NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Organisms and Populations in Hindi and English to Study Online updated for new academic session 2025-26 based on latest NCERT Books 2025-26. NCERT Solutions based on latest NCERT Books are also given to download in PDF format. Explore Your Knowledge with the others via Discussion Forum.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 11
Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Organisms and Populations Solutions
| Class: 12 | Science |
| Subject: | Biology |
| Chapter 11: | Organisms and Populations |
| Mode of Solutions: | Images and Videos |
| Session: | Academic Year 2025-26 |
| Medium: | Hindi and English Medium |
Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Solutions in English
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 is given below to download in PDF format free updated for new academic session 2025-26 based on latest NCERT Books. Download Offline Apps based on new NCERT Solutions following the latest CBSE Syllabus. Join the Discussion Forum to ask your doubts and discuss the questions asked by the other users.
Important Terms related to Chapter 11
1. Organisms: Organisms form the basic unit of study in ecology.
2. Species: Organisms with similar features and the potential to interbreed among themselves and produce fertile offspring, constitute a species.
3. Populations: Population is a group of individuals of the same species, inhabiting in a given area. Interspecific competition for basic needs operate among the individuals of population.
4. Biological Community: Biological community is constituted by an assemblage of the populations of all different species that live in an area and interact with each other. A biotic community has a distinct species composition and structure.
Ecology
A branch of science that studies interactions among organisms and their physical environment. Ecology is basically concerned with four levels of biological organisation – Organisms, population, communities and biomes. Ramdeo Mishra is called as the Father of Ecology in India.
1. Ecosystem: Is a biological system in nature and composed of a biotic community integrated with its physical (abiotic) environment through the exchange of energy and recycling of the nutrients.
2. Biomes: Biomes is a very large unit, constituting of a major vegetation type and associate fauna found is a specified zone. Annual Variations is the intensity, duration of temperature and precipitation account for the formation of major biomes like desert, rain, forest and Tundra.
3. Habitat: Habitat is the place where an organism lives.
Major Biomes of India: Tropical rain forest, deciduous forest, desert, sea coast. Regional and local variations within each biome lead to formation of a wide variety of habitats.
Niche
1. The ecological niche of an organism represents the range of conditions that it can tolerate the resources it utilises and its functional role in the ecological system. Each species occupies a distinct niche and no two species occupy the same niche.
2. Biosphere: It is the sum total of all the biomes on the earth.
3. Environment: Environment is a sum total of all biotic and abiotic factors that surround and potentially influence an organism. Temperature, water, light and soil are the major abiotic factors.
Most living organisms cannot survive at temperature above 45°C°. How are some microbes able to live in habitats with temperatures exceeding 100°C?
Archaebacteria (Thermophiles) are ancient forms of bacteria found in hot water springs and deep sea hydrothermal vents. They are able to survive in high temperatures (which far exceed 100°C) because their bodies have adapted to such environmental conditions. These organisms contain specialized thermo-resistant enzymes, which carry out metabolic functions that do not get destroyed at such high temperatures.
Important Questions on 12th Biology Chapter 11
How is diapause different from hibernation?
Diapause is a stage of suspended development to cope with unfavourable conditions. Many species of Zooplankton and insects exhibit diapause to tide over adverse climatic conditions during their development. Hibernation or winter sleep is a resting stage where in animals escape winters (cold) by hiding themselves in their shelters. They escape the winter season by entering a state of inactivity by slowing their metabolism. The phenomenon of hibernation is exhibited by bats, squirrels, and other rodents.
Define phenotypic adaptation. Give one example.
Phenotypic adaptation involves changes in the body of an organism in response to genetic mutation or certain environmental changes. These responsive adjustments occur in an organism in order to cope with environmental conditions present in their natural habitats. For example, desert plants have thick cuticles and sunken stomata on the surface of their leaves to prevent transpiration. Similarly, elephants have long ears that act as thermoregulators.
If a marine fish is placed in a fresh water aquarium, will the fish be able to survive? Why or why not?
If a marine fish is placed in a fresh water aquarium, then its chances of survival will diminish. This is because their bodies are adapted to high salt concentrations of the marine environment. In fresh water conditions, they are unable to regulate the water entering their body (through osmosis). Water enters their body due to the hypotonic environment outside. This results in the swelling up of the body, eventually leading to the death of the marine fish.
Name important defence mechanisms in plants against herbivory.
Several plants have evolved various mechanisms both morphological and chemical to protect themselves against herbivory. Morphological defence mechanisms: Cactus leaves (Opuntia) are modified into sharp spines (thorns) to deter herbivores from feeding on them. Sharp thorns along with leaves are present in Acacia to deter herbivores. In some plants, the margins of their leaves are spiny or have sharp edges that prevent herbivores from feeding on them. Chemical defence mechanisms: All parts of Calotropis weeds contain toxic cardiac glycosides, which can prove to be fatal if ingested by herbivores. Chemical substances such as nicotine, caffeine, quinine, and opium are produced in plants as a part of self-defence.
What is the ecological principle behind the biological control method of managing with pest insects?
The basis of various biological control methods is on the concept of predation. Predation is a biological interaction between the predator and the prey, whereby the predator feeds on the prey. Hence, the predators regulate the population of preys in a habitat, thereby helping in the management of pest insects.
An orchid plant is growing on the branch of mango tree. How do you describe this interaction between the orchid and the mango tree?
An orchid growing on the branch of a mango tree is an epiphyte. Epiphytes are plants growing on other plants which however, do not derive nutrition from them. Therefore, the relationship between a mango tree and an orchid is an example of commensalisms, where one species gets benefited while the other remains unaffected. In the above interaction, the orchid is benefited as it gets support while the mango tree remains unaffected.
Give an example for an endothermic animal.
Endothermic animal: Birds such as crows, sparrows, pigeons, cranes, etc. and mammals such as bears, cows, rats, rabbits, etc. are endothermic animals.
Define population and community.
Population: A population can be defined as a group of individuals of the same species residing in a particular geographical area at a particular time and functioning as a unit. For example, all human beings living at a particular place at a particular time constitute the population of humans. Community: A community is defined as a group of individuals of different species, living within a certain geographical area. Such individuals can be similar or dissimilar, but cannot reproduce with the members of other species.
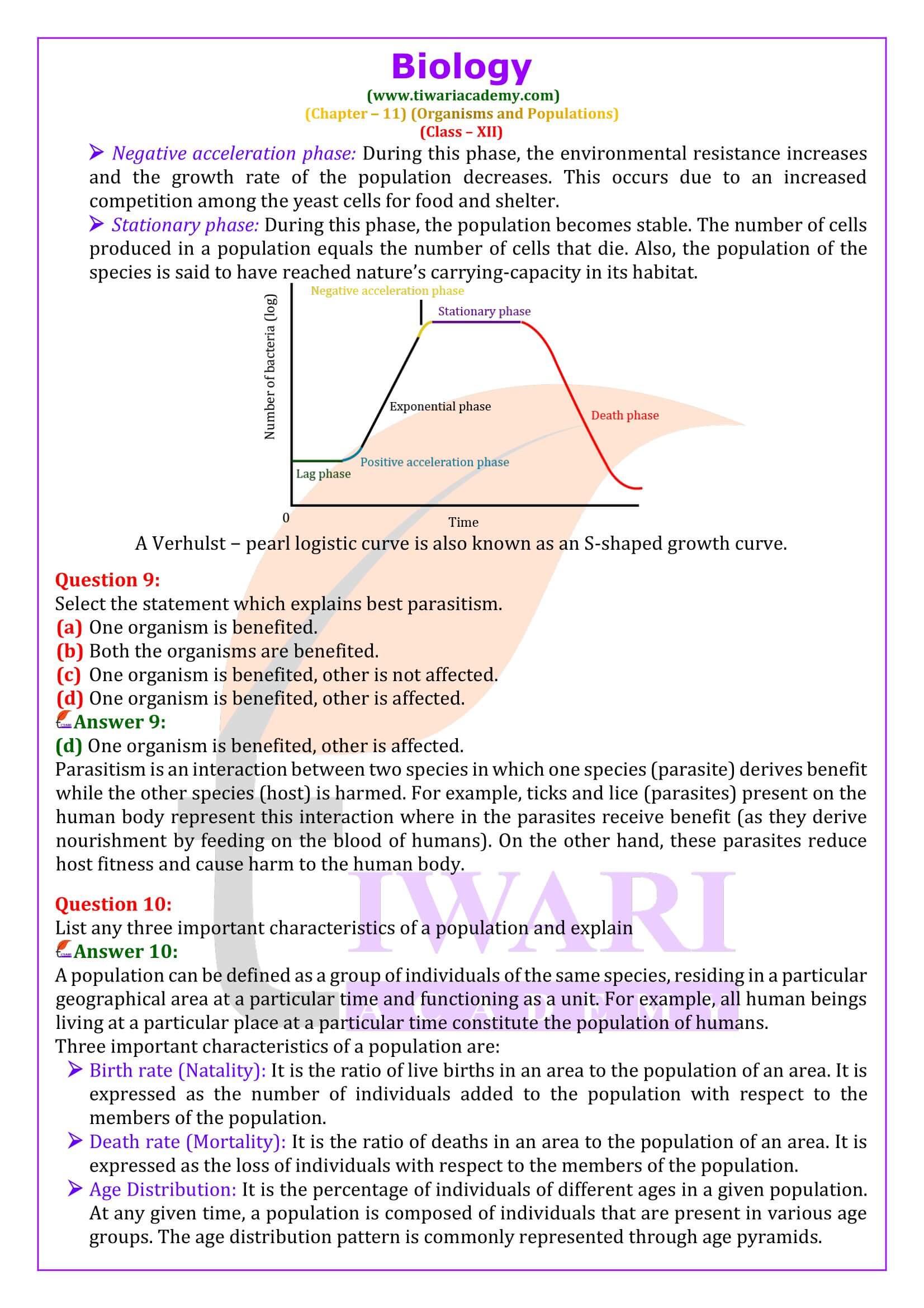
List any three important characteristics of a population and explain
A population can be defined as a group of individuals of the same species, residing in a particular geographical area at a particular time and functioning as a unit. For example, all human beings living at a particular place at a particular time constitute the population of humans. Three important characteristics of a population are: Birth rate (Natality): It is the ratio of live births in an area to the population of an area. It is expressed as the number of individuals added to the population with respect to the members of the population. Death rate (Mortality): It is the ratio of deaths in an area to the population of an area. It is expressed as the loss of individuals with respect to the members of the population. Age Distribution: It is the percentage of individuals of different ages in a given population. At any given time, a population is composed of individuals that are present in various age groups. The age distribution pattern is commonly represented through age pyramids.