NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry in Hindi and English Medium exercises, MCQ and intext questions updated and modified for new academic session 2024-25. All the questions are as per new edition NCERT textbook published for 2024-25 exams.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 NCERT Book
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 Hindi Medium
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 Revision Book
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 Study Material 1
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 Study Material 2
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 Study Material 3
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 Assignment 1
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 Assignment 2
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 Assignment 3
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 Assignment 4
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 Assignment 5
- Class 11 Chemistry NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 all Subjects NCERT Solutions
Basic Concepts of Chemistry
Chemistry is the branch of science that deals with the properties, composition, and structure of elements and compounds, how they can change, and the energy that is released or absorbed when they change.
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 MCQ
Under the same conditions, nitrogen and oxygen are taken in the same mass. the ratio of their volumes will be
A symbol not only represents the name of the element but also represents
Which of the following terms are unitless?
Importance of Chemistry
Chemistry is essential for meeting our basic needs of food, clothing, shelter, health, energy, and clean air, water, and soil. Chemical technologies enrich our quality of life in numerous ways by providing new solutions to problems in health, materials, and energy usage.
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 MCQ with Answers
Which of the following statements about a compound is incorrect?
One mole of calcium phosphide on reaction with excess of water gives
Nature of Matter
The following is the nature of matter: Atoms that have protons, neutrons, electrons and a nucleus consist of matter. It generally exists in four states i.e. liquid, solid, gaseous and plasma state. The universe itself is a matter. Not all forms of energy are matter.
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 1 Important Extra Questions
What is the basic concept of chemistry?
Chemistry is defined as the study of the composition, structure and properties of matter and the reactions by which one form of matter may be converted into another form. The Basic Concepts of Chemistry is that it is an active evolving science and has vital importance to the entire world.
How do we calculate molar mass?
The molar mass is the mass of one mole of a sample. To find the molar mass, add the atomic masses (atomic weights) of all of the atoms in the molecule. Find the atomic mass for each element by using the mass given in the Periodic Table or table of atomic weights.
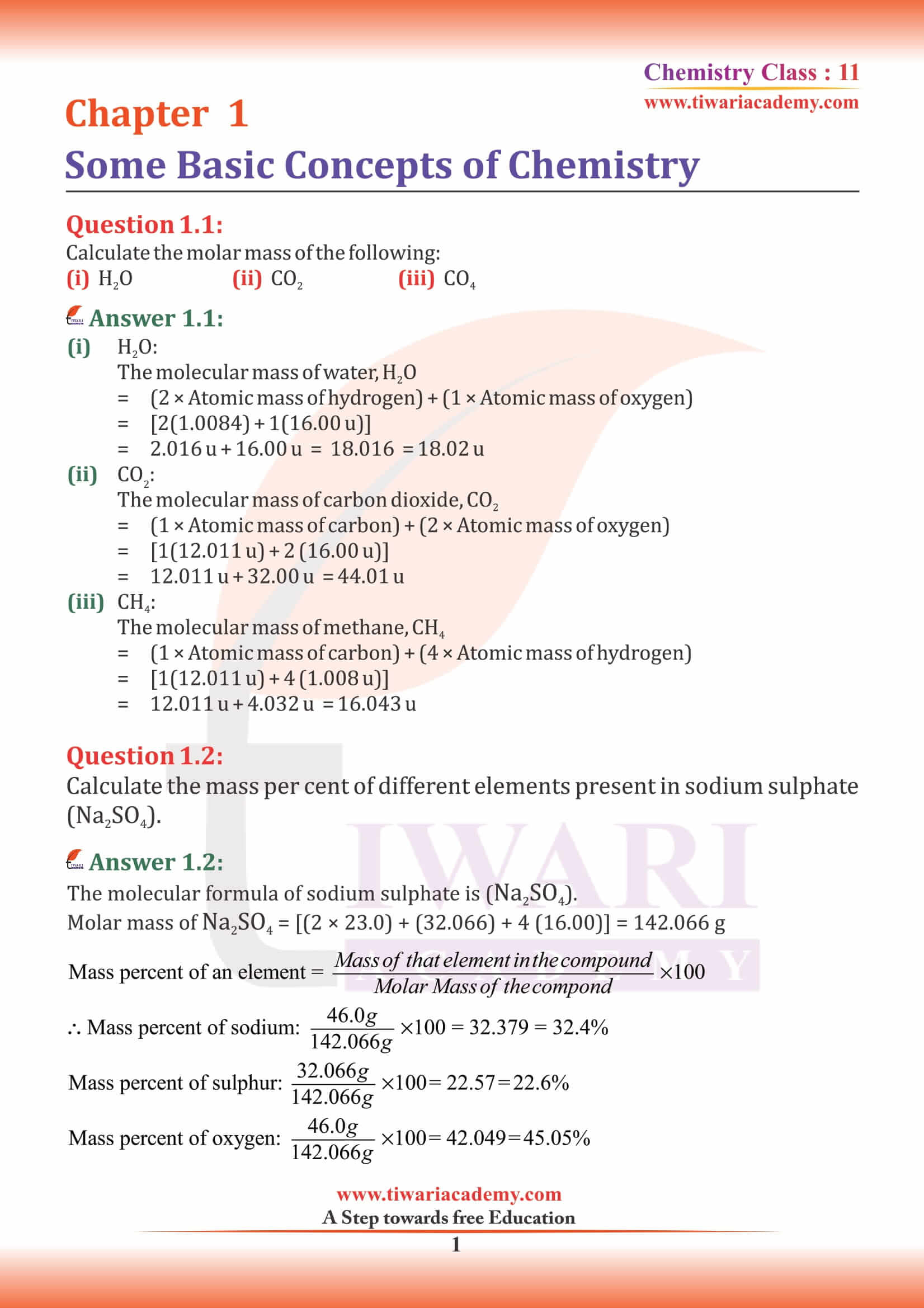
Calculate the molar mass of the following: (i) H₂O (ii) CO₂ (iii) CH₄
(i)
H₂O = 2 × H + 1 × O.
2 × 1 + 1 × 16 = 18.
(ii)
CO₂ = 12 × 1 + 2 × 16 = 44.
(iii)
CH₄ = 1 × C + 4 × H.
1 × 12 + 4 × 1 = 16.
States of Matter
matter can exist in three physical states viz., solid, liquid and gas. different states of matter exhibit the following characteristics:
- (i) Solids have definite volume and definite shape.
- (ii) Liquids have definite volume but do not have definite shape. They take the shape of the container in which they are placed.
- (iii) Gases have neither definite volume nor definite shape. They completely occupy the space in the container in which they are placed.
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Physical Properties
Examples of physical properties are temperature, malleability, appearance, texture, odour, colour, shape, solubility, melting, freezing, and boiling point. Volume, mass, length, density, pressure, viscosity, and hardness are a few more physical properties. - Chemical Properties
Chemical properties are those that get observed or measured when the substance undergoes a chemical change. Examples of chemical properties are – toxicity, chemical stability, the heat of combustion, flammability, reactivity, and enthalpy of formation.
Avogadro’s Law
Avogadro proposed that equal volumes of all gases at the same temperature and pressure should contain equal number of molecules.
Dalton’s Atomic Theory
The following are the Dalton’s Atomic Theory:
- Matter consists of indivisible atoms.
- All atoms of a given element have identical properties, including identical mass. Atoms of different elements differ in mass.
- Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine in a fixed ratio.
- Chemical reactions involve reorganisation of atoms. These are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.