NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants updated for New Academic Session 2025-26 to Study Online in Hindi and English Medium. Latest NCERT Books and NCERT Textbook Solutions are also available in PDF file format. Ask your Questions or answer your friend’s questions under the Discussion Forum. It is a platform of sharing the knowledge.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 1
Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Solutions
| Class: 12 | Science |
| Subject: | Biology |
| Chapter 1: | Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants |
| Content: | NCERT Solutions with Extra Questions |
| Academic Session: | CBSE 2025-26 |
| Medium: | Hindi and English Medium |
Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 Solutions in English
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants is given below to download in PDF form or use it online for new academic year 2025-26. All the solutions are based on latest NCERT Books following the latest CBSE Syllabus.
Extra Questions Class 12 Biology Chapter 1
Give the scientific name of a plant with came to India as a contaminant with imported wheat and causes pollen allergy.
Parthenium hysterophorus (carrot grass)
Why are pollen grains produced in enormous quantity in maize?
To ensure pollination because Maize is pollinated by wind.
In some species of Asteraceae and grasses, seed are formed without fusion of gametes. Mention the scientific term for such of reproduction.
Apomixis
If the diploid number of chromosomes in an angiospermic plant is 16. Mention number of chromosomes in the endosperm and antipodal cell.
Chromosomes in endosperm and 8 chromosomes in antipodal cells.
Important Terms related to Chapter 1
1. Autogamy: When pollen grains of a flower are transferred from anther to stigma of the same flower.
2. Coleorhiza: A protective sheath of radicle in monocot seed.
3. Coleoptile: A protective sheath of plumule in monocot seed.
4. Nucellus: Multicellular tissue in the centre of ovule in which embryo sac is present.
5. Viability of Seed: Ability of seed to retain the power of germination.
6. Sporopollenin is one of the most resistant organic substance. It is not affected by high temperature, strong acids or alkali. No enzyme can degrade it.
7. Pollen Products: Pollen grains are rich in carbohydrates, proteins and unsaturated fats. Their consumption is believed to increase performance of athlete and horses. They are used in the form of tablets and syrups.
Points to Remember
1. Pollen Viability: Pollens of wheat and rice remain viable for 30 minutes. Pollens of same other plants may remain viable for several months. Pollens can be cryopreserved in liquid nitrogen (-196°C) in pollen banks.
2. Dicot Embryo: A typical dicot embryo consist of an embryonal axis and two cotyledons. The portion of embryonal axis above the level of cotyledons is the epicotyl and the portion below the level of cotyledons is hypocotyl.
3. Monocot Embryo: Monocot (Rice, Maize etc.) has one cotyledon called Scutellum. The embryonal axis has the radicle and root cap enclosed by a sheath called Coleorrhiza. The upper end (epicotyle) has plumule which is covered by hollow foliar structure called the coleoptile.
4. Apomixis: Apomixis is a form of asexual repduction that mimics sexual reproduction where seeds are formed without fertilisation.
Important Questions on 12th Biology Chapter 1
Name the parts of an angiosperm flower in which development of male and female gametophyte take place.
The male gametophyte or the pollen grain develops inside the pollen chamber of the anther, whereas the female gametophyte (also known as the embryo sac) develops inside the nucellus of the ovule from the functional megaspore.
Arrange the following terms in the correct developmental sequence: Pollen grain, sporogenous tissue, microspore tetrad, pollen mother cell, male gametes.
The correct development sequence is as follows: Sporogenous tissue – pollen mother cell – microspore tetrad – Pollen grain – male gamete During the development of microsporangium, each cell of the sporogenous tissue acts as a pollen mother cell and gives rise to a microspore tetrad, containing four haploid microspores by the process of meiosis (microsporogenesis). As the anther matures, these microspores dissociate and develop into pollen grains. The pollen grains mature and give rise to male gametes.
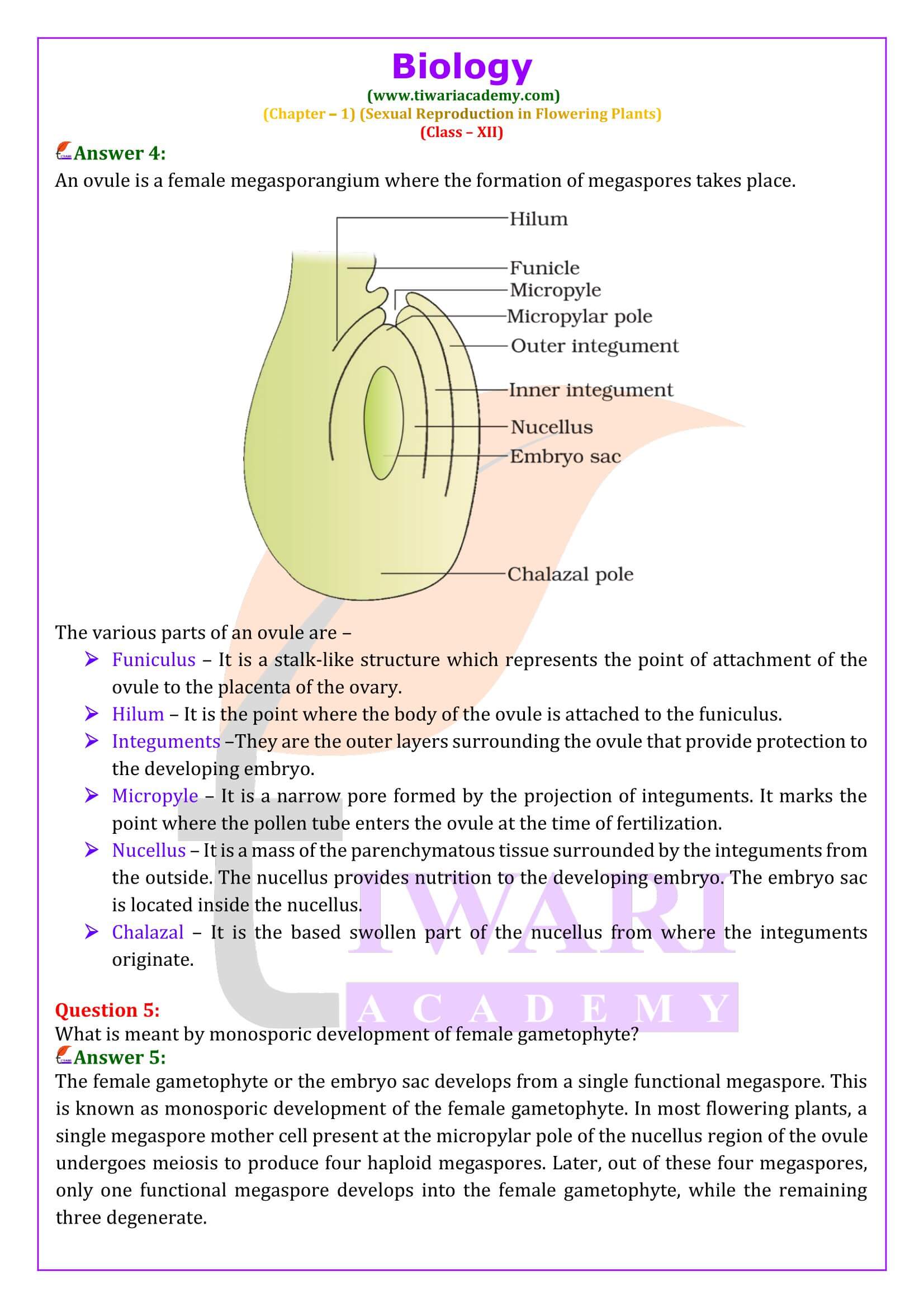
What is meant by monosporic development of female gametophyte?
The female gametophyte or the embryo sac develops from a single functional megaspore. This is known as monosporic development of the female gametophyte. In most flowering plants, a single megaspore mother cell present at the micropylar pole of the nucellus region of the ovule undergoes meiosis to produce four haploid megaspores. Later, out of these four megaspores, only one functional megaspore develops into the female gametophyte, while the remaining three degenerate.
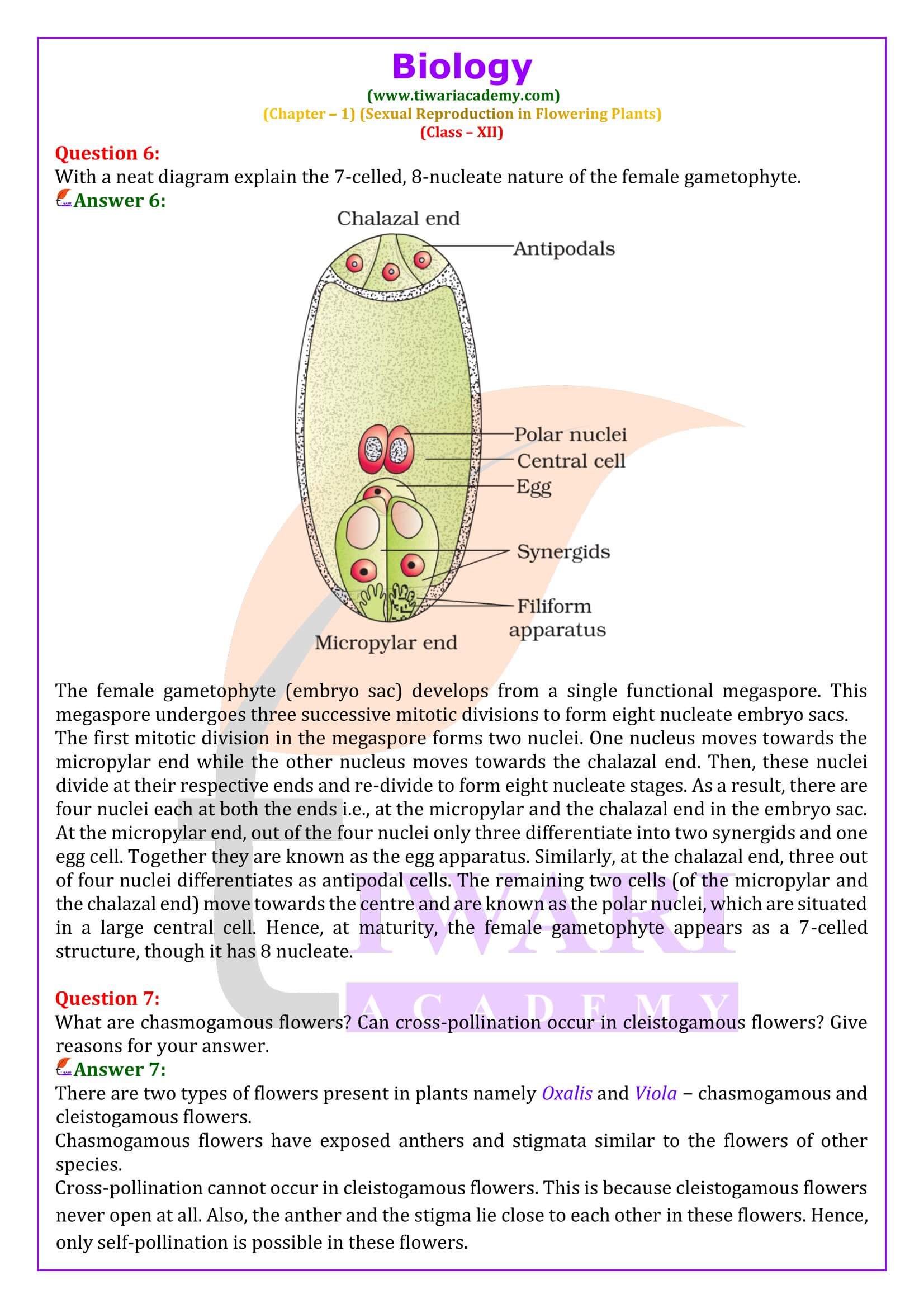
What are chasmogamous flowers? Can cross-pollination occur in cleistogamous flowers? Give reasons for your answer.
There are two types of flowers present in plants namely Oxalis and Viola − chasmogamous and cleistogamous flowers. Chasmogamous flowers have exposed anthers and stigmata similar to the flowers of other species. Cross-pollination cannot occur in cleistogamous flowers. This is because cleistogamous flowers never open at all. Also, the anther and the stigma lie close to each other in these flowers. Hence, only self-pollination is possible in these flowers.
Mention two strategies evolved to prevent self-pollination in flowers.
Self-pollination involves the transfer of pollen from the stamen to the pistil of the same flower. Two strategies that have evolved to prevent self-pollination in flowers are as follows: In certain plants, the stigma of the flower has the capability to prevent the germination of pollen grains and hence, prevent the growth of the pollen tube. It is a genetic mechanism to prevent self-pollination called self- incompatibility. Incompatibility may be between individuals of the same species or between individuals of different species. Thus, incompatibility prevents breeding. In some plants, the gynoecium matures before the androecium or vice-versa. This phenomenon is known as protogyny or protandry respectively. This prevents the pollen from coming in contact with the stigma of the same flower.
What is self-incompatibility? Why does self-pollination not lead to seed formation in self-incompatible species?
Self-incompatibility is a genetic mechanism in angiosperms that prevents self-pollination. It develops genetic incompatibility between individuals of the same species or between individuals of different species. The plants which exhibit this phenomenon have the ability to prevent germination of pollen grains and thus, prevent the growth of the pollen tube on the stigma of the flower. This prevents the fusion of the gametes along with the development of the embryo. As a result, no seed formation takes place.
What is bagging technique? How is it useful in a plant breeding programme?
Various artificial hybridization techniques (under various crop improvement programmes) involve the removal of the anther from bisexual flowers without affecting the female reproductive part (pistil) through the process of emasculation. Then, these emasculated flowers are wrapped in bags to prevent pollination by unwanted pollen grains. This process is called bagging. This technique is an important part of the plant breeding programme as it ensures that pollen grains of only desirable plants are used for fertilization of the stigma to develop the desired plant variety.
Why do you think the zygote is dormant for some time in a fertilized ovule?
The zygote is formed by the fusion of the male gamete with the nucleus of the egg cell. The zygote remains dormant for some time and waits for the endosperm to form, which develops from the primary endosperm cell resulting from triple fusion. The endosperm provides food for the growing embryo and after the formation of the endosperm, further development of the embryo from the zygote starts.
If one can induce parthenocarpy through the application of growth substances, which fruits would you select to induce parthenocarpy and why?
Parthenocarpy is the process of developing fruits without involving the process of fertilization or seed formation. Therefore, the seedless varieties of economically important fruits such as orange, lemon, water melon etc. are produced using this technique. This technique involves inducing fruit formation by the application of plant growth hormones such as auxins.
What is apomixis and what is its importance?
Apomixis is the mechanism of seed production without involving the process of meiosis and syngamy. It plays an important role in hybrid seed production. The method of producing hybrid seeds by cultivation is very expensive for farmers. Also, by sowing hybrid seeds, it is difficult to maintain hybrid characters as characters segregate during meiosis. Apomixis prevents the loss of specific characters in the hybrid. Also, it is a cost-effective method for producing seeds.