NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 2 Biological Classification in Hindi and English Medium to Study online as well as download in PDF format free for new academic session 2024-25. NCERT Solutions are applicable for all boards like Gujrat, UP, MP, CBSE, etc. who are using NCERT Books as course books.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 2
| Class: 11 | Biology |
| Chapter 2: | Biological Classification |
| Content: | NCERT Textbook and Extra Questions |
| Medium: | Hindi and English Medium |
| Content Type: | Text, Images and PDF Format |
Class 11 Biology Chapter 2 Solutions in English
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 2 is given below to download in PDF format updated for new session 2024-25. Join the Discussion Forum to ask the questions and discussion your educational problems. Download NCERT Books based on latest CBSE Syllabus 2024-25 for all boards who are following CBSE NCERT Books as a course books.
Important Terms on Biological Classification
Two kingdom classification: Given by Carolous Linneaeus – Kingdom – plantae and kingdom –Animalia.
Five kingdom classification: By R.H. Whittaker, Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia are the five kingdoms.
11th Biology Chapter 2 Extra Questions
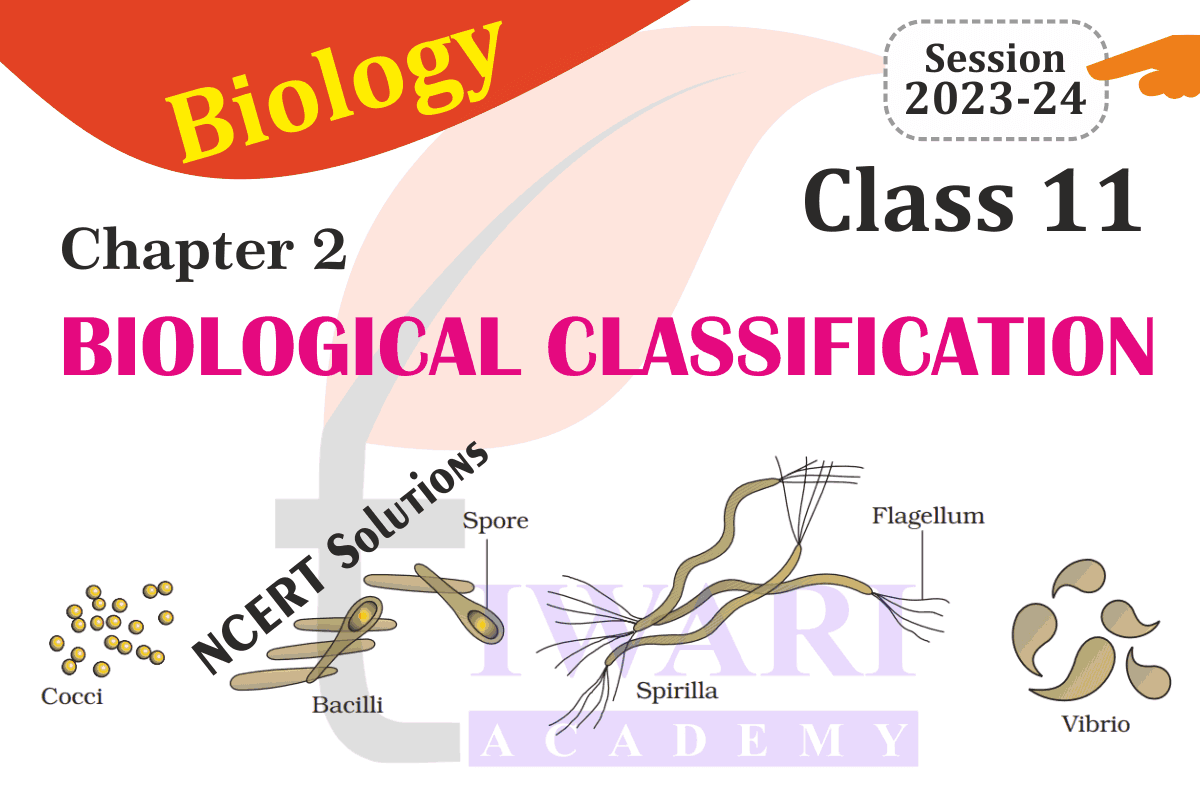
Describe Kingdom MONERA?
Kingdom MONERA:
1. Has bacteria as sole members.
2. Bacteria can have shapes like: Coccus (spherical), Bacillus (rod-shaped), Vibrium (comma shaped) and spirillum (spiral shaped).
3. Bacteria found almost everywhere and can be Photosynthetic autotrophs, Chemosyn thetic autotrophs or Heterotrophs.
4. Halophiles (salt-loving), hermoacidophiles (in hot springs)
5. Methanogens (in marsh and in gut of ruminant animals. Produce methane gas.)
6. Photosynthetic autotrophs like Cyanobacteria (Blue-green algae BGA). Some like Anabaena and Nostoc have specialized cells called heterocysts for nitrogen fixation.
Give brief idea of Kingdom PROTISTA?
Kingdom PROTISTA:
I. Comprises of all single celled eukaryotes
II. Forms a link between plants, animals and fungi.
1. Chrysophytes (Has diatoms and golden algae/desmids) Fresh water/marine, photosynthetic, microscopic plankton.
2. Dinoflagellates: Marine, photosynthetic cell wall has stiff cellulose plates.
3. Euglenoids: Found in stagnant fresh water. Have protein rich layer – pellicle – which makes body flexible.
4. Slime Moulds: Saprophytic protists, under suitable conditions form an aggregates called plasmodium, grows on decaying twigs and leaves.
5. Protozoans: Are heterotrops and live as predators or parasites. Have four major groups.
KINGDOM FUNGI
1. Heterotrophic organisms
2. Non chlorpohyllous hyphae
3. Reprouction can take place by vegetative means fragmentation, fission and budding. Asexual reproduction by spores – conidia, sporangiospores or zoospores. Sexual reproduction by Oospores, ascospores and basidiospores – produced in fruiting bodies.
4. Network of hyphae called mycelium
5. Hyphae which have multinucleate cytoplasm are called coenocytic hyphae
6. Cell wall of chitin and polysaccharides
7. Cosmopolitan. Grow in warm and humid places.
8. Saprophytic, parasitic, symbiotic (Lichen and Mycorrhiza) e.g., Puccinia, (wheat rust disesae), Penicillium, Yeast is a unicellular fungus.
Viruses
1. They did not find a place in classification.
2. Not truly living.
3. Non-cellular organisms which take over the machinery of host cell on entering it and become living but as such they have inert crystalline structure appear non-living. So, difficult to call them living or non-living.
4. Virus means venom of poisonous fluid. Pastuer gave the term virus.
5. D.J. Ivanowsky found out that certain microbes caused Tobacco Mosaic Disease in tobacco plant.
6. Viruses are obligate parasites.
Important Questions on 11th Biology Chapter 2
Discuss how classification systems have undergone several changes over a period of time?
The classification systems have undergone several changes with time. The first attempt of classification was made by Aristotle. He classified plants as herbs, shrubs, and trees. Animals, on the other hand, were classified on the basis of presence or absence of red blood cells. This system of classification failed to classify all the known organisms. Therefore, Linnaeus gave a two kingdom system of classification. It consists of kingdom Plantae and kingdom Animalia. However, this system did not differentiate between unicellular and multicellular organisms and between eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Therefore, there were large numbers of organisms that could not be classified under the two kingdoms. To solve these problems, a five kingdom system of classification was proposed by R.H Whittaker in 1969. On the basis of characteristics, such as cell structure, mode of nutrition, presence of cell wall, etc., five kingdoms, Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia were formed.
State two economically important uses of Heterotrophic bacteria and Archaebacteria.
Heterotrophic bacteria a) They act as decomposers and help in the formation of humus. b) They help in the production of curd from milk. c) Many antibiotics are obtained from some species of bacteria. d) Many soil bacteria help in fixation of atmospheric nitrogen. Archaebacteria a) Methane gas is produced from the dung of ruminants by the methanogens. b) Methanogens are also involved in the formation of biogas and sewage treatment.
What is the nature of cell-walls in diatoms?
The cell walls of diatoms are made of silica. Their cell wall construction is known as frustule. It consists of two thin overlapping shells that fit into each other such as a soap box. When the diatoms die, the silica in their cell walls gets deposited in the form of diatomaceous earth. This diatomaceous earth is very soft and quite inert. It is used in filtration of oils, sugars, and for other industrial purposes.
Find out what do the terms ‘algal bloom’ and ‘red-tides’ signify.
Algal bloom Algal bloom refers to an increase in the population of algae or blue-green algae in water, resulting in discoloration of the water body. This causes an increase in the biological oxygen demand (BOD), resulting in the death of fishes and other aquatic animals. Red-tides Red tides are caused by red dinoflagellates (Gonyaulax) that multiply rapidly. Due to their large numbers, the sea appears red in colour. They release large amounts of toxins in water that can cause death of a large number of fishes.
How are viroids different from viruses?
Viroids were discovered in 1917 by T.O. Denier. They cause potato spindle tuber disease. They are smaller in size than viruses. They also lack the protein coat and contain free RNA of low molecular weight.
Describe briefly the four major groups of Protozoa.
Protozoa are microscopic unicellular protists with heterotrophic mode of nutrition. They may be holozoic, saprobic, or parasitic. These are divided into four major groups. (1) Amoeboid protozoa or sarcodines They are unicellular, jelly-like protozoa found in fresh or sea water and in moist soil. Their body lacks a periplast. Therefore, they may be naked or covered by a calcareous shell. They usually lack flagella and have temporary protoplasmic outgrowths called pseudopodia. These pseudopodia or false feet help in movement and capturing prey. They include free living forms such as Amoeba or parasitic forms such as Entamoeba. (2) Flagellated protozoa or zooflagellates They are free living, non-photosynthetic flagellates without a cell wall. They possess flagella for locomotion and capturing prey. They include parasitic forms such as Trypanosoma, which causes sleeping sickness in human beings. (3) Ciliated protozoa or ciliates They are aquatic individuals that form a large group of protozoa. Their characteristic features are the presence of numerous cilia on the entire body surface and the presence of two types of nuclei. All the cilia beat in the same direction to move the water laden food inside a cavity called gullet. They include organisms such as Paramoecium, Vorticella,etc. (4) Sporozoans They include disease causing endoparasites and other pathogens. They are uninucleate and their body is covered by a pellicle. They do not possess cilia or flagella. They include the malaria causing parasite Plasmodium.
Plants are autotrophic. Can you think of some plants that are partially heterotrophic?
Plants have autotrophic mode of nutrition as they contain chlorophyll pigment. Thus, they have the ability to prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis. However, some insectivorous plants are partially heterotrophic. They have various means of capturing insects so as to supplement their diet with required nutrients derived from insects, causing proliferation of growth. The examples include pitcher plant (Nepenthes), Venus fly trap, bladderwort, and sundew plant.
What do the terms phycobiont and mycobiont signify?
Phycobiont refers to the algal component of the lichens and mycobiont refers to the fungal component. Algae contain chlorophyll and prepare food for fungi whereas the fungus provides shelter to algae and absorbs water and nutrients from the soil. This type of relationship is referred to as symbiotic.
What are the characteristic features of Euglenoids?
Some characteristic features of Euglenoids are as follows. Euglenoids (such as Euglena) are unicellular protists commonly found in fresh water. Instead of cell wall, a protein-rich cell membrane known as pellicle is present. They bear two flagella on the anterior end of the body. A small light sensitive eye spot is present. They contain photosynthetic pigments such as chlorophyll and can thus prepare their own food. However, in absence of light, they behave similar to heterotrophs by capturing other small aquatic organisms. They have both plant and animal-like features, which makes them difficult to classify.
Viruses are sub-microscopic infectious agents that can infect all living organisms. A virus consists of genetic material surrounded by a protein coat. The genetic material may be present in the form of DNA or RNA. Most of the viruses, infecting plants, have single stranded RNA as genetic material. On the other hand, the viruses infecting animals have single or double stranded RNA or double stranded DNA. Bacteriophages or viruses infecting bacteria mostly have double stranded DNA. Their protein coat called capsid is made up of capsomere subunits. These capsomeres are arranged in helical or polyhedral geometric forms. A.I.D.S, small pox, mumps, and influenza are some common examples of viral diseases.
Organize a discussion in your class on the topic- Are viruses living or non-living?
Viruses are microscopic organisms that have characteristics of both living and non-living. A virus consists of a strand of DNA or RNA covered by a protein coat. This presence of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) suggests that viruses are alive. In addition, they can also respond to their environment (inside the host cell) in a limited manner. However, some other characters, such as their inability to reproduce without using the host cell machinery and their acellular nature, indicate that viruses are non-living. Therefore, classifying viruses has remained a mystery for modern systematic.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 2 Biological Classification.
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 2 Biological Classification in PDF format free. Download option is given so that students can use it without internet. If you don’t wish to download, STUDY ONLINE option is also available. This page provides all the answers of Exercise given at the end of the chapter of Class 11 Biology Chapter 2 Biological Classification.