NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 13 Animal Jumps revised for Session 2025-26. It helps students understand patterns, sequences and number jumps in a fun way. The chapter uses activities with animals like rabbits, frogs and kangaroos to teach skip counting, multiplication patterns and number lines. Through playful exercises, learners explore how animals “jump” forward or backward by fixed numbers, strengthening concepts of arithmetic progressions, addition, subtraction and logical reasoning. Perfect for improving mental math and observation skills.
Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 13 Solutions
Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 13 MCQ
Class 5 Math Magic Chapter 13 Solutions
Class 5 Maths all Chapters Solutions
Animal Jumps Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 13 Solutions
Page 164
Find the hidden numbers
Numbers put in this box get multiplied by a number and come out.
(a) Can you guess the multiplier if you see the 4 numbers coming out of the box?
(b) Is there more than one possible multiplier?
(c) What numbers might have been put inside the box?

Answer:
(a) To find the multiplier, we need to figure out a number that, when multiplied by other numbers, gives us 28, 36, 48 and 72.
28/4 = 7
36/4 = 9
48/4 = 12
72/4 = 18
As we can see to divide given number with 4 we will get 7, 9, 12, 18. So, we can multiply the numbers with 4:
7 × 4 = 28
9 × 4 = 36
12 × 4 = 48
18 × 4 = 72
Therefore, the multiplier is 4.
(b) Yes, we can say it is also a multiple of 2.
(c) As we found earlier, the numbers inside the box are 7, 9, 12 and 18, because when these numbers are multiplied by 4, we get the numbers that came out: 28, 36, 48 and 72.
So, the numbers that might have been put inside the box are 7, 9, 12 and 18
A number, when arranged in an array, shows the factors of that number. Are there other numbers that are factors of 15? Try to make other arrays for the number 15.
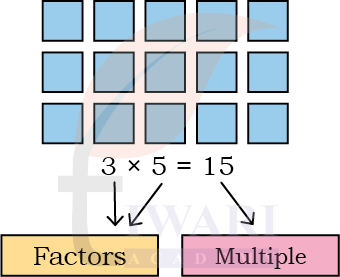
Answer:
All the arrays we can make for 15:
1 row × 15 columns = 15
3 rows × 5 columns = 15
5 rows × 3 columns = 15
15 rows × 1 column = 15
So the full list of factors of 15 is 1, 3, 5, 15.
Let Us Do Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 13 on Page 165
Page 165
Let Us Do
Make different arrays for the following numbers. Identify the factors in each case.
(a) 10
(b) 14
(c) 13
(d) 20
(e) 25
(f) 32
(g) 37
(h) 46
(i) 54
Numbers like 13 and 37 are called prime numbers. Why?
Answer:
Arrays (factor pairs): The different ways to arrange it as rows × columns
Factors: All the numbers that divide it exactly (listed smallest to largest)
(a) 10
Arrays (factor pairs): 1 × 10, 2 × 5
Factors: 1, 2, 5, 10
(b) 14
Arrays: 1 × 14, 2 × 7
Factors: 1, 2, 7, 14
(c) 13
Arrays: 1 × 13 only
Factors: 1, 13
13 is a prime number because we cannot make any array other than 1 × 13.
So it has only two factors: 1 and itself.
(d) 20
Arrays: 1 × 20, 2 × 10, 4 × 5
Factors: 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 20
(e) 25
Arrays: 1 × 25, 5 × 5
Factors: 1, 5, 25
(f) 32
Arrays: 1 × 32, 2 × 16, 4 × 8
Factors: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32
(g) 37
Arrays: 1 × 37 only
Factors: 1, 37
37 is a prime number.
(h) 46
Arrays: 1 × 46, 2 × 23
Factors: 1, 2, 23, 46
(i) 54
Arrays: 1 × 54, 2 × 27, 3 × 18, 6 × 9
Factors: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18, 27, 54
Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 13 Animal Jumps on Page 165
Page 165
Animal Jumps
12 is the first common multiple of 3 and 4. What are some other common multiples of 3 and 4? You can continue the number line or take help from the times tables of 3 and 4.
Answer:
The multiples of 3 are: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, …
The multiples of 4 are: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, …
The common multiples of 3 and 4 are: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72 and so on.
The common multiples of 3 and 4 are multiples of 12. The first common multiple is 12 and after that, the common multiples increase by 12 each time.
Page 166
A spider takes a jump of 3 every time. A grasshopper takes a jump of 6 each time. Use the number line to find the common multiples of 3 and 6.

Answer:
Spider (jumps of 3) Lands at: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24…
Grasshopper (jumps of 6): Lands at: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36…
Common multiples of 3 and 6 are the positions where both insects land: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36…
6 and 12 are two common multiples of 3 and 6. You can continue the pattern to find more common multiples. What do you notice about the common multiples of 3 and 6? Discuss.
Answer:
From the number line, the common multiples shown for 3 and 6 are: 6, 12, …
Every multiple of 6 is also a multiple of 3.
So, the common multiples of 3 and 6 are exactly the multiples of 6.
Examples:
6 = 3 × 2 and 6 × 1
12 = 3 × 4 and 6 × 2
18 = 3 × 6 and 6 × 3
Hence, all common multiples of 3 and 6 are multiples of 6.
This happens because 6 itself is a multiple of 3.
12 and 24 are two of the common multiples of 4 and 6. List a few more.
Answer:
The multiples of 4 are: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, …
The multiples of 6 are: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, …
The common multiples of 4 and 6 are: 12, 24, 36 and so on.
Page 166 Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 13 Let Us Do
Page 166
Let Us Do
1. Find 5 common multiples of the following pairs of numbers.
(a) 2 and 3
Answer:
Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, …
Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, …
Common multiples: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30
(b) 5 and 8
Answer:
Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, …
Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, …
Common multiples: 40, 80, 120, 160, 200
(c) 2 and 4
Answer:
Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, …
Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, …
Common multiples: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20
(d) 3 and 9
Answer:
Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, …
Multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, …
Common multiples: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45
(e) 5 and 10
Answer:
Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, …
Multiples of 10: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, …
Common multiples: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50
(f) 9 and 12
Answer:
Multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54, …
Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, …
Common multiples: 36, 72, 108, 144, 180
(g) 8 and 12
Answer:
Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80, …
Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, 96, 108, …
Common multiples of: 24, 48, 72, 96, 120
(h) 6 and 8
Answer:
Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, …
Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, …
Common multiples: 24, 48, 72, 96, 120
(i) 6 and 9
Answer:
Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, …
Multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, …
Common multiples: 18, 36, 54, 72, 90
What do you notice about the common multiples of different pairs of numbers? Discuss in class.
Answer:
The common multiples are usually multiples of the least common multiple (LCM) of the two numbers.
For example, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6, so the common multiples are all multiples of 6.
Some numbers might have only a few common multiples early on, while others, like 5 and 10, have many multiples that overlap (10, 20, 30, etc.).
As we increase the numbers, the common multiples get larger.
2. Food is available at the end of a cobbled road. Robby, the rabbit, takes a jump of 4 each time. Deeku, the deer, takes a jump of 6 each time. They both start at 0. Will both Robby and Deeku reach the food? Who will reach first? How do you know? Explain your answer.
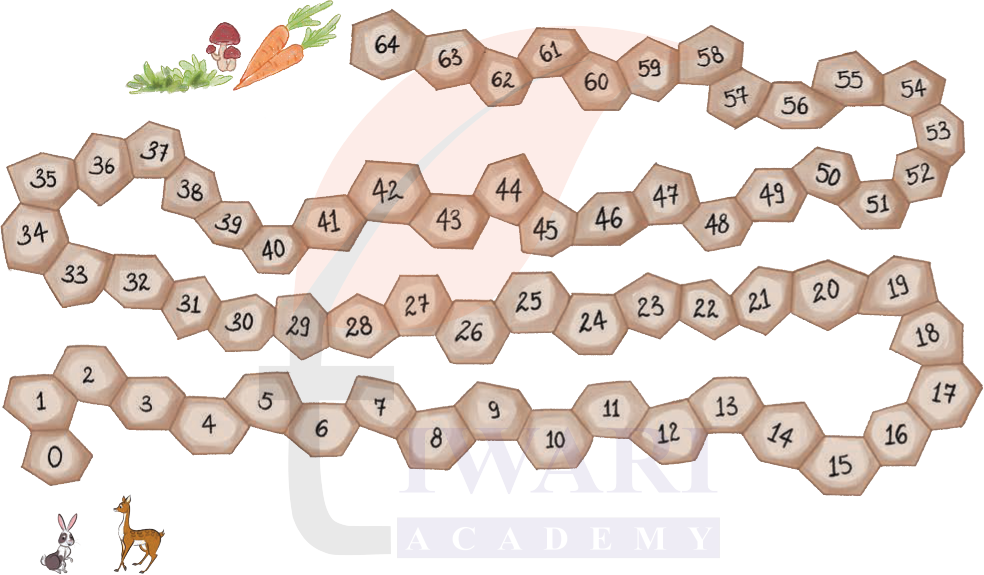
Answer:
Robby starts at 0 and he jumps by 4 each time.
So, Robby’s positions will be: 0, 4, 8, …, 64.
Deeku starts at 0 and he jumps by 6 each time.
So, Deeku’s positions will be: 0, 6, 12, …,60, 66.
Robby will reach the food and Deeku will not land on the food spot (64).
We know this because 64 is a multiple of 4 but not a multiple of 6.
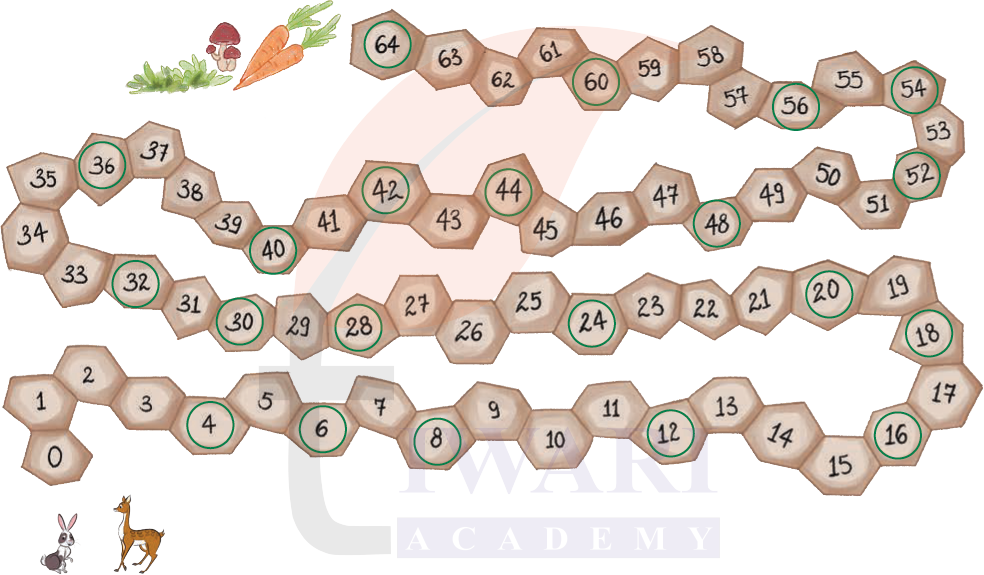
3. Mowgli’s friends live along the trail on the marked places below. Which of his friends will he be able to visit, if he jumps by 2 steps starting from 0?

Answer:
Mowgli is jumping by 2 steps, he will land on the following positions: 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16…
From this, we can see that Mowgli will meet:
Ant at position 4
Frog at position 12
Bird at position 14
Bear at position 30
Rabbit at position 50
Did Mowgli meet the ant, frog, bird and the rabbit? Notice their positions— 4, 12, 14, and 50. 2 is a common factor of these numbers.
Answer:
Yes, Mowgli will meet ant, frog, bird and the rabbit.
Because mowgli is jumping by 2 steps and the position of ant, frog, bird and the rabbit are common factor of 2.
That is 4, 12, 14, 50.
Which of his friends will he be able to meet if he jumps by 3 steps? 3 is a common factor of the numbers 9, 21, 39, and 57.
Answer:
The positions where Mowgli can land when he jumps by 3 steps are: 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30…
From this, we can see that Mowgli will meet:
Spider at position of 9
Frog at position of 12
Snake at position of 21
Bear at position 30
Deer at position 39
Monkey at position of 57
Which numbers will he touch if he jumps by 5 steps? _______ 5 is a common factor of the numbers _______
Answer:
The positions where Mowgli can land when he jumps by 5 steps are: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40…
5 is a common factor of the numbers: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40…
So, Mowgli will meet his friends at positions 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30.
Which numbers will he touch if he jumps by 10 steps? ______ 10 is a common factor of the numbers ______.
Answer:
The positions where Mowgli can land when he jumps by 10 steps are: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50…
10 is a common factor of the numbers: 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50…
So, Mowgli will meet his friends at positions 10, 20, 30, 40 and 50.
4. Let us find some common factors of the numbers 24 and 36. Note that all jumps in the following questions start from 0.
(a) Can we jump by 2 steps at a time to reach both 24 and 36? Yes/No. 2 is/is not a common factor of 24 and 36.
Answer:
We can divide both numbers by 2.
24 ÷ 2 = 12
36 ÷ 2 = 18
Both 24 and 36 can be divided by 2, 2 is a common factor of 24 and 36.
Yes, we can jump by 2 steps to reach both 24 and 36.
(b) Can we jump by 3 steps at a time to reach both 24 and 36? Yes/No. 3 is/is not a common factor of 24 and 36.
Answer:
We can divide both numbers by 3.
24 ÷ 3 = 8
36 ÷ 3 = 12
Both 24 and 36 can be divided by 3, 3 is a common factor of 24 and 36.
Yes, we can jump by 3 steps to reach both 24 and 36.
(c) Can we jump by 4 steps at a time to reach both 24 and 36? Yes/No. 4 is/is not a common factor of 24 and 36.
Answer:
We can divide both numbers by 4.
24 ÷ 4 = 6
36 ÷ 4 = 9
Both 24 and 36 can be divided by 4, 4 is a common factor of 24 and 36.
Yes, we can jump by 4 steps to reach both 24 and 36.
(d) What other jumps can we take to reach both 24 and 36?
Answer:
We already know 2, 3 and 4 are common factors. Let’s find all the factors:
Factors of 24: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24
Factors of 36: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, 36
Common factors of 24 and 36 are: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
So, the other jumps we can take to reach both 24 and 36 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 and 12.
(e) How many common factors can you find for 24 and 36? List them.
Answer:
Factors of 24: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24
Factors of 36: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, 36
Common factors of 24 and 36 are: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
So there are 6 common factors.
(f) What about jumping by 1 step each time to reach both 24 and 36?
Answer:
Yes, because 1 is a factor of every number. So it divides both 24 and 36.
5. What are the common factors of 12 and 13?
Answer:
Factors of 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
13 is a prime number, which means it has only two factors: 1 and 13.
Only common factor of 12 and 13 is 1.
6. Find which of the following numbers can be reached by jumps of 4 steps?

4 is the common factor of the numbers _____.
Answer:
We can check each number to see if it’s divisible by 4.
10 ÷ 4 = 2.5
16 ÷ 4 = 4
27 ÷ 4 = 6.75
36 ÷ 4 = 9
48 ÷ 4 = 12
16, 36 and 48 can be reached by jumps of 4 steps.
4 is the common factor of the numbers 16, 36 and 48.
7. Find the common factors of the following pairs of numbers.
(a) 12 and 16
Answer:
Factors of 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
Factors of 16: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16
Common factors: 1, 2, 4
(b) 8 and 12
Answer:
Factors of 8: 1, 2, 4, 8
Factors of 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
Common factors: 1, 2, 4
(c) 4 and 16
Answer:
Factors of 4: 1, 2, 4
Factors of 16: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16
Common factors: 1, 2, 4
(d) 2 and 9
Answer:
Factors of 2: 1, 2
Factors of 9: 1, 3, 9
Common factors: 1
(e) 3 and 5
Answer:
Factors of 3: 1, 3
Factors of 5: 1, 5
Common factors: 1
(f ) 12 and 15
Answer:
Factors of 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
Factors of 15: 1, 3, 5, 15
Common factors: 1, 3
(g) 20 and 5
Answer:
Factors of 20: 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 20
Factors of 5: 1, 5
Common factors: 1, 5
(h) 9 and 21
Answer:
Factors of 9: 1, 3, 9
Factors of 21: 1, 3, 7, 21
Common factors: 1, 3
(i) 6 and 27
Answer:
Factors of 6: 1, 2, 3, 6
Factors of 27: 1, 3, 9, 27
Common factors: 1, 3
What do you notice about the common factors of different pairs of numbers. Discuss in class.
Answer:
The number 1 is always a common factor of any pair of numbers because every number is divisible by 1.
Some numbers have more common factors.
For example, 12 and 16 both share 1, 2 and 4 as common factors.
The pairs where the numbers have no other common factors except 1 (like 2 and 9 or 3 and 5) are called coprime numbers or relatively prime.
These numbers have no other common factor except 1.
8. State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F).
(a) Factors of even numbers must be even.
Answer:
False (F)
Even numbers are numbers that are divisible by 2, like 2, 4, 6, 8, etc.
However, the factors of an even number include both even and odd numbers.
For example, the factors of 6 are 1, 2, 3 and 6.
Here, 1 and 3 are odd numbers.
So, not all factors of even numbers are even.
(b) Multiples of odd numbers cannot be even.
Answer:
False (F)
Odd numbers are numbers like 1, 3, 5, 7, etc.
However, multiples of odd numbers can be even.
For example, the multiple of 3 is 6 (which is even).
So, multiples of odd numbers can be even.
(c) Factors of odd numbers cannot be even.
Answer:
True (T)
Odd numbers are not divisible by 2. So, their factors can only be odd.
For example, the factors of 9 are 1, 3 and 9 — all of them are odd.
Therefore, odd numbers do not have even factors.
(d) One of the common multiples of two consecutive numbers is their product.
Answer:
True (T)
Consecutive numbers are numbers that come one after the other, like 3 and 4 or 10 and 11.
The product of two consecutive numbers will always be a common multiple of those numbers.
For example, for 3 and 4, their product is 12 and 12 is a common multiple of both 3 and 4.
(e) The only common factor of any two consecutive numbers is 1.
Answer:
True (T)
Consecutive numbers have no other common factor except 1.
For example, 4 has factors 1, 2 and 4 and that of 5 has 1, 5.
The only number common between them is 1.
So, the only common factor of any two consecutive numbers is always 1.
(f) 0 cannot be a factor of any number.
Answer:
(f) True (T)
0 cannot be a factor of any number, because multiplying any number by 0 gives 0.
But dividing by 0 is not possible (undefined).
Therefore, 0 is not a factor of any number.
9. Sher Khan, the tiger, goes hunting every 3rd day. Bagheera, the panther, goes hunting every 5th day. If both of them start on the same day, on which days will they be hunting together?
Answer:
Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30…
Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35…
The first number that appears in both lists is 15.
They will hunt together on the 15th, 30th day etc.
10. (a) In the trail shown earlier, Sher Khan’s house is on number 25 and that of Baloo the bear is on number 30. Mowgli wants to meet his friend Baloo the bear but wants to avoid Sher Khan’s house. How long (in steps) could each jump be?
Answer:
We are looking for a number that:
Goes into 30 exactly (divides 30) but does not go into 25 (doesn’t land on 25)
Factors of 30: 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15, 30
If he jumps 1 steps: He lands on 1, 2, 3… 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, Lands on 25
If he Jump 2 steps: 2, 4, 6… 24, 26, Skips 25
If he Jump 3 steps: 3, 6, 9… 24, 27, 30, Skips 25
If he jumps 5 steps: He lands on 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, Lands on 25
If he Jump 6 steps: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, Skips 25
If he Jump 10 steps: 10, 20, 30, Skips 25
If he Jump 15 steps: 15, 30, Skips 25
So he can choose: 2, 3, 6, 10, 15 as jump lengths to avoid 25 and reach 30.
(b) What number of jumps (in steps) he could choose so that he can meet both Kaa, the snake, at 21 and Akela, the wolf, at 35?
Answer:
Kaa (the snake) is at 21 and Akela (the wolf) is at 35.
To meet both, Mowgli must choose a jump size that lands exactly on 21 and 35.
So, we find the common factor of 21 and 35.
Factors of 21: 1, 3, 7, 21
Factors of 35: 1, 5, 7, 35
Common factors = 1 and 7
If Mowgli jumps by 7 steps:
7 × 3 = 21 (meets Kaa)
7 × 5 = 35 (meets Akela)
Mowgli should jump by 7 steps. This way, he can meet both Kaa and Akela.
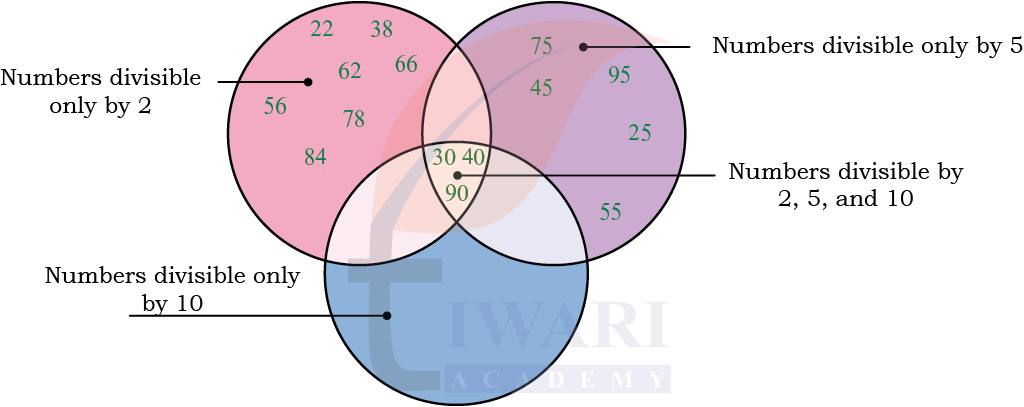
11. Sort the following numbers into those that are-
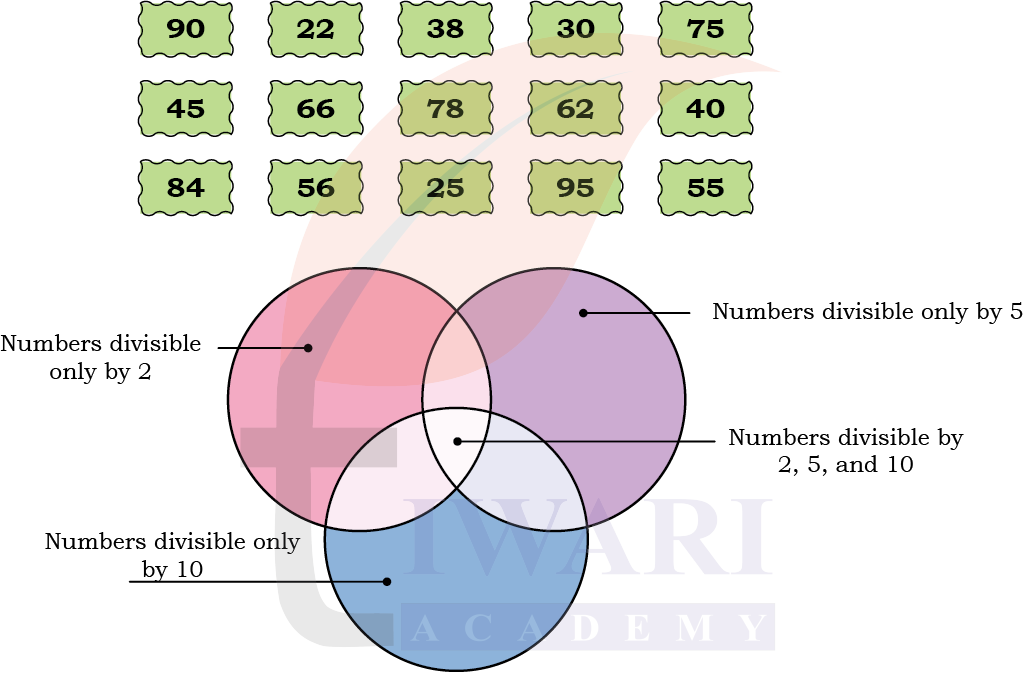
(a) divisible by 2 only
Answer:
This means the number can be divided only by 2 but not by 5 or 10.
In other words, the number is a multiple of 2, but not a multiple of 5 or 10.
Numbers divisible by 2 only are those whose last digit is even and not ending in 0 or 5.
Given numbers: 90, 22, 38, 30, 75, 45, 66, 78, 62, 40, 84, 56, 25, 95, 55
So, the numbers divisible by 2 only: 22, 38, 78, 62, 84, 56.
(b) divisible by 5 only
Answer:
This means the number can be divided only by 5 but not by 2 or 10.
In other words, the number is a multiple of 5, but not a multiple of 2 or 10.
Numbers divisible by 5 only are those whose last digit is 5 (but not 0).
Given numbers: 90, 22, 38, 30, 75, 45, 66, 78, 62, 40, 84, 56, 25, 95, 55
So, the number divisible by 5 only: 75, 45, 25, 95, 55.
(c) divisible by 10 only
Answer:
This means the number can be divided only by 10 not possible to find.
Because if a number divisible of 10 it will automatically makes it divisible by both 2 and 5.
(d) divisible by 2, 5, and 10.
Answer:
Divisible by 2: A number is divisible by 2 if its last digit is even (0, 2, 4, 6 or 8).
Divisible by 5: A number is divisible by 5 if its last digit is either 0 or 5.
Divisible by 10: A number is divisible by 10 if its last digit is 0.
Divisible by 2, 5 and 10: 30, 40,90