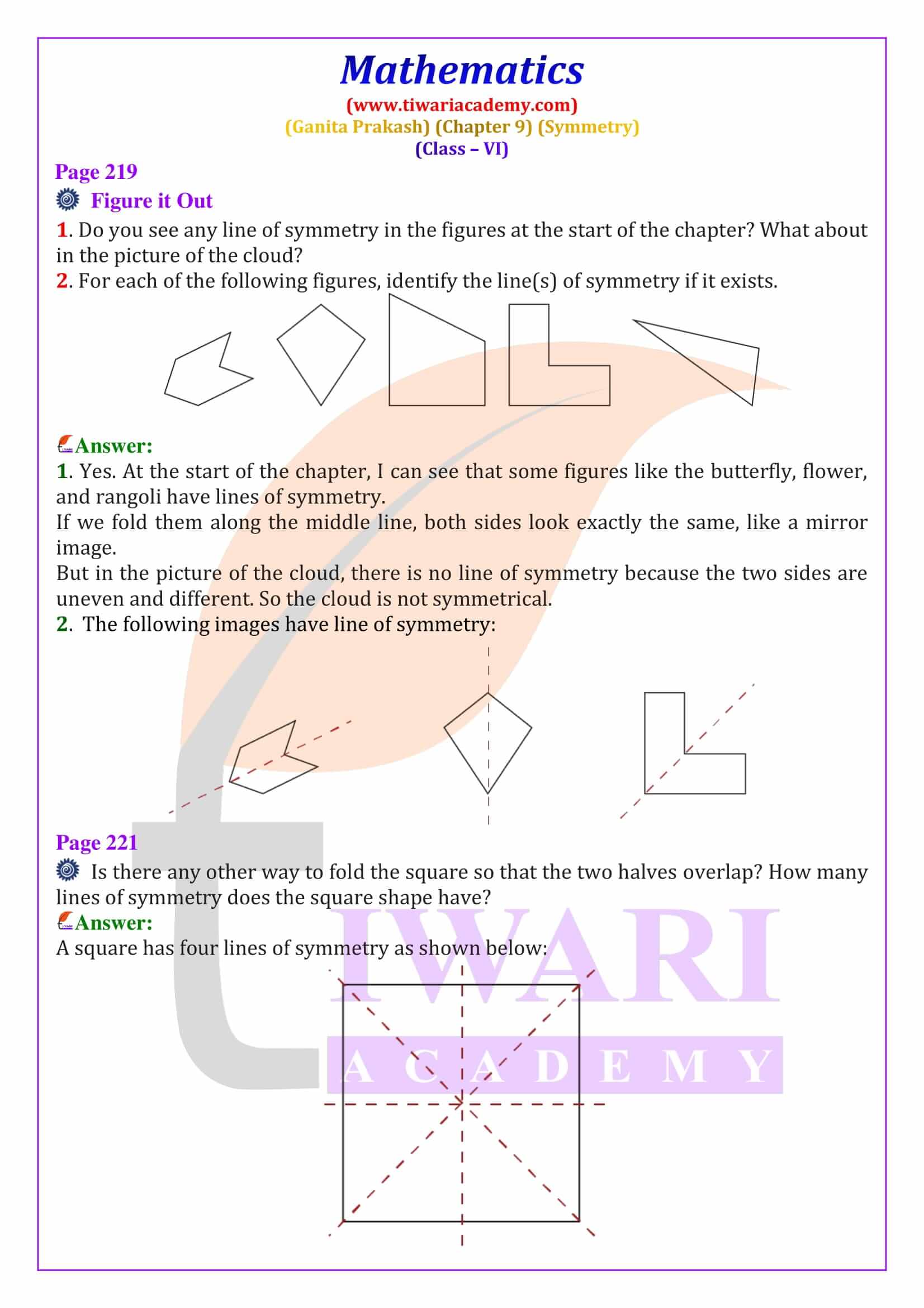
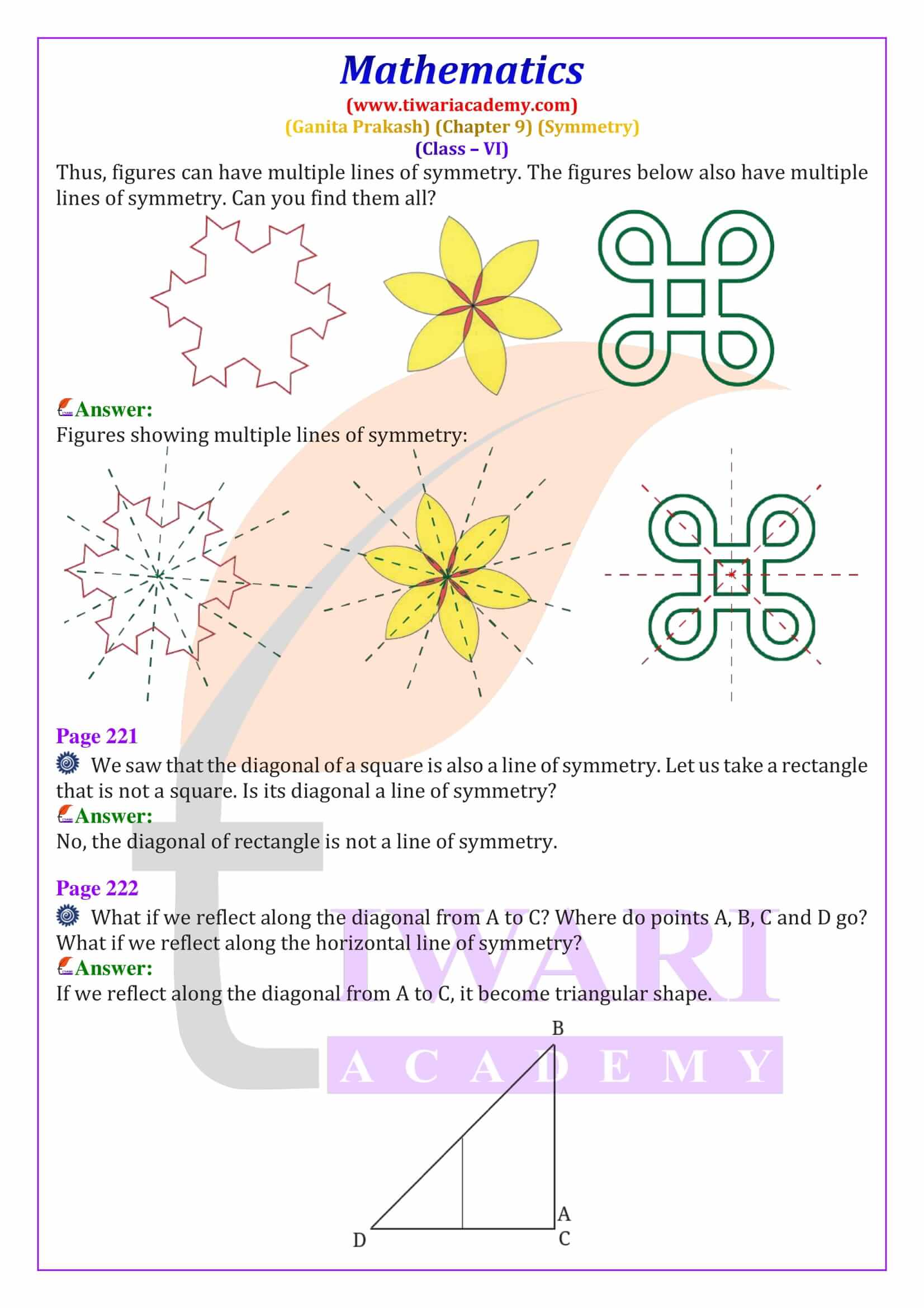
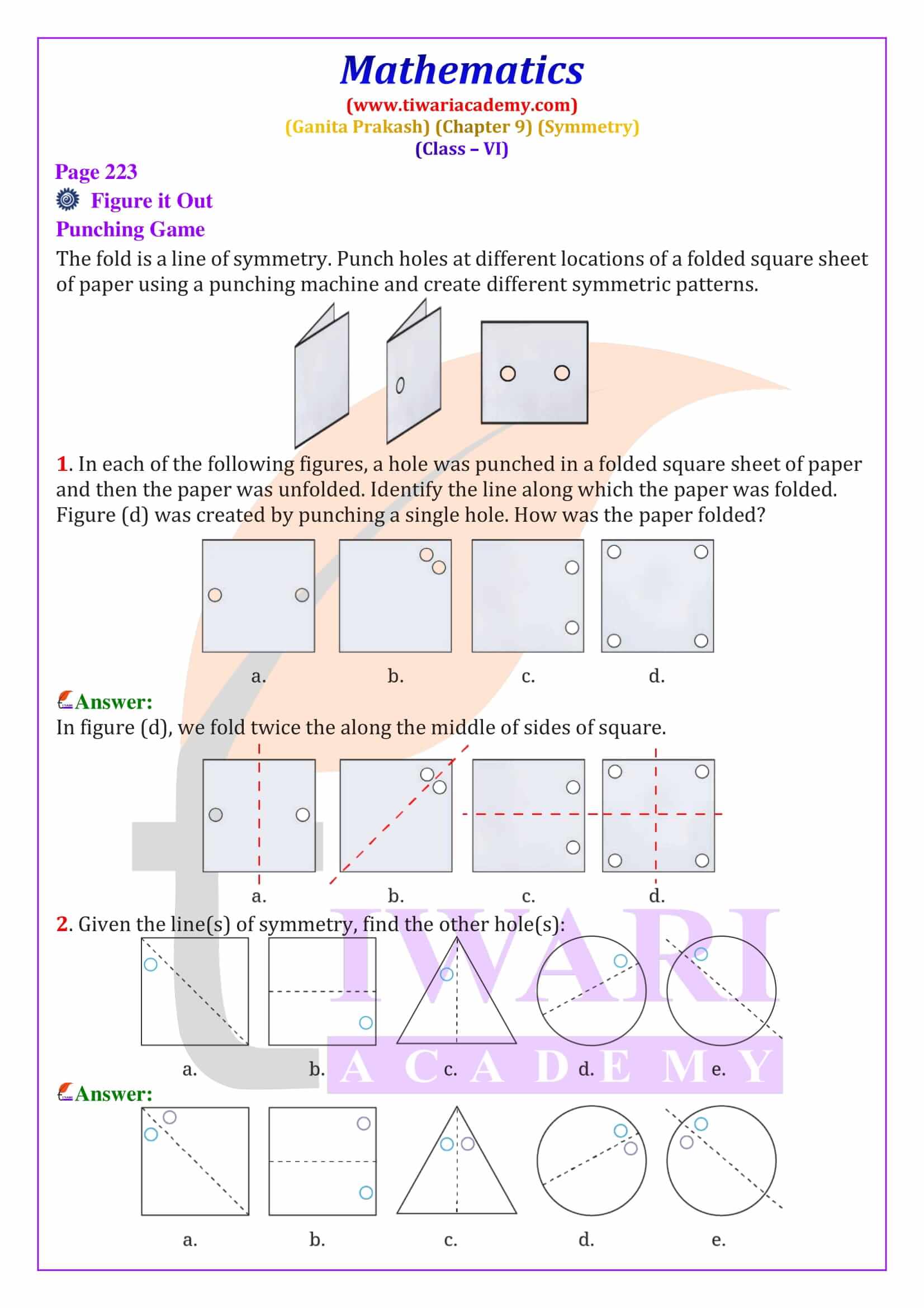
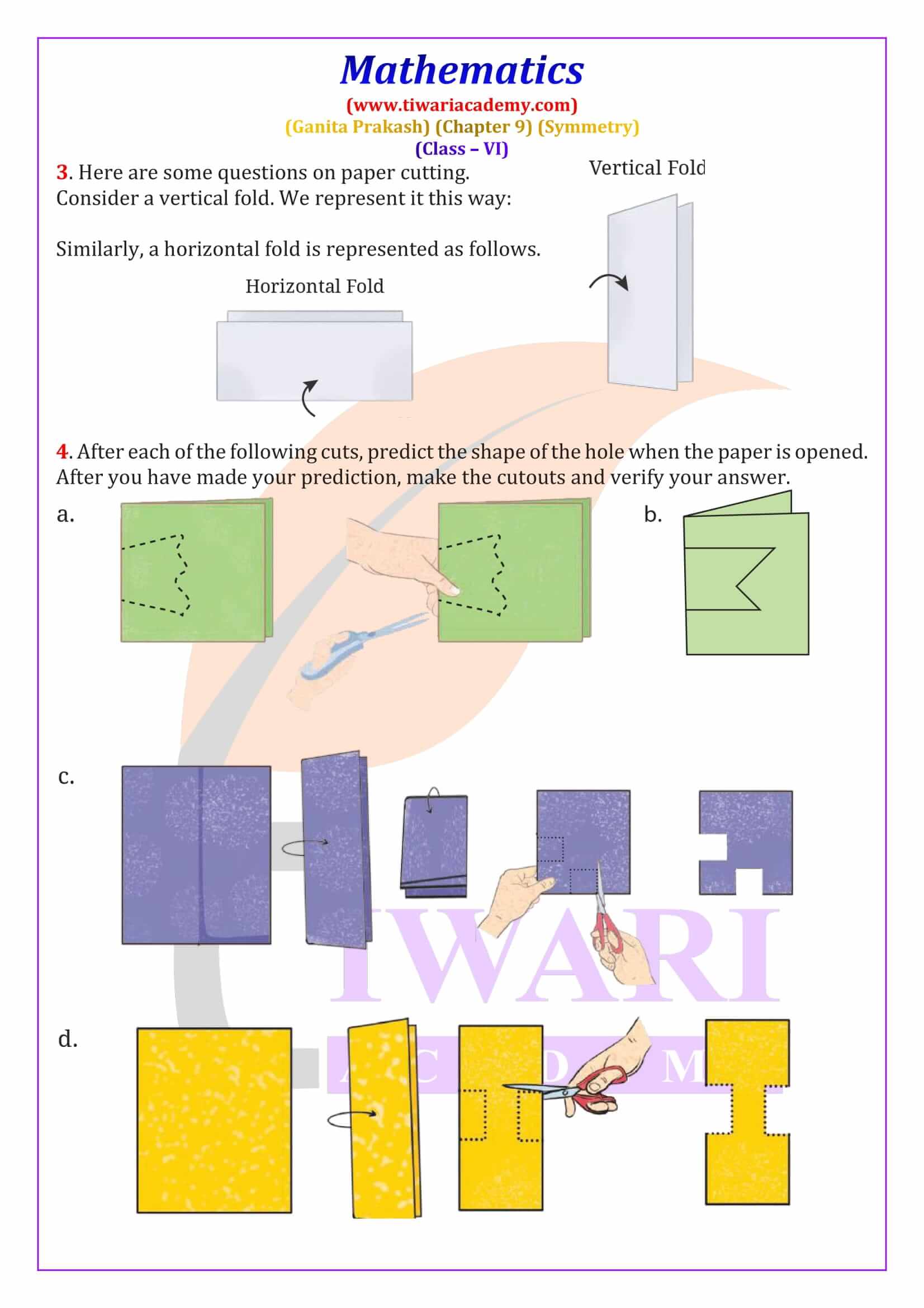
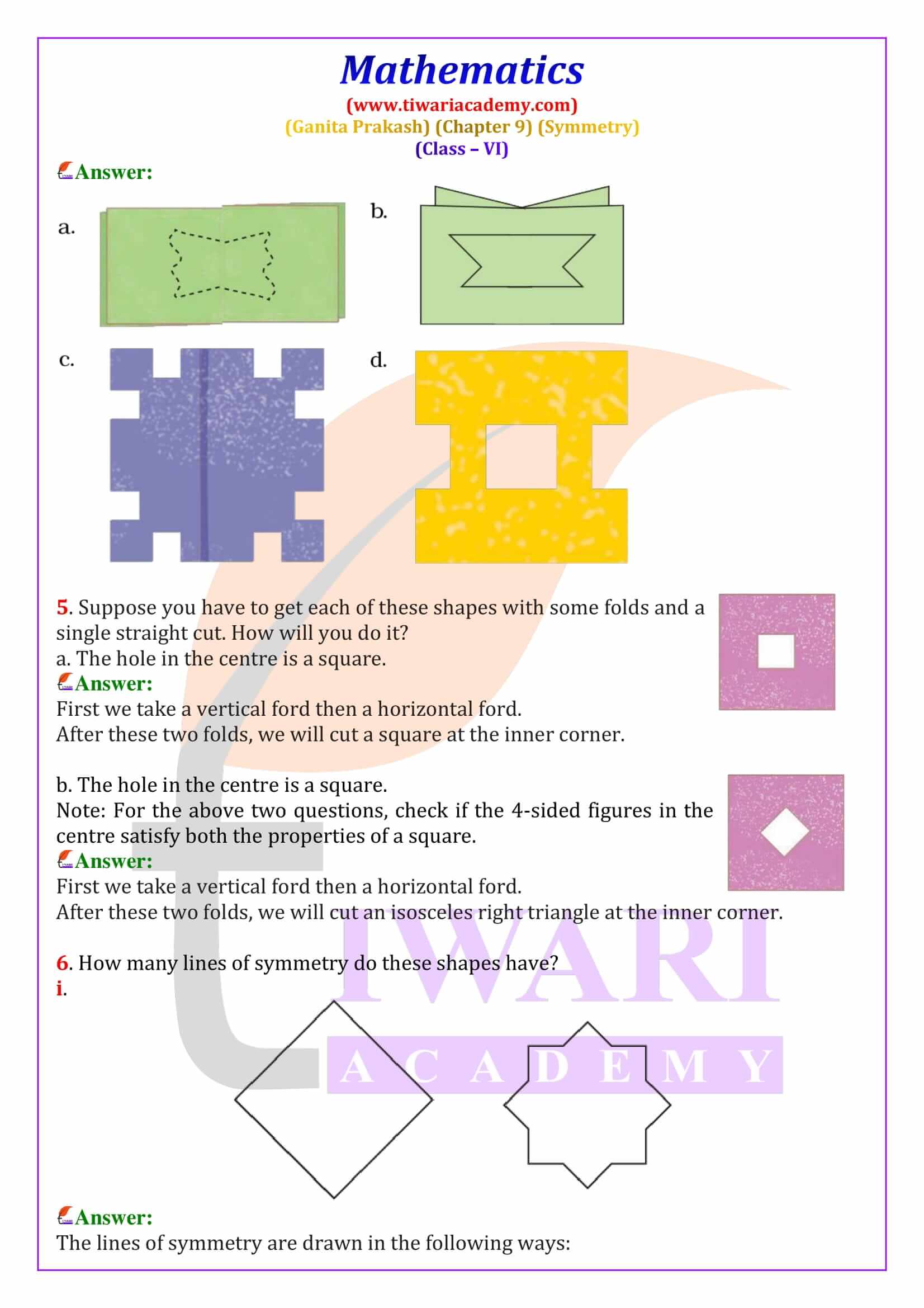
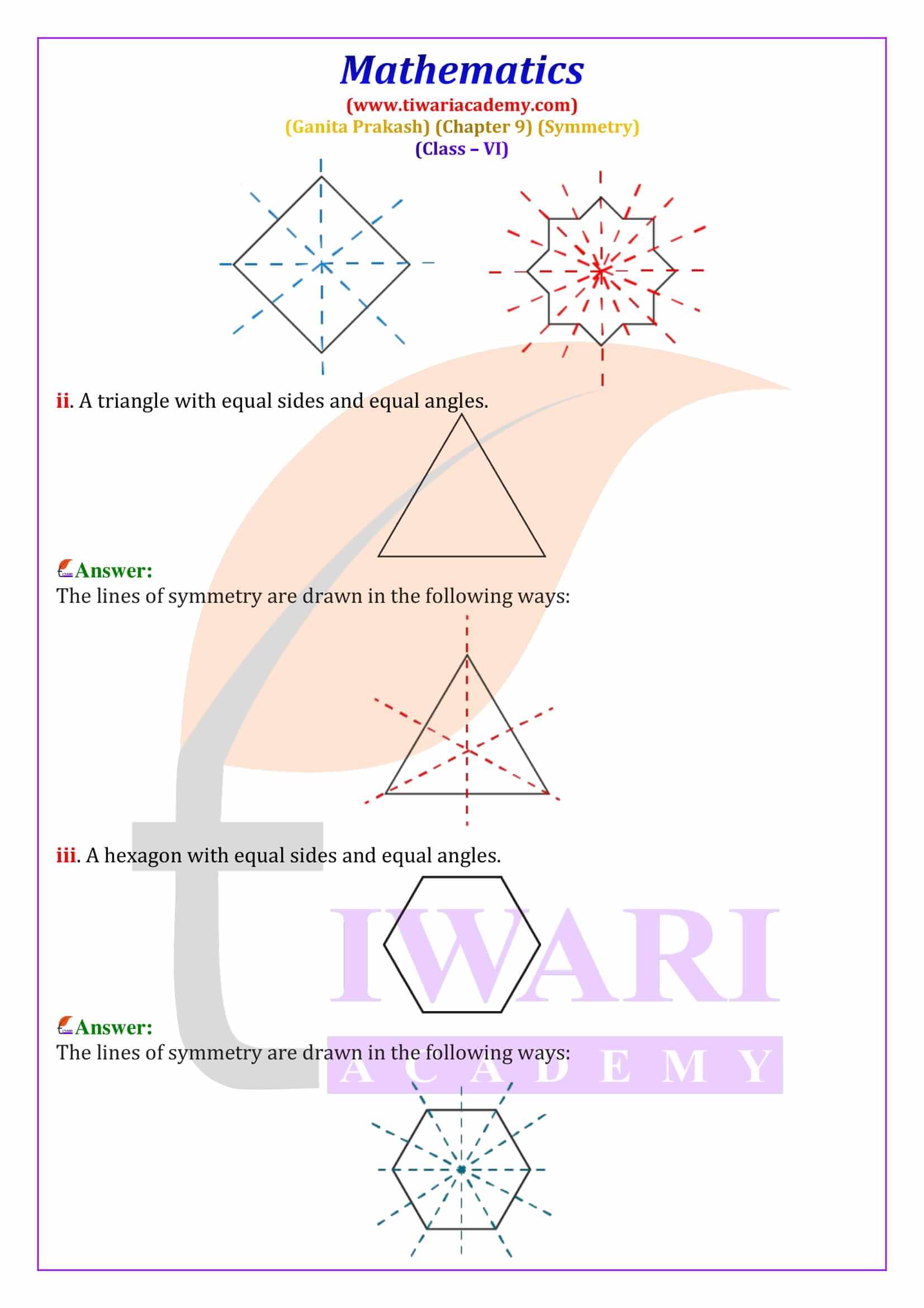
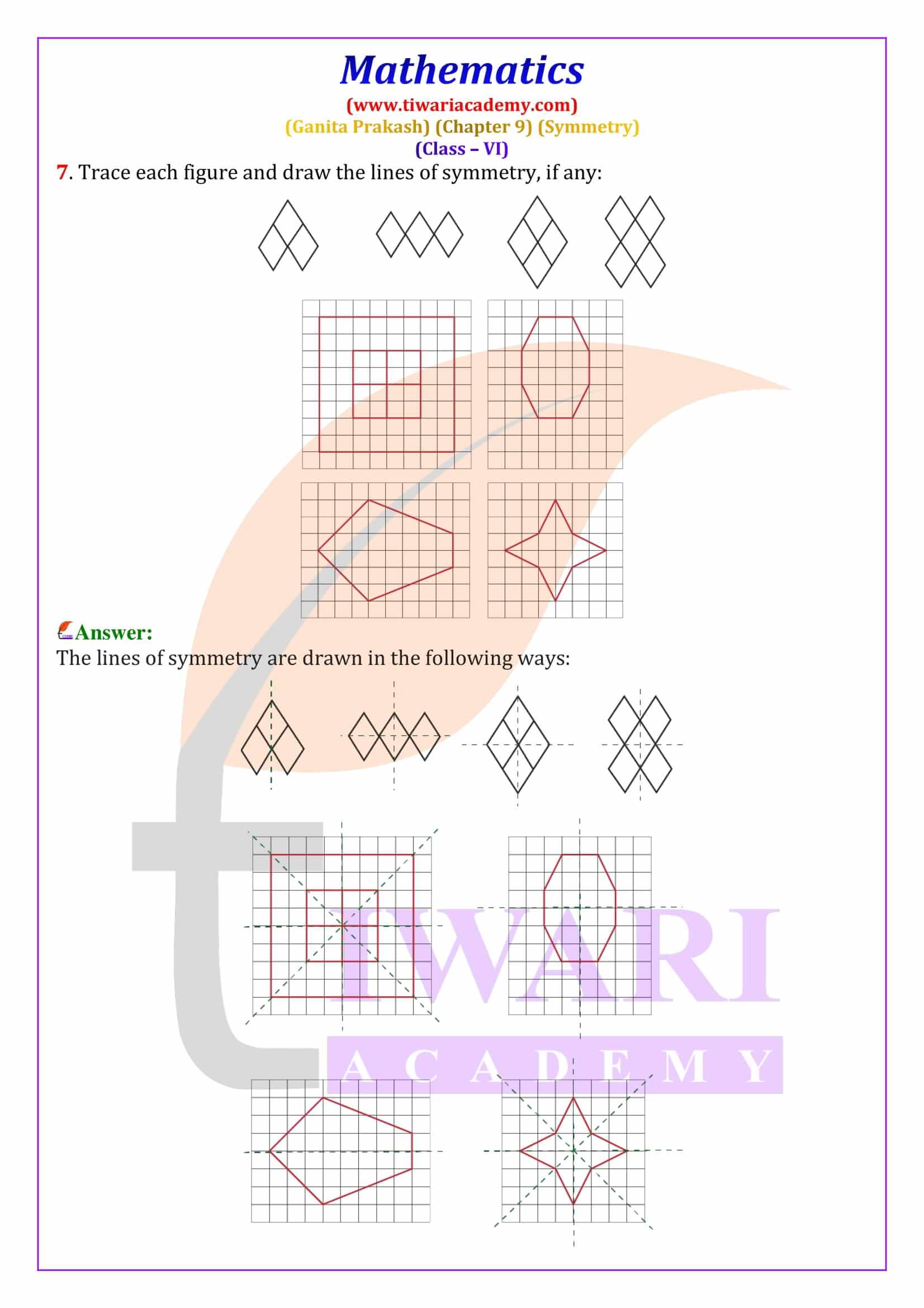
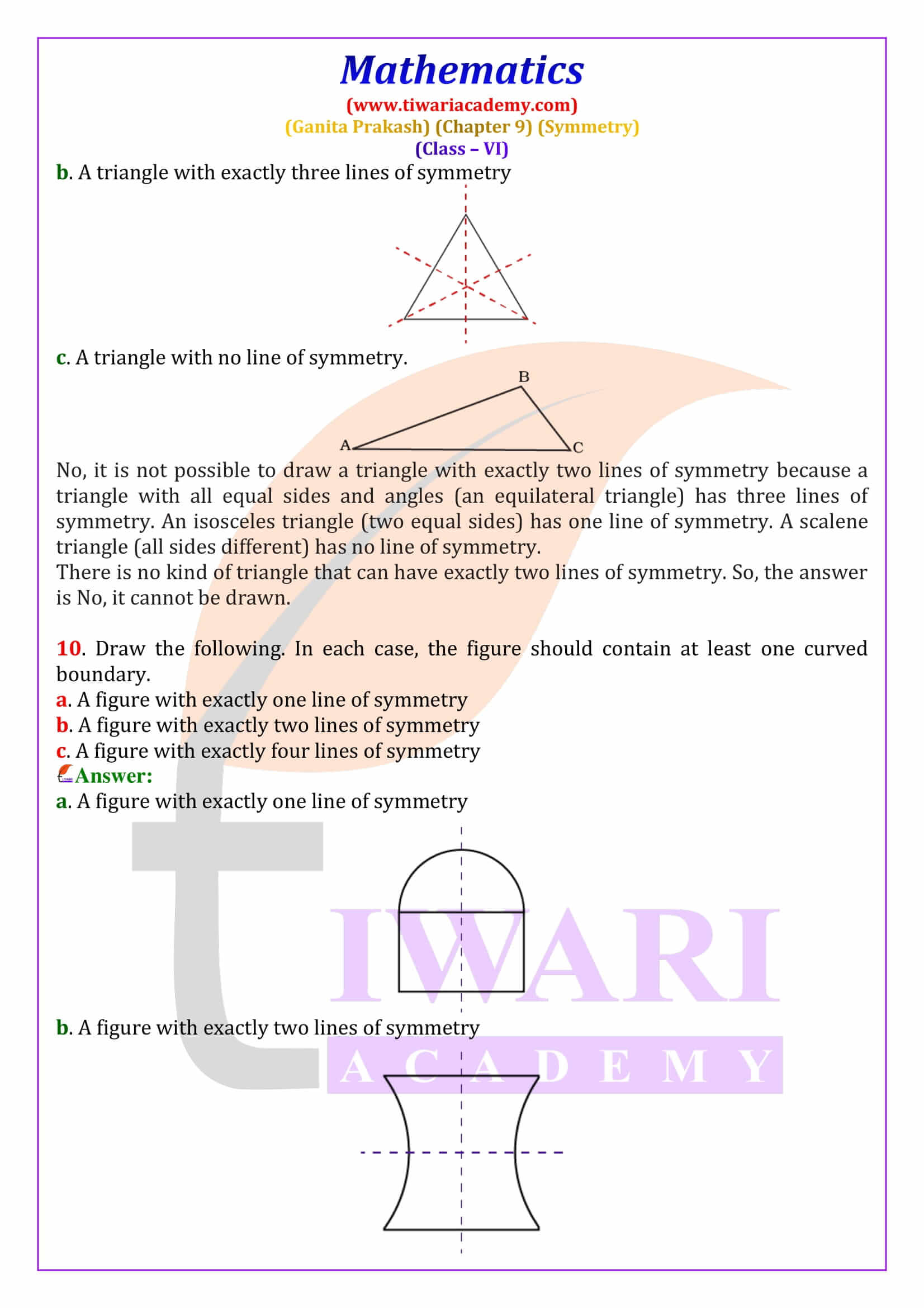
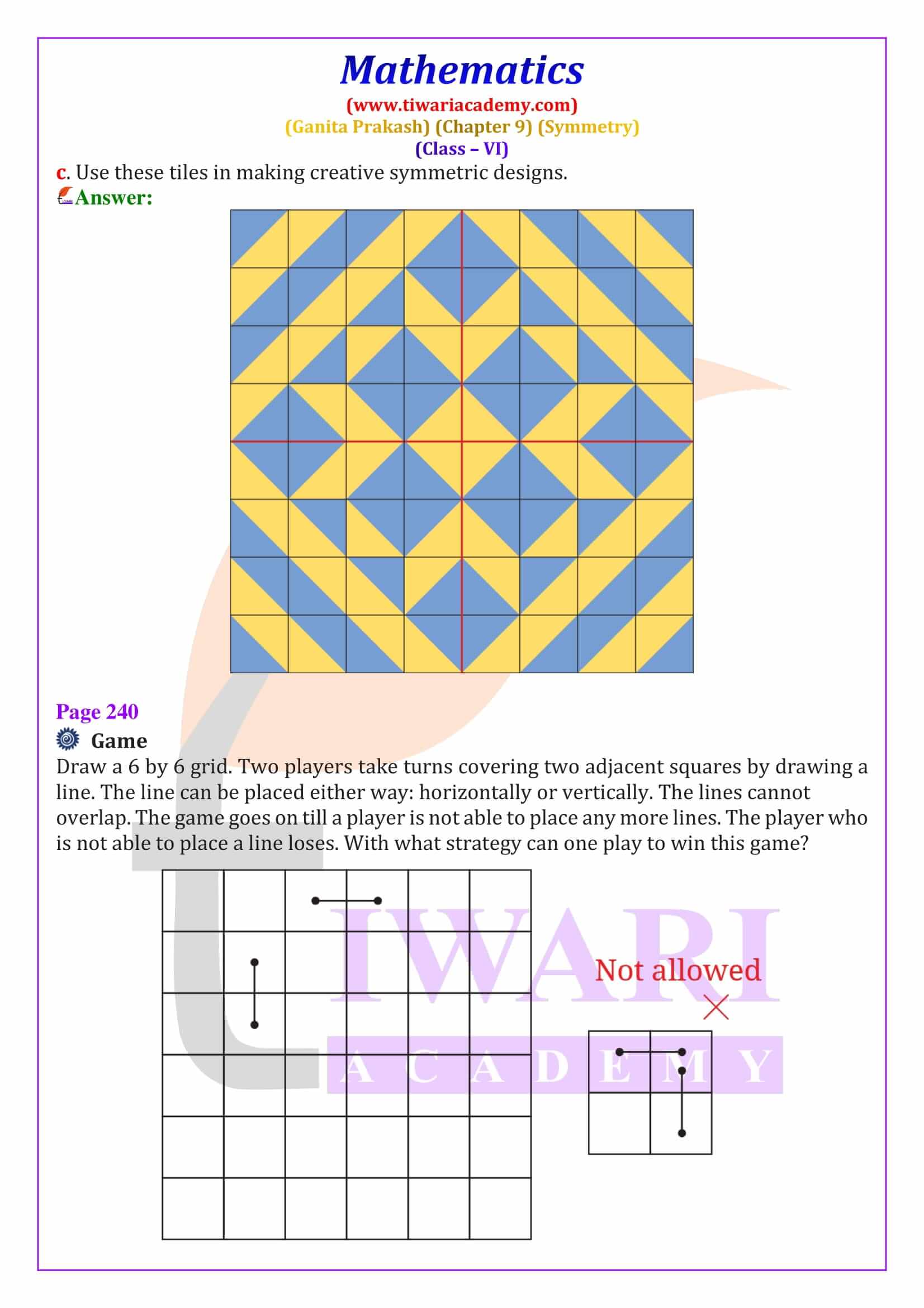
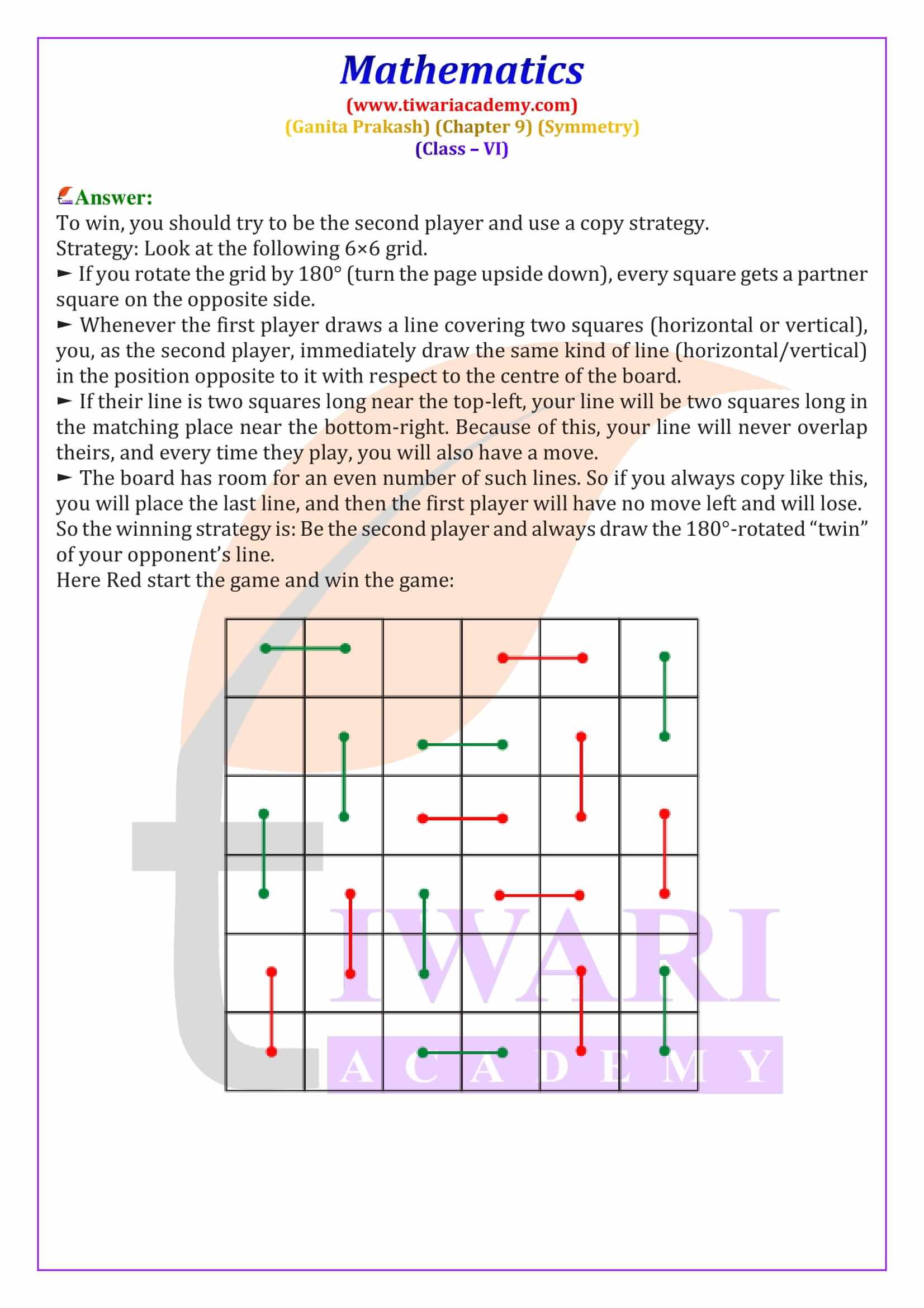
Class 6 Maths Chapter 9 Symmetry Solutions from Ganita Prakash explain line of symmetry, reflection symmetry and rotational symmetry with clear, step-by-step answers. These NCERT based solutions help students solve textbook questions confidently and prepare effectively for CBSE exams.
Class 6 Maths Chapter 9 Symmetry – Step-by-Step Solutions
Why Use These Solutions?
- 100% aligned with Ganita Prakash Class 6.
- Written in simple language.
- Diagram-based explanations.
- Ideal for CBSE exams.
NCERT Class 6 Maths Chapter 9 Symmetry Solutions
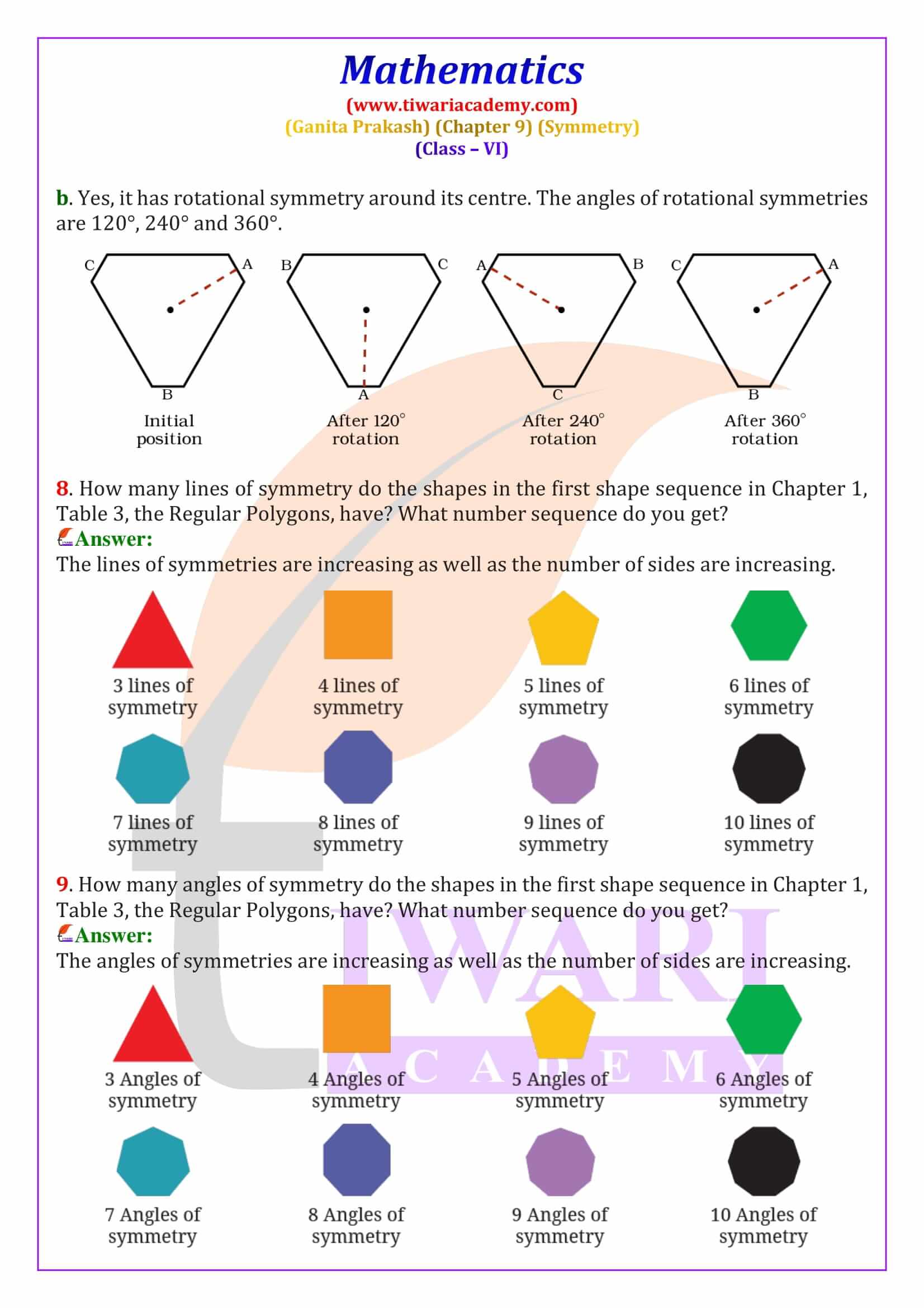
Class 6 Maths Chapter 9 Symmetry – Ganita Prakash Solutions
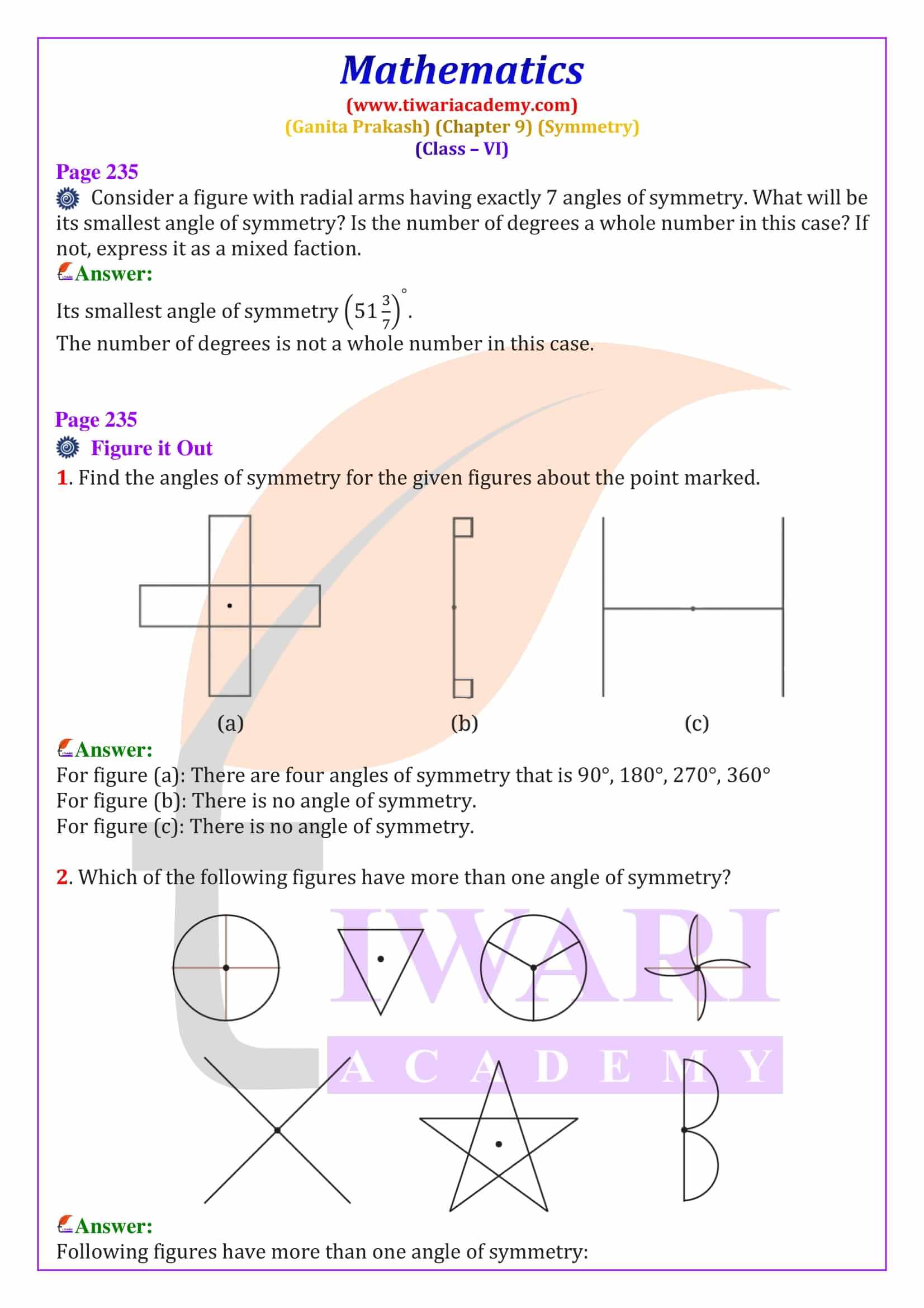
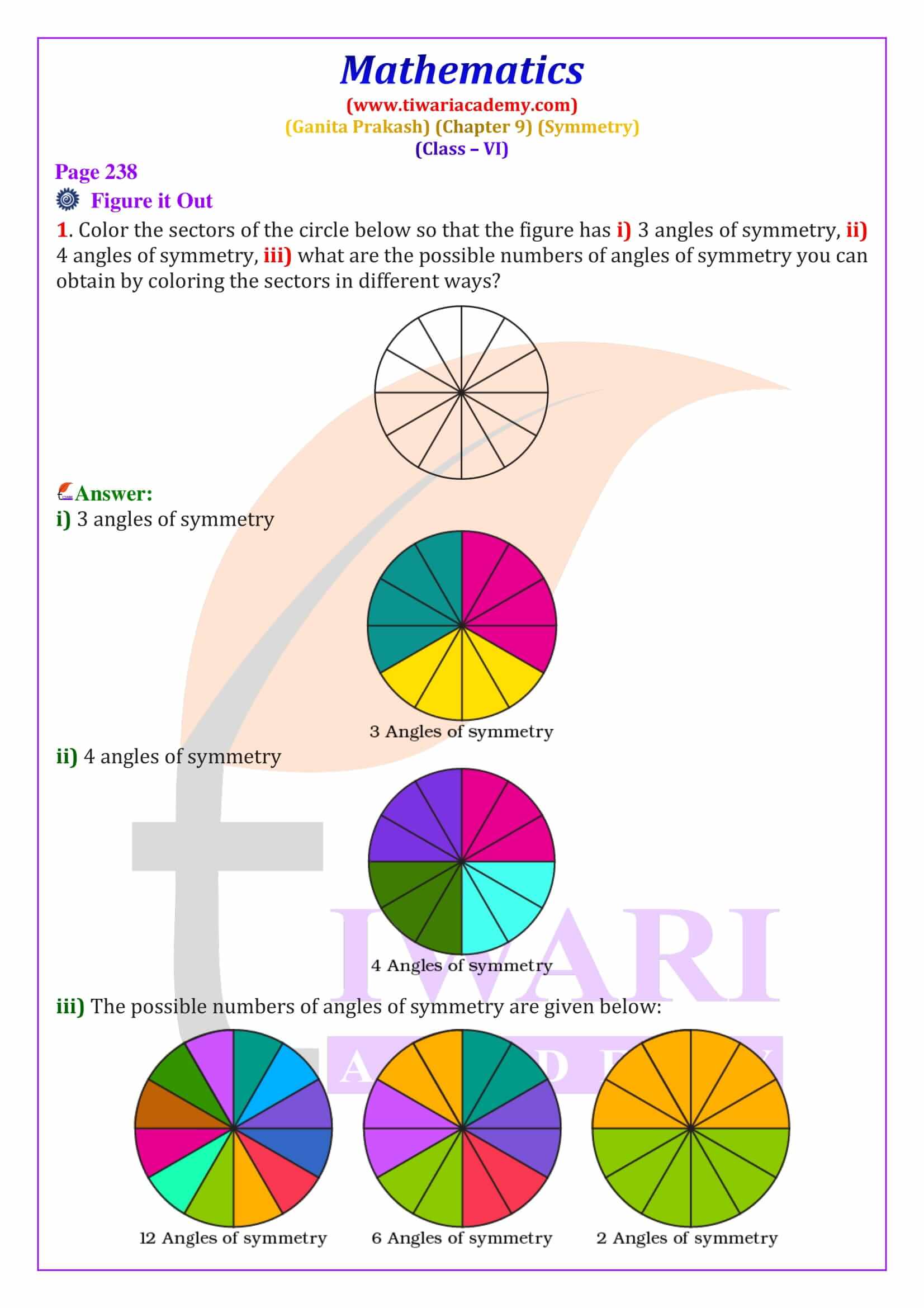
Class 6 Maths Chapter 9 Symmetry solutions help students understand one of the most visual chapters in the Ganita Prakash Maths textbook. This chapter explains symmetry using real-life examples such as flowers, butterflies, rangoli designs and famous monuments. Symmetry is defined as a property where a figure looks the same when folded or rotated. These NCERT Class 6 Maths Symmetry solutions are written in simple language to support concept clarity, exam preparation, and quick revision for CBSE students.

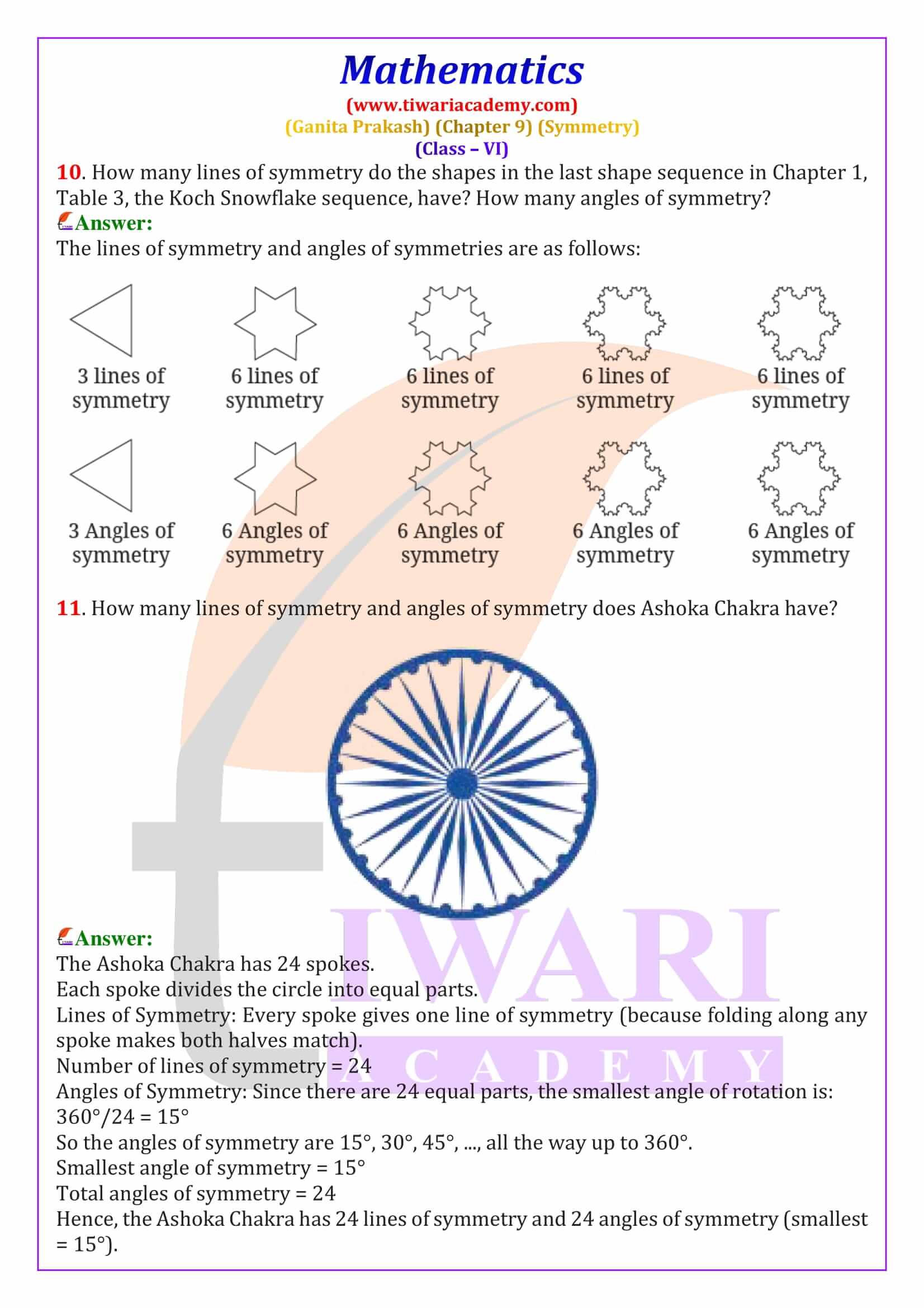
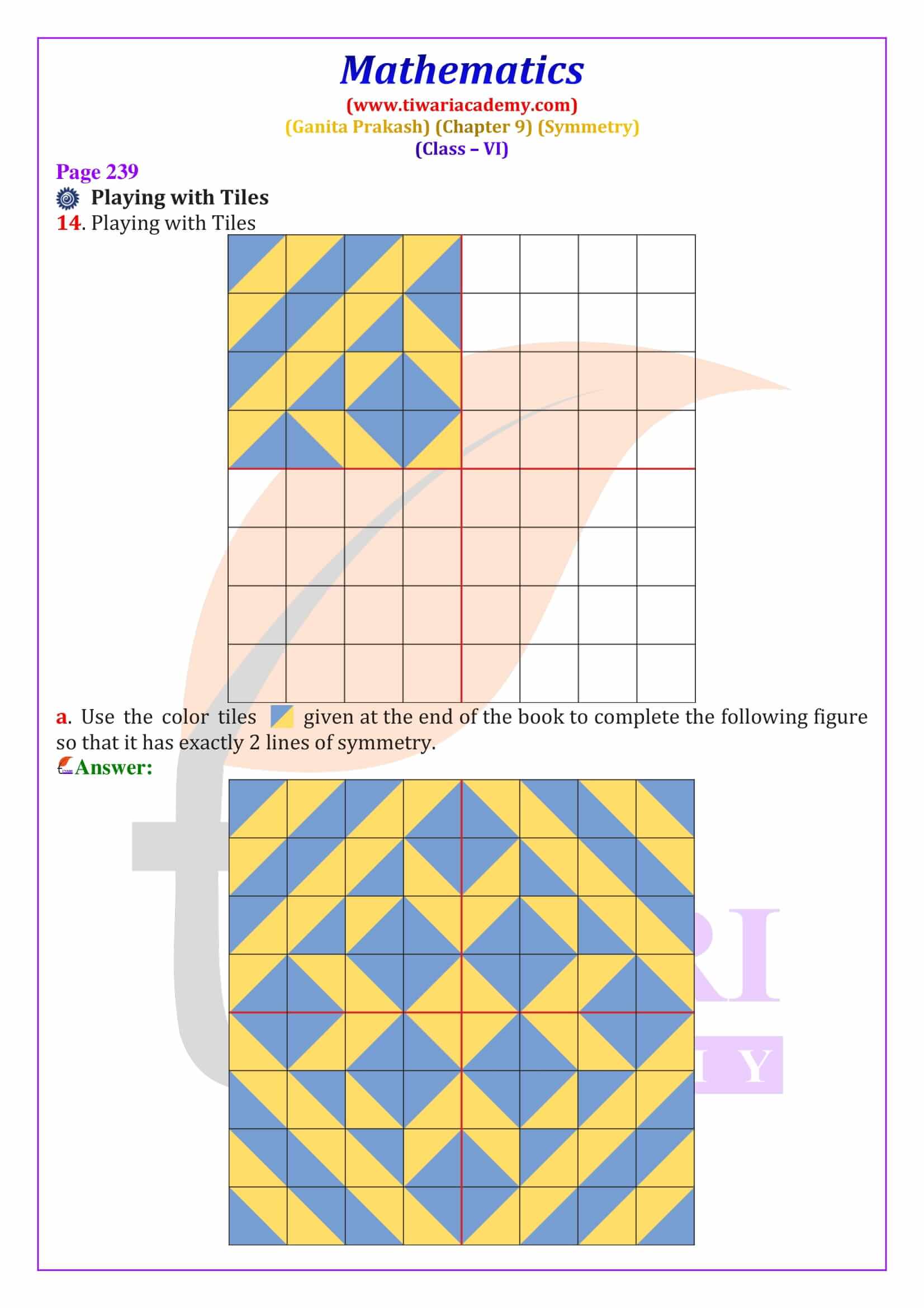
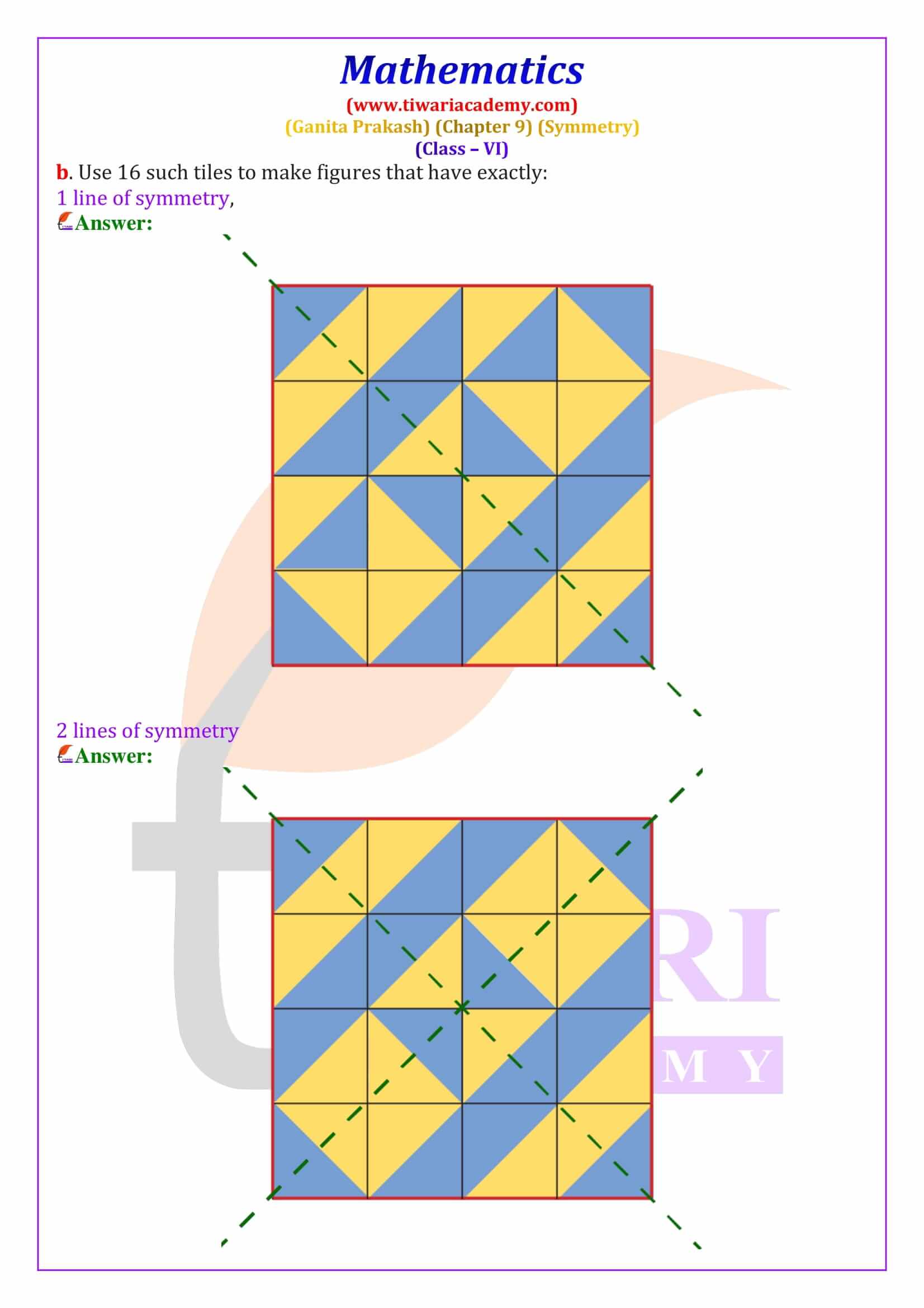
Line of Symmetry – Definition, Types and Examples
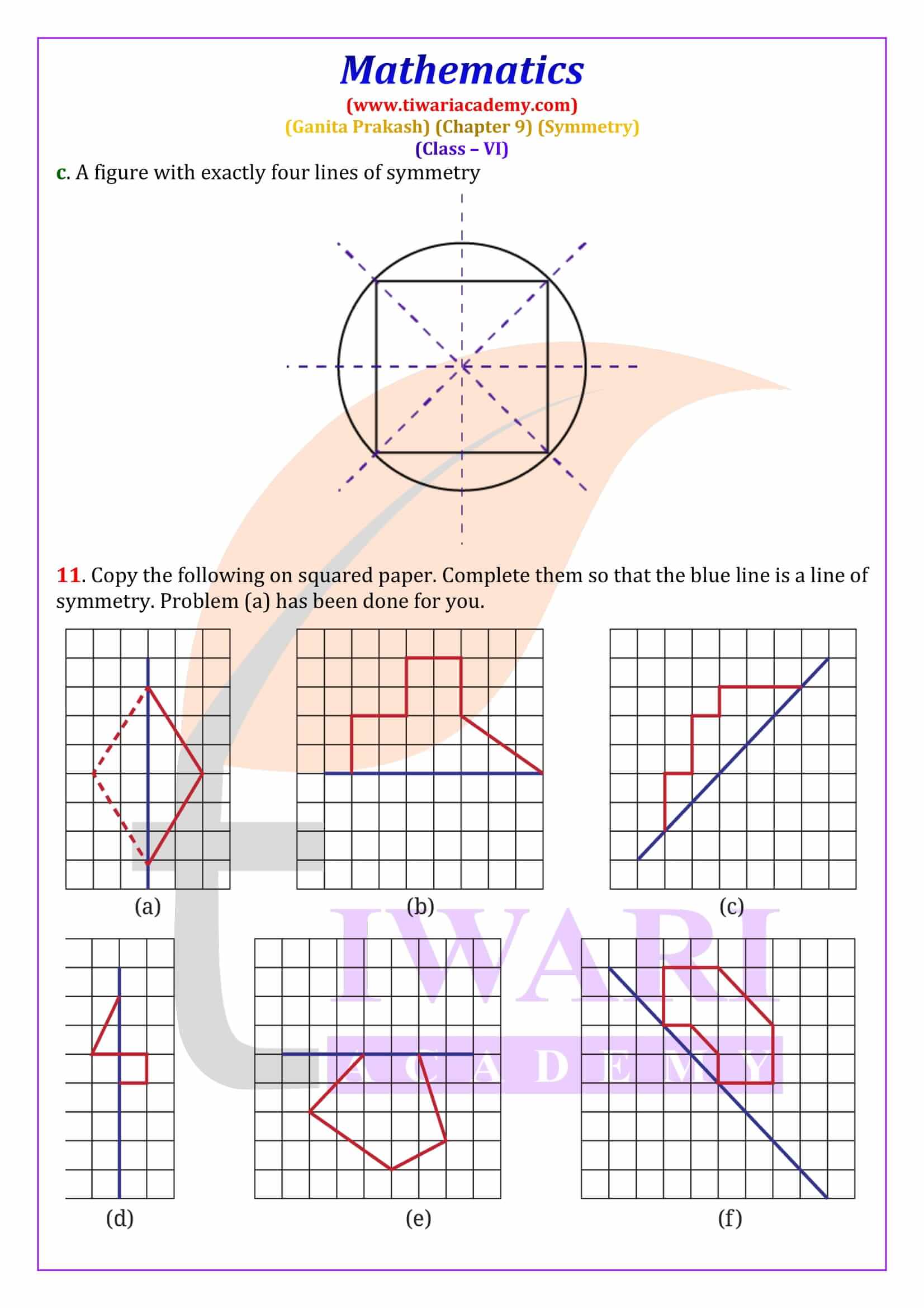
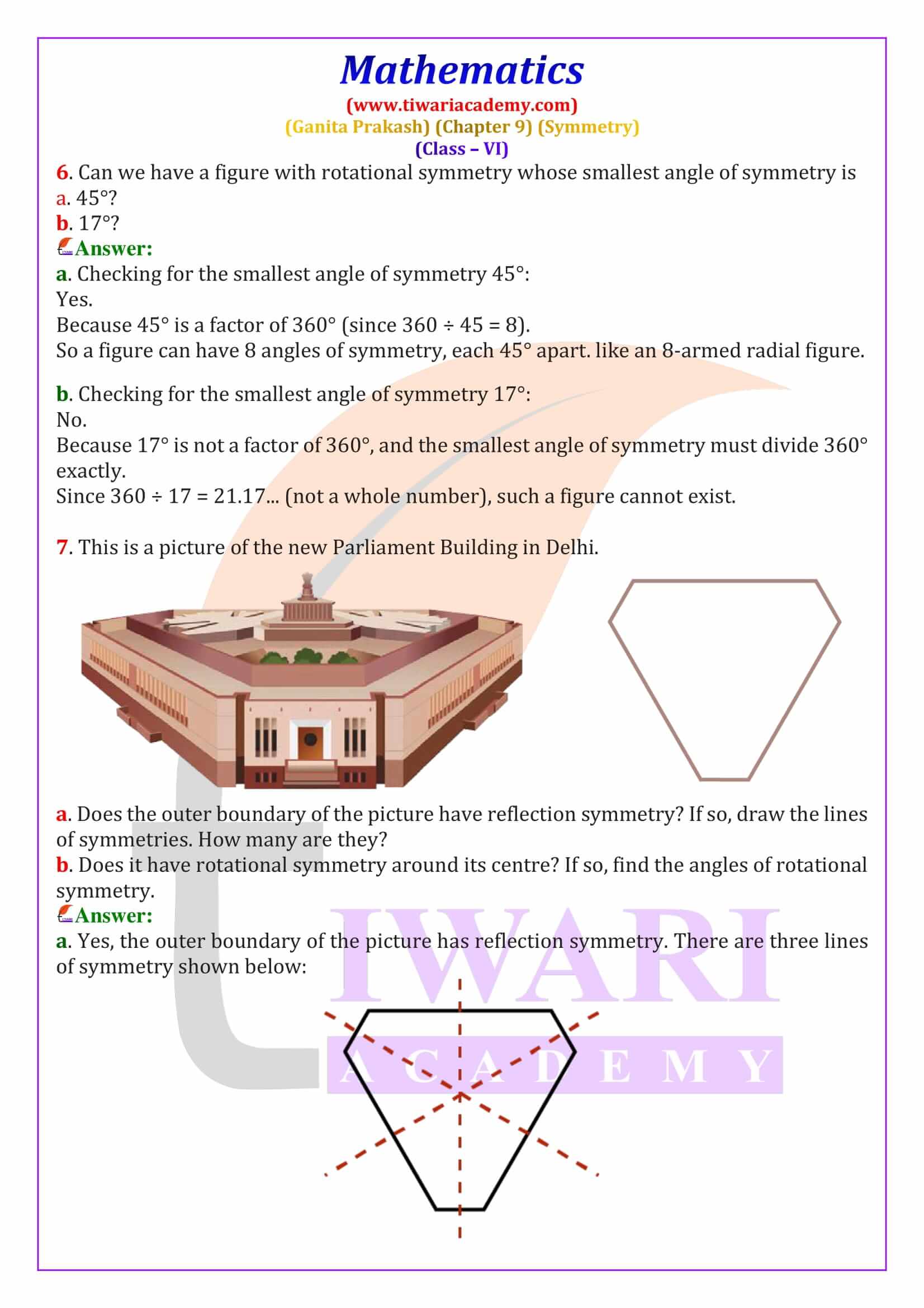
A line of symmetry is a line that divides a figure into two equal and identical mirror halves. When folded along this line, both parts overlap exactly. In Class 6 Maths Chapter 9, students learn to identify lines of symmetry in common shapes such as squares, rectangles, triangles and hexagons. For example, a square has four lines of symmetry, while an equilateral triangle has three. These line of symmetry questions and answers for Class 6 are explained step-by-step to help students score well in exams.
Reflection Symmetry and Paper Folding Questions
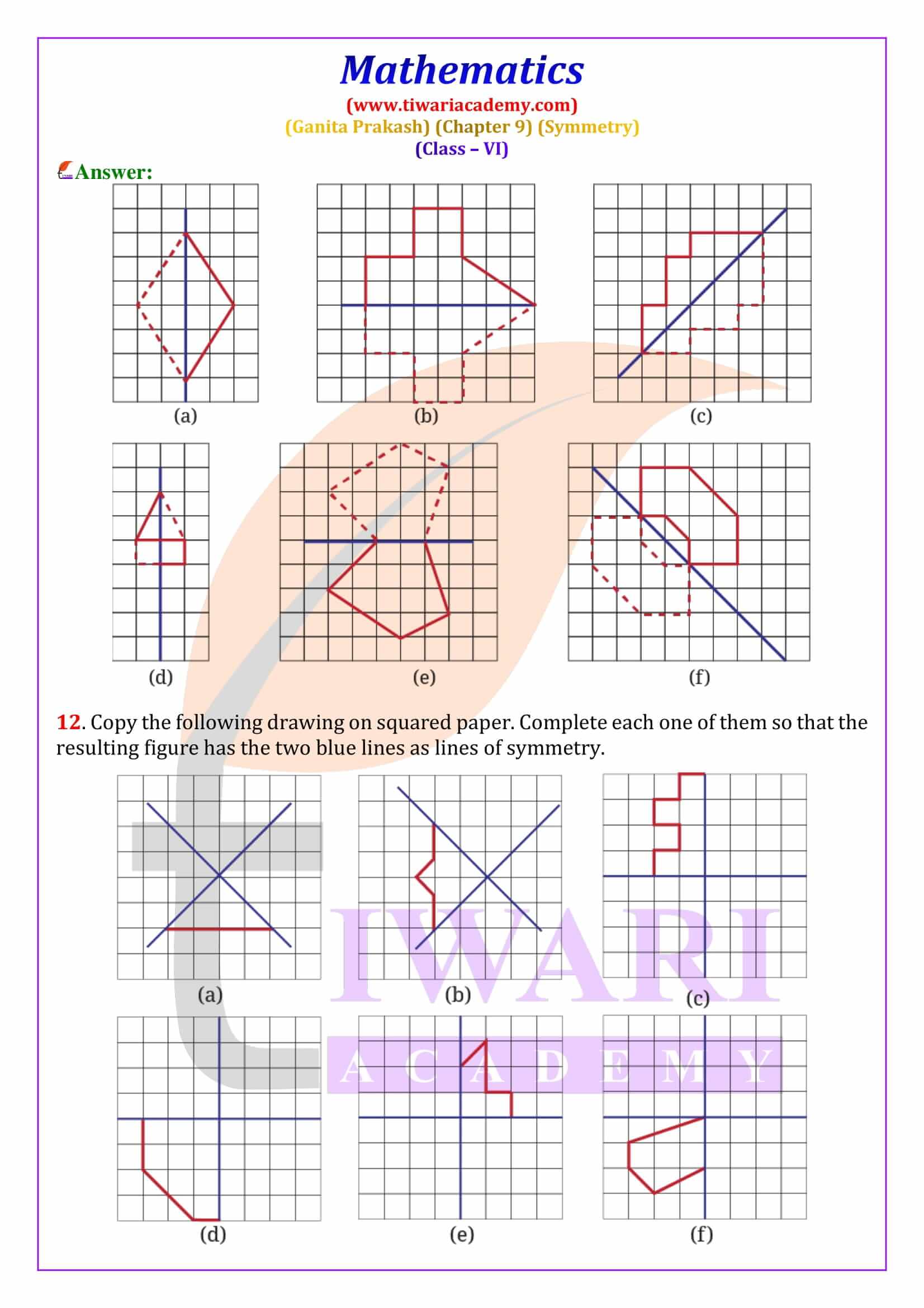
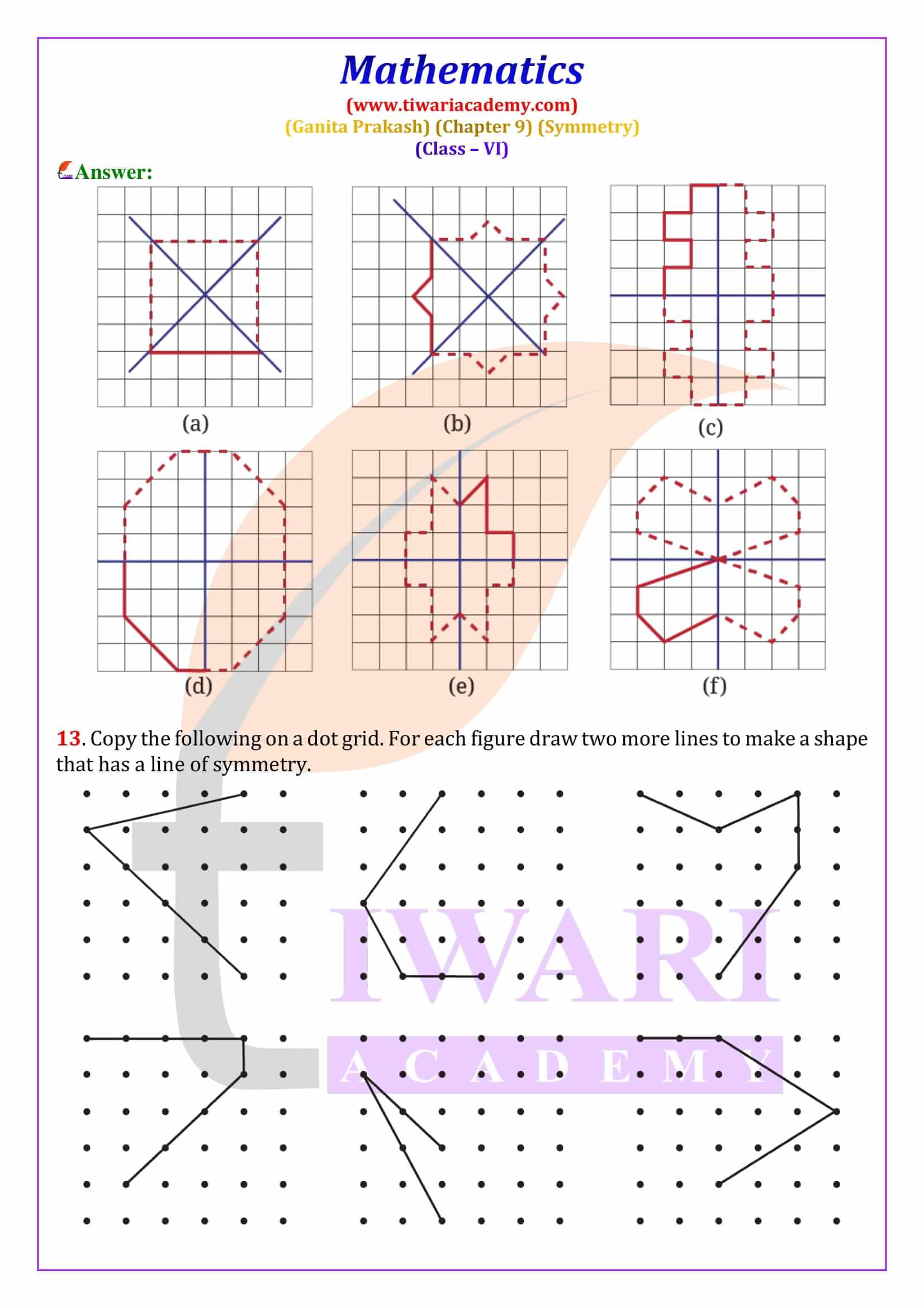
Figures that have a line of symmetry also show reflection symmetry, where one half of the figure is the mirror image of the other. The chapter includes hands-on activities like paper folding, ink blot patterns, cutting and punching to explain reflection symmetry clearly. Many Class 6 Maths Symmetry exercise questions ask students to identify the fold line or find missing holes after unfolding paper. The solutions provided here explain the reasoning clearly, making them ideal for homework and practice.
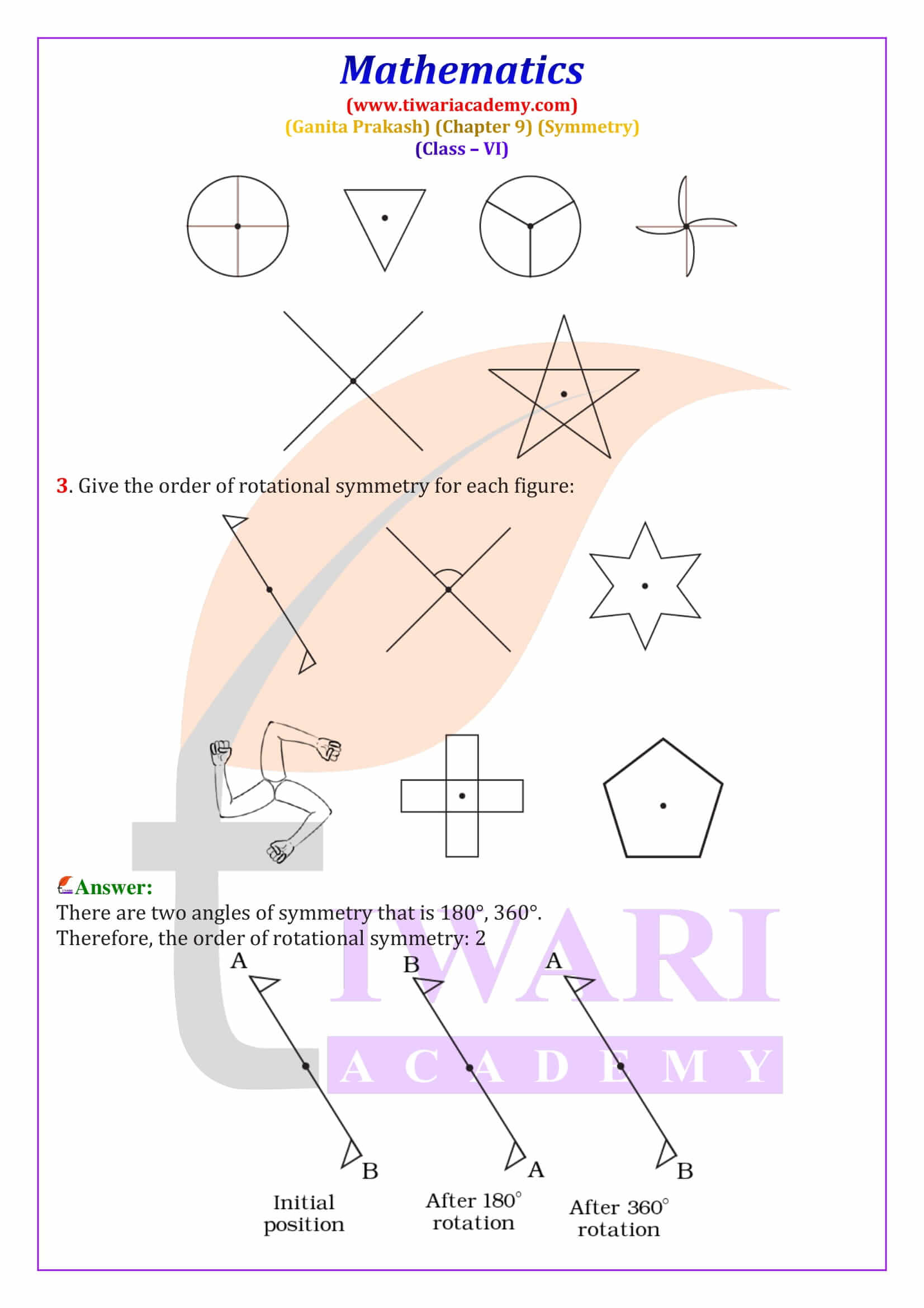
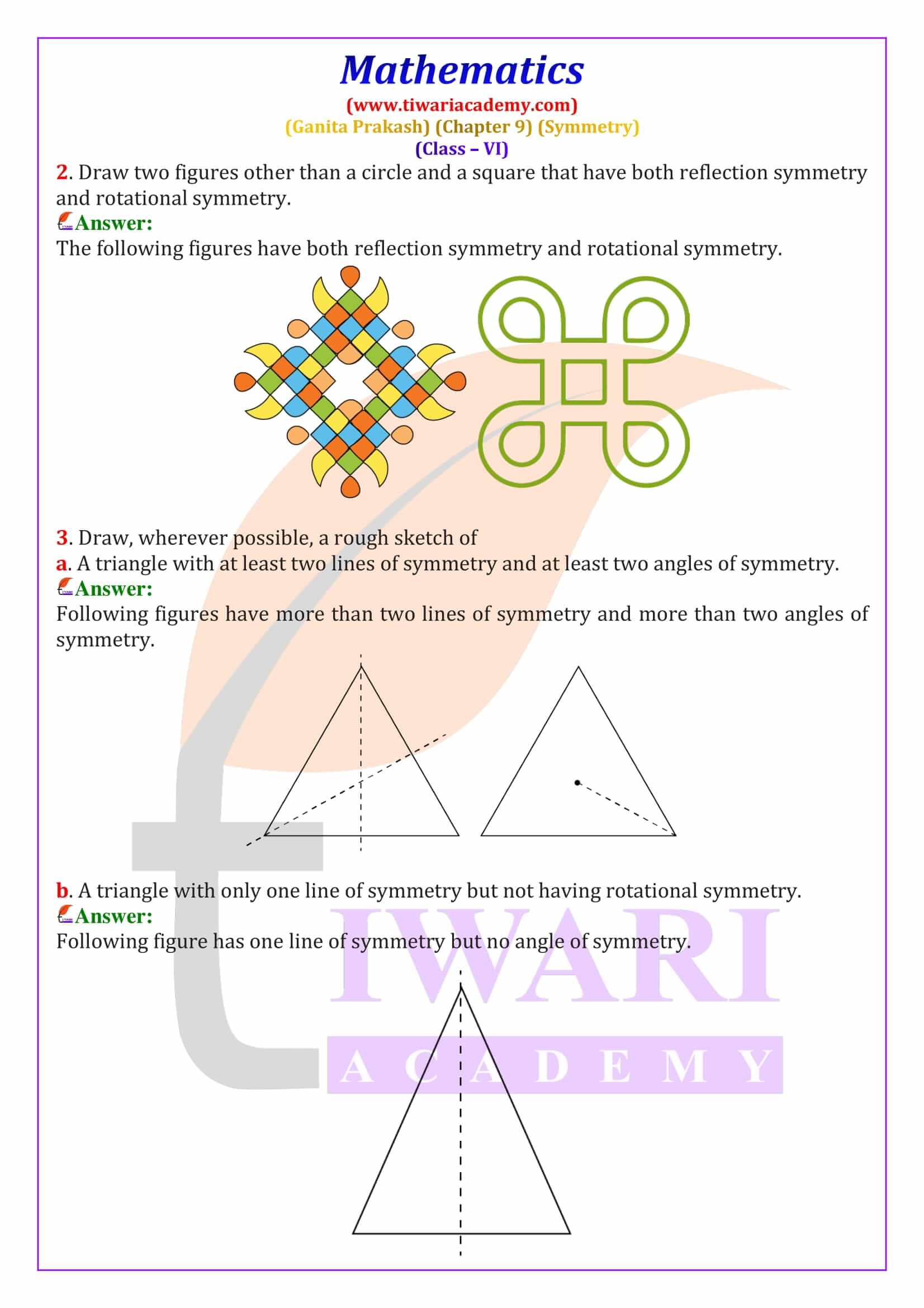
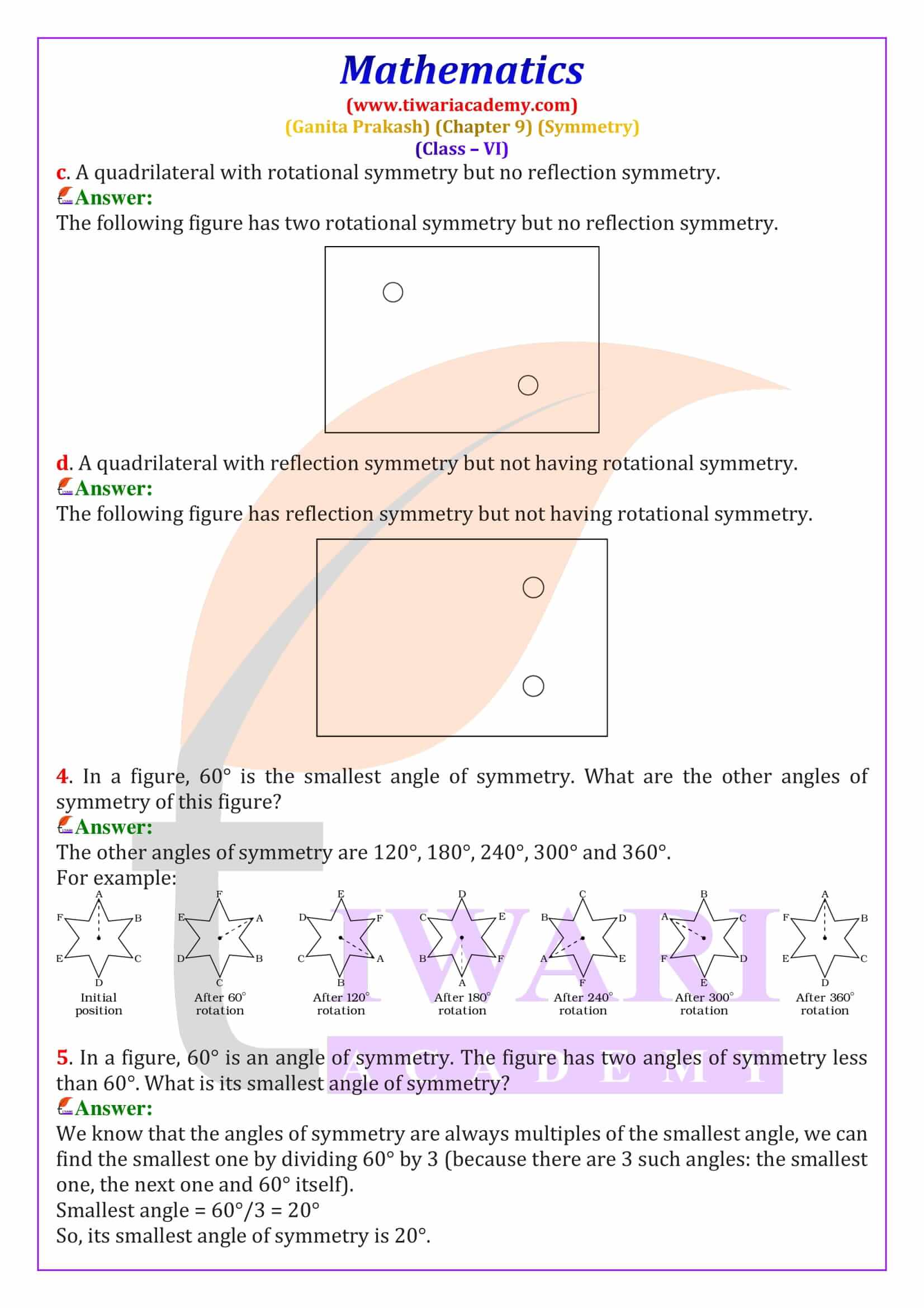
Rotational Symmetry – Meaning and Angle of Rotation
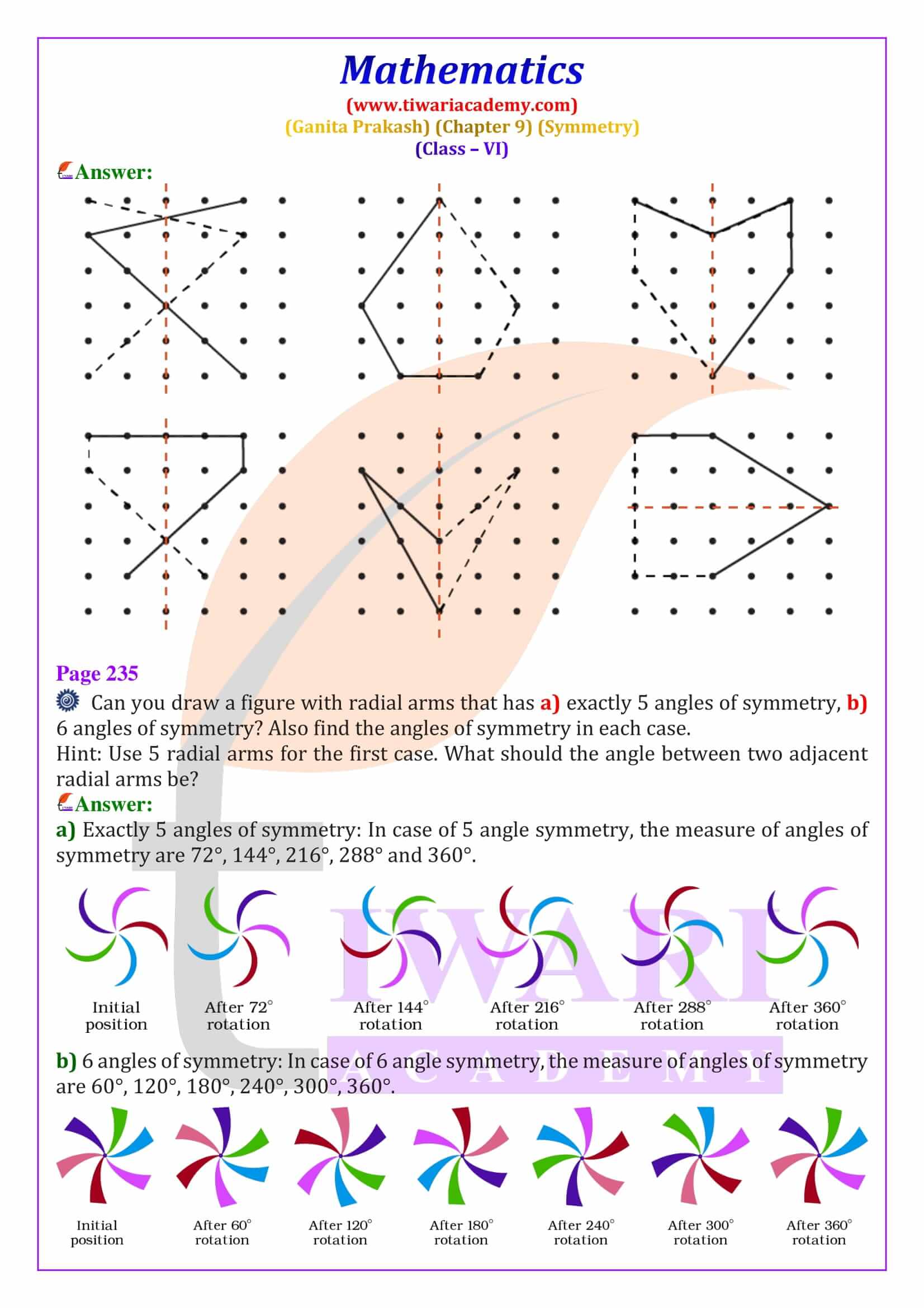
Rotational symmetry occurs when a figure looks the same after being rotated around a fixed point called the centre of rotation. In Ganita Prakash Chapter 9, students learn about angles of rotational symmetry such as 90°, 120° and 180°. For example, a square has rotational symmetry at 90°, 180°, and 270°. These Class 6 Maths rotational symmetry solutions explain how to identify angles of symmetry using diagrams and logical steps.
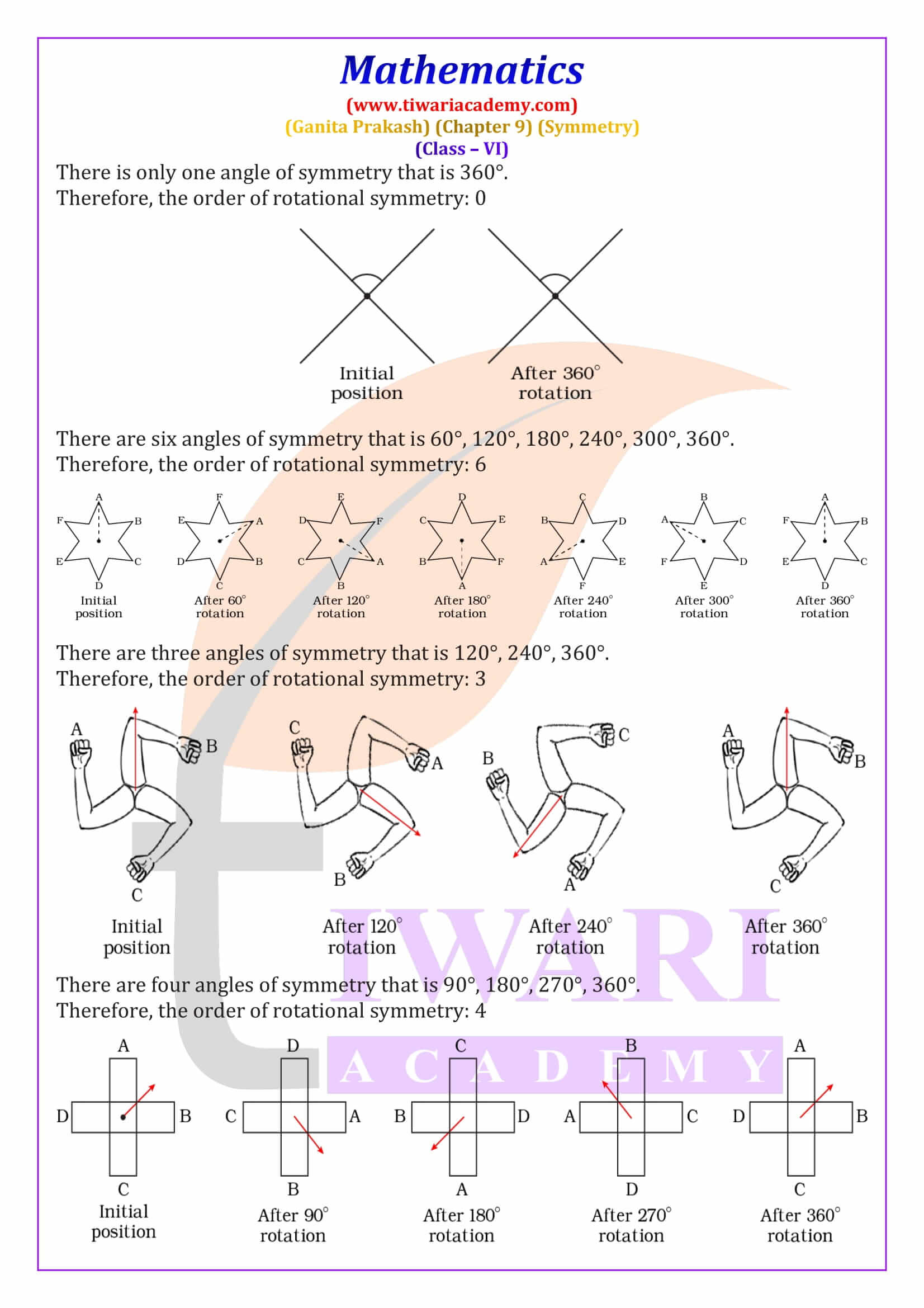
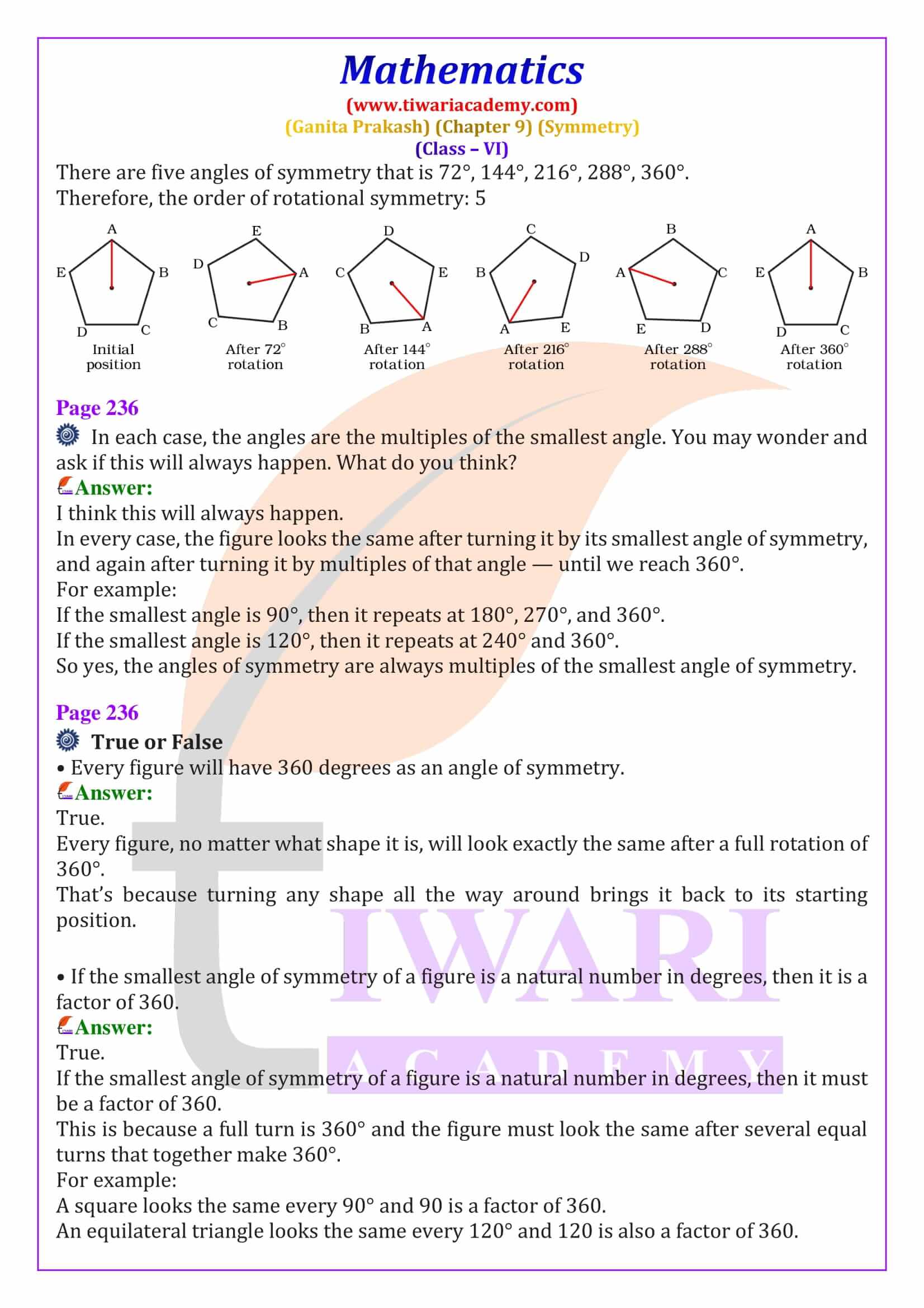
Order of Rotational Symmetry and Special Shapes
The order of rotational symmetry is the number of times a figure matches itself during one complete rotation of 360 degrees. Regular shapes like squares, equilateral triangles, and regular polygons have fixed orders of symmetry. A circle is a special figure because it has infinite lines of symmetry and infinite angles of rotational symmetry. This section explains how to find the smallest angle of symmetry using the formula 360° ÷ order of symmetry, an important exam concept.
Why Use These Class 6 Symmetry Solutions
These Class 6 Maths Ganita Prakash Chapter 9 Symmetry solutions are fully aligned with the latest textbook and CBSE exam pattern. The content is student-friendly, concept-focused and ideal for revision, homework help and exam preparation. With clear explanations, symmetry diagrams and step-by-step answers, this page is a reliable resource for students looking for NCERT Class 6 Maths Chapter 9 solutions and quick conceptual clarity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is Class 6 Maths Chapter 9 Symmetry difficult?
No, Class 6 Maths Chapter 9 Symmetry is not difficult if the concepts are understood visually. The chapter mainly focuses on observing shapes, folding figures, and identifying patterns, which makes it easier than calculation-based chapters in Ganita Prakash.
How can Class 6 students solve the Symmetry chapter easily?
Students can solve Class 6 Maths Symmetry easily by practicing with diagrams, using paper folding and understanding examples given in Ganita Prakash Chapter 9. Drawing figures neatly and checking overlap by imagination helps avoid mistakes.
Which topic is most important in Class 6 Maths Chapter 9?
The most important topics in Class 6 Maths Chapter 9 Symmetry are line of symmetry, rotational symmetry and order of rotational symmetry. These concepts are frequently asked in exams and form the base for higher-class geometry.
How to score full marks in Symmetry chapter Class 6?
To score full marks in Class 6 Maths Chapter 9, students should practice identifying lines of symmetry, drawing symmetrical figures correctly and understanding rotational angles. Neat diagrams and clear reasoning are essential for scoring well.
Are diagrams important in Class 6 Maths Symmetry questions?
Yes, diagrams are very important in Class 6 Maths Symmetry. Most questions are based on drawing, completing figures or identifying symmetry visually. Clear and accurate diagrams help students get full marks.
Is Symmetry chapter useful for higher classes?
Yes, Symmetry is a foundational chapter 9. Concepts learned in Class 6 Maths Ganita Prakash Chapter 9 are used later in geometry, transformations, coordinate geometry and even physics diagrams in higher classes.