NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 5 Far and Near explain the concepts of measuring distance and length using different units like millimetres, centimetres, metres and kilometres. Maths Mela chapter 5 helps children understand conversions between units, estimating distances and comparing objects. Activities like measuring lines, sprouts and real-life distances make learning interesting. Through examples of monuments, journeys and playground tasks, students improve practical skills of measurement. These solutions build accuracy, observation and logical thinking in children.
Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 5 Solutions
Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 5 MCQ
Class 5 Math Magic Chapter 5 Solutions
Class 5 Maths all Chapters Solutions
Far and Near Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 5 Solutions
Page 57
Let Us Find
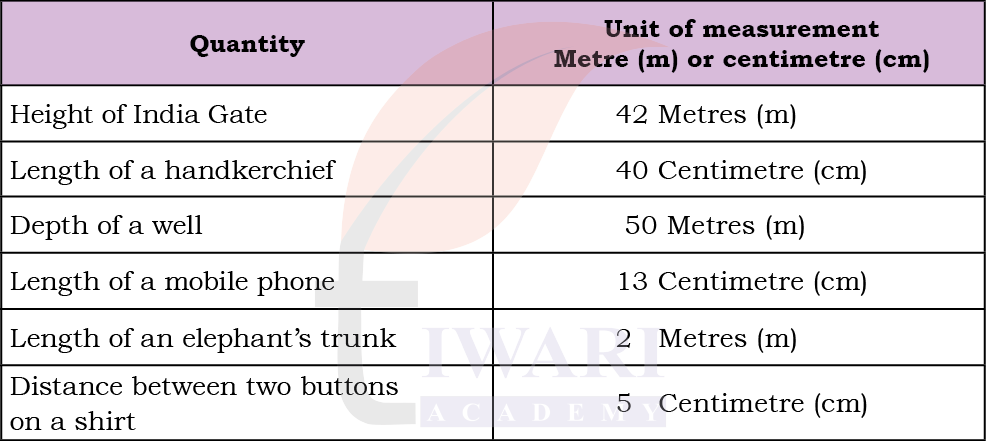
Identify the appropriate units for measuring each of the following.
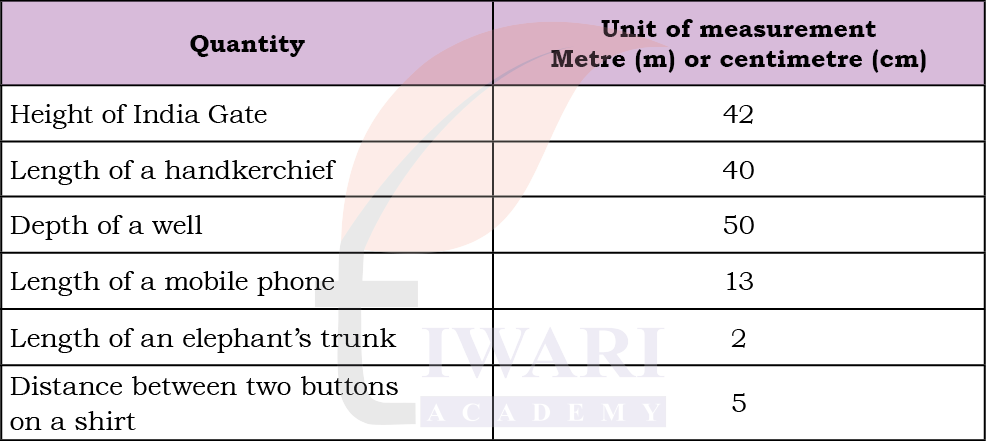
Answer:
Page 57
Different Units but Same Measure
Shikha and Sonu are measuring the lengths of saris and stoles in the village weaving centre. Find which measures represent the same sari or stole. You can take help of the double number line below.

Answer:

Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 5 Questions on Comparing
Page 58
Let Us Compare
Ritika is comparing the lengths of different rods. Compare them using <, =, > signs. (Page58) (Picture of blanks)
(a) 456 cm ____ 5 m
See Solution456 cm ___ 5 m
We know that 5 m = 500 cm
Therefore, 456 cm < 500 cm
So, 456 cm < 5 m.
(b) 55 cm + 200 cm ____ 200 cm + 54 cm
See Solution55 cm + 200 cm ___ 200 cm + 54 cm
LHS = 55 + 200 = 255 cm
RHS = 200 + 54 = 254 cm
Here, 255 cm > 254 cm
Therefore, 55 cm + 200 cm > 200 cm + 54 cm.
(c) 6 m 5 cm ___ 6 m 50 cm
See Solution6 m 5 cm ___ 6 m 50 cm
LHS = 6 m 5 cm = 605 cm
RHS = 6 m 50 cm = 650 cm
Here, 605 cm < 650 cm
Therefore, 6 m 5 cm < 6 m 50 cm.
(d) 2 m 150 cm ___ 3 m 50 cm
See Solution2 m 150 cm ___ 3 m 50 cm
LHS = 2 m 150 cm = 200 cm + 150 cm = 350 cm
RHS = 3 m 50 cm = 300 cm + 50 cm = 350 cm
Here, 350 cm = 350 cm
Therefore, 2 m 150 cm = 3 m 50 cm.
(e) 238 cm ____ 138 cm + 1 m
See Solution238 cm ___ 138 cm + 1 m
LHS = 238 cm
RHS = 138 cm + 1 m = 138 cm + 100 cm = 238 cm
Here, 238 cm = 238 cm
Therefore, 238 cm = 138 cm + 1 m.
2. World’s tallest statue

(a) What is the difference between the height of the tallest statue in the world and the Statue of Liberty?
See SolutionHeight of Statue of Unity = 183 m
Height of Statue of Liberty = 93 m
Difference = 183 m – 93 m = 90 m
So, the difference between the height of the tallest statue in the world and the Statue of Liberty is 90 m.
(b) Identify the statues whose heights have the least difference.
See SolutionHeight of Statue of Liberty = 93 m
Height of The Motherland Calls = 91 m
Difference = 2 m.
(c) Identify the statues whose heights have the largest difference.
See SolutionTallest statue: Statue of Unity (183 m)
Shortest statue: Christ the Redeemer (38 m)
Difference = 183 m – 38 m = 145 m.
(d) The height of which statue will be equal to the height of the Statue of Unity, if it is doubled?
See SolutionHeight of Statue of Unity = 183 m
We have to find a statue whose height × 2 = 183 m
So, Height = 183 m ÷ 2 = 91.5 m
Looking at the list, the height of The Motherland Calls is 91 m, which is very close. The height of Guanvin is 108 m (108×2 = 216), Spring Buddha is 128 m (128×2 = 256).
So, 91 m is the closest.
Hence, the height of The Motherland Calls will be equal to the height of the Statue of Unity, if it is doubled.
Page 59
Let Us Do
Measure 100 m and 200 m on your school playground or any other place in and around your school, using a Long Tape. Mark these points and draw a straight line. Walk on the lines and count the number of steps. Use this relationship between the number of steps taken and distance walked to find distances around you for at least 3 locations. Wherever possible, walk and find the number of steps. Otherwise, find the distance and estimate the number of steps.
(a) Identify and write the locations that are the nearest and the farthest
from your home.
Nearest location _______________________________________________________.
Farthest location ______________________________________________________.
See AnswerNearest and farthest location from my home
Nearest location: My school playground (about 200 m)
Farthest location: Railway station (about 2 km = 2000 m).
(b) Write the distances obtained above in increasing order.
_______________, _________________, _________________, __________________.
See AnswerDistances in increasing order
Playground – 200 m
Market – 500 m
Park – 800 m
Railway station – 2000 m
So, in order: 200 m, 500 m, 800 m, 2000 m.
(c) Name a location that is equal to or more than 1,000 m from your home.
See AnswerLocation equal to or more than 1000 m
The Railway station (2000 m) is more than 1000 m from my home.
Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 5 Questions to Explore
Page 59
Let Us Explore
When we walk 1,000 m, we say we have walked 1 km.
1,000 m = 1 km
Kilo stands for thousand. This unit is used to measure long distances.

Answer:

Page 60
Kilometre Race
Sheena and Jennifer are helping to organise a 3-km race. Help them with the arrangements for the race.
1. Water stations are to be arranged after every 500 m. How many water stations must be set up? At what positions from the starting point will these water stations be placed?
See SolutionTo make 1 km rope we need 1000 m of ropes.
For a 3 km race 3000 m rope
Water stations every 500 m:
Number of stations: 3000 m ÷ 500 m = 6 stations
Positions: 500 m, 1000 m, 1500 m, 2000 m, 2500 m, 3000 m.
2. Children need to stand at an interval of 300 m to direct the runners. How many children are needed? At what positions from the starting point will the children be standing?
See SolutionChildren every 300 m:
Number of children:
3000 m ÷ 300 m
= 10 children
Positions: 300 m, 600 m, 900 m, 1200 m, 1500 m, 1800 m, 2100 m, 2400 m, 2700 m, 3000 m.
3. Red and blue flags are to be placed alternately at every 50 m. How many red and blue flags are needed till the finish line?
See SolutionFlags every 50 m (Red and Blue alternately):
Number of flag points: 3000 m ÷ 50 m = 60 points
Since they are alternate (Red, Blue, Red, Blue…), there will be an equal number of each.
Number of Red flags: 30
Number of Blue flags: 30.
Page 60
Let Us Do
The longest train journey in India is by The Vivek Express which runs from Dibrugarh in Assam to Kanniyakumari in Tamil Nadu. Look at the stations on the route shown in the table below and answer the questions.

1. The total length of the route from Dibrugarh to Kanniyakumari is _______________ km.
See AnswerTotal distance mentioned in the table last row kaniyakumari 4187km.
2. The distance between Vijayawada and Jalpaiguri road is _______________.
See SolutionDistance between Vijayawada (2,800 km) and Jalpaiguri Road (983 km):
Difference = 2800 km – 983 km = 1817 km.
3. Distance between Vijayawada and Visakhapatnam is _______________.
See SolutionDifference = 2800 km – 2450 km = 350.
4. Which two stations are farther apart — Guwahati and Dimapur or Bhubaneswar and Jalpaiguri Road?
See SolutionDistance between Guwahati and Dimapur
= 556 km – 306 km
= 250 km
Distance between Bhubaneswar and Jalpaiguri Road
= 2007 km – 983 km
= 1,024 km
So, Bhubaneswar and jalpaiguri road are farther apart.
5. What is the distance between Guwahati and Coimbatore JN?
See SolutionDistance between Coimbatore and Guwahati
= 3675 km – 556 km = 3119 km.
Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 5 Measuring Based Questions
Page 61
Let Us Measure
Measure the lines in the design and write their measurements in cm and mm.

Answer:
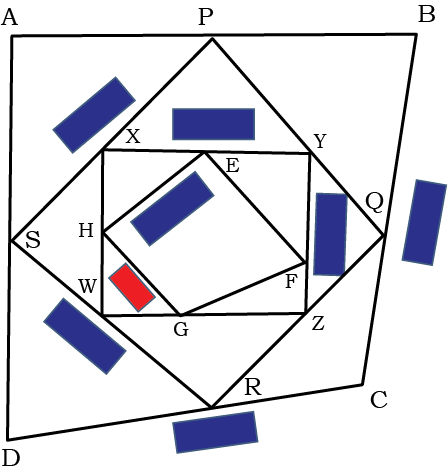
Side lengths of the following:
ABCD = 10 cm 0 mm
XYZW = 9 cm 0 mm
PQRS = 7 cm 5 mm
EFGH = 5 cm 5 mm
Length and width of Blue boxes: Length = 3 cm; Width = 1 cm
Length and width of Red box: Length = 1 cm 60 mm; Width = 90 mm.
Page 62
Let Us Do
Soak some seeds of whole moong or black or white chana overnight. Next morning, take them out and wrap them in a moist cloth to sprout them. Over the next 4 days, take out one seed each day and measure the length of sprout. For ease of measurement, you can either place the seed on a paper and mark the length of the sprout, or use a thread to find its length.
| Number of days | Length of the sprout (in mm) |
|---|---|
| Day 1 | – |
| Day 2 | – |
| Day 3 | – |
| Day 4 | – |
Answer:
| Number of days | Length of the sprout (in mm) |
|---|---|
| Day 1 | 5 mm |
| Day 2 | 12 mm |
| Day 3 | 25 mm |
| Day 4 | 41 mm |
Page 62
Let Us Draw
Draw lines of the following lengths in your notebook using a scale.
1. 5 cm 5 mm
2. 3 cm 6 mm
3. 8 cm 3 mm
4. 36 mm
5. 67 mm
How did you draw lines of lengths 36 mm and 67 mm? Share your thoughts in class.
Answer:

To draw a line of 36 mm:
First, I looked at the scale.
On the scale, 1 cm = 10 mm.
So, 36 mm means 3 cm and 6 mm.
I kept my pencil on 0, then marked a point at 3 cm 6 mm, and joined the two points with a straight line.
To draw a line of 67 mm:
Again, I checked the scale.
67 mm = 6 cm and 7 mm.
I placed the scale at 0, then marked at 6 cm 7 mm, and drew the line neatly.
My thought:
I learned that whenever the number is in mm, I can convert it into cm and mm to make it easy. This way, I don’t get confused with big numbers.
Page 63
Let Us Do
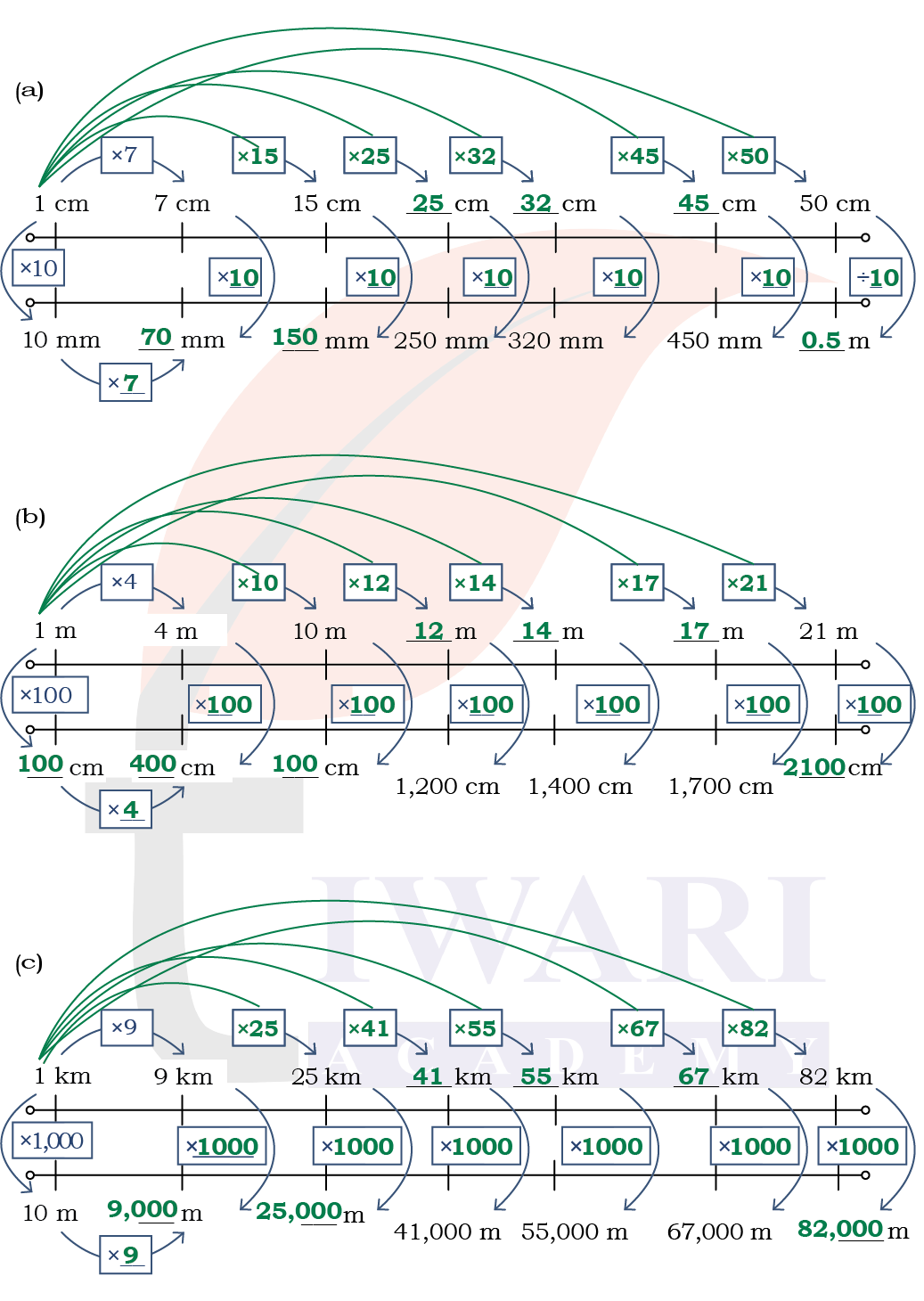
1. Fill in the blanks appropriately in the double number lines given below.
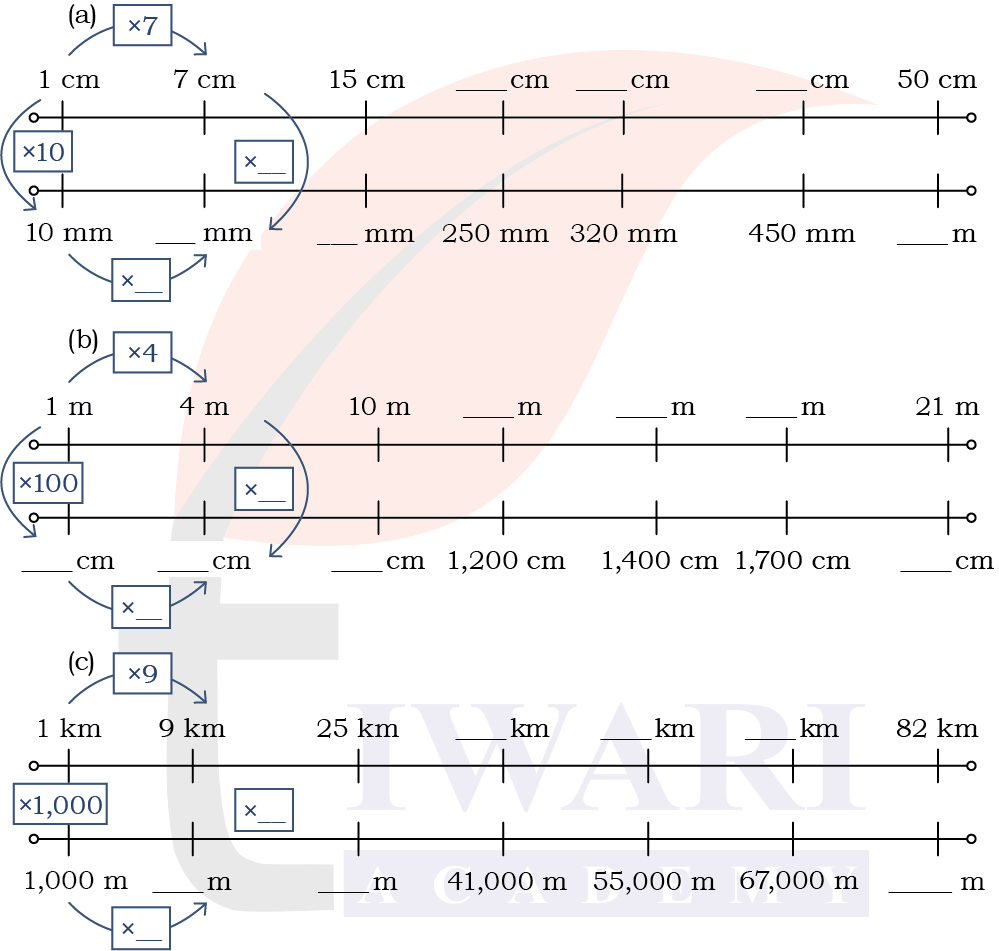
Answer:
2. Use your understanding from above to fill in the blanks appropriately.
(a) 4 cm 5 mm = ______ mm
(b) 89 mm = ____ cm ____ mm
(c) 234 cm = ____ mm
(d) 514 mm = ____ cm ____ mm
(e) 6 m 34 cm = ____ cm
(f) 20 m 12 cm = ____ cm
(g) 397 m = ______ cm
(h) 5,792 cm = ______m ______ cm
(i) 9,108 cm = ______ m ______ cm
(j) 34 km = _______ m
(k) 6,870 m = ____ km ____ m
(l) 10,552 m = ____ km ___ m
(m) 29 km 30 m = ____ m
(n) 32 km 359 m = ____ m
See Solution(a) 4 cm 5 mm = 45 mm
(b) 89 mm = 8 cm 9 mm
(c) 234 cm = 2340 mm
(d) 514 mm = 51 cm 4 mm
(e) 6 m 34 cm = 634 cm
(f) 20 m 12 cm = 2012 cm
(g) 397 m = 39700 cm
(h) 5,792 cm = 57 m 92 cm
(i) 9,108 cm = 91 m 8 cm
(j) 34 km = 34000 m
(k) 6,870 m = 6 km 870 m
(l) 10,552 m = 10 km 552 m
(m) 29 km 30 m = 29030 m
(n) 32 km 359 m = 32359 m.
Page 65
Let Us Do
1. Rani has two red-coloured ribbon rolls, one of length 3 m 75 cm and another 2 m 25 cm long. How much ribbon does she have?
See SolutionRani’s Ribbon:
Length 1: 3 m 75 cm
Length 2: 2 m 25 cm
Total: 3 m 75 cm + 2 m 25 cm = 5 m 100 cm
But 100 cm = 1 m, so total length is 6 m.
2. The distance from Bhopal to Sanchi is 48 km 700 m. Bhadbhada Ghat waterfall is on the way and 17 km 900 m away from Bhopal. How far is Sanchi from the waterfall?
See SolutionTotal distance: 48 km 700 m
Distance to waterfall from Bhopal: 17 km 900 m
We know that 48 km 700 m = 47 km 1700 m [Since 1 km = 1000 m]
Now, difference
= 47 km 1700 m – 17 km 900 m
= (47 – 17) km + (1700 – 900) m
= 30 km 800 m
So, Sanchi is 30 km 800 m away from the waterfall.
3. Gulmarg Gondola in Gulmarg, Kashmir is the second longest and second highest cable car in the world. It is divided into two sections. The first section covers 2 km 300 m and the second section covers 2 km 650 m. What is the total distance covered by the cable car?
See SolutionLength of cable car in Section 1: 2 km 300 m
Length of cable car in Section 2: 2 km 650 m
Total length of cable car:
= 2 km 300 m + 2 km 650 m
= 4 km 950 m.
4. Circle the bigger length and find the difference.
(a) 11 mm and 1 cm – Difference ________________
See Solution11 mm and 1 cm
1 cm = 10 mm
Bigger: 11 mm
Difference: 11 mm – 10 mm = 1 mm.
(b) 26 mm and 2 cm – Difference ________________
See Solution26 mm and 2 cm
2 cm = 20 mm
Bigger: 26 mm
Difference: 26 mm – 20 mm = 6 mm.
(c) 20 cm and 201 mm – Difference ________________
See Solution20 cm and 201 mm
20 cm = 200 mm
Bigger: 201 mm
Difference: 201 mm – 200 mm = 1 mm.
(d) 1,020 mm and 1 m – Difference ________________
See Solution1,020 mm and 1m
1 m = 1000 mm
Bigger: 1020 mm
Difference: 1020 mm – 1000 mm = 20 mm.
(e) 2 m and 245 cm – Difference ________________
See Solution2 m and 245 cm
2 m =200 cm
Bigger: 245 cm
Difference: 245 cm – 200 cm = 45 cm.
(f) 5,678 m and 6 km – Difference ________________
See Solution5,678 m and 6 km
6 km = 6000 m
Bigger: 6 km (6000 m)
Difference: 6000 m – 5678 m = 322 m.
(g) 6 km 1,480 m and 7 km 479 m – Difference ________________
See Solution6 km 1,480 m and 7 km 479 m
Now, 6 km 1,480 m = 7480 m
and 7 km 479 m 7479 m
Bigger: 6 km 1480 m
Difference: 7480 m – 7479 m = 1 m.
Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 5 Length Division
Page 66
Multiplying and Dividing Lengths
1. We need a 1 m 80 cm cloth to make a shirt for a 10-year old child. How much cloth will be needed to make shirts for 20 such children?
See SolutionThe length of cloth for 1 shirt = 1 m 80 cm
So, the length of cloth for 20 shirts
= 20 × 1 m 80 cm
= 20 × 1 m and 20 × 80 cm
= 20 m + 1600 cm
= 20 m + 16 m
= 36 m.
2. A shop sells cloth for making bags at ₹100 for 5 m. How much money is needed to buy a 1 m cloth?
If 5 m cloth costs ₹100, then a 1 m cloth
costs 100 ÷ 5 = ₹20.
Now, use the double number line to find the cost of the cloth or the length of cloth that we can buy at a particular cost.

Answer:

3. Anita is making an embroidery on the border of a sari. She needs a 1 m long thread to embroider a 50 cm sari. How much thread would she need for a 5 m sari border?
A 1 m long thread costs ₹50. How much money will be needed to buy the thread?
See SolutionThread for 50 cm border = 1 m = 100 cm
Thread for 1 cm border = 100/50 = 2 cm
Thread for 5 m (500 cm) border = 2 × 500 = 1000 cm = 10 m
Cost of 1 m thread = ₹50
Cost of 10 m thread = 10 × ₹50 = ₹500.
4. A road 12 km 600 m long is being laid in a town. The workers lay an equal length of road each day, and complete the work in 6 days. How much road-laying work is done on each day?
See SolutionTotal road: 12 km 600 m = 12600 m
Number of days: 6
Road laid per day = 12600 m ÷ 6 = 2100 m
= 2 km 100 m.


