NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 7 Heat Transfer in Nature for new session 2025-26. The NCERT Curiosity Solutions give clear explanations of key concepts like conduction, convection and radiation. These solutions help students understand how heat moves through solids, liquids and gases using real-life examples and engaging activities. The Curiosity solutions also cover the water cycle, land or sea breezes and innovative practices like ice stupas, making learning interactive, relatable and useful for both exams and everyday understanding.
Class 7 Science Solutions
Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 7 Solutions
Let Us Enhance Our Learning
1. Choose the correct option in each case.
(i) Your father bought a saucepan made of two different materials, A and B, as shown in Fig. 7.14. The materials A and B have the following properties-
(a) Both A and B are good conductors of heat
(b) Both A and B are poor conductors of heat
(c) A is a good conductor and B is a poor conductor of heat
(d) A is a poor conductor and B is a good conductor of heat

See Answer(i) (c) A is a good conductor and B is a poor conductor of heat. (Pan body needs to conduct heat; handle needs to insulate).
(ii) Pins are stuck to a metal strip with wax and a burning candle is kept below the rod, as shown in Fig. 7.15. Which of the following will happen?
(a) All the pins will fall almost at the same time
(b) Pins I and II will fall earlier than pins III and IV
(c) Pins I and II will fall later than pins III and IV
(d) Pins II and III will fall almost at the same time
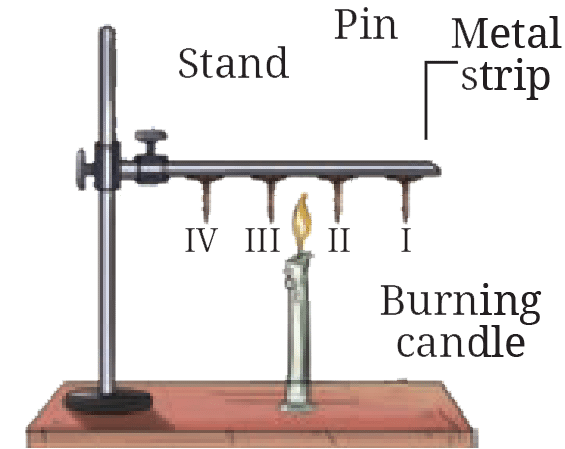
See Answer(ii) (b) Pins I and II will fall earlier than pins III and IV. (Heat conducts from the end near pin I towards pin IV, melting wax sequentially).
(iii) A smoke detector is a device that detects smoke and sounds an alarm. Suppose you are fitting a smoke detector in your room. The most suitable place for this device will be:
(a) Near the floor
(b) In the middle of a wall
(c) On the ceiling
(d) Anywhere in the room
See Answer(iii) (c) On the ceiling. (Smoke rises due to convection).
2. A shopkeeper serves you cold lassi in a tumbler. By chance, the tumbler had a small leak. You were given another tumbler by the shopkeeper to put the leaky tumbler in it. Will this arrangement help to keep the lassi cold for a longer time? Explain.
See AnswerYes.
Explanation: The air trapped between the two tumblers acts as an insulator (poor conductor of heat). This slows down heat transfer from the surroundings to the cold lassi.
3. State with reason(s) whether the following statements are True [T] or False [F].
(i) Heat transfer takes place in solids through convection. [ ]
(ii) Heat transfer through convection takes place by the actual movement of particles. [ ]
(iii) Areas with clay materials allow more seepage of water than those with sandy materials. [ ]
(iv) The movement of cooler air from land to sea is called land breeze. [ ]
See Answer(i) [F] False. Correct: Heat transfer in solids is mainly through conduction.
(ii) [T] True. Convection involves movement of fluid particles.
(iii) [F] False. Correct: Sandy materials allow more/faster seepage than clay due to larger particle spaces.
(iv) [T] True. Land breeze is cool air moving from land to sea, usually at night.
4. Some ice cubes placed in a dish melt into water after sometime. Where do the ice cubes get heat for this transformation?
See AnswerThe ice cubes absorb heat from their surroundings (the dish and the surrounding air).
5. A burning incense stick is fixed, pointing downwards. In which direction would the smoke from the incense stick move? Show the movement of smoke with a diagram.
See AnswerThe smoke would move upwards.
Explanation: Smoke consists of hot gases which are less dense than cool air and rise due to convection. (Diagram would show stick pointing down, smoke rising up).
6. Two test tubes with water are heated by a candle flame as shown in Fig. 7.16. Which thermometers (Fig. 7.16a or Fig. 7.16b) will record a higher temperature? Explain.
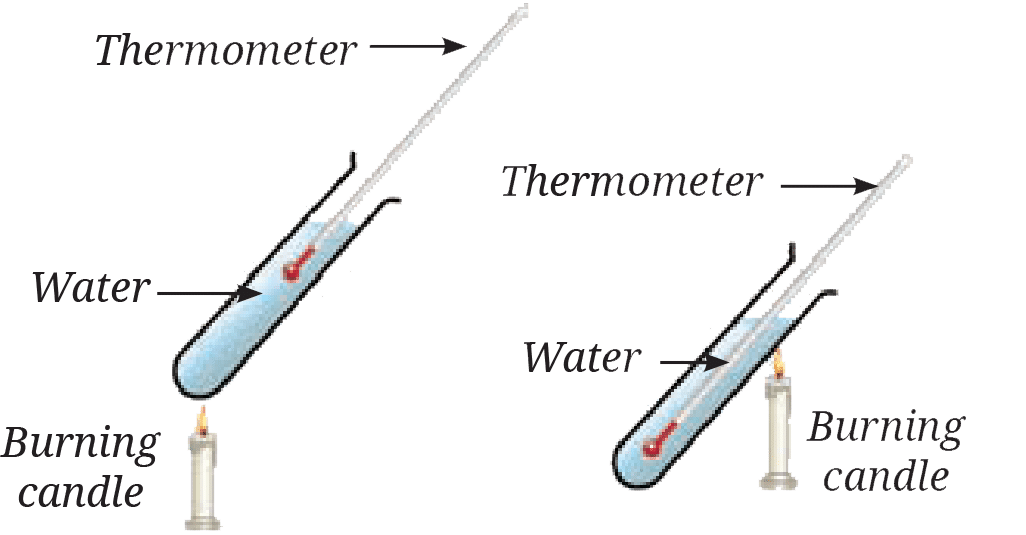
See AnswerThe thermometer in Fig. 7.16b (heated from the bottom) will record a higher temperature throughout the water faster.
Explanation: Heating from the bottom (b) sets up efficient convection currents, circulating and heating the water quickly. Heating from the top (a) mainly heats the top layer, relying on slower conduction to heat the rest.
7. Why are hollow bricks used to construct the outer walls of houses in hot regions?
See AnswerThe air trapped inside the hollow spaces acts as an insulator (poor conductor of heat). This reduces heat transfer from the hot outside, keeping the house cooler.
8. Explain how large water bodies prevent extreme temperature in areas around them.
See AnswerWater heats up and cools down slower than land. During the day, it absorbs heat, keeping coastal areas cooler. At night, it releases heat slowly, keeping coastal areas warmer than inland areas, thus moderating the temperature range. Sea and land breezes also contribute.
9. Explain how water seeps through the surface of the Earth and gets stored as groundwater.
See AnswerSurface water seeps into the ground through spaces between soil/rock particles (infiltration). It moves downwards until it fills these spaces in saturated layers called aquifers, where it is stored as groundwater. Seepage is faster through porous materials like sand/gravel.
10. The water cycle helps in the redistribution and replenishment of water on the Earth. Justify the statement.
See AnswerJustification: The water cycle involves evaporation (water to vapour), condensation (vapour to clouds) and precipitation (water returning to Earth). This process transports water from oceans/lakes/etc. to the atmosphere and then distributes it over land and sea via rain/snow, replenishing rivers, lakes and groundwater.
Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 7 Very Short Answer Type Questions
What is conduction?
See AnswerConduction is the transfer of heat through solids from the hotter part to the colder part without the movement of particles.
Which materials are poor conductors of heat?
See AnswerWood, plastic, air, clay and wool are poor conductors of heat.
Why is a metal pan used for cooking?
See AnswerBecause metals are good conductors of heat, they allow heat to spread evenly and quickly.
Name the three modes of heat transfer.
See AnswerConduction, convection, and radiation.
Which process allows heat transfer from the Sun to Earth?
See AnswerRadiation.
Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 7 Short Answer Type Questions
Why do pins attached to a metal strip fall one after the other during heating?
See AnswerHeat travels from the hot end to the colder end through conduction. The wax near each pin melts as heat reaches it, making the pins fall in sequence.
Why do we wear woollen clothes in winter?
See AnswerWool traps air and since air is a poor conductor of heat, it helps keep body heat from escaping, keeping us warm.
What causes land and sea breeze?
See AnswerLand heats up and cools down faster than sea water. This temperature difference causes wind to move from sea to land during the day (sea breeze) and vice versa at night (land breeze).
How does a bukhari keep a room warm?
See AnswerA bukhari uses conduction to heat its surface, convection to circulate warm air, and radiation to transfer heat to nearby people and objects.
Why is it comfortable to wear white clothes in summer?
See AnswerWhite or light-coloured clothes reflect most of the Sun’s heat, keeping the body cooler in hot weather.
Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 7 Descriptive Answer Type Questions
Explain the process of convection in liquids using an activity.
See AnswerWhen a candle heats the base of a beaker filled with water and potassium permanganate, the water at the bottom becomes warm, expands, and rises. Cooler water from the sides moves down to replace it, creating a circular flow. This movement of particles carrying heat is called convection.
How does the use of hollow bricks help in temperature control in houses?
See AnswerHollow bricks trap air in their cavities. Since air is a poor conductor of heat, it reduces heat transfer. Thus, such walls help keep houses warm in winter and cool in summer, making them energy-efficient.
What is infiltration and how does it affect groundwater levels?
See AnswerInfiltration is the process of water seeping through the soil and rocks. This water collects in underground layers called aquifers. Less infiltration due to concrete surfaces or overuse of groundwater can lead to water scarcity.
How does heat transfer through radiation differ from conduction and convection?
See AnswerRadiation does not need a medium and transfers heat through electromagnetic waves. Conduction and convection require a medium and involve contact or particle movement. Radiation is how the Sun’s heat reaches the Earth.
Explain the water cycle using heat transfer processes.
See AnswerThe Sun’s heat causes evaporation and transpiration. Water vapour rises and cools, forming clouds (condensation). Clouds release water as rain, snow or hail (precipitation). Some water infiltrates the ground, becoming groundwater, completing the cycle.
Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 7 Exploring Questions
Why does smoke from incense or firewood rise upward?
See AnswerHot air is lighter and rises. Smoke, being warm and less dense than surrounding air, also rises through convection. This principle is used in designing chimneys and ventilation systems.
Why is water served in clay or porcelain cups instead of metal ones during summers?
See AnswerClay and porcelain are poor conductors of heat. They do not heat up quickly, keeping water cool longer. In contrast, metals conduct heat easily and make the drink warmer quickly.
Why do we feel warm even when we sit at a distance from a fire?
See AnswerThis warmth is due to radiation, where heat travels through space without needing any medium. It directly warms objects and our body from the fire’s surface.
What are aquifers and why are they important for survival?
See AnswerAquifers are underground layers of porous rock or soil that store water. They provide groundwater for drinking, farming, and daily use. Excessive extraction and poor recharge can deplete them.
How do ice stupas in Ladakh help in water conservation?
See AnswerIce stupas are man-made ice towers that store winter water in frozen form. They melt slowly in spring, supplying water during dry months for agriculture and household use—an example of innovation using natural principles.
What are the three methods of heat transfer explained in Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 7?
In Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 7, the three methods of heat transfer are conduction, convection and radiation.
1. Conduction happens in solids when heat passes from one particle to the next without the particles moving from their places.
2. Convection occurs in liquids and gases, where the heated particles move and carry heat with them.
3. Radiation is the transfer of heat without any medium; for example, the heat we feel from the Sun or a fire. These methods work differently but often act together, such as when heating water in a metal pan on a stove.
Why do people living in cold places use double-layered wooden walls, as discussed in Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 7?
Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 7 explains that in very cold regions like Uttarkashi in the Himalayas, homes are often built with double-layered wooden walls filled with cow dung or mud. These materials are poor conductors of heat, meaning they do not allow heat to escape easily. This design traps warmth inside the house and prevents heat loss, making homes more comfortable in harsh winters. Similarly, some homes use hollow bricks that trap air to regulate temperature. These construction techniques use the science of heat transfer to protect people from extreme climates.
How does the water cycle relate to heat transfer, as taught in Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 7?
According to Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 7, the water cycle is driven by the Sun’s heat, which causes evaporation of water from oceans, lakes and plants (transpiration). The water vapour rises, cools and condenses to form clouds. Later, it falls as precipitation (rain, snow, hail). Water also infiltrates the ground and gets stored in aquifers. This continuous cycle depends on radiation from the Sun to evaporate water and convection to move vapour upwards. Thus, heat transfer plays a key role in recycling and redistributing Earth’s water, ensuring availability for all living organisms.
What is the main thing to understand in Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 7?
The most important thing to understand in Chapter 7 is the three ways heat transfers—conduction, convection, and radiation. These explain how heat moves through solids, liquids, gases and even space. Real-life examples like land and sea breeze, hot utensils and sunlight make the concept easier to grasp. Once you get the basic idea, the rest of the chapter becomes simple and logical.
Is Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 7 full of tough science terms?
No, Class 7 Science Curiosity Chapter 7 actually uses easy, relatable examples like boiling water, warming hands near a fire or why we wear wool in winter. The terms like convection or radiation might sound new at first, but they’re explained with everyday situations. With a few diagrams and practice, you’ll find this chapter is more about understanding than memorizing.
How can I remember the difference between conduction, convection and radiation in Chapter 7?
Here’s a quick trick:
- Conduction = direct contact (like a metal spoon in hot soup).
- Convection = movement of fluids (like hot air rising or sea breeze).
- Radiation = no contact needed (like heat from the Sun).
Drawing a small table or chart and relating each to real-life examples makes them easy to remember for exams and everyday understanding.


