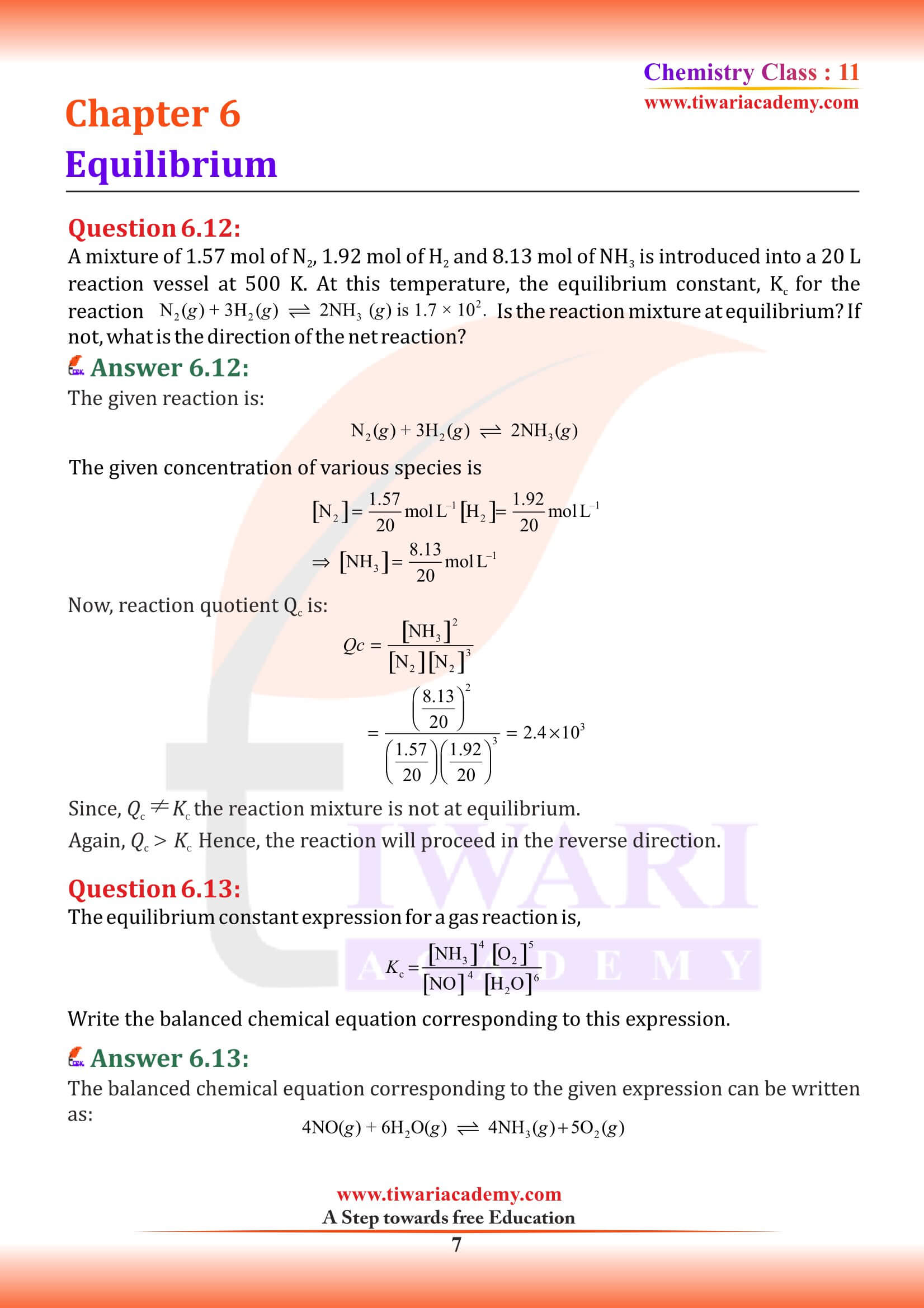
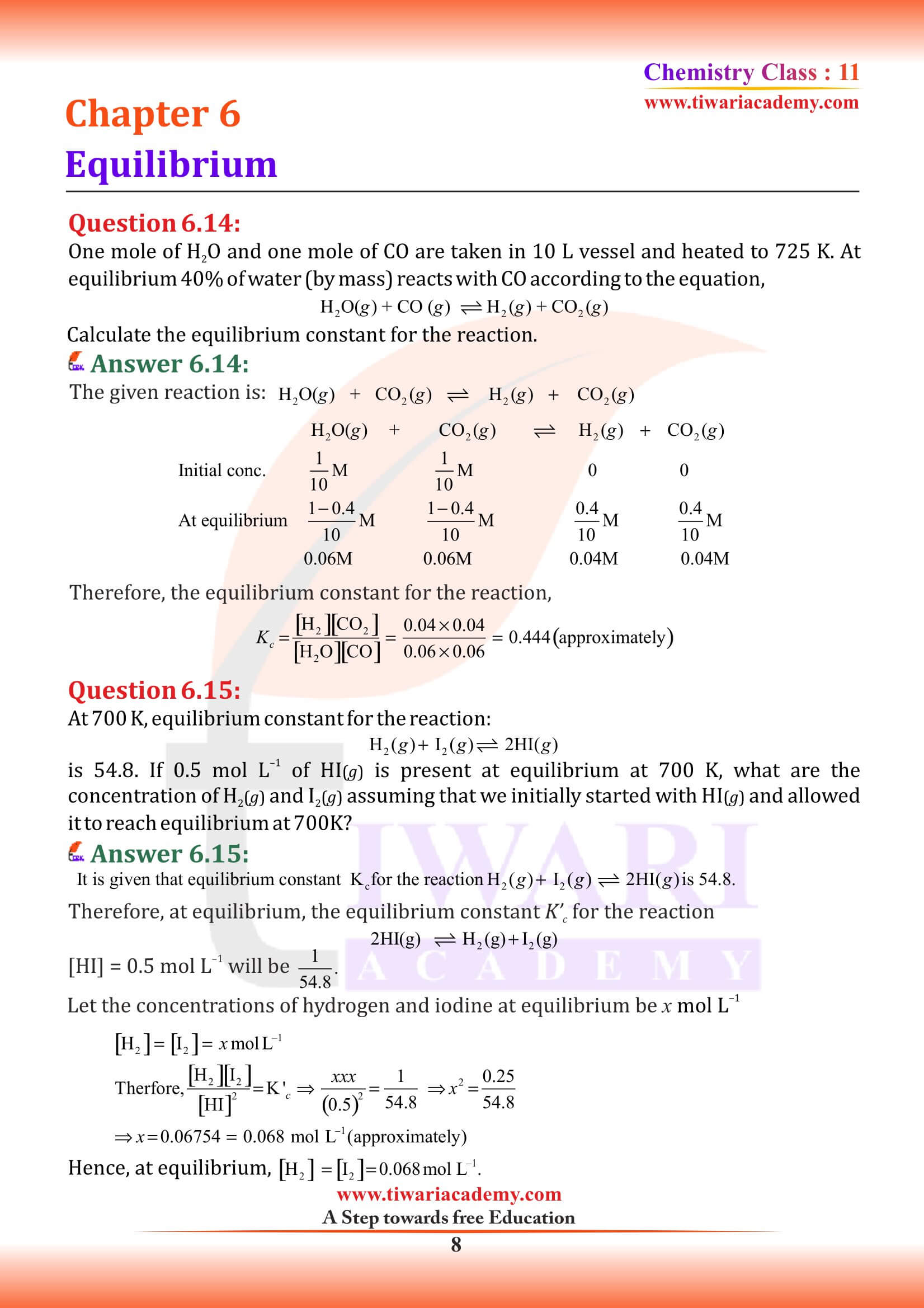
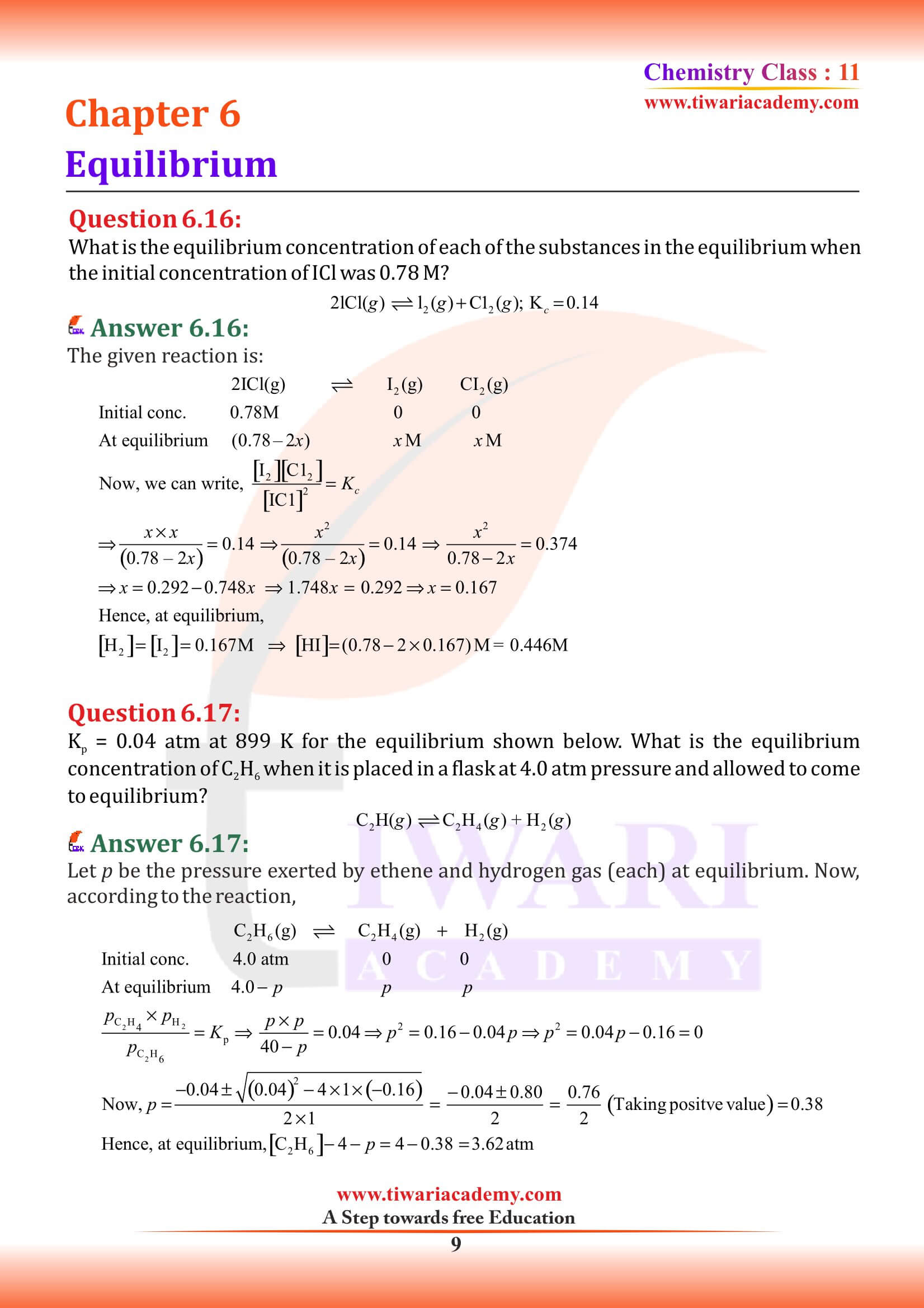
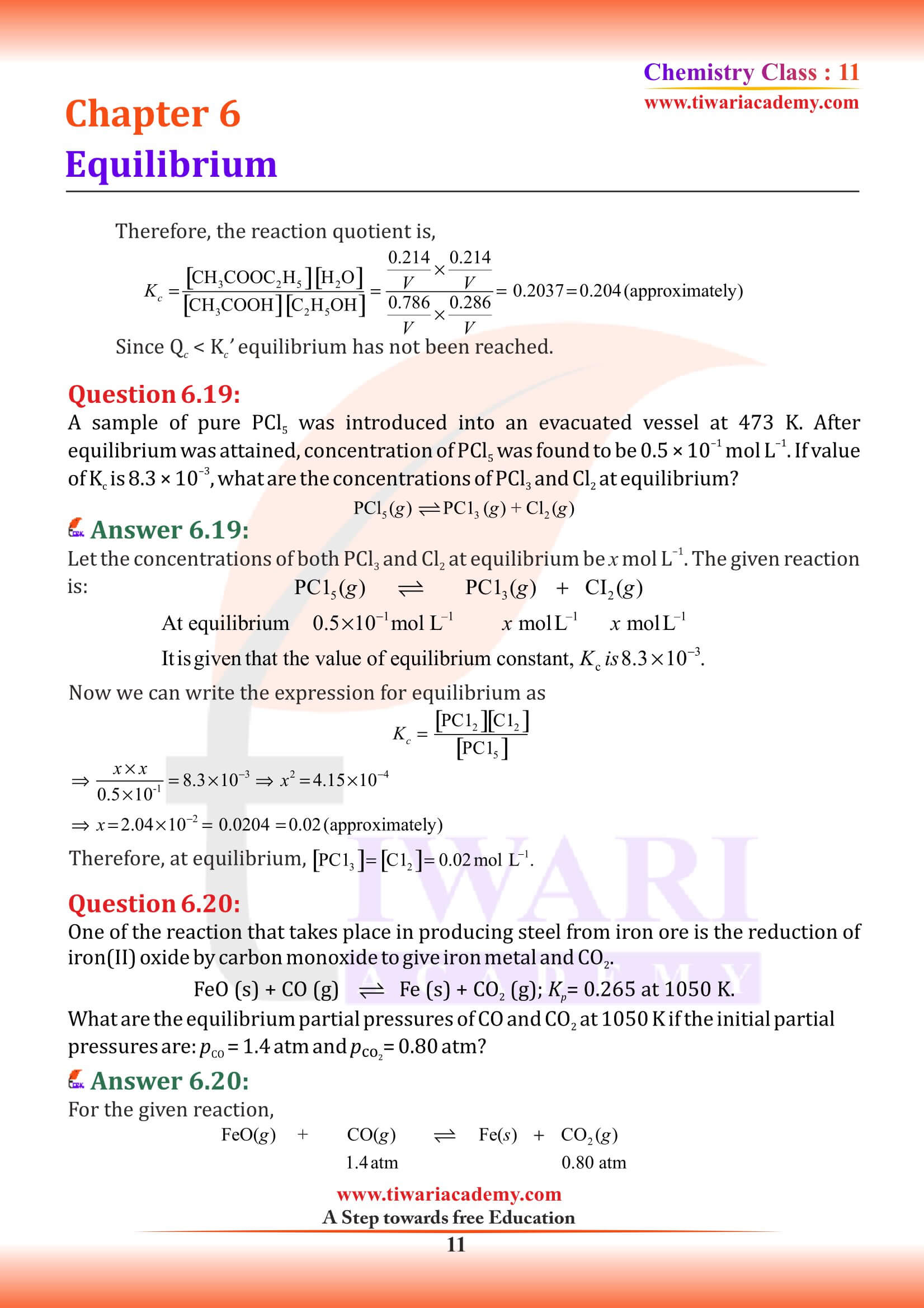
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Equilibrium in Hindi and English Medium with MCQ, exercises, extra important questions and intext questions for new session 2025-26. We have the entire solutions for class 11 chemistry chapter 6 follow the new edition NCERT textbooks published for academic year 2025-26.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 NCERT Book
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Hindi Medium
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Revision Book
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Study Material 1
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Study Material 2
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Study Material 3
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Assignment
- Class 11 Chemistry NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 all Subjects NCERT Solutions
Chemical Equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium is defined as a dynamic state where the concentration of all reactants remains constant. They may not be equal but they are not changing. In a chemical reaction, a double arrow indicates an equilibrium situation.
Example:
At equilibrium, the rate of evaporation is equal to the rate of condensation. It may be represented by
H₂O (l) ⇌ H₂O (vap)
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 MCQ
We know that the relationship between Kc and Kp is Kp = Kc(RT)∆n. What would be the value of ∆n for the reaction NH₄Cl(s) ⇌ NH₃(g) + HCl(g)
For the reaction H₂ (g) + I₂ (g) ⇌ 2HI (g), the standard free energy is ∆G > 0. The equilibrium constant (K) would be
Which of the following is not a general characteristic of equilibria involving physical processes?
The pH of neutral water at 25°C is 7.0. As the temperature increases, ionisation of water increases, however, the concentration of H⁺ ions and OH⁻ ions are equal. What will be the pH of pure water at 60°C?
Equilibrium in Physical Processes
Equilibrium represents the state of a process in which the properties like temperature, pressure, concentration of the system does not show any change with the passage of time. If the opposing processes involve only physical changes, the equilibrium is called physical equilibrium. For example:
- 1. solid ⇌ liquid
- 2. liquid ⇌ gas
- 3. solid ⇌ gas
Equilibrium in Chemical Processes – Dynamic Equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium is a state in which the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the backward reaction. In other words, there is no net change in concentrations of reactants and products. This kind of equilibrium is also called dynamic equilibrium.
For a better comprehension, let us consider a general case of a reversible reaction,
A + B ⇌ C + D
Formation of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen is a dynamic equilibrium.
N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g) ⇌ 2NH₃ (g)
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Important Extra Questions
The aqueous solution of sugar does not conduct electricity. However, when sodium chloride is added to water, it conducts electricity. How will you explain this statement on the basis of ionisation and how is it affected by concentration of sodium chloride?
(A) Sugar does not ionise in water but NaCl ionises completely in water and produces Na⁺ and Cl⁻ ions.
(B) Conductance increases with increase in concentration of salt due to release of more ions.
BF₃ does not have proton but still acts as an acid and reacts with NH₃. Why is it so? What type of bond is formed between the two?
BF₃ acts as a Lewis acid as it is electron deficient compound and coordinate bond is formed as given below:
H₃ N → BF₃
On the basis of the equation pH = – log [H⁺], the pH of 10⁻⁸ mol dm⁻³ solutions of HCl should be 8. However, it is observed to be less than 7.0. Explain the reason
Concentration of 10⁻⁸ mol dm⁻³ indicates that the solution is very dilute. Hence, the contribution of H₃O⁺ concentration from water is significant and should also be included for the calculation of pH.
Law of Chemical Equilibrium
At a given temperature, the product of concentrations of the reaction products raised to the respective stoichiometric coefficient in the balanced chemical equation divided by the product of concentrations of the reactants raised to their individual stoichiometric coefficients has a constant value. This is known as the Equilibrium Law or Law of Chemical Equilibrium.
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Questions
Acidity of BF₃ can be explained on the basis of which of the following concepts?
In which of the following solvents is silver chloride most soluble?
What will be the correct order of vapour pressure of water, acetone and ether at 30°C. Given that among these compounds, water has maximum boiling point and ether has minimum boiling point?
At a particular temperature and atmospheric pressure, the solid and liquid phases of a pure substance can exist in equilibrium. Which of the following term defines this temperature?
Equilibrium Constant
Equilibrium constant is the ratio of velocity constant of forward reaction to velocity constant of backward reaction. Also defined as It is the ratio of product to molar concentration of product to the product of molar concentration of reactants.
The equilibrium constant for a general reaction,
a A + b B ⇌ c C + d D
Kc = [C]ᶜ [D]ᵈ / [A]ᵅ[B]ᵇ
Kc = 1/ Kc
Equilibrium constant for the reverse reaction is the inverse of the equilibrium constant for the reaction in the forward direction.
What are Acids?
According to Arrhenius theory, acids are substances that dissociates in water to give hydrogen ions H+(aq). Examples of acids are Hydrochloric acid (HCl), Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), Nitric acid (HNO₃).
What do you know about Bases?
Bases are substances that produce hydroxyl ions OH–(aq). sodium hydroxide, calcium carbonate and potassium oxide are examples of bases.
Salts
a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt (NaCl), with positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions.
The pH Scale
pH is a measure of how acidic or basic water is. The range goes from 0 – 14, with 7 being neutral. pH of less than 7 indicate acidity, whereas a pH of greater than 7 indicates a base. pH is really a measure of the relative amount of free hydrogen and hydroxyl ions in the water.