NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 4 The World of Metals and Non-metals for Session 2025-26. Class 7th Science gives clear and accurate explanations to all questions, helping students understand the properties, uses and differences between metals and non-metals. NCERT Curiosity Chapter 4 solutions include concept-based answers, practical examples and activity-based learning to build strong scientific understanding. Aligned with the latest curriculum, they support students in preparing for exams and improving their overall performance in science.
Class 7 Science Solutions
Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 4 Solutions
Let Us Enhance Our Learning
1. Which metal is commonly used to make food packaging materials as it is cheaper, and its thin sheets can be folded easily into any shape?
(i) Aluminium
(ii) Copper
(iii) Iron
(iv) Gold
See Answer(i) Aluminium. (Aluminium foil is commonly used for wrapping food. Metals can be beaten into thin sheets due to malleability.)
2. Which of the following metal catches fire when it comes in contact with water?
(i) Copper
(ii) Aluminium
(iii) Zinc
(iv) Sodium
See Answer(iv) Sodium. (Sodium reacts vigorously with oxygen and water, generating heat and is stored in kerosene to prevent this.)
3. State with reason(s) whether the following statements are True [T] or False [F].
(i) Aluminium and copper are examples of non-metals used for making utensils and statues. [ ]
(ii) Metals form oxides when combined with oxygen, the solution of which turns blue litmus paper to red. [ ]
(iii) Oxygen is a non-metal essential for respiration. [ ]
(iv) Copper vessels are used for boiling water because they are good conductors of electricity. [ ]
See Answer(i) [F] False. Aluminium and copper are metals, known for properties like lustre and hardness.
(ii) [F] False. Metal oxides are generally basic in nature, and basic solutions turn red litmus paper blue.
(iii) [T] True. Oxygen is a non-metal essential for survival (respiration).
(iv) [F] False. Copper vessels are used for boiling water because they are good conductors of heat, not primarily electricity, allowing heat to transfer efficiently to the water.
4. Why are only a few metals suitable for making jewellery?
See AnswerMetals suitable for jewellery need specific properties: Lustre (shiny appearance); Malleability & Ductility (easily shaped and drawn into wires); Resistance to Corrosion (don’t tarnish easily); Rarity/Value. Metals like gold and silver possess these qualities well.
5. Match the uses of metals and non-metals given in Column I with the jumbled names of metals and non-metals given in Column II.

See Answer(i) Used in electrical wiring – (c) PEPORC (COPPER).
(ii) Most malleable and ductile – (e) OGDL (GOLD).
(iii) Living organisms cannot survive without it – (a) ENXYGO (OXYGEN).
(iv) Plants grow healthy when fertilisers containing it are added to the soil – (d) TENGOINR (NITROGEN).
(v) Used in water purification – (b) NECOHIRL (CHLORINE).

6. What happens when oxygen reacts with magnesium and sulfur. What are the main differences in the nature of products formed?
See AnswerWhen magnesium (a metal) reacts with oxygen (burns), it forms magnesium oxide. When sulfur (a non-metal) reacts with oxygen (burns), it forms sulfur dioxide gas. Main Difference: Magnesium oxide (metal oxide) forms a basic solution in water. Sulfur dioxide (non-metal oxide) forms an acidic solution in water. Generally, metal oxides are basic and non-metal oxides are acidic.
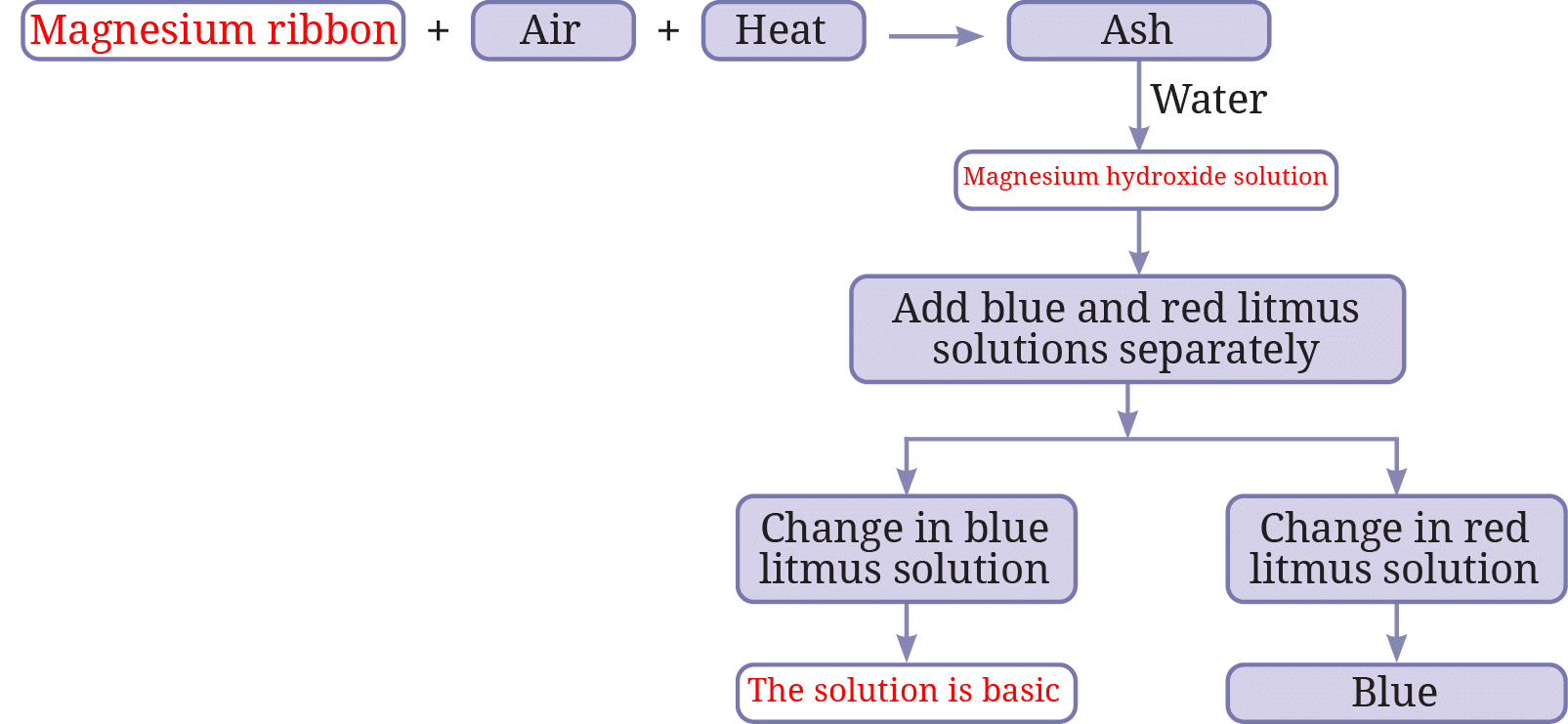
7. Complete the following flow chart: (Flow chart depicts burning magnesium)
See AnswerStarting material (?) = Magnesium ribbon
Magnesium ribbon + Air + Heat -> Ash = Magnesium oxide
Ash (Magnesium oxide) + Water -> Solution (?) = Magnesium hydroxide solution
Add litmus: Change in blue litmus = No change; Change in red litmus = Turns blue.
Conclusion (?) = The solution is basic.
8. You are provided with the following materials. Discuss which material would be your choice to make a pan that is most suitable for boiling water and why?
Iron, copper, sulfur, coal, plastic, wood, cardboard
See AnswerThe best choice would be copper or iron.
Reason: Pans for boiling water need to transfer heat efficiently. Metals like copper and iron are good conductors of heat. Materials like sulfur, coal, plastic, wood and cardboard are poor conductors of heat and unsuitable for cooking vessels.
9. You are provided with three iron nails, each dipped in oil, water and vinegar. Which iron nail will not rust, and why?
See AnswerThe iron nail dipped in oil will likely not rust (or rust much slower than the others).
Reason: Rusting requires both air (oxygen) and water. Oil prevents the iron surface from contacting air and moisture, inhibiting rust.
10. How do the different properties of metals and non-metals determine their uses in everyday life?
See AnswerProperties determine uses:
Metals: Good Electrical Conductivity (wires); Good Heat Conductivity (cookware); Malleability/Ductility (sheets, wires, jewellery); Strength (structures, tools); Sonority (bells); Lustre (decoration).
Non-metals: Poor Conductivity (insulation, handles); Gaseous State (Oxygen for breathing, Nitrogen for fertilizers); Specific Chemical Properties (Chlorine for purification, Iodine as antiseptic, Carbon for life); Brittleness (not for structures needing strength).
11. One of the methods of protecting iron from getting rusted is to put a thin coating of zinc metal over it. Since sulfur does not react with water, can it be used for this purpose? Justify your answer.
See AnswerNo, sulfur cannot effectively be used for this purpose.
Justification: Sulfur is brittle and does not form a durable, adherent protective layer like zinc metal does in galvanization. A sulfur coating would likely crack or flake off.
12. An ironsmith heats iron before making tools. Why is heating necessary in this process?
See AnswerHeating iron makes it softer and much more malleable. This allows the ironsmith to beat the hot iron with a hammer and shape it into desired forms, like tools, relatively easily.
Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 3 Very Short Answer Type Questions
What is malleability?
See AnswerMalleability is the property of a material that allows it to be beaten into thin sheets without breaking. Most metals, like gold and aluminium, are malleable.
Name two metals used to make kitchen utensils.
See AnswerAluminium and copper are commonly used metals for making kitchen utensils due to their good heat conductivity and malleability.
What kind of sound do metals make when struck?
See AnswerMetals produce a ringing sound when struck. This property is called sonority and metals are said to be sonorous.
Which metal remains in liquid form at room temperature?
See AnswerMercury is the only metal that exists in liquid form at room temperature.
What is rusting?
See AnswerRusting is the formation of a brown coating on iron when it reacts with moisture and air. It is a type of corrosion.
Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 3 Short Answer Type Questions
Why are electrical wires usually made of copper or Aluminium?
See AnswerCopper and Aluminium are excellent conductors of electricity and are ductile, allowing them to be drawn into thin wires. These properties make them ideal for electrical wiring in homes and appliances.
What happens when magnesium ribbon burns in air?
See AnswerMagnesium ribbon burns with a dazzling white flame in air and forms magnesium oxide, a white powder. When dissolved in water, it turns red litmus blue, showing it is basic in nature.
Why are metals used for making cooking utensils?
See AnswerMetals like aluminium and copper conduct heat efficiently and distribute it evenly, making them ideal for cooking. Their hardness and durability add to their usefulness in kitchens.
What is ductility? Give two examples of ductile metals.
See AnswerDuctility is the property by which a material can be drawn into thin wires. Gold and copper are ductile metals widely used in jewellery and electrical wiring, respectively.
Why do we store sodium metal in kerosene?
See AnswerSodium reacts violently with air and water, producing heat and flammable gases. Storing it in kerosene prevents exposure to moisture and air, thus avoiding dangerous reactions.
Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 4 Descriptive Questions
Explain the difference between metals and non-metals with examples.
See AnswerMetals are lustrous, malleable, ductile, and good conductors of heat and electricity (e.g., iron, aluminium). Non-metals are dull, brittle, and poor conductors (e.g., sulfur, carbon). Metals form basic oxides, while non-metals form acidic oxides. Each group has unique properties, making them useful in different areas like construction, medicine and agriculture.
Why does an iron nail rust when exposed to both air and water?
See AnswerRusting occurs when iron reacts with both air (oxygen) and water (moisture). The experiment with iron nails in three different conditions shows that brown deposits form only when both elements are present, confirming that moist air causes rusting.
Why are most handles of kitchen tools made from wood or plastic?
See AnswerWood and plastic are poor conductors of heat. When used for handles, they protect users from burns while cooking. Metals conduct heat quickly, so handles made entirely of metal could become too hot and unsafe.
How does the oxide of sulfur differ from the oxide of magnesium in nature?
See AnswerSulfur oxide is acidic in nature. It turns blue litmus red. In contrast, magnesium oxide is basic and turns red litmus blue. This shows that oxides of non-metals are acidic, while those of metals are basic.
What does the Iron Pillar of Delhi teach us about ancient Indian metallurgy?
See AnswerThe Iron Pillar of Delhi, over 1600 years old, has resisted rusting despite harsh weather. This showcases the advanced metallurgical skills of ancient India in preventing corrosion through special techniques still not fully understood.
Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 4 Exploring Questions
How do metals and non-metals affect our daily lives in different ways?
See AnswerMetals are essential for infrastructure, tools, transportation, and electronics due to their strength, conductivity and durability. Non-metals like oxygen and carbon are vital for respiration and food. Iodine is used for wounds, and nitrogen for fertilisers. Both groups contribute significantly to health, agriculture and technology.
If sulfur is soft, non-sonorous, and poor conductor, can it be used for making wires? Why or why not?
See AnswerNo, sulfur cannot be used to make wires. It lacks ductility, breaks easily and doesn’t conduct electricity. In contrast, metals like copper and aluminium are ductile and conductive, making them suitable for wiring in homes and devices.
Why is the discovery of iron considered more significant in history than copper, despite copper being discovered earlier?
See AnswerAlthough copper was discovered earlier due to its easier extraction, iron had a greater impact due to its strength and usefulness in making superior agricultural tools, weapons and structures. This advancement helped in the growth of civilizations.
Can sulfur be used to prevent rusting of iron like zinc is used in galvanisation? Why or why not?
See AnswerNo, sulfur cannot be used for rust prevention. It is a non-metal and does not form a protective barrier. Zinc, being a metal, forms a coating that protects iron from air and moisture, thereby preventing rusting.
Which materials would you choose to make a pan for boiling water and why?
See AnswerI would choose copper or aluminium because both are excellent conductors of heat and can withstand high temperatures. Their malleability allows shaping into pans and their durability makes them ideal for daily cooking tasks.
Let’s Discuss Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 4
Why do iron objects rust when kept in open air and water, as explained in Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 4?
In Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 4, it is clearly shown through an experiment that rusting of iron occurs only when both air (oxygen) and water (moisture) are present. Iron reacts with oxygen and water from the environment to form a reddish-brown substance called rust. This process is called rusting and it is a type of corrosion. When an iron nail is kept only in dry air or only in water, it does not rust. However, if it is exposed to moist air, rust forms. This damages tools, machines, and structures over time. Preventive methods like painting, oiling or galvanising are used to stop rusting.
What is the difference between the oxides formed by metals and non-metals in Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 4?
According to Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 4, when metals like magnesium burn in air, they form basic oxides such as magnesium oxide. These turn red litmus paper blue. On the other hand, non-metals like sulfur form acidic oxides such as sulfur dioxide when burned. When dissolved in water, sulfur dioxide forms sulfurous acid, which turns blue litmus paper red. This difference is due to the chemical nature of metals and non-metals. Metal oxides are generally basic, while non-metal oxides are acidic. This is one of the key differences between metals and non-metals, and it helps in identifying unknown substances in chemistry.
Why can metals be used for making wires but non-metals cannot, as mentioned in Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 4?
In Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 4, it is explained that metals are ductile, which means they can be drawn into thin wires without breaking. Copper, aluminium and gold are common examples of ductile metals. They are also good conductors of electricity, which makes them ideal for wiring in homes, appliances, and electronic devices. Non-metals, like sulfur and coal, are brittle and break easily when stretched. They also do not allow electricity to pass through them. Therefore, they cannot be used for making wires. This is why wires are always made of metals like copper or aluminium, and not from non-metals.
Is it necessary to do all the experiments in Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 4?
Doing the activities or at least observing them helps a lot in understanding the concepts. You don’t need a lab setup—some tests, like checking conductivity or sonority, can be done at home using simple objects. They make learning more fun and practical and also help you remember better during exams.
What is the easiest way to remember the difference between metals and non-metals in Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 4?
An easy way to remember the difference is by using a simple table or flashcards. For example, metals are shiny, hard and conduct electricity (like copper and iron), while non-metals are usually dull, brittle and poor conductors (like sulfur and carbon). Associating examples from real life—like wires for metals and matchsticks for non-metals—also helps in quick recall during tests or class discussions.
Do I need to remember all the properties of metals and non-metals for Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 4?
Yes, but focus on the most important properties like malleability, ductility, conductivity and the nature of oxides. You don’t need to memorise long definitions—just understand what each property means and be able to give simple examples. Most questions in exams come from basic differences and real-life applications of these properties.


