NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Computer Science Chapter 1 History of Computer updated for CBSE session 2024-25. The grade 5 computer book chapter 1 includes assignments, notes and worksheets for CBSE and State board students.
Class 5 Computer Science Chapter 1 History of Computer
History of Computer
Let us Learn about the history of computers. Essentially there are three kinds of calculating devices viz, manual, mechanical and automatic. Abacus, Napiers Bones, Pascal’s Adding Machine and Leibniz’s calculator were early manual devices.
Abacus (1100 BC)
The first calculating device was Abacus. Abacus was used by Babylonians as an aid to simple arithmetic operations. It was used in China in 1300 A.D. It was a major tool for calculation until the 16th century.
Abacus is a frame with beads on strong wires or rods. It consists of beads divided into two parts. In the first part there are two beads and in the second parts there are five beads. Addition and multiplication of numbers are done using the place value of the digits of the numbers and position of beads in the abacus.
Pascaline (1642)
A French mathematician named Blaise Pascal developed a calculator. It calculated faster than the abacus. It was known as the first real Mechanical calculator and was called Pascals’ Machine.
Blaise Pascal invented an adding machine in 1642 which was made up of gears. The machine was named as adding machine and was capable of additions and subtractions.
Leibniz’s Calculator (1671)
In 1671, G.W. Leibniz invented a calculator which could multiply, divide, add and subtract.
Charles Babbage
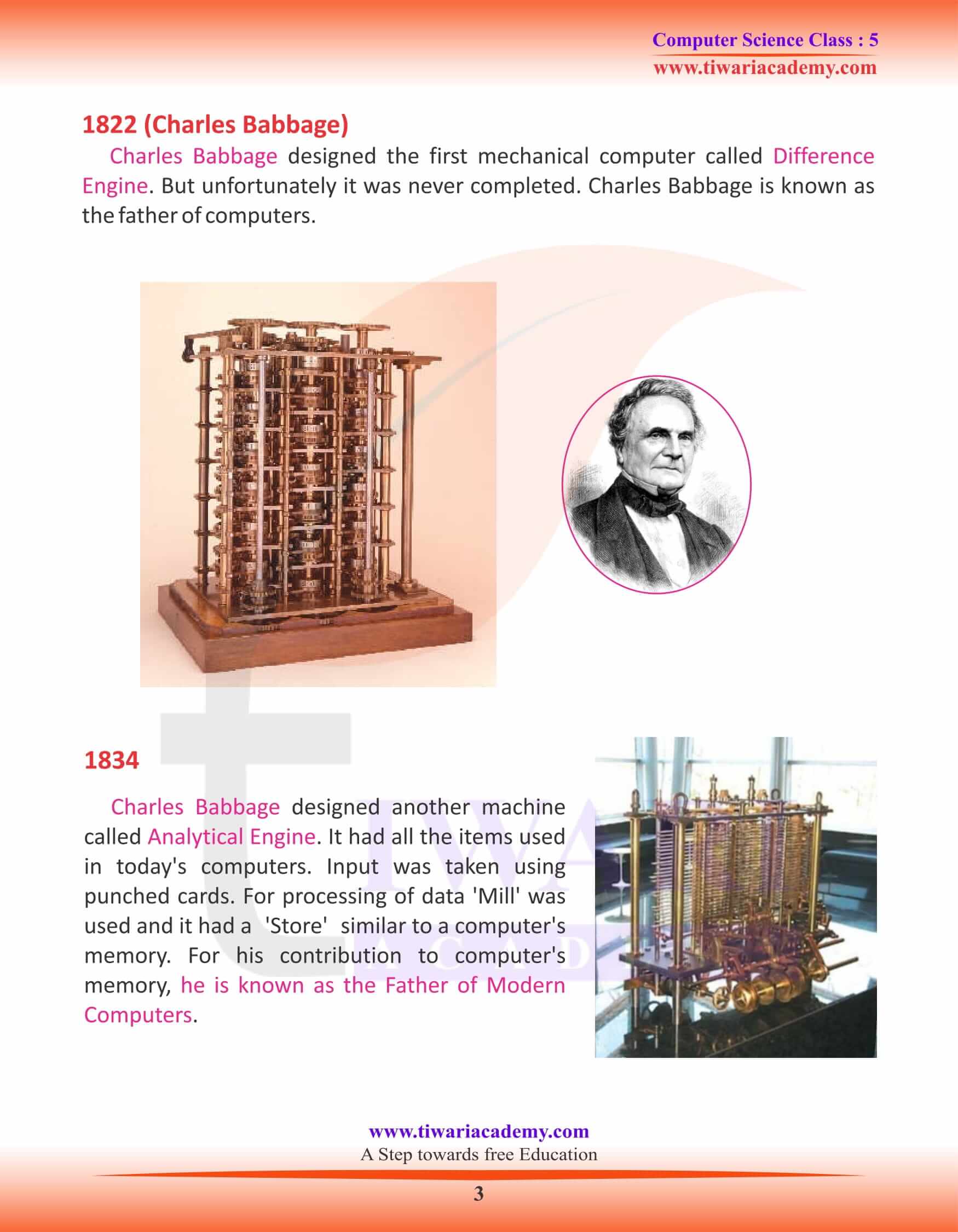
1822 (Charles Babbage)
Charles Babbage designed the first mechanical computer called Difference Engine. But unfortunately it was never completed. Charles Babbage is known as the father of computers.
1834
Charles Babbage designed another machine called Analytical Engine. It had all the items used in today’s computers. Input was taken using punched cards. For processing of data ‘Mill’ was used and it had a ‘Store’ similar to a computer’s memory. For his contribution to computer’s memory, he is known as the Father of Modern Computers.
1941
Prof. Harvard Aiken designed a computer based on the ideas of Charles Babbage for a computer company called IBM. IBM stands for International Business Machines. This computer was called Harvard MARK-I and it worked electro-mechanically. It was 51 feet long and 8 feet high.
First Digital Computer
1943-45 (First Digital Computer)
ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator), a totally electronic digital computer was designed as first of its kind. It was designed for the specific purpose of computing values for the United States’ army. It had a shortcoming that it took days to rewire the machine for each new problem. It was also enormous occupying a very big area. It could do around 1,00,000 calculations per second.
1945
In 1945 when ENIAC was nearing completion, planning began for ENIAC’s successor EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Computer). Much of its electrical engineering was developed by John Mauchly, J. Presper Eckert Jr., John Von Neumann and others. This computer’s design was that of a stored-program computer. It was the first computer which used the magnetic tape.
1949
EDSAC stands for Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Computer. It was constructed by Maurice Wilkes. He had suggested that besides doing calculations, a computer can also store programs. This was the first stored program computer with significant calculating ability. EDSAC ran its first program in 1949.
1950
The first Generation of computers UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer) was designed by J. Presper Eckert and John Mauchly. It used an operator keyboard and the magnetic tape for input. It was designed as a commercial data processing computer. It was the fastest business machine yet built. It was produced in the USA.
1950
Floppy Disk was invented at the Imperial University in Tokyo by Dr. Yoshiro Nakamats. It is an important storage device.
1956-1963
In the second generation of computer, vacuum tubes were replaced by transistors. Computers become smaller, faster and cheaper. They used less energy then before. It was possible to do
programming in these computers. Example of second generation computers are IBM1401, 1BM 350 RAMAC.
1964
First Super computer, the control data CDC6600 was developed.
1968
LOGO programming language was developed by Seymour Papert during this period.
1970
First RAM chip was introduced by Intel Corporation. It was called 1103 and had a capacity of 1024 bits.
In the third generation computers Integrated Circuits were developed. Transistors became smaller and were placed on silicon chips called semi-conductors. It helped to increase the speed of the computer. Also, different programs could run on these computers at the same time. IBM 360 is an example of third generation computer.
1985
Microsoft came out with its Windows 1.0 operating system.
1998
Microsoft released Windows 1998 operating system.
2001
Microsoft released Windows XP operating system.
2009
Microsoft released Windows 7 operating system.
2014
Microsoft released Windows 10 operating system.
2021
Microsoft released Windows 11 operating system
Microsoft Windows Operating System
In the fourth generation microchips were developed. These computers are still in use and are being developed further. Microprocessor chips were developed at this stage. 0 and 1 were coded to do arithmetical operations. These are known as binary numbers. These computers are fast and efficient. Examples are Personal Computers, Workstation etc.
Fifth generation computers are still under progress and development.
They have very high storage capacity, with speed and efficiency. Computers of this generation are called super computers. It has many CPUs connected together and can carry out a large number of scientific operations in a short time. Computers are being developed to enable them to think on their own, like human beings do. It is called artificial intelligence. Robots work on this technology.