NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control and Coordination in Hindi and English Medium to Study online or download in PDF file format free updated for academic session 2025-26. Download NCERT Solutions for boards like UP, MP, CBSE, etc. who are following NCERT Books as course books. Visit to Discussion Forum and enjoy the world of knowledge.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 18
Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control and Coordination Solutions
| Class: 11 | Biology |
| Chapter 18: | Neural Control and Coordination |
| Content: | Exercises Question Answers |
| Mode of content: | Videos, PDF and Images |
| Academic Year: | Session 2025-26 |
| Medium Applied: | Hindi, English |
Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Solutions in English
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 in PDF to free download. If you have any doubt regarding to NIOS Board, please visit to Discussion Forum and ask your query to get proper guidance. Download NCERT Books 2025-26 and Offline Apps based on latest CBSE Syllabus.
Important Notes on Neural Control & Coordination
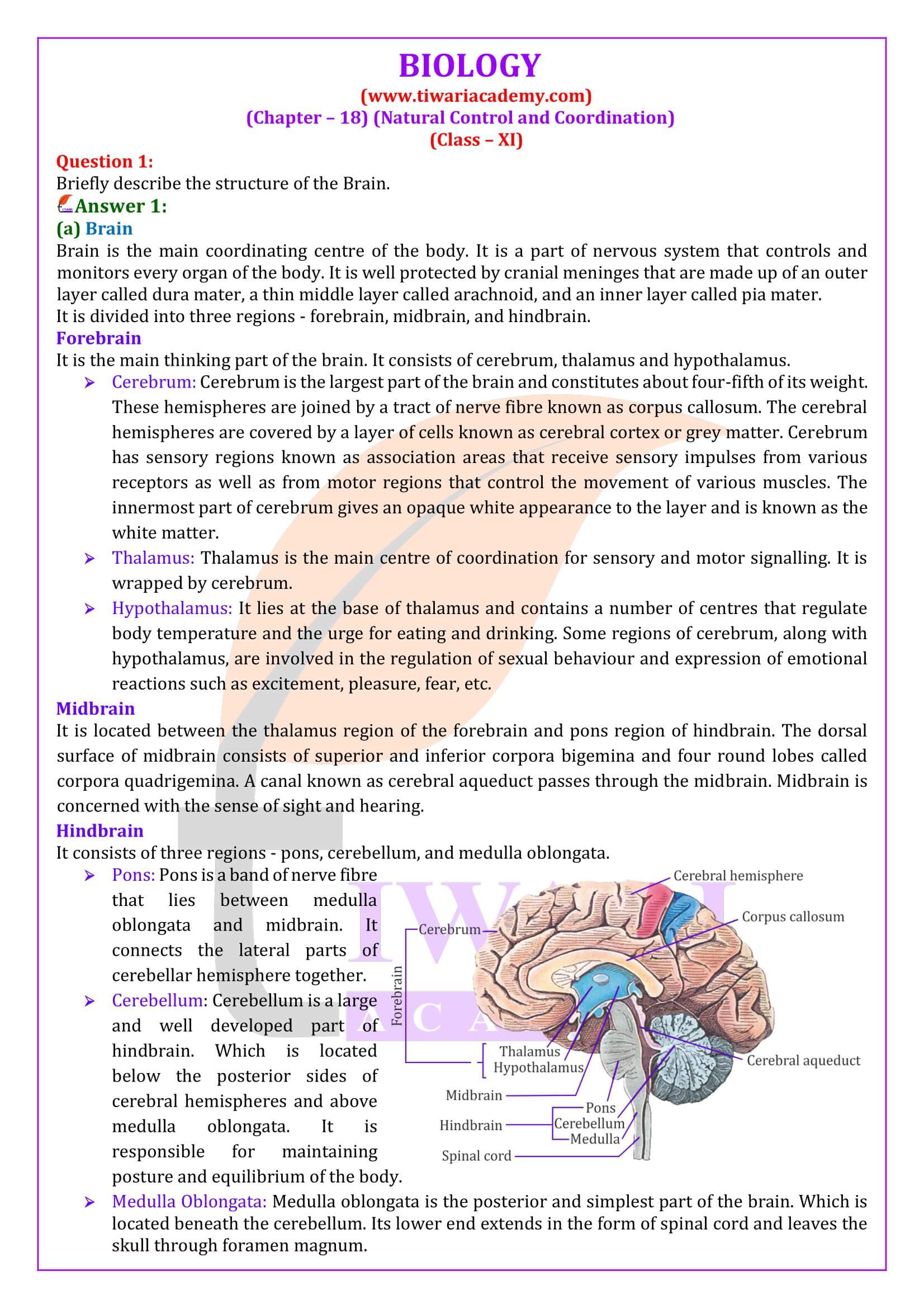
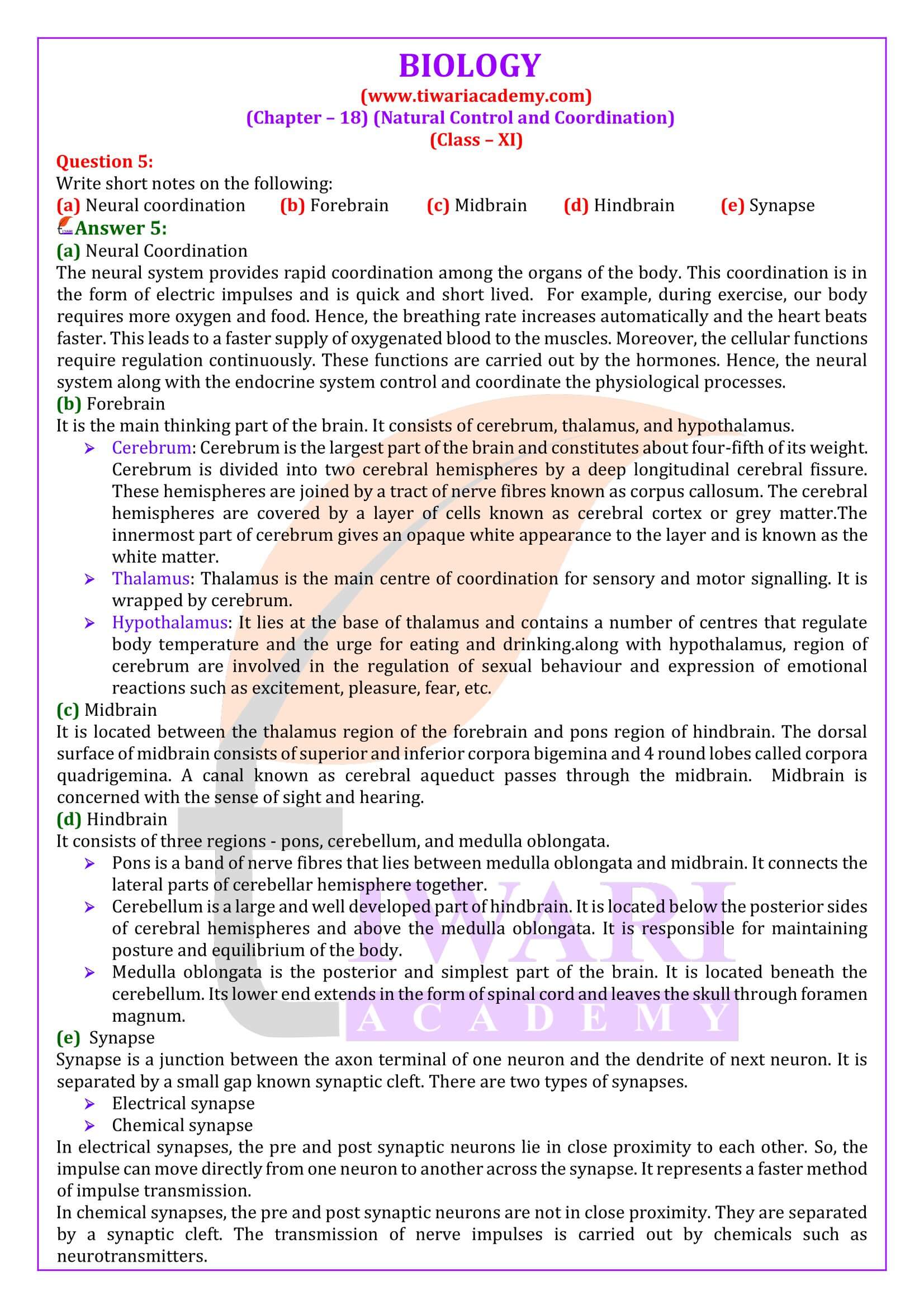
HUMAN BRAIN
1. Human brain is the major portion of central neural system. Which is well protected by the skull.
2. The brain is surrounded by three cranial meninges
i). Duramater – outer layer
ii). Arachnoid – middle layer
iii). Piamter – Inner layer-remain in contact with brain
FUNCTIONS OF PARTS OF BRAIN
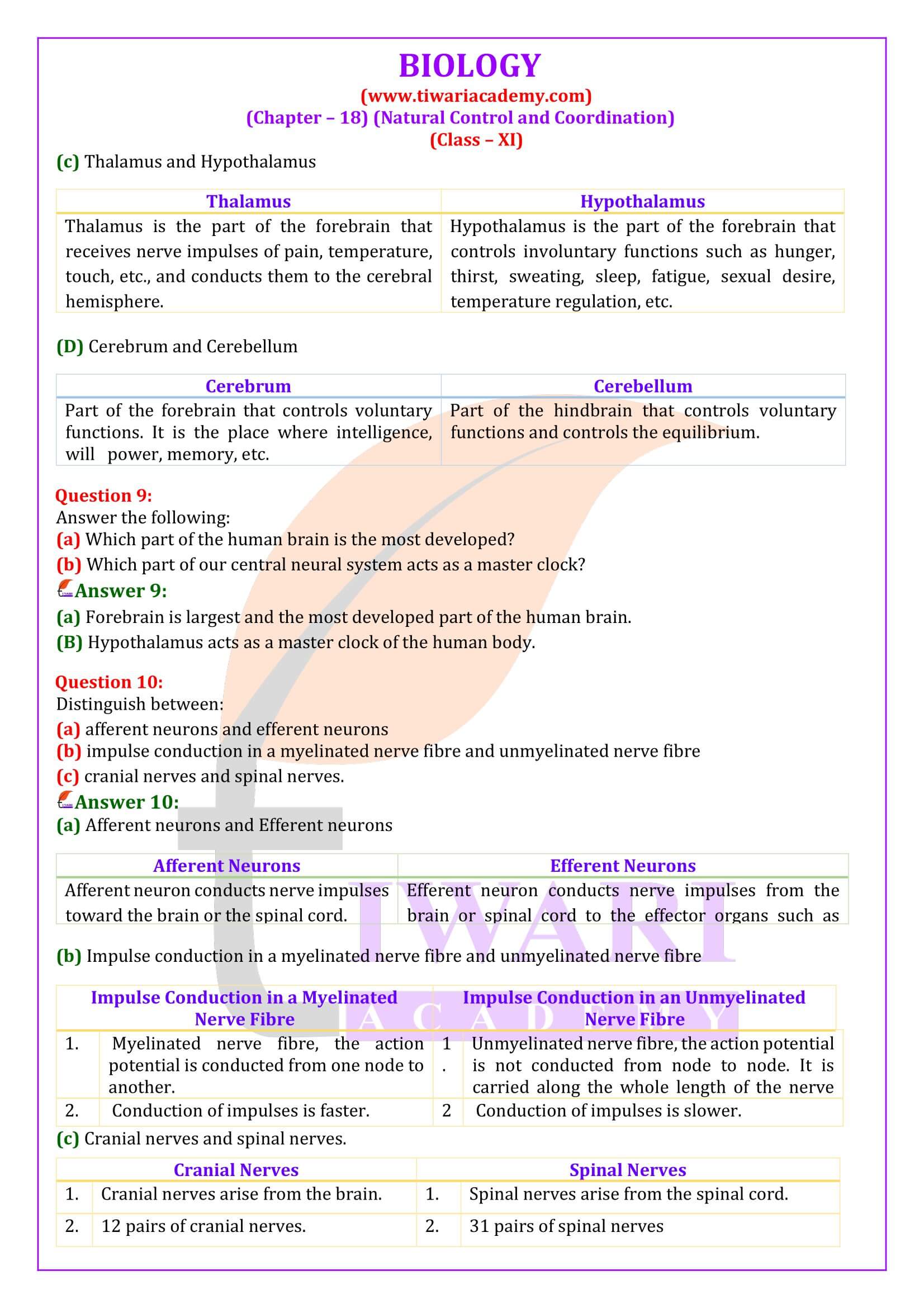
1. Cerebrum: Centre of intelligence, memory and imagination, reasoning, judgement, expression of will power.
2. Thalamus: Acts as relay centre to receive and transmit general sensation of pain, touch and temperature.
3. Hypothalamus: Centre for regulation of body temperature, urge for eating and drinking.
4. Mid-brain: Responsible to coordinate visual reflexes and auditory reflexes.
5. Cerebellum: Maintains posture and equilibrium of the body as well as coordinates and regulates voluntary movement.
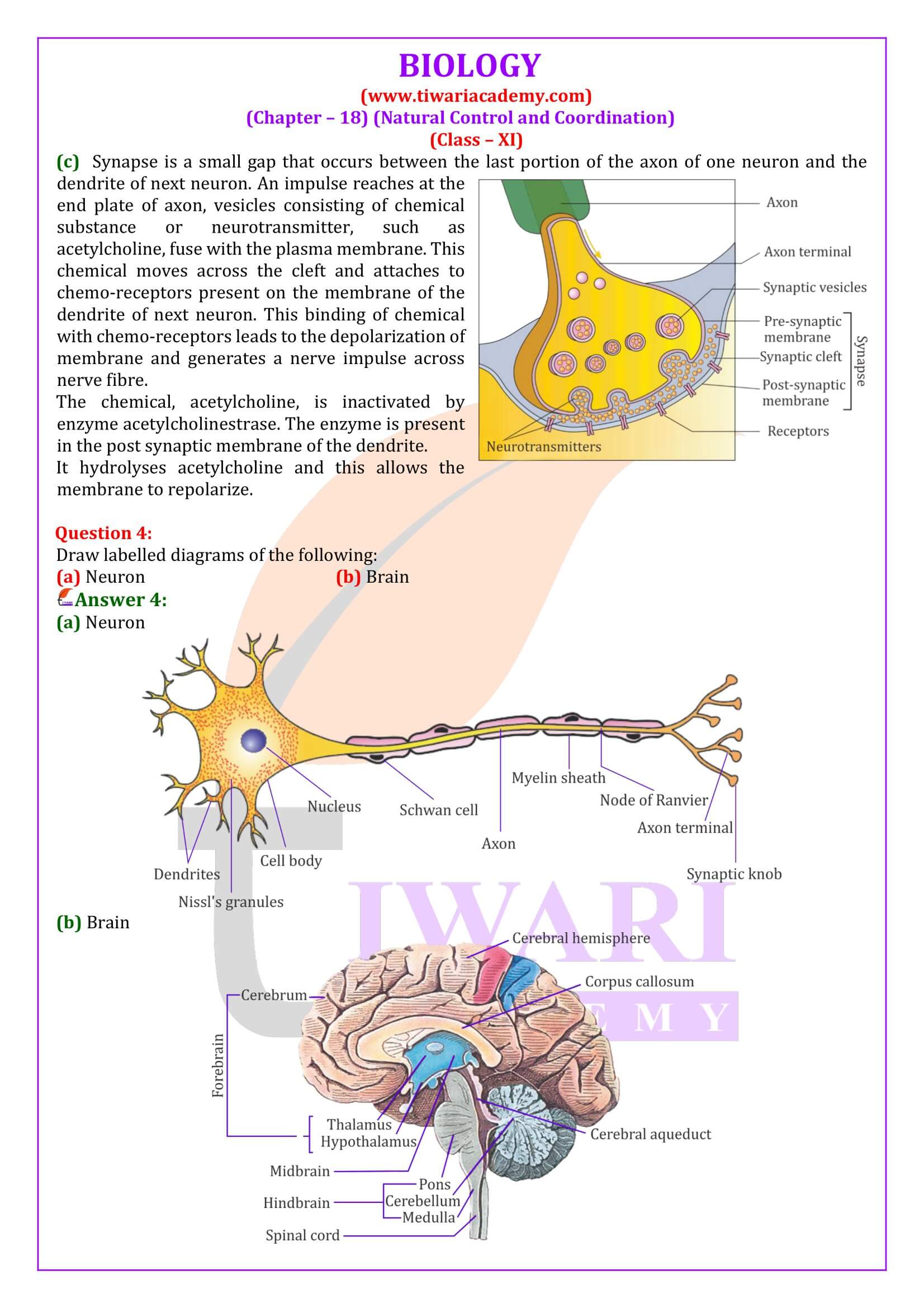
Transmission of Impulses at Synapse
1. At electrical synapses: Here the membrane of pre and post-syneptic neuron are in very close proximity. Electric current can ¯ow directly from one neuron into other across these synapses, like impulse conduction along a single axon.
2. At chemical synapses: Here the membrane of pre and post-syneptic neuron are separated by fluid filled space called synaptic cleft. Neurotransmitter are involved here.
Important Questions on 11th Biology Chapter 18
How do you perceive the colour of an object?
Photoreceptors are cells that are sensitive to light. They are of two types – rods and cones. These are present in the retina. Cones help in distinguishing colours. There are three types of cone cells – those responding to green light, those responding to blue light, and those responding to red light.
Which part of our body helps us in maintaining the body balance?
Vestibular apparatus is located in the internal ear, above the cochlea and helps in maintaining body balance. Crista and macula are the sensory spots of the vestibular apparatus controlling dynamic equilibrium.
How does the eye regulate the amount of light that falls on the retina.
Pupil is the small aperture in the iris that regulates the amount of light entering the eye. Cornea, aqueous humour, lens, and vitreous humour act together and refract light rays, focussing them onto the photoreceptor cells of the retina.
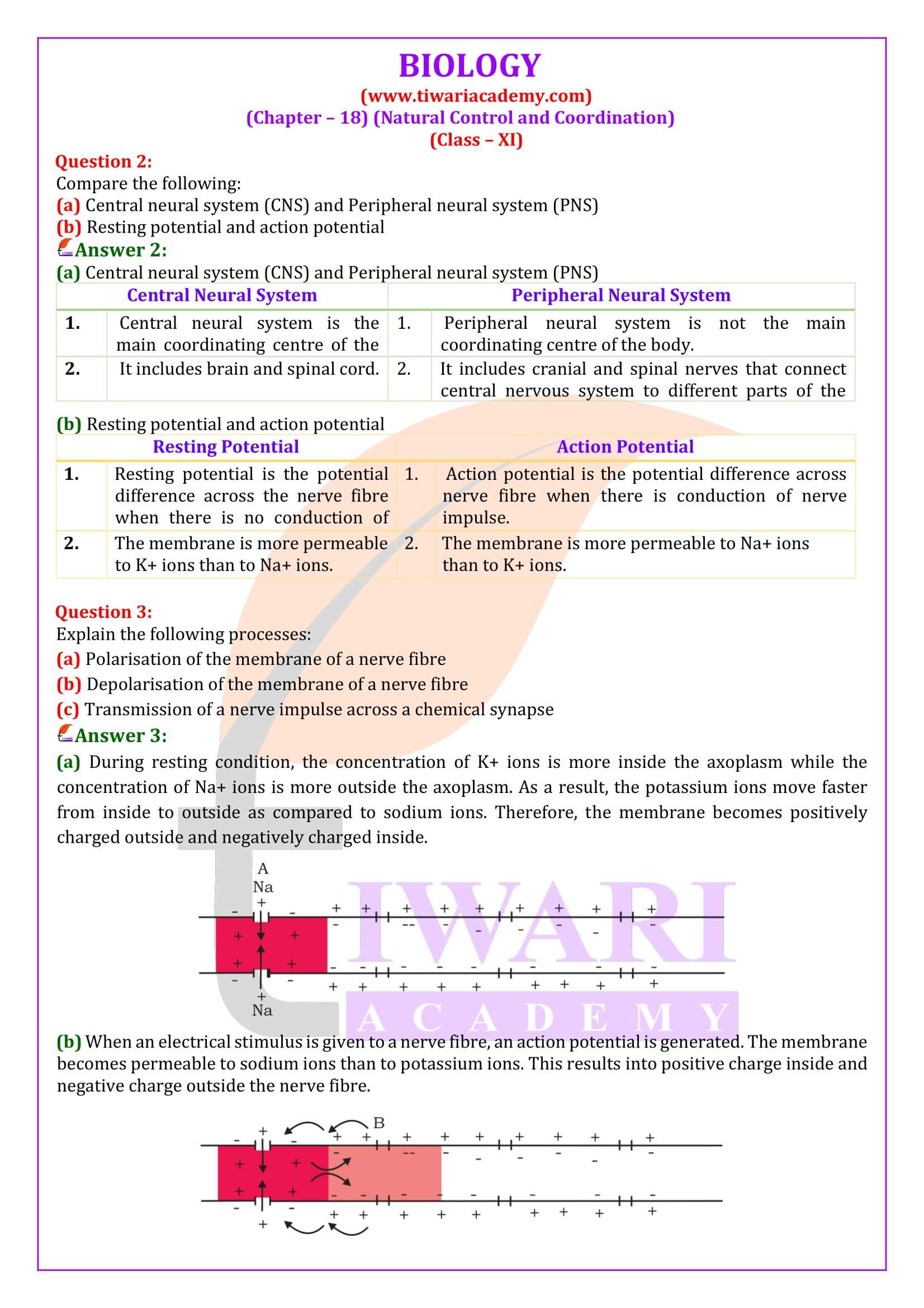
Explain the role of Na+ in the generation of action potential.
Sodium ions play an important role in the generation of action potential. When a nerve fibre is stimulated, the membrane potential decreases. The membrane becomes more permeable to Na+ ions than to K+ ions. As a result, Na+ diffuses from the outside to the inside of the membrane. This causes the inside of the membrane to become positively-charged, while the outer membrane gains a negatively charge. This reversal of polarity across the membrane is known as depolarisation. The rapid inflow of Na+ ions causes the membrane potential to increase, thereby generating an action potential.
Explain the mechanism of generation of light-induced impulse in the retina.
Retina is the innermost layer of the eye. It contains three layers of cells – inner ganglion cells, middle bipolar cells, and outermost photoreceptor cells. Photoreceptor cells are composed of a protein called opsin and an aldehyde of vitamin A called retinal. When light rays are focused on the retina through the cornea, retinal gets dissociated from opsin. As a result, the structure of opsin gets changed. This in turn causes the permeability of the membrane to change, thereby generating a potential difference in the cells. Consequently, an action potential is generated in the ganglion cells and is transmitted to the visual cortex of the brain via the optic nerves. In the cortex region of the brain, the impulses are analysed and the image is formed on the retina.
Mechanism through which a sound produces a nerve impulse in the inner ear.
The pinna of the external ear collects the sound waves and directs them to the tympanic membrane (ear drum) via the external auditory canal. The ear drum then vibrates the sound waves and conducts them to the internal ear through the ear ossicles. The ear ossicles increase the intensity of the sound waves. These vibrating sound waves are conducted through the oval window to the fluid in the cochlea. Consequently, a movement is created in the lymph. This movement produces vibrations in the basilar membrane, which in turn stimulate the auditory hair cells. These cells generate a nerve impulse, conducting it to the auditory cortex of the brain via afferent fibres. The auditory cortex region interprets the nerve impulse and sound is recognised.
Which part of the ear determines the pitch of a sound?
Cochlea determines the pitch of a sound.
Which part of the human brain is the most developed?
Forebrain is largest and the most developed part of the human brain.
Which part of our central neural system acts as a master clock?
Hypothalamus acts as a master clock of the human body.
Important Terms related to Chapter 18
1. Blind spot: A spot on retina which is free from rods and cones and lack the ability for vision.
2. Cerebrospinal fluid: An alkaline fluid present in between inner two layer of meninges, surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
3. Cerebellum: A part of hind brain that controls the balance and posture of the body.
4. Cochlea: A spirally coiled part of internal ear which is responsible for hearing.
5. Corpus callosum: A curved thick bundle of nerve fibres that joins two cerebral hemisphere.
6. Pons: Thick bundles of fibres on the ventral side of brain below cerebellum.
7. Foramen magnum: A big aperture in the skull posteriorly through which spinal cord emerges out.
8. Spinal cord: A tubular structure connected with medulla oblongata of brain and situated in the neural canal of the vertebral column, covered by meninges.
9. Synaptic cleft: A narrow fluid filled space which separates two membranes of the two neurons at the synapse.