NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science Civics Chapter 4 Judiciary in Hindi and English Medium updated for new academic session 2024-25. Class 8 Political Science Chapter 4 solutions are modified and revised according to rationalised NCERT Books issued for 2024-25 exams.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science Civics Chapter 4
| Class: 8 | Political Science |
| Subject: | Social Science – Civics |
| Chapter 4: | Judiciary |
| Session: | 2024-25 |
Class 8 Civics Chapter 4 Question Answers
CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science Civics Chapter 4 Judiciary in PDF free download updated form for session 2024-25. Download all contents and solutions for offline use or if you don’t want to download, use online.
Extra Questions on 8th Civics Chapter 4
What is an Independent Judiciary?
It is the independence of the judiciary that allows the courts to play a central role in ensuring that there is no misuse of power by the legislature and the executive. It also plays a crucial role in protecting the Fundamental Rights of citizens because anyone can approach the courts if they believe that their rights have been violated.
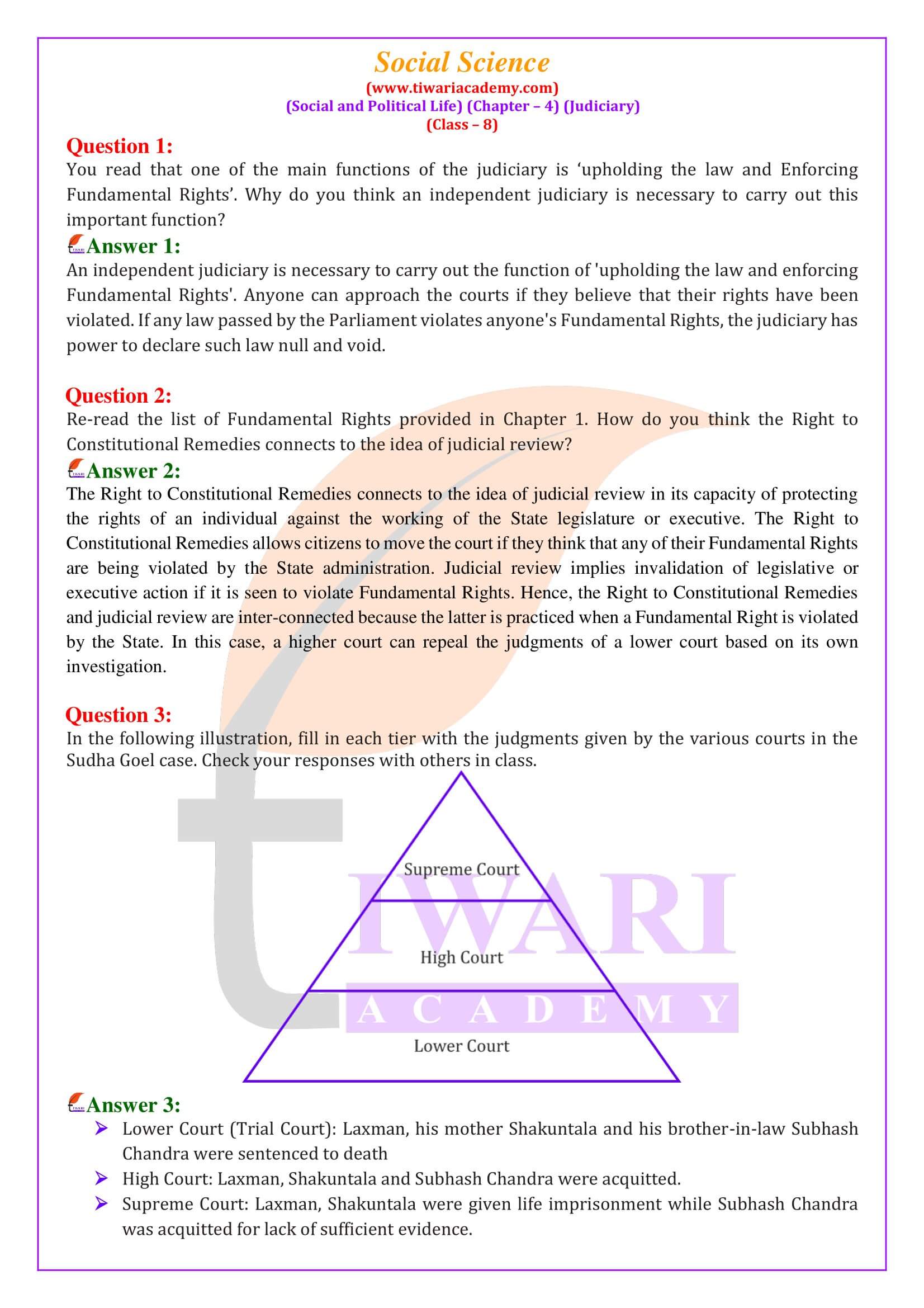
What is the Structure of Courts in India?
There are three different levels of courts in our country. There are several courts at the lower level while there is only one at the apex level.
1. The courts that most people interact with are what are called subordinate or district courts. These are usually at the district or Tehsil level or in towns and they hear many kinds of cases.
2. Each state is divided into districts that are presided over by a District Judge.
3. Each state has a High Court which is the highest court of that state.
4. At the top is the Supreme Court that is located in New Delhi and is presided over by the Chief Justice of India. The decisions made by the Supreme Court are binding on all other courts in India.
Important Notes on 8th Civics Chapter 4
Role of the Judiciary:
Courts take decisions on a very large number of issues. They can decide that no teacher can beat a student or about the sharing of river waters between states or they can punish people for particular crimes.
Broadly speaking, the work that the judiciary does can be divided into the following:
1. Judicial Review: As the final interpreter of the Constitution, the judiciary also has the power to strike down particular laws passed by the Parliament if it believes that these are a violation of the basic structure of the Constitution. This is called judicial review.
2. Dispute Resolution: The judicial system provides a mechanism for resolving disputes between citizens, between citizens and the government, between two state governments and between the centre and state governments.
3. Upholding the Law and Enforcing Fundamental Rights: Every citizen of India can approach the Supreme Court or the High Court if they believe that their Fundamental Rights have been violated.
Important Questions on 8th Civics Chapter 4
You read that one of the main functions of the judiciary is ‘upholding the law and Enforcing Fundamental Rights’. Why do you think an independent judiciary is necessary to carry out this important function?
An independent judiciary is necessary to carry out the function of ‘upholding the law and enforcing Fundamental Rights’. Anyone can approach the courts if they believe that their rights have been violated. If any law passed by the Parliament violates anyone’s Fundamental Rights, the judiciary has power to declare such law null and void.
Re-read the list of Fundamental Rights provided in Chapter 1. How do you think the Right to Constitutional Remedies connects to the idea of judicial review?
The Right to Constitutional Remedies connects to the idea of judicial review in its capacity of protecting the rights of an individual against the working of the State legislature or executive. The Right to Constitutional Remedies allows citizens to move the court if they think that any of their Fundamental Rights are being violated by the State administration. Judicial review implies invalidation of legislative or executive action if it is seen to violate Fundamental Rights. Hence, the Right to Constitutional Remedies and judicial review are inter-connected because the latter is practiced when a Fundamental Right is violated by the State. In this case, a higher court can repeal the judgments of a lower court based on its own investigation.
Why do you think the introduction of Public Interest Litigation (PIL) in the 1980s is a significant step in ensuring access to justice for all?
The Supreme Court in the early 1980s devised a mechanism of Public Interest Litigation or PIL to increase access to justice. It allowed any individual or organisation to file a PIL in the High Court or the Supreme Court on behalf of those whose rights were being violated. The legal process was greatly simplified and even a letter or telegram addressed to the Supreme Court or the High Court could be treated as a PIL. In the early years, PIL was used to secure justice on a large number of issues such as rescuing bonded labourers from inhuman work conditions; and securing the release of-prisoners in Bihar who had been kept in jail even after their punishment terms was complete. Thus, the introduction of PIL is really a significant step in ensuring access to justice for all.
Re-read excerpts from the judgment on the Olga Tellis vs Bombay Municipal Corporation case. Now write in your own words what the judges meant when they said that the Right to Livelihood was part of the Right to Life.
In Olga Tellis vs. Bombay Municipal Corporation case, the judges said that the Right to Livelihood was part of the Right to Life. They stated that life does not merely imply an animal existence; it cannot be lived without a means of living, that is, “the means of livelihood”. In the case of Olga Tellis vs Bombay Municipal Corporation, the people live in slum. They have small jobs in the city and for them there is nowhere else to live. The eviction of their slum will lead to deprivation of their livelihood and consequently to the deprivation of life. Thus, it can be said that Right to Life means the need of basic requirements of livelihood i.e., food, shelter and cloth.
Write a story around the theme, ‘Justice delayed is justice denied’.
Nitin Narang was a bank officer. After retirement he came back to his forefather’s house. He requested the tenant to vacate the house. But the tenant did not vacate the house. Tenant challenged that if Nitin Narang wanted to have his house vacated, he should move to court for justice. He was compelled to live in a rented house. The owner lodged litigation against the tenant. After fighting the case for five years, the owner won the case. The decision was made in his favour by the Trial Court. But the tenant appealed in the High Court against the lower court decision. It again took five years for justice. In the meantime Nitin Narang kept on living in the rented house because unless there was judgement, he had no other option. In such a situation we can definitely say, ‘Justice delayed is justice denied’.