NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 8 Weight and Capacity updated for Session 2025-26. Class 5 Math Mela Solutions help students understand measurement of mass and capacity through real-life examples. This chapter includes activities like reading weighing scales, converting grams into kilograms, litres into millilitres and solving word problems based on cost and quantity. The solutions strengthen problem-solving skills by using the unitary method, estimations and logical reasoning. Step-by-step explanations make learning simple and interactive, ensuring strong conceptual clarity for exams and daily life.
Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 8 Solutions
Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 8 MCQ
Class 5 Math Magic Chapter 8 Solutions
Class 5 Maths all Chapters Solutions
Weight and Capacity Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 8 Solutions
Page 104
Check! Check!
Anu has recorded the weights of the items in her house. Check if she has
recorded them correctly by putting a tick against them if they look correct.
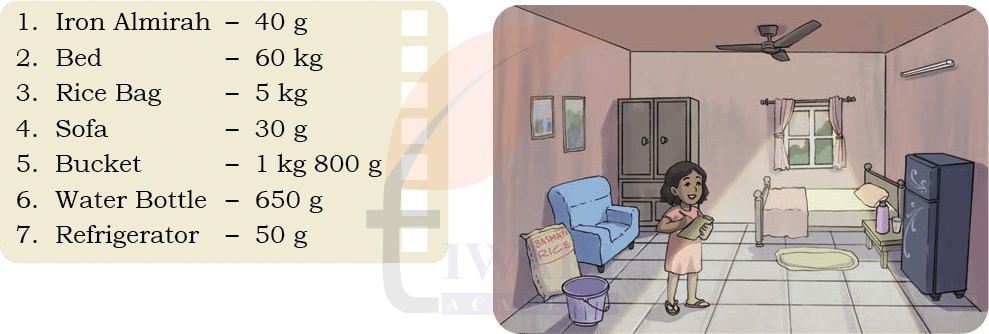
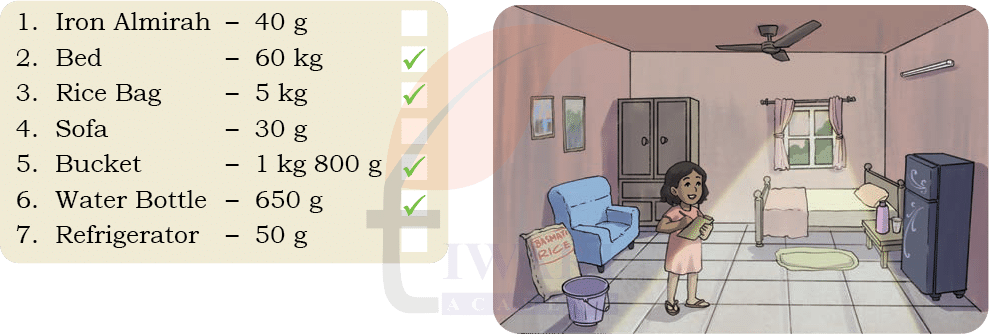
See SolutionSome weights written are clearly wrong:
Iron Almirah – 40 g (impossible, far too light)
Sofa – 30 g (impossible)
Refrigerator – 50 g (impossible)
Some are quite reasonable:
Bed – 60 kg (correct)
Bag of rice – 5 kg (reasonable)
Bucket – 1 kg 800 g (possible if it’s a heavy metal/plastic bucket)
Water bottle – 650 g (possible when filled)
Page 104
Let Us Do
Read the scales. Write the correct weight in the space given below.
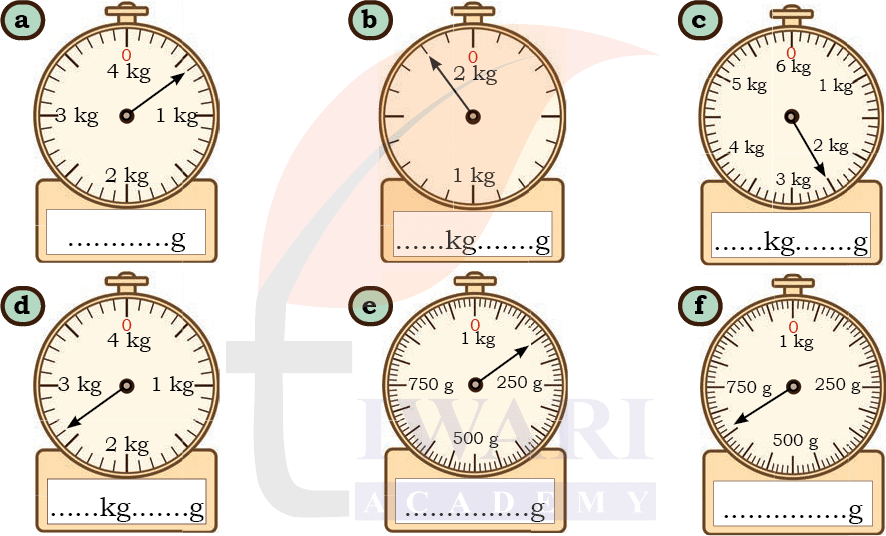
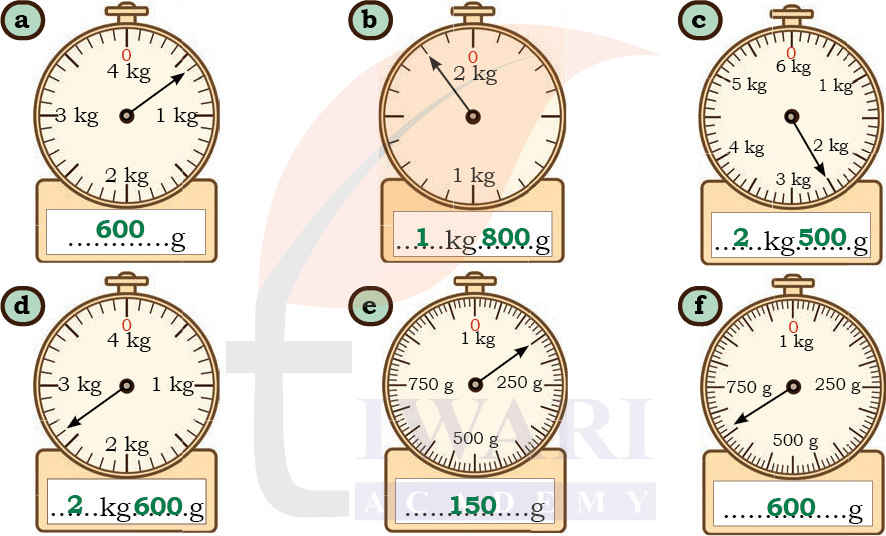
See Solutiona) 600g
b) 1kg 800g
c) 2kg 500g
d) 2kg 600g
e) 150g
f) 660g
Page 105
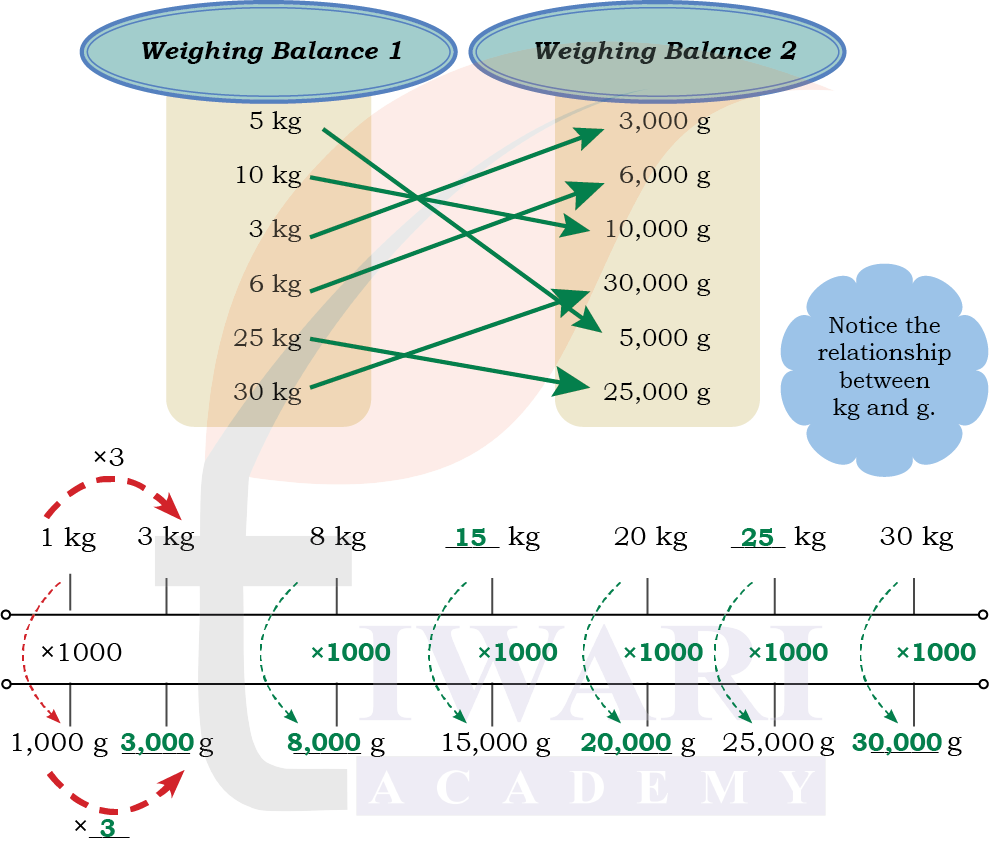
Different Units but Same Measure
Match the bags that have the same weights. You can use the double number
line given below.
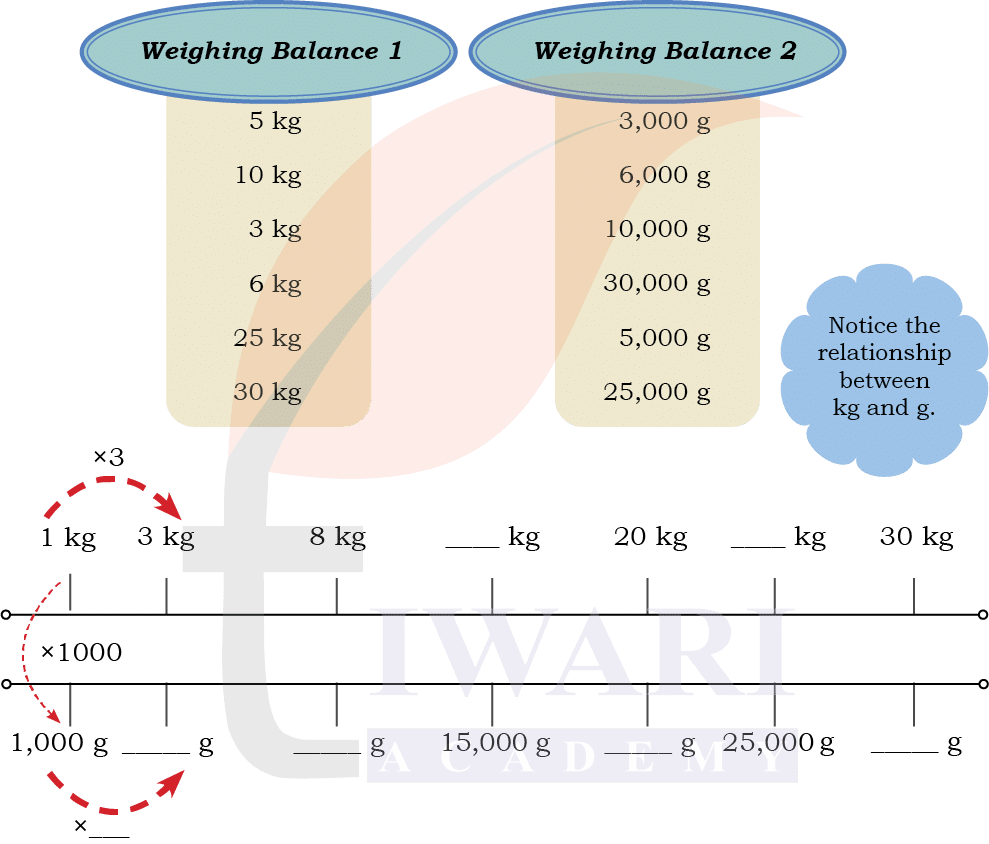
Answer:
Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 8 Questions on Let Us Find
Page 106
Let Us Find
1. Shamim and Rehan observed someone buying sugar weighing 5 kg 50 g. They thought of the quantity in grams. How much is it?

See Solution1 kg = 1000 g
So, 5 kg = 5000 g
Therefore, 5 kg 50 g = 5000 g + 50 g = 5050 g
2. Complete the conversions by filling in the blanks. You can use the double number line given below on which some numbers have been marked.

(a) 7 kg 67 g = ___________ g (d) 10,760 g = _____ kg ____ g
(b) 3 kg 300 g = ___________ g (e) 4,080 g = _____ kg ____ g
(c) 8 kg 69 g = ___________ g (f) 12,042 g = _____ kg ____ g
See Solutiona) 7 kg 67 g = 7,000 g + 67 g = 7,067 g
b) 3 kg 300 g = 3,000 g + 300 g = 3,300 g
c) 8 kg 69 g = 8,000 g + 69 g = 8,069 g
d) 10760 g = 10,000 g + 760 g = 10 kg 760 g
e) 4080 g = 4,000 g + 80 g = 4 kg 80 g
f) 12042 g = 12,000 g + 42 g = 12 kg 42 g

Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 8 Comparison Based Questions
Page 107
Comparison between Different Weights
1. Harpreet’s family planned a picnic over the weekend. Her mother and father packed different food items to take along. The following is the list of fruits they carried.
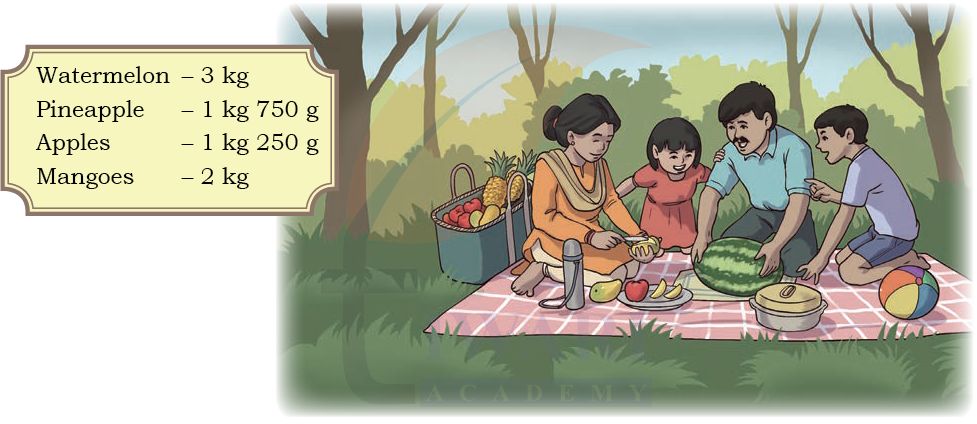

Among the fruits they carried, which one has the
(a) highest weight? __________
(b) least weight? __________
(c) Arrange the items in descending order of their weight.
__________ __________ __________ __________
See Solutiona) Highest weight : Watermelon (3 kg)
b) Least weight : Apples (1 kg 250 g)
c) Descending order of weight:
Watermelon (3 kg), Mangoes (2 kg), Pineapple (1 kg 750 g), Apples (1 kg 250 g)
2. Compare the weights using <, =, > signs.
(a) 1 kg 600 g __________ 1,700 g
(b) 1 kg 600 g __________ 1 kg 60 g
(c) 10 kg 35 g __________ 10035 g
(d) 1 kg 600 g __________ 2 kg 500 g
(e) 5 kg 50 g __________ 4 kg 500 g
(f) 900 g + 7,000 g __________ 7 kg + 900 g
See Solution(a) 1 kg 600 g < 1,700 g (b) 1 kg 600 g > 1 kg 60 g
(c) 10 kg 35 g = 10035 g
(d) 1 kg 600 g < 2 kg 500 g (e) 5 kg 50 g > 4 kg 500 g
(f) 900 g + 7,000 g = 7 kg + 900 g
Page 108
Let Us Find
1. If a sugar sachet weighs 5g, how much will it be in milligrams?
See SolutionWe know:
1 gram (g) = 1000 milligrams (mg)
So, 5 g = 5 × 1000 mg = 5000 mg
2. Complete the double number line below appropriately.

Answer:

3. An ornament weighs 4 g 100 mg. What will be the weight in milligrams?

See Solution1 g = 1000 mg
4 g = 4 × 1000 = 4000 mg
So, total weight = 4000 + 100 mg = 4100 mg
4. A goldsmith has made an ornament weighing 10 g 500 mg. What will its weight be in milligrams? _____________________
See Solution1 g = 1,000 milligram
10 g = 10,000 milligram
10 g 500 = 10,000 + 500 = 10,500 milligram
5. Compare the weights using <, =, > signs.
(a) 20 g ___________ 200 mg
(b) 16 g 50 mg ___________ 50 g 16 mg
(c) 2,010 mg___________ 2 g 100 mg
(d) 9,000 mg ___________ 90 g
(e) 5,000 g___________ 7,500 g
(f) 800 mg + 88 mg___________ 880 mg + 8 mg
See Solution(a) 20 g > 200 mg
(b) 16 g 50 mg < 50 g 16 mg
(c) 2,010 mg < 2 g 100 mg
(d) 9,000 mg < 90 g
(e) 5,000 g < 7,500 g
(f) 800 mg + 88 mg = 880 mg + 8 mg
6. Observe the pictures given below and fill in the blanks.

Answer:
5000 × 4 = 2,00,000 kg

7. Answer the following questions.
(a) 5,000 kg = ______ quintals = _____ tonne
(b) 9,000 kg = ______ quintals
(c) ______ kg = 8 tonnes
See Solution(a) 5,000 kg = 50 quintals = 5 tonne
(b) 9,000 kg = 90 quintals
(c) 8000 kg = 8 tonnes
Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 8 Weight Related Questions
Page 109
King’s Weight
In a kingdom, the king donates wheat grains equal to 10 times his weight on his birthday.
(a) If he donates 800 kg of wheat grain this birthday, what is his current weight? _______ kg.
(b) If he had donated 780 kg of wheat grain on his last birthday, what was his weight last year? _______ kg.
(c) How much weight did he gain in a year until this birthday?_______ kg.
See Solution(a) He donates = 800 kg of wheat grain
It is 10 times of kings weight, so his weight = 800 /10 = 80 kg.
(b) He donates = 780 kg of wheat grain
It is 10 times of kings weight, so his weight = 780 /10 = 78 kg.
(c) Weight gained in a year = 80 kg – 78 kg = 2 kg.
Page 111
Let Us Do
1. A restaurant owner uses 5 kg 200 g, 8 kg 900 g, and 12 kg 600 g of onions over 3 days. What is the total weight of onions used by the restaurant owner in 3 days?
See SolutionUses of onions on 1st day = 5 Kg 200 g
Uses of onions on 2nd day = 8 kg 900 g
Uses of onions on 3rd day = 12 kg 600 g
Total weight of the onions used in 3 days
= 5 kg 200 g + 8 kg 900 g + 12 kg 600 g
= 25 kg + 1 kg 700 g
= 26 kg 700 g
2. Aarav is helping his grandfather at the fruit stall. He lifts two baskets of apples weighing 2 kg 100 g and 3 kg 950 g. What is the total weight of apples he lifted?
See SolutionFirst basket weight = 2 kg 100 g
Second basket weight = 3 kg 950 g
Total weight of two basket
= 2 kg 100 g + 3 kg 950 g
= 5 kg + 1 kg 50 g
= 6 kg 50 g
3. 4 kg 500 g of sand is used from a sack weighing 10 kg. How much sand is left in the sack?
See SolutionWeight of the used sand = 4 kg 500 g
Total sand weight = 10 kg
Remaining sand weight
= 10 kg – 4 kg 500 g
= 5 kg 500 g
4. A rice sack weighs 9 kg 750 g. After some rice is used, it weighs 3 kg 700 g. How much rice was used?
See SolutionTotal weight of rice sack = 9 kg 750 g
Sack weight after used rice = 3 kg 700 g
Weight of used rice
= 9 kg 750 g – 3 kg 750 g
= 6 kg 50 g
5. A delivery truck delivered 17 kg 900 g of supplies in the morning and 12 kg 700g in the afternoon. How much total supplies did it deliver?
See SolutionWeight of the delivered supplies in the morning = 17 kg 900 g
Weight of the delivered supplies in the afternoon = 12 kg 700 g
Weight of the total supplies delivered
= 17 kg 900 g + 12 kg 700 g
= 29 kg + 1 kg 600 g
= 30 kg 600 g
6. A box of books weighs 14 kg 750 g. After removing some books, the weight of the box is 10 kg 500 g. What is the weight of the books removed?
See SolutionWeight of a box of books = 14 kg 750 g
Weight of a box after some books removed = 10 kg 500 g
Weight of the books removed
= 14 kg 750 g – 10 kg 500 g
= 4 kg 250 g
7. In a community kitchen of a Gurdwara, 65 kg of flour was purchased on one day. Out of this, 42 kg 275 g flour was used for preparing langar. The next day, an additional 52 kg 500 g of flour was bought. What is the total quantity of flour now available in the kitchen store?
See SolutionWeight of flour purchased = 65 kg
Weight of flour used in langar = 42 kg 275 g
Weight of flour purchased next day = 52 kg 500 g
Total quantity of flour now available in kitchen store
= 65 kg – 42 kg 275 g + 52 kg 500 g
= 75 kg 225 g
Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 8 Practice Questions
Page 112
Let Us Do
1. The cost of some grocery items is given in the following table.
Find the total cost of each item.
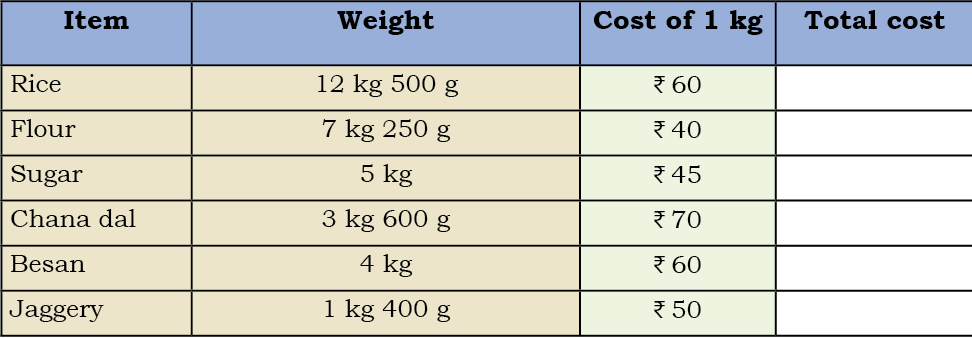
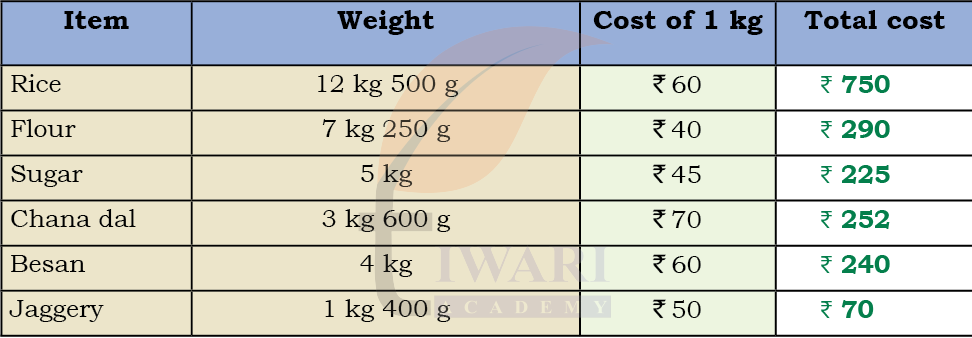
See SolutionTotal Cost = Weight in kg × Rate per kg
► Rice
Weight = 12 kg 500 g = 12.5 kg
Rate = ₹60 per kg
Total = 12.5 × 60 = ₹750
► Flour
Weight = 7 kg 250 g = 7.25 kg
Rate = ₹40 per kg
Total = 7.25 × 40 = ₹290
► Sugar
Weight = 5 kg
Rate = ₹45 per kg
Total = 5 × 45 = ₹225
► Chana Dal
Weight = 3 kg 600 g = 3.6 kg
Rate = ₹70 per kg
Total = 3.6 × 70 = ₹252
► Besan
Weight = 4 kg
Rate = ₹60 per kg
Total = 4 × 60 = ₹240
► Jaggery
Weight = 1 kg 400 g = 1.4 kg
Rate = ₹50 per kg
Total = 1.4 × 50 = ₹70
2. 4 people need 500 g rice for a meal. How much rice will be needed for 8 people if they eat similar quantity of rice?

See SolutionFor 4 people, rice needed = 500 g
For 1 person, rice needed = 500/4 = 125 g
So, for 8 people, rice needed = 8 × 125 = 1000 g = 1 kg
Therefore, 8 people will need 1 kg of rice.

3. 5 kg of tomatoes cost ₹73. How much will 10 kg of tomatoes cost?

See SolutionCost of 5 kg tomatoes = ₹73
Therefore, Cost of 1 kg = 73/5 = ₹14.60
So, Cost of 10 kg = 14.60 × 10 = ₹146
Hence, 10 kg of tomatoes will cost ₹146.

4. Nitesh is a scrap dealer. How much would he have paid for
(a) 16 kg of old newspaper, if he paid ₹8 for every 1 kg of newspaper?
See SolutionPrice of 1 kg newspaper = ₹8
Price of 16 kg newspaper = 16 × 8 = ₹128
(b) 20 kg iron, if he paid ₹200 for every 10 kg of iron?
See SolutionPrice of 10 kg iron = ₹200
Price of 1 kg iron = 200 ÷ 10 = ₹20
Price of 20 kg iron = 20 × 20 = ₹400

(c) 10 kg plastic, if he paid ₹30 for 5 kg of plastic?
Make double number lines for answering (b) and (c).
See SolutionPrice of 5 kg plastic = ₹30
Price of 1 kg plastic = 30 ÷ 5 = ₹6
Price of 10 kg plastic = 10 × 6 = ₹60

Page 113
Measuring Capacity
1. You must have seen tea being prepared at your home. How much water and milk do we need to make 2 cups of tea?
See SolutionWe need 200 ml of water and 200 ml of milk to make 2 cups of tea.
Do we need 1 L of water to make 2 cups of tea?
See SolutionNo, 1 l of water is far too much to make two cups of tea.
Is 500 ml of water enough for 2 cups of tea?
See SolutionNo, 500 ml of water is also much for 2 cup of tea.
2. A bucket can hold a maximum of 20 ml of water. Is this statement correct? Which unit should be used in such a situation?
See SolutionThe statement : A bucket can hold a maximum of 20 ml of water is incorrect. The correct unit here is litres (L), not millilitres (ml)
Page 113
Big to Small to Big
1. Ramiz brings a 500 ml water bottle to school. He drinks two bottles at school. How much water does he drink at school?
See SolutionCapacity of 1 water bottle = 500 ml
So, the capacity of 2 water bottle = 500 ml + 500 ml = 1000 ml
Ramiz drinks 1000 ml /1 litres of water in a day.
Ramiz drinks ___________ml + ___________ml = _________ml.
Ramiz drinks ____ l of water in a day.
See SolutionRamiz drinks 500 ml + 500 ml = 1000 ml.
Ramiz drinks 1 l of water in a day.
2. Muskaan drinks 3 l of water in a day. How many times would she need to refill a 500 ml water bottle? ________________.
Muskaan drinks _________ ml of water in a day.
See SolutionCapacity of water bottle = 500 ml
Total consumption of water in a day by Muskaan = 3 litres
Number of refills needed = 3,000 ml ÷ 500 ml = 6 times
Muskaan drinks 3,000 ml of water in a day.
3. Write the total capacity of the following containers in each blank.

See SolutionFirst Jug: 1 litres + 500 ml + 100 ml = 1 litres 600 ml
Second Jug: 1 litres + 500 ml = 1 litres 500 ml
Third Jug: 100 ml + 100 ml + 500 ml = 700 ml
Fourth Jug: 1 litres + 1 litres + 100 ml = 2 litres 100 ml

Page 114
Different Units but Same Measure
The Milkman’s Delivery
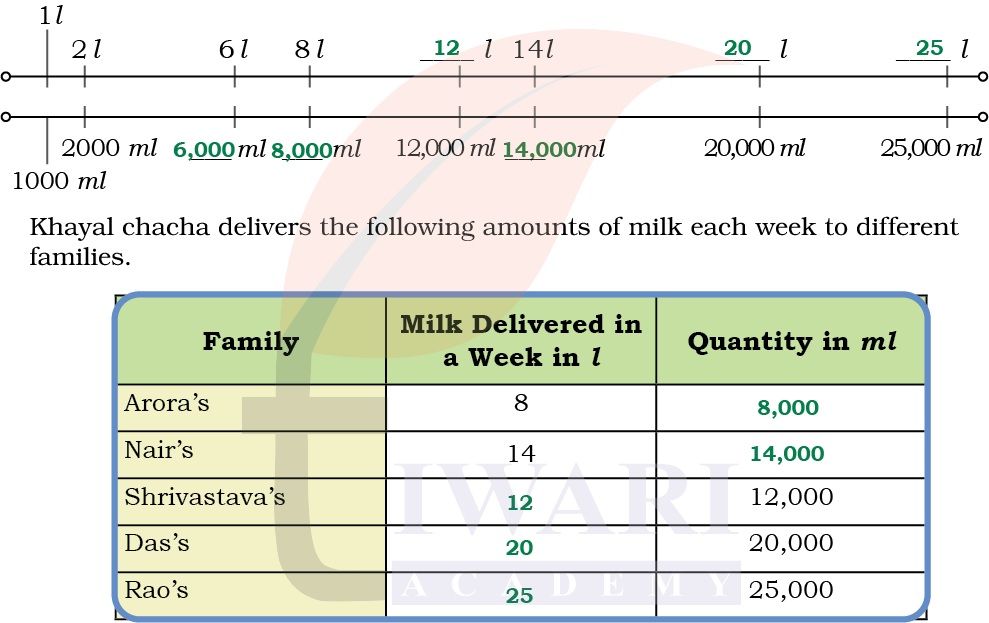
Khayal chacha delivers fresh cow milk to homes. Bhalerao’s family orders 2l of milk everyday.
This family has a vessel marked in ml only. What mark will you see in the vessel corresponding to 2 l?
Answer:
Page 115
Let Us Think
1. Mary and Daisy filled their bottle with 1l 400 ml of water. They wondered about the capacity of the bottle in ml. How much is it?

See Solution1litre = 1000 ml
So, 1 l 400 ml = 1000 ml + 400 ml = 1400 ml
Hence, the bottle’s capacity is 1400 ml.
2. Convert and fill in the blanks appropriately. You can use the double
number line given earlier.
(a) 3 l 8 ml = _____ml
(b) 9 l 90 ml = _____ ml
(c) 14,075 ml = ____l ____ml
(d) 8 l 86 ml = ____ ml
(e) 12,200 ml = ____ l ____ ml
(f) 18,350 ml = ____l ____ml
See Solution(a) 3 l 8 ml = 3008 ml
(b) 9 l 90 ml = 9090 ml
(c) 14,075 ml = 14 l 75 ml
(d) 8 l 86 ml = 8086 ml
(e) 12,200 ml = 12 l 200 ml
(f) 18,350 ml = 18 l 350 ml
Page 115
Let Us Compare
1. Kiran owns a petrol pump. She records the details of the sales of petrol in a day.

See SolutionShe records the details of the sales of petrol in l and ml.
2.

(a) How much more fuel is bought for buses than for trucks?
See SolutionTotal Quantity of fuel in trucks = 1500 litres
Total Quantity of fuel in buses = 1800 litres
Quantity of more fuel bought
= 1800 – 1500 = 300 litres

(b) What is the total quantity of fuel filled from the petrol pump on that day?
See SolutionTotal quantity of fuel filed from petrol pump on the day
= 1500 +1800 + 500 + 96 + 125
= 4021 litres
3. Compare the following quantities using the signs <, =, >.
(a) 5 l 600 ml ___________ 5,400 ml
(b) 10 l 100 ml ___________ 1 l 600 ml
(c) 190 ml + 800 ml ___________ 800 ml +109 ml
(d) 3 l 600 ml ___________ 3,600 ml
(e) 4 l 50 ml ___________ 4 l 500 m
See Solution(a) 5 l 600 ml = 5,400 ml
(b) 10 l 100 ml > 1 l 600 ml
(c) 190 ml + 800 ml > 800 ml +109 ml
(d) 3 l 600 ml = 3,600 ml
(e) 4 l 50 ml < 4 l 500 m
4. Sam and Tina fill petrol in their bikes. Tina bought 2 l 500 ml of petrol. Sam bought 2 l 800 ml more petrol than Tina. How much petrol did Sam buy?
See SolutionTina’s petrol = 2 l 500 ml = 2500 ml
Extra petrol Sam bought = 2 l 800 ml = 2800 ml
Sam’s petrol = 2500 ml + 2800 ml = 5300 ml
In litres: 5300 ml = 5 l 300 ml
So, Sam bought 5 l 300 ml of petrol.
Page 118
Let Us Solve
1. Riya is filling water bottles for a picnic. She fills one 2 l bottle and four 500 ml bottles. Her friend, Aarav fills three 750 ml bottles. Who filled more water, Riya or Aarav? How much more?
See SolutionWater filled by Riya = 4 × 500 ml + 2 l
= 2,000 ml + 2 l
= 2 l + 2 l = 4 l.
Water filled by Aarav = 3 × 750 ml
= 2,250 ml = 2 l 250 ml.
So, Riya filled more water.
2. A bottle of milk is poured equally into 8 glasses, leaving 120 ml of milk in the bottle.
(a) If each glass has a capacity of 360 ml, what is the total capacity of 8 glasses?
(b) How much milk was there in the bottle initially?
(c) If 1 l of milk costs ₹40, how much will 3 l milk cost?
See Solution(a) Capacity of 8 glasses = 8 × 360 ml = 2,880 ml = 2 l 880 ml.
b) Milk present in the bottle initially
= Milk poured in 8 glasses + Milk left in the bottle
= 2,880 ml + 120 ml
= 3,000 ml = 3 l.
c) Cost of 1 l milk is = ₹40
Cost of 3 l milk = 40 × 3 = ₹120
3. A juice vendor has a 5 l container of orange juice. Each glass has a capacity 250 ml.
(a) How many full glasses can he serve before the container becomes empty?
See SolutionNumber of full glasses
Total juice = 5 l = 5000 ml
Capacity of 1 glass = 250 ml
Number of glasses = 5000/250 = 20
So, he can serve 20 full glasses.
(b) If he has already served 10 glasses, how much juice is left?
See SolutionJuice left after 10 glasses
Juice served in 10 glasses = 10 × 250 = 2500 ml
Remaining juice = 5000 − 2500 = 2500 ml = 2 l 500 ml
So, 2 l 500 ml of juice is left.
(c) If 250 ml of juice is sold at ₹25, how much will he earn by selling 5 l juice?
See SolutionEarnings from 5 l juice
1 glass (250 ml) sells for ₹25
Total glasses from 5 l = 20
Total earnings = 20 × 25 = ₹500
So, he will earn ₹500.
4. In a factory, 8 l 400 ml of oil needs to be equally poured into 7 containers
for storage. How much oil will each container hold?
See SolutionOil stored in each container = 8 l 400 ml ÷ 7
= 8,400 ml ÷ 7
= 1,200 ml = 1 l 200 ml.
Therefore, each container will hold 1 l 200 ml oil.
5. If one container can hold 1 l 75 ml of buttermilk, how much buttermilk
will be there in 8 such containers?
See SolutionCapacity of one container to hold buttermilk
1 l 75 ml = 1,000 ml + 75 ml = 1,075 ml.
Capacity of 8 container to hold buttermilk
8 × 1,075 ml = 8,600 ml = 8 l 600 ml.


