Class 8 English Grammar Chapter 15 Active and Passive Voice. When the Subject of a Verb acts or the Subject is the doer of the action, the verb is said to be in the Active Voice. When the Subject of a Verb is acted upon, or the Subject is the receiver of the action, the verb is said to be in the Passive Voice. For example, Active Voice: Reena writes a letter. Passive Voice: A letter is written by Reena. There is no difference in the meanings of these two sentences. These are simply two different ways of saying the same thing. But in the first sentence, Subject performs the action, while in the second sentence, the Subject of the Verb is acted upon.
Voice in grammar, particularly in English, has a unique ability to shift the focus of a sentence from the doer of an action to the receiver of that action. Chapter 15 of Class 8 English Grammar, elaborately covered in NCERT Solutions by platforms like Tiwari Academy, delves into this intriguing concept, enabling students to comprehend and use both Active and Passive Voices proficiently.
| Class: 8 | English Grammar |
| Chapter: 15 | Active and Passive Voice |
| Academic Session: | 2024-25 |
| Study Material: | Textbook and Revision Notes |
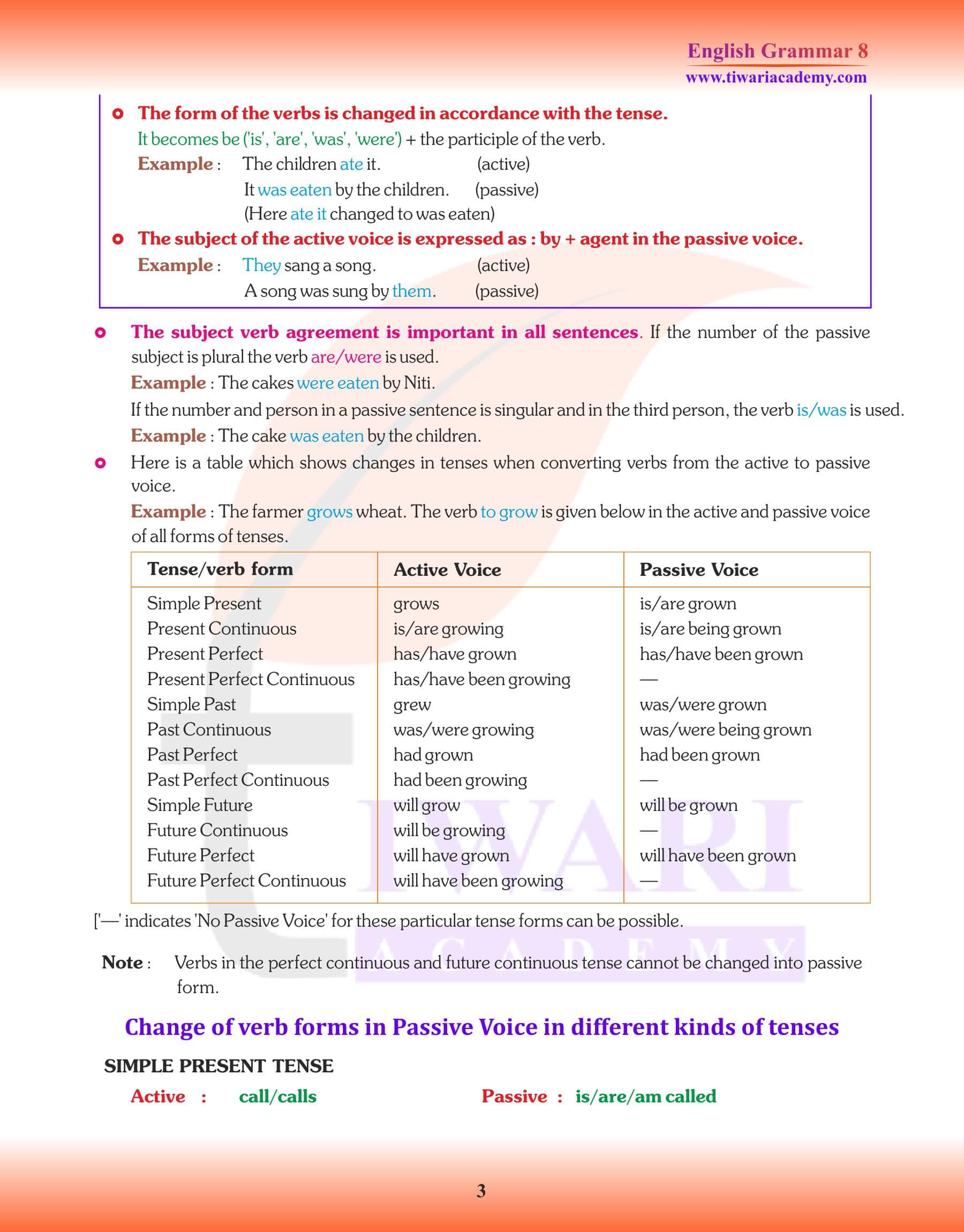
Rule for the Change of Voice
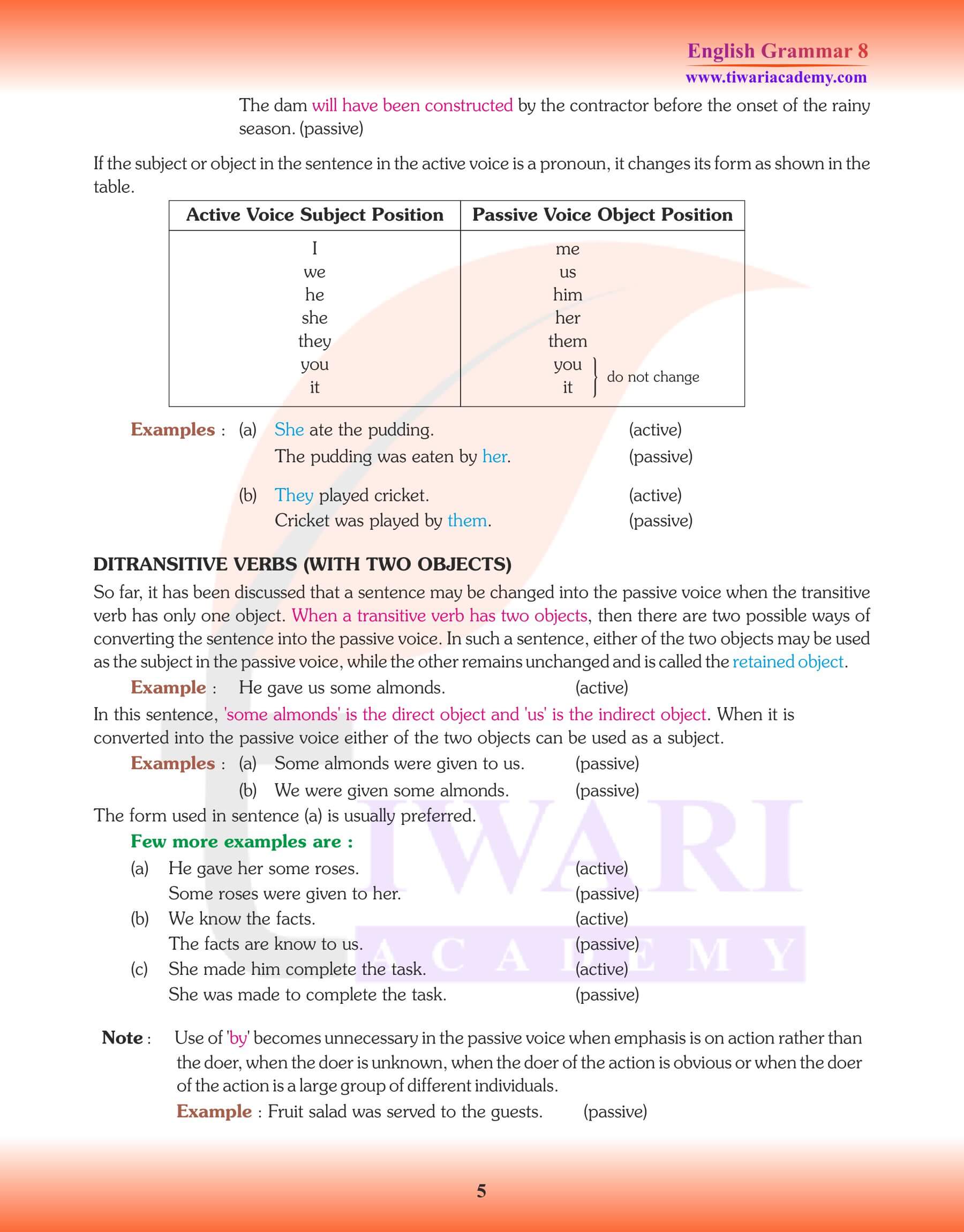
- When a verb is changed from the Active into Passive Voice, the object of the Active Verb becomes the Subject and vice-versa.
- Change the verb into third form and put proper form of the verb “to be” (is, am, are, was, were, be, been, being) before it according to the tense of the main verb in the Passive Voice and the number (Singular/ Plural) of the new Subject.
- “By” is used with the agent of the action (= doer of the action) because it is necessary to complete the sense.
- The tense of the verb does not change.
- Only the transitive verbs can be changed into Passive Voice but not the Intransitive Verbs.
Let’s decode the difference between these two voices:
Active Voice: Here, the emphasis is on the subject, which actively performs the action. The formula to remember is: Subject + Verb + Object. Consider the sentence, ‘Reena writes a letter.’ In this instance, ‘Reena’, the subject, is carrying out the action of writing.
Passive Voice: This voice spotlights the action’s receiver. The formula is: Object + Auxiliary Verb + Past Participle + (by + Subject). Taking the earlier example and converting it, we get, ‘A letter is written by Reena.’ Notice how the focus has shifted from Reena to the letter, even though the core meaning remains unchanged.
| Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|
| She helps me. | I am helped by her. |
| He teaches us. | We are taught by him. |
| She respects us. | We are respected by her. |
| He cut trees. | Trees were cut by him. |
| Someone has stolen my purse. | My purse has been stolen. |
| People always admire the brave. | The brave are always admired. |
However, it’s crucial to realize that these aren’t just arbitrary shifts in sentence structures. Each voice serves a distinct purpose in communication. The active voice often brings clarity and directness to the statement, making it concise. On the other hand, the passive voice can be employed when the action’s doer is unknown, insignificant, or when the emphasis should be on the action itself.
| Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|
| Do I teach you? | Are you taught by me? |
| Does he take tea? | Is tea taken by him? |
| Who tells you that? | By whom are you told that? |
| How do you beat him? | How is he beaten by you? |
| Does she help me? | Am I helped by her? |
By diving deeper into the chapter, students will encounter numerous examples and exercises curated by platforms like Tiwari Academy, guiding them through the nuances of these voices. They’ll learn how to effortlessly switch between active and passive constructs, expanding their repertoire of sentence formation.
Active Passive in Present Continuous Tense
| Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|
| He is flying a kite. | A kite is being flown by him. |
| She is buying apples. | Apples are being bought by her. |
| He is not eating bread. | Bread is not being eaten by him. |
| I am not teaching you. | You are not being taught by me. |
| Is Ram building a house? | Is a house being built by Ram? |
Active Passive in Present Perfect Tense
| Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|
| We have solved the sums. | The sums have been solved by us. |
| We have not bought a car. | A car has not been bought by us. |
| Has she stolen your watch? | Has your watch been stolen by her? |
| I have not written letters. | Letters have not been written by me. |
| Why have you missed the bus? | Why has the bus been missed by you? |
In essence, the mastery over Active and Passive Voices does not just amplify students’ grammatical accuracy but also their versatility in expressing thoughts, making their communication more dynamic and adaptive to diverse contexts.
Active Passive in Past Indefinite Tense
| Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|
| The peon posted the letter. | The letter was posted by the peon. |
| Did the teacher punish the students? | Were the students punished by the teacher? |
| We did not grow rice. | Rice was not grown by us. |
| Did he run a great risk? | Was a great risk run by him? |
| She did not obey her parents. | Her parents were not obeyed by her. |