocity of the photon Hence, it can be inferred from equations (i) and (ii) that the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation is equal to the de Broglie wavelength of the photon.
Quarks inside protons and neutrons are thought to carry fractional charges [(+2/3)e ; (−1/3)e]. Why do they not show up in Millikan’s oil-drop experiment?
Quarks inside protons and neutrons carry fractional charges. This is because nuclear force increases extremely if they are pulled apart. Therefore, fractional charges may exist in nature; observable charges are still the integral multiple of an electrical charge.
Why should gases be insulators at ordinary pressures and start conducting at very low pressures?
At atmospheric pressure, the ions of gases have no chance of reaching their respective electrons because of collision and recombination with other gas molecules. Hence, gases are insulators at atmospheric pressure. At low pressures, ions have a chance of reaching their respective electrodes and constitute a current. Hence, they conduct electricity at these pressures.
Every metal has a definite work function. Why do all photoelectrons not come out with the same energy if incident radiation is monochromatic? Why is there an energy distribution of photoelectrons?
The work function of a metal is the minimum energy required for a conduction electron to get out of the metal surface. All the electrons in an atom do not have the same energy level. When a ray having some photon energy is incident on a metal surface, the electrons come out from different levels with different energies. Hence, these emitted electrons show different energy distributions.