NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology: Principles and Processes to Study Online or download in PDF format Free to use offline updated for new academic session 2024-25. Download NCERT Books based on latest CBSE Syllabus 2024-25 for UP Board, CBSE, MP Board and all other board who are following NCERT.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 9
Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology: Principles and Processes Solutions
| Class: 12 | Science |
| Subject: | Biology |
| Chapter 9: | Biotechnology: Principles and Processes |
| Content: | NCERT Solution and Practice Questions |
| Academic Session: | 2024-25 |
| Medium: | Hindi and English |
Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Solutions in English
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 in PDF format to free download for academic session 2024-25. Offline Apps based on NCERT Solutions are free to download and use it offline without internet.
Principles of Biotechnology
1. Genetic Engineering: The techniques used to alter the chemistry of genetic material (DNA/RNA) and introduction of it into organisms to change its phenotype.
2. Chemical Engineering: Use of contamination free chemical engineering process of growth of desired microbe or cell in large quantity to obtain biotechnological product like enzyme, antibiotic, vaccine etc.
3. Cloning Vectors: A small, self-replicating DNA molecule into which foreign DNA is inserted. It replicates inside the host cell. The vectors that may be used in genetic engineering are plasmids, bacteriophages, animal, plant, virus, YACs and BACs and some yeasts.
4. Plasmid: Extra chromosomal, self-replicating circular DNA molecule found in certain bacteria and in some yeasts. It has a few genes. Plasmids are used as cloning vectors in genetic engineering. Plasmids were discovered by William Hays and Joshua Leduberg in 1952. The most widely used vector in cloning is pBR322.
5. Ti Plasmid: It is an extrachromosomal, double stranded and self-replicating DNA molecule found in Agra bacteriumtumifaciens. If causes tumour in plants.
But now Ti Plasmid has been modified into a cloning vector by which desired genes can be delivered into many plants.
Important Terms related to Chapter 9
1. Features of cloning vector: Origin of replication (Ori) selectable marker and cloning sites are the features that are required to facilitate cloning into a vector.
2. Origin of Replication (Ori): This is a sequence from where replication starts and any piece of DNA when linked to this sequence can be made to replicate within the host cells. This sequence is also responsible for controlling the copy number of the linked DNA.
3. Cloning Sites: A location on a cloning vector into where a foreign gene can be introduced is called recognition site. The vector must have very few (preferably single) recognition sites. The presence of more than one recognition sites within the vector will produce several fragments which will make the process of gene cloning more complicated. Therefore, the foreign DNA is ligated at a restriction site present in one of the two antibiotic resistance gene.
4. Selectable Marker: It is a gene which helps in identifying and eliminating non-trans formants from trans formants (having recombinant DNA) by selectively permitting the growth of trans formants. The process through which as piece of DNA is introduced in a host bacterium is called transformation. The genes encoding resistance to antibiotics are considered useful selectable marker for E coli.
5. Small Size of Vector: This facilitates the introduction of DNA into the host easily.
Important Questions on 12th Biology Chapter 9
From what you have learnt, can you tell whether enzymes are bigger or DNA is bigger in molecular size? How did you know?
Enzymes are smaller in size than DNA molecules. We know this because DNA contains genetic information for the development and functioning of all living organisms. It contains instructions for the synthesis of proteins and DNA molecules. On the other hand, enzymes are proteins which are synthesised from a small stretch of DNA known as ‘genes’, which are involved in the production of the polypeptide chain.
What would be the molar concentration of human DNA in a human cell?
The molar concentration of human DNA in a human diploid cell is as follows: ⇒ Total number of chromosomes × 6.023 × 10^23 ⇒ 46 × 6.023 × 10^23 ⇒ 2.77 × 10^23 moles Hence, the molar concentration of DNA in each diploid cell in humans is 2.77 × 10^23 moles.
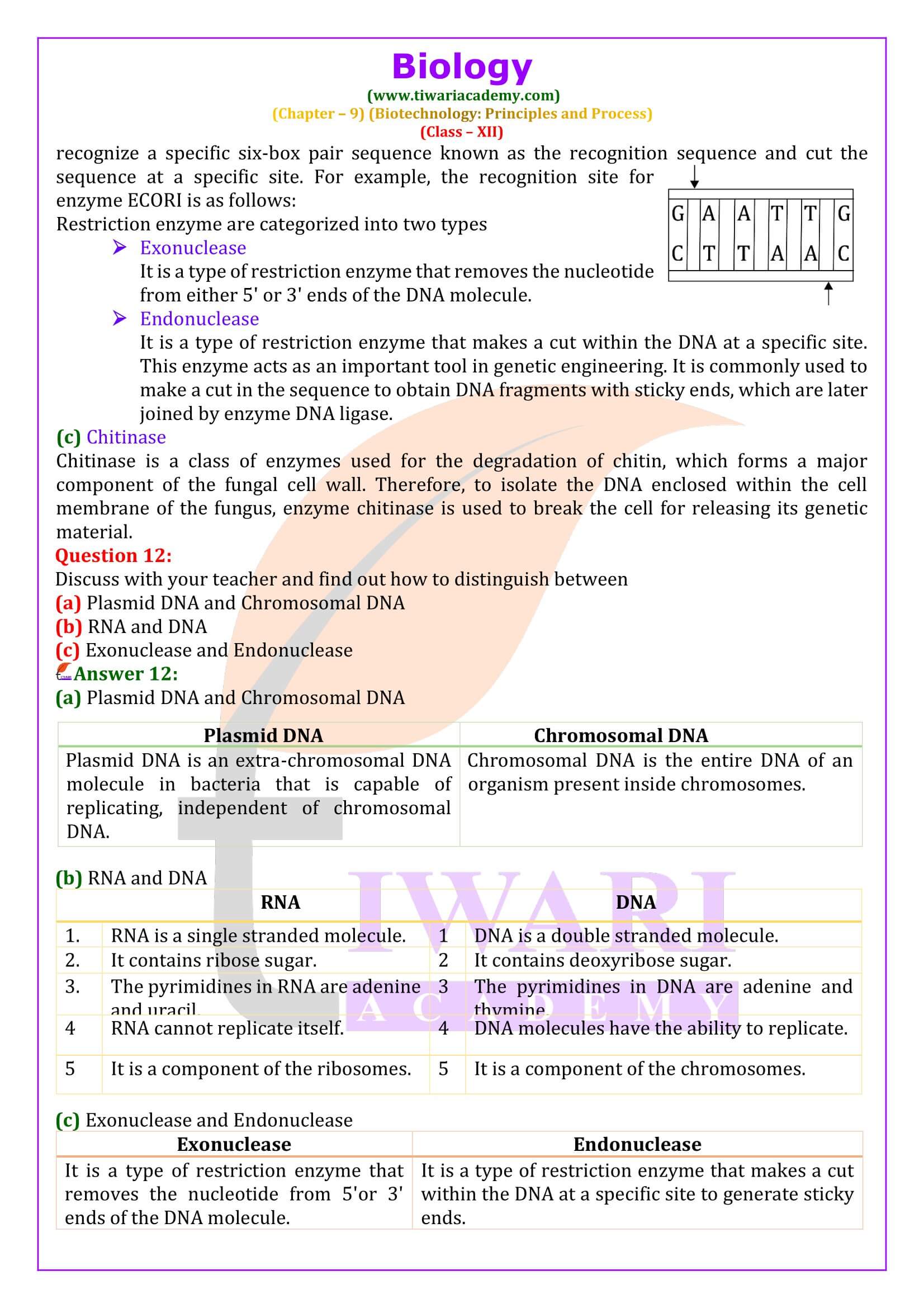
Do eukaryotic cells have restriction endonucleases? Justify your answer.
No, eukaryotic cells do not have restriction endonucleases. This is because the DNA of eukaryotes is highly methylated by a modification enzyme, called methylase. Methylation protects the DNA from the activity of restriction enzymes .These enzymes are present in prokaryotic cells where they help prevent the invasion of DNA by virus.
Besides better aeration and mixing properties, what other advantages do stirred tank bioreactors have over shake flasks?
The shake flask method is used for a small-scale production of biotechnological products in a laboratory. On the other hand, stirred tank bioreactors are used for a large-scale production of biotechnology products. Stirred tank bioreactors have several advantages over shake flasks. Some of them are Small volumes of culture can be taken out from the reactor for sampling or testing. It has a foam breaker for regulating the foam. It has a control system that regulates the temperature and pH.
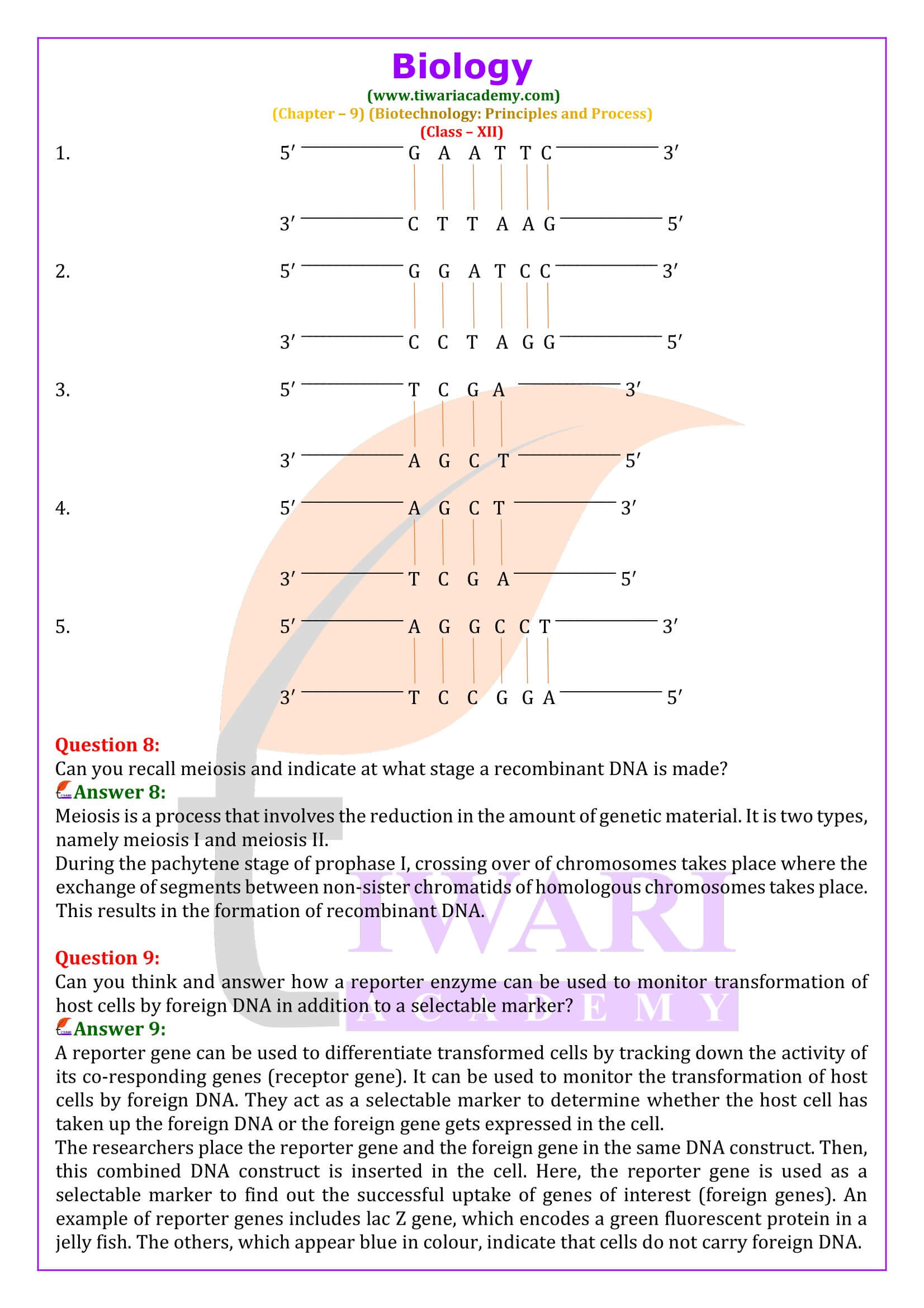
Can you recall meiosis and indicate at what stage a recombinant DNA is made?
Meiosis is a process that involves the reduction in the amount of genetic material. It is two types, namely meiosis I and meiosis II. During the pachytene stage of prophase I, crossing over of chromosomes takes place where the exchange of segments between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes takes place. This results in the formation of recombinant DNA.
Can you think and answer how a reporter enzyme can be used to monitor transformation of host cells by foreign DNA in addition to a selectable marker?
A reporter gene can be used to differentiate transformed cells by tracking down the activity of its co-responding genes (receptor gene). It can be used to monitor the transformation of host cells by foreign DNA. They act as a selectable marker to determine whether the host cell has taken up the foreign DNA or the foreign gene gets expressed in the cell. The researchers place the reporter gene and the foreign gene in the same DNA construct. Then, this combined DNA construct is inserted in the cell. Here, the reporter gene is used as a selectable marker to find out the successful uptake of genes of interest (foreign genes). An example of reporter genes includes lac Z gene, which encodes a green fluorescent protein in a jelly fish. The others, which appear blue in colour, indicate that cells do not carry foreign DNA.