NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 16 Excretory Products and Their Elimination in Hindi and English Medium to Study online as well as download in PDF format free updated for new academic session 2024-25. Download latest and updated NCERT Books for new academic session 2024-25. Visit to Discussion Forum and join the world of knowledge.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 16
Class 11 Biology Chapter 16 Excretory Products and Their Elimination Solutions
| Class: 11 | Biology |
| Chapter 16: | Excretory Products and their Elimination |
| Content: | Exercises Solutions and Study Material |
| Mode of Content: | Images, PDF and Video format |
| Academic Session: | Year 2024-25 |
| Medium: | Hindi and English |
Class 11 Biology Chapter 16 Solutions in English
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 16 in PDF to free download for session 2024-25. Download latest NCERT Books based on the current CBSE Syllabus. Offline Apps and NCERT Solutions 2024-25 are updated for new session for all boards using NCERT Books. Ask your questions in FAQ section of Discussion Forum and get the proper response. If you have any doubt regarding to NIOS visit to discussion forum and clear your confusion.
Important Notes on Excretory Products & Elimination
TYPES OF NEPHRONS
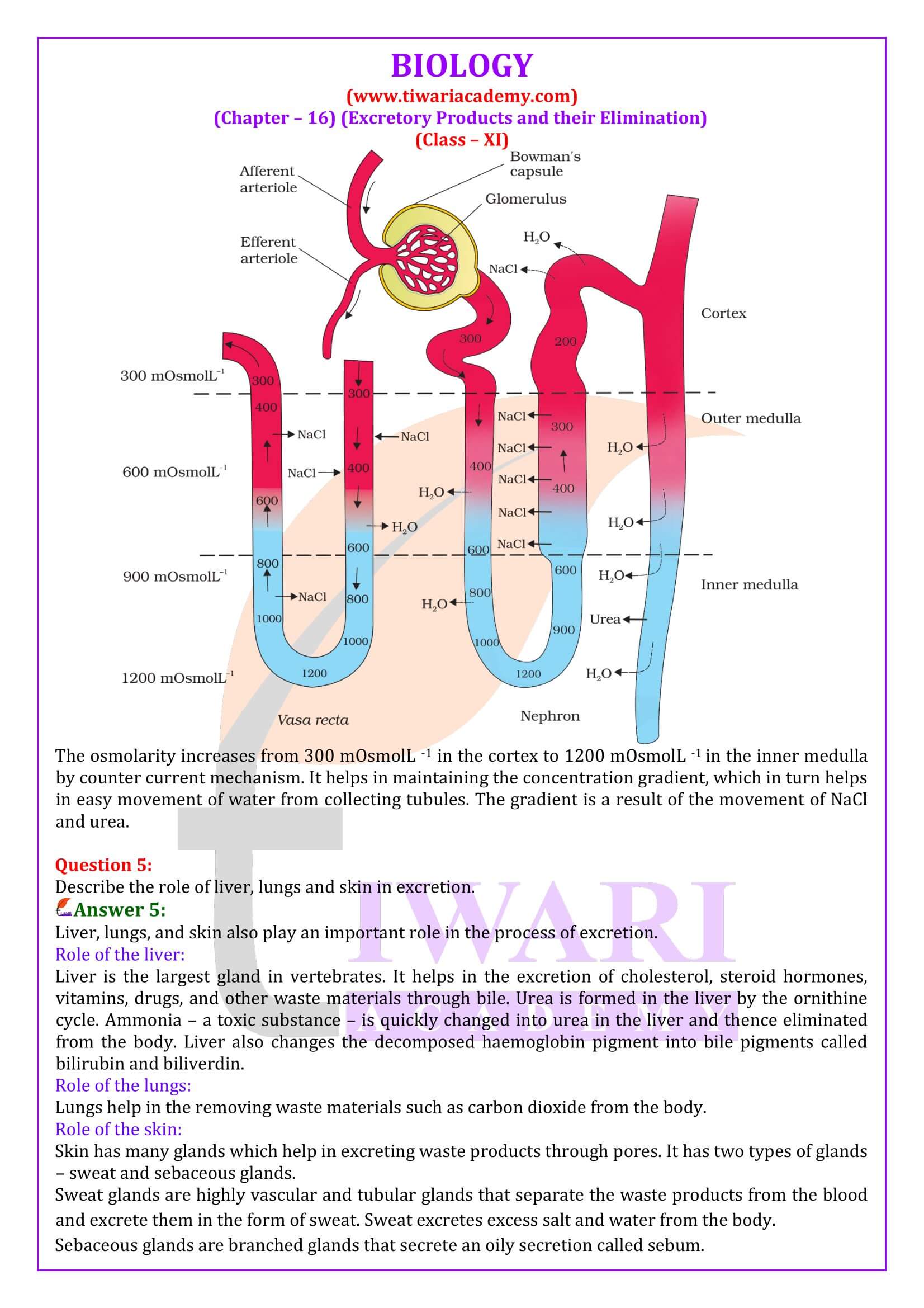
1. Juxtamedullary Nephron – About 15% of total nephrons, Glomeruli are found in inner region of cortex, large in size, long loop of Henle and found deep in medulla, associated with vasa recta control plasma volume when water supply is short.
2. Cortical Nephron – About 85% of total nephron mainly lie in renal cortex, glomeruli found in outer cortex, short loop of Henle, extends very little in medulla. They do not have vasa recta.
AMMONOTELISM
1. The animals which excrete ammonia are called ammonotelic and excretion of ammonia is known as ammonotelism e.g. Amoeba, sycon, hydra, liver fluke, tapeworm, Leech, Prawn, bony fishes etc.
2. Ureotelism: Excretion of urea is known as ureotelism and the animals which excrete urea are ureotelic animals for example Mammals, many terrestrial amphibians and marine fishes and sting rays etc.
3. Uricotelism: Excretion of uric-acid is known as uricotelism and the animals are called uricotelic for example most insects, land snails, lizards, snakes and birds.
4. Nephrons: The structural and functional unit of kidneys. Each kidney contains about one million of nephrons.
5. Structure of Nephron: A nephron consists of Glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule, PCT (Proximal convoluted tubule). JG A (Juxaglomerular Apparatus) and the collecting duct.
6. Glomerular Filtration: The filtration of blood in glomerulus, about 1100-1200 ml of blood is filtered by the kidney per minute.
7. Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR): The amount of filtrate formed by the kidney per minute is called GFR. In a healthy individual it is about, 125 ml/minute, i.e. 180 litres per day.
Important Questions on 11th Biology Chapter 16
Define Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR).
Glomerular filtration rate is the amount of glomerular filtrate formed in all the nephrons of both the kidneys per minute. In a healthy individual, it is about 125 mL/minute. Glomerular filtrate contains glucose, amino acids, sodium, potassium, urea, uric acid, ketone bodies, and large amounts of water.
Explain the autoregulatory mechanism of GFR.
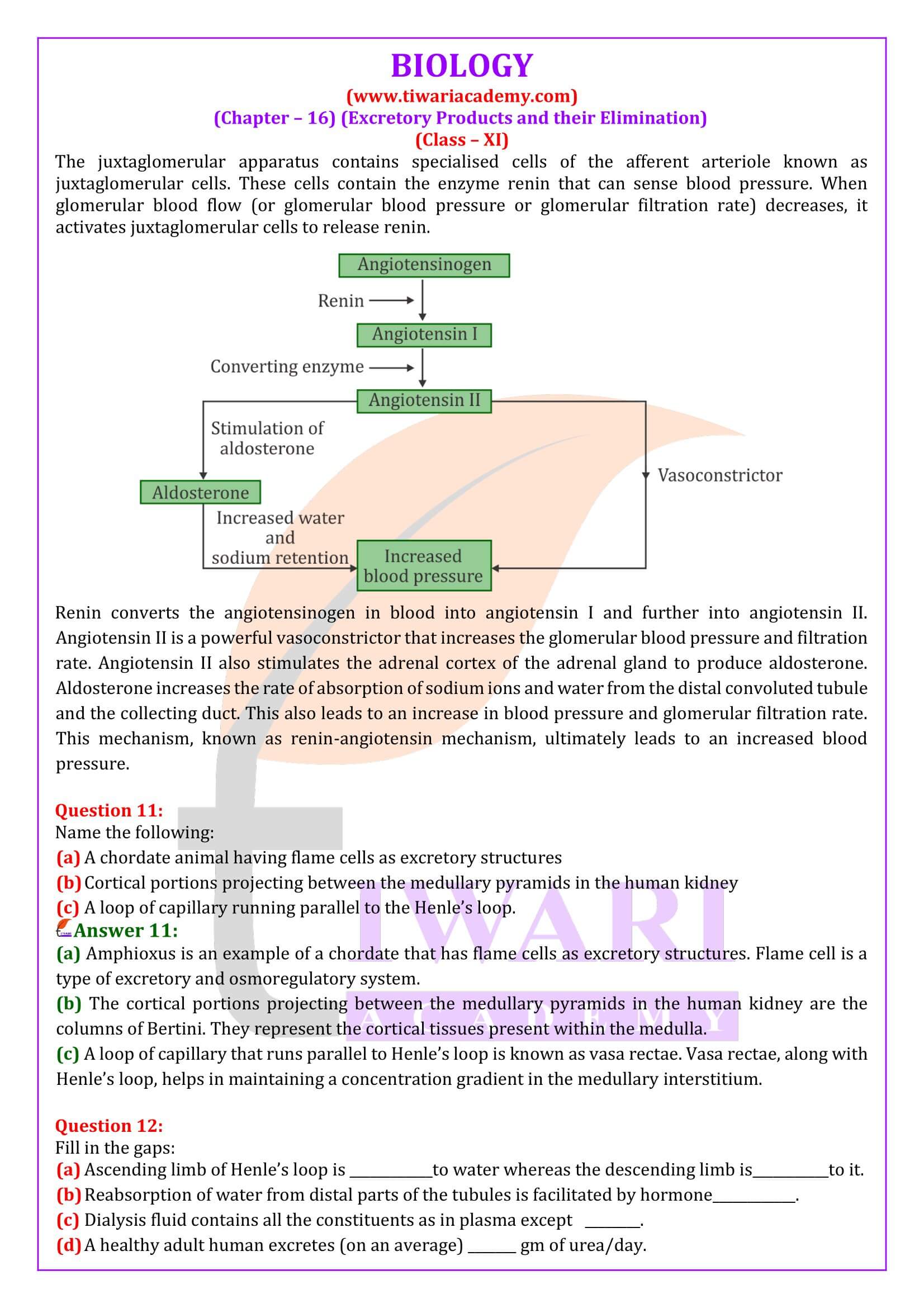
Answer 2: The mechanism by which the kidney regulates the glomerular filtration rate is autoregulative. It is carried out by the juxtaglomerular apparatus. Juxtaglomerular apparatus is a microscopic structure located between the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle and the returning distal convoluted tubule of the same nephron. It plays a role in regulating the renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate. When there is a fall in the glomerular filtration rate, it activates the juxtaglomerular cells to release renin. This stimulates the glomerular blood flow, thereby bringing the GFR back to normal. Renin brings the GFR back to normal by the activation of the reninangiotensin mechanism.
Describe the role of liver, lungs and skin in excretion.
Liver, lungs, and skin also play an important role in the process of excretion. Role of the liver: Liver is the largest gland in vertebrates. It helps in the excretion of cholesterol, steroid hormones, vitamins, drugs, and other waste materials through bile. Urea is formed in the liver by the ornithine cycle. Ammonia – a toxic substance – is quickly changed into urea in the liver and thence eliminated from the body. Liver also changes the decomposed haemoglobin pigment into bile pigments called bilirubin and biliverdin. Role of the lungs: Lungs help in the removing waste materials such as carbon dioxide from the body. Role of the skin: Skin has many glands which help in excreting waste products through pores. It has two types of glands – sweat and sebaceous glands. Sweat glands are highly vascular and tubular glands that separate the waste products from the blood and excrete them in the form of sweat. Sweat excretes excess salt and water from the body. Sebaceous glands are branched glands that secrete an oily secretion called sebum.
Explain micturition.
Micturition is the process by which the urine from the urinary bladder is excreted. As the urine accumulates, the muscular walls of the bladder expand. The walls stimulate the sensory nerves in the bladder, setting up a reflex action. This reflex stimulates the urge to pass out urine. To discharge urine, the urethral sphincter relaxes and the smooth muscles of the bladder contract. This forces the urine out from the bladder. An adult human excretes about 1 – 1.5 litres of urine per day.
What is meant by the term osmoregulation?
Osmoregulation is a homeostatic mechanism that regulates the optimum temperature of water and salts in the tissues and body fluids. It maintains the internal environment of the body by water and ionic concentration.
Terrestrial animals are generally either ureotelic or uricotelic, not ammonotelic, why?
Terrestrial animals are either ureotelic or uricotelic, and not ammonotelic. This is because of the following two main reasons: Ammonia is highly toxic in nature. Therefore, it needs to be converted into a less toxic form such as urea or uric acid. Terrestrial animals need to conserve water. Since ammonia is soluble in water, it cannot be eliminated continuously. Hence, it is converted into urea or uric acid. These forms are less toxic and also insoluble in water. This helps terrestrial animals conserve water.
What is the significance of juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) in kidney function?
Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) is a complex structure made up of a few cells of glomerulus, distal tubule, and afferent and efferent arterioles. It is located in a specialised region of a nephron, wherein the afferent arteriole and the distal convoluted tubule (DLT) come in direct contact with each other. The juxtaglomerular apparatus contains specialised cells of the afferent arteriole known as juxtaglomerular cells. These cells contain the enzyme renin that can sense blood pressure. When glomerular blood flow (or glomerular blood pressure or glomerular filtration rate) decreases, it activates juxtaglomerular cells to release renin. Renin converts the angiotensinogen in blood into angiotensin I and further into angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is a powerful vasoconstrictor that increases the glomerular blood pressure and filtration rate. Angiotensin II also stimulates the adrenal cortex of the adrenal gland to produce aldosterone. Aldosterone increases the rate of absorption of sodium ions and water from the distal convoluted tubule and the collecting duct. This also leads to an increase in blood pressure and glomerular filtration rate. This mechanism, known as renin-angiotensin mechanism, ultimately leads to an increased blood pressure.
Steps of Urine Formation
1. Glomerular Filtration – Blood is filtered by glomerulus through three membranes i.e., endothelium of blood vessel, filtration slits of Bowman’s capsule and basement membrane between these two layers. This filtration is called ultrafiltration as all constituents of plasma comes into filtrate except proteins.
2. Reabsorption – 90% of filtrate is reabsorbed by the renal tubules by active or passive mechanism. It is evident by the fact that out of 180L of filtrate formed per day only 1.5 L of urine released.
3. Secretion – Tubular cells secrete H+, K+, ammonia into the urine. It maintains acid-base balance of body fluids.