Class 7 English Grammar Chapter 16 The Active and Passive Voice. A Verb is said to be in the Active Voice when its subject is doing the action. It is said to be in the Passive Voice when its subject is being acted upon. For example, Manank writes a letter is Active Voice but A letter is written by Mayank Passive Voice.
Grade 7 English Grammar Chapter 16 The Active and Passive Voice
Voice in grammar plays a pivotal role in portraying the manner in which an action is communicated, and Chapter 16 of Class 7 English Grammar elucidates this concept in-depth. Two primary voices dictate the positioning of the subject in relation to the action – Active and Passive. When the subject stands as the doer of the action, the verb is said to be in the Active Voice. An illustration of this is: “Manank writes a letter,” where Manank, the subject, is the one carrying out the action.
| Class: 7 | English Grammar |
| Chapter: 16 | The Active and Passive Voice |
| Academic Session: | 2025-26 |
| Study Material: | Textbook and Revision Book |
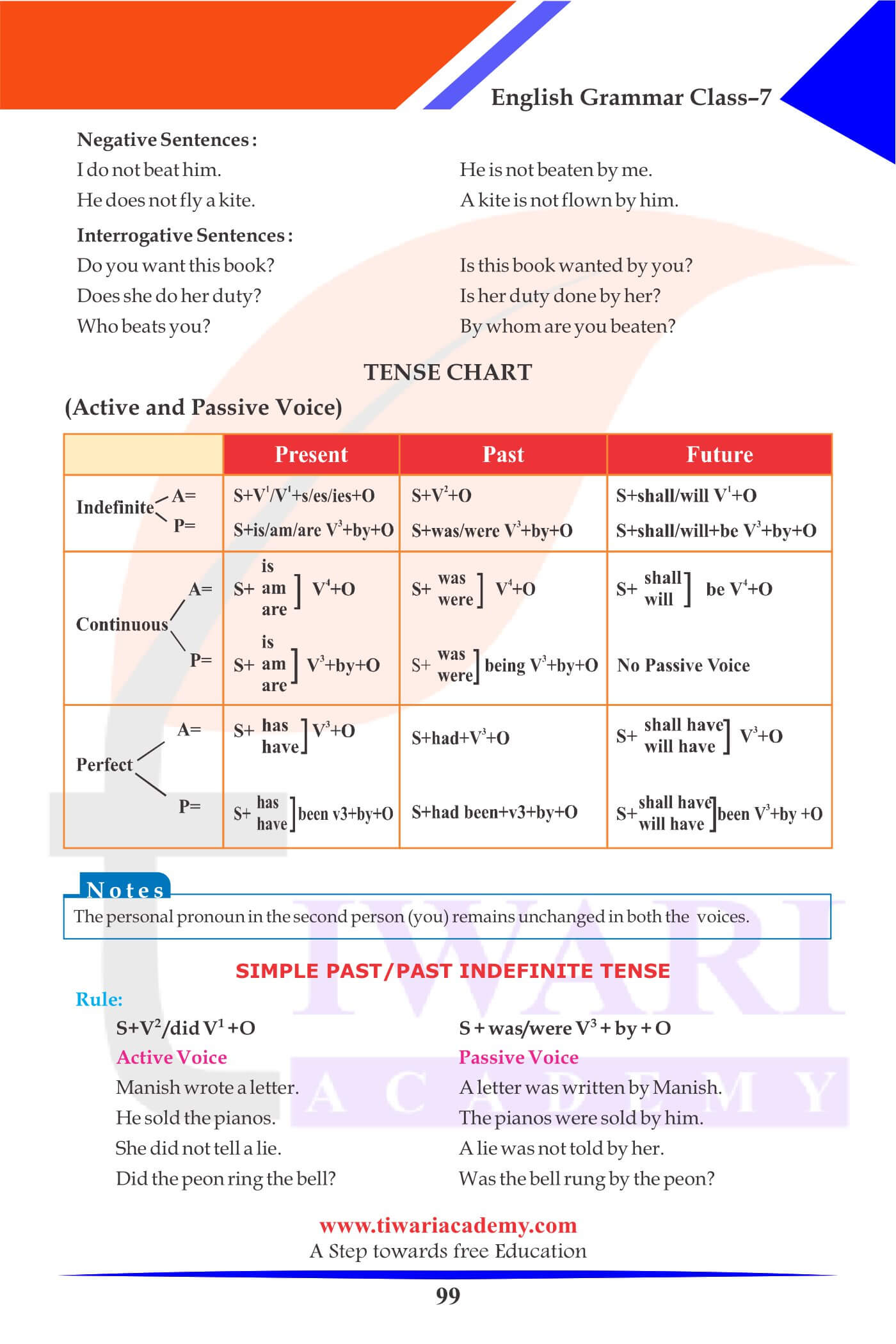
Rules for the Change of Voice
- When a verb is changed from the Active into Passive, the Object of the Active Verb becomes the Subject of the Passive Voice.
- Nominative Case of the Pronoun is changed into Objective Case.
- Only transitive verbs have passive voice.
- Change the verb into third form and put proper form of “to be” (is, am, are, was, were, be, been, being) before if according to the tense of the main verb in the Passive Voice and the number (singular/plural) of the new subject.
- By is used with the agent of action (= doer of the action). But it has to be kept in mind that where action is very important and the agent is unimportant, the preposition “by” and the agent are left out.
- Only transitive verbs have passive voice. If an intransitive Verb becomes Transitive, it too can have its Passive Voice.
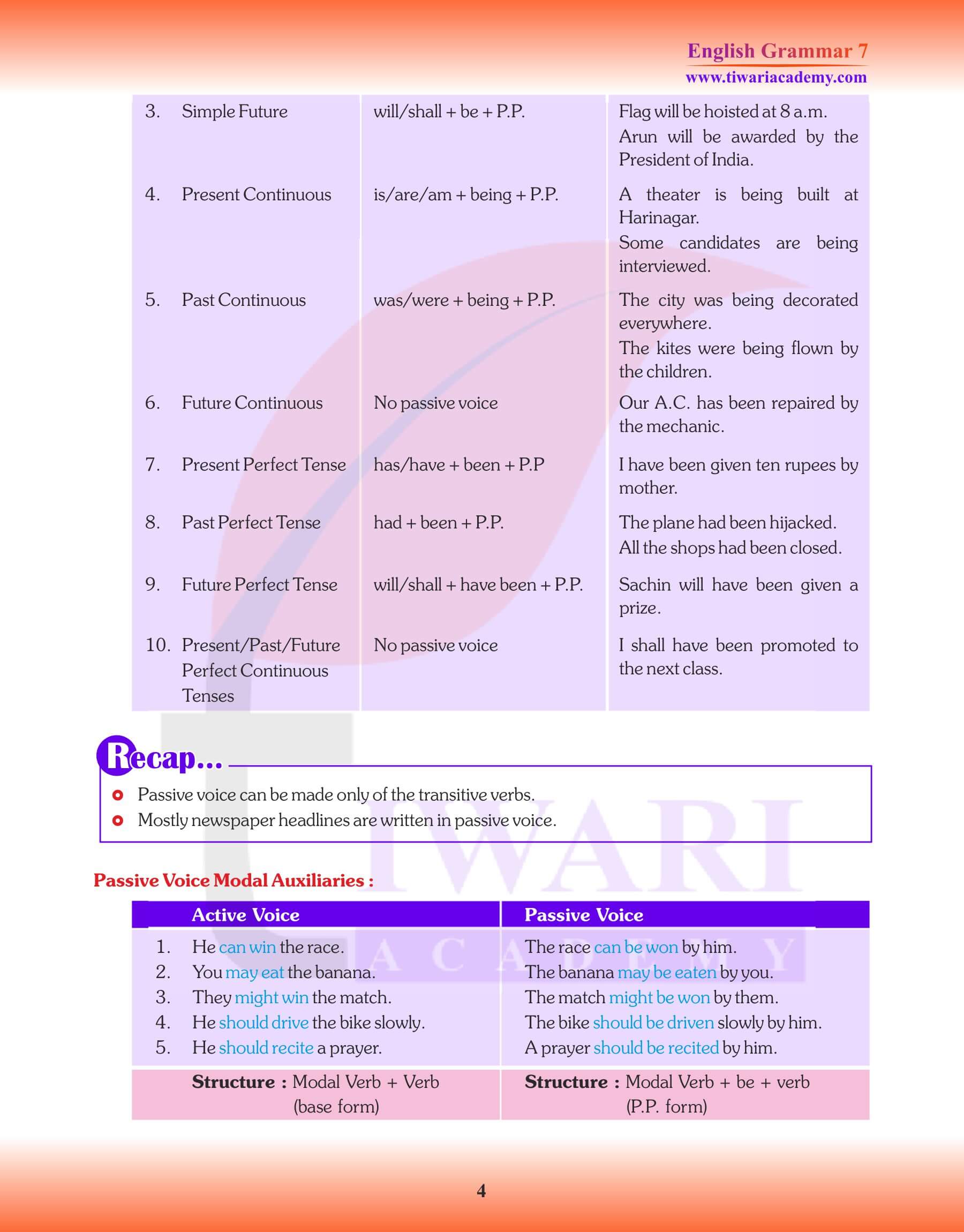
- Only eight tenses can be changed into passive voice.
- Future Continuous Tense and the three Perfect Continuous Tenses have no passive forms.
Conversely, when the action is done to the subject, the verb adopts the Passive Voice. A quintessential example of this voice can be observed in the statement: “A letter is written by Manank.” Here, the letter, despite being the subject, receives the action rather than executing it. By understanding the distinction between these voices, learners can enhance the versatility and precision of their written and spoken English.
Simple Present Tense
| Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|
| We love our country. | Our country is loved by us. |
| My mother loves me. | I am loved by my mother. |
| He does not fly a kite. | A kite is not flown by him. |
| I do not beat him. | He is not beaten by me. |
| Do you want this book? | Is this book wanted by you? |
| Does she do her duty? | Is her duty done by her? |
Simple Past Tense
| Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|
| She did not tell a lie. | A lie was not told by her. |
| Did the peon ring the bell? | Was the bell rung by the peon? |
| He sold the pianos. | The pianos were sold by him. |
| Manish wrote a letter. | A letter was written by Manish. |
| Who told a lie? | By whom was a lie told? |
| What did he want? | What was wanted by him? |
Simple Future Tense
| Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|
| We shall have our lunch at noon. | Our lunch will be had by us at noon. |
| She will not teach us. | We shall not be taught by her. |
| Will you buy this car? | Will this car be bought by you? |
| Who will help you? | By whom will you be helped? |
| He will not help you. | You will not be helped by him. |
| I shall beat you. | You will be beaten by me. |
Present Continuose Tense
| Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|
| Why are you teasing me? | Why am I being teased by you? |
| Is he beating the dog? | Is the dog being beaten by him? |
| He is not scolding you. | You are not being scolded by him. |
| She is not abusing me. | I am not being abused by her. |
| They are singing a song. | A song is being sung by them. |
| Is she buying toys? | Are toys being bought by her? |
| She is telling a story. | A story is being told by her. |
Past Continuous Tense
| Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|
| You were not wasting your time. | Your time was not being wasted by you. |
| Was she not cooking food? | Was food not being cooked by her? |
| What was he doing? | What was being done by him? |
| Who was speaking the truth? | By whom was the truth being spoken? |
| She was opening the door. | The door was being opened by her. |
| He was not helping us. | We were not being helped by him. |
| We were making a noise. | A noise was being made by us. |