NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 13 Exercise 13.1 Symmetry in Hindi and English Medium updated for CBSE and State Boards. Find updated NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 13 Exercise 13.1, covering Symmetry in Hindi and English. Ideal for CBSE and State Boards at Tiwari Academy.
6th Maths Exercise 13.1 Solutions in Hindi and English Medium
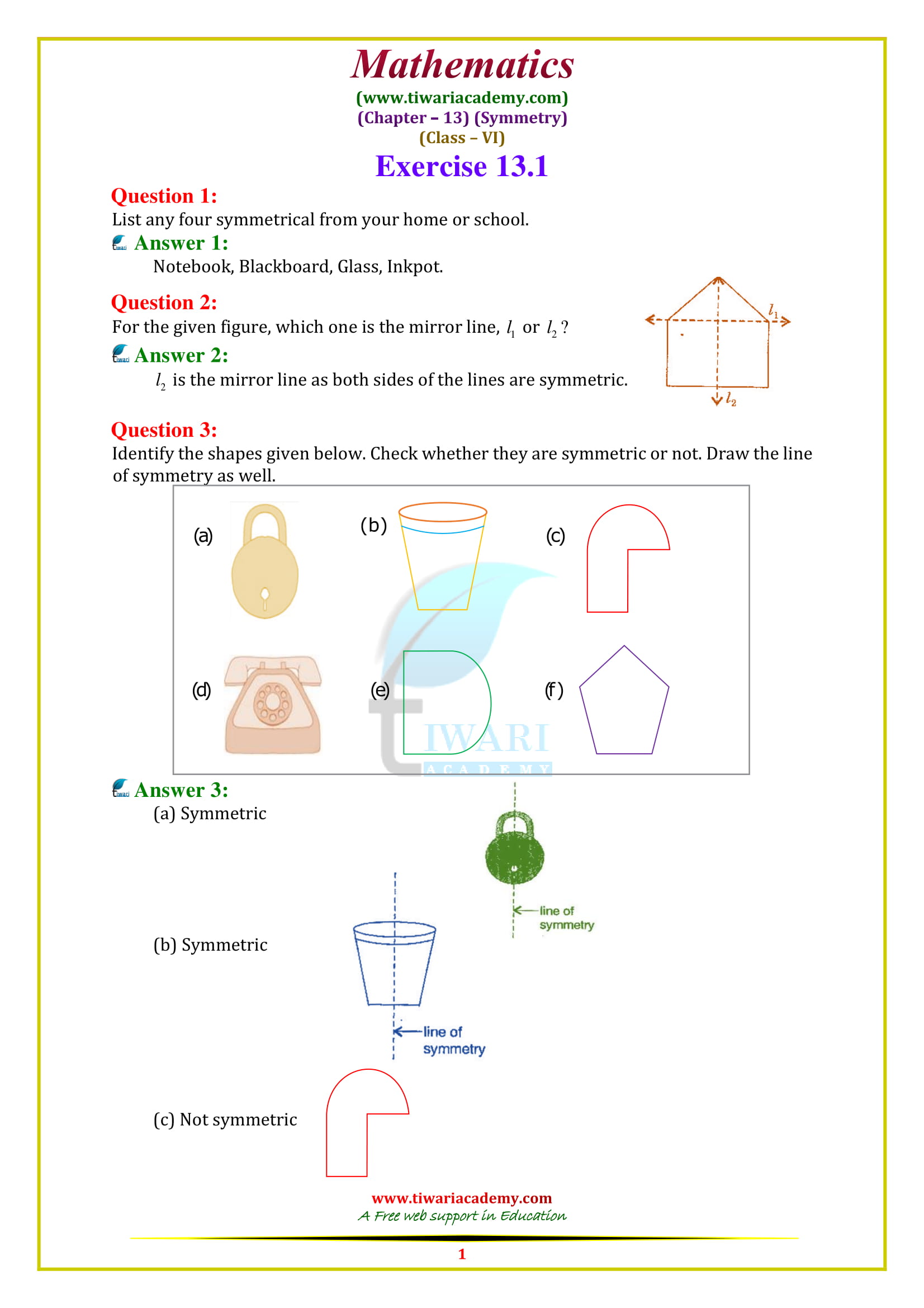
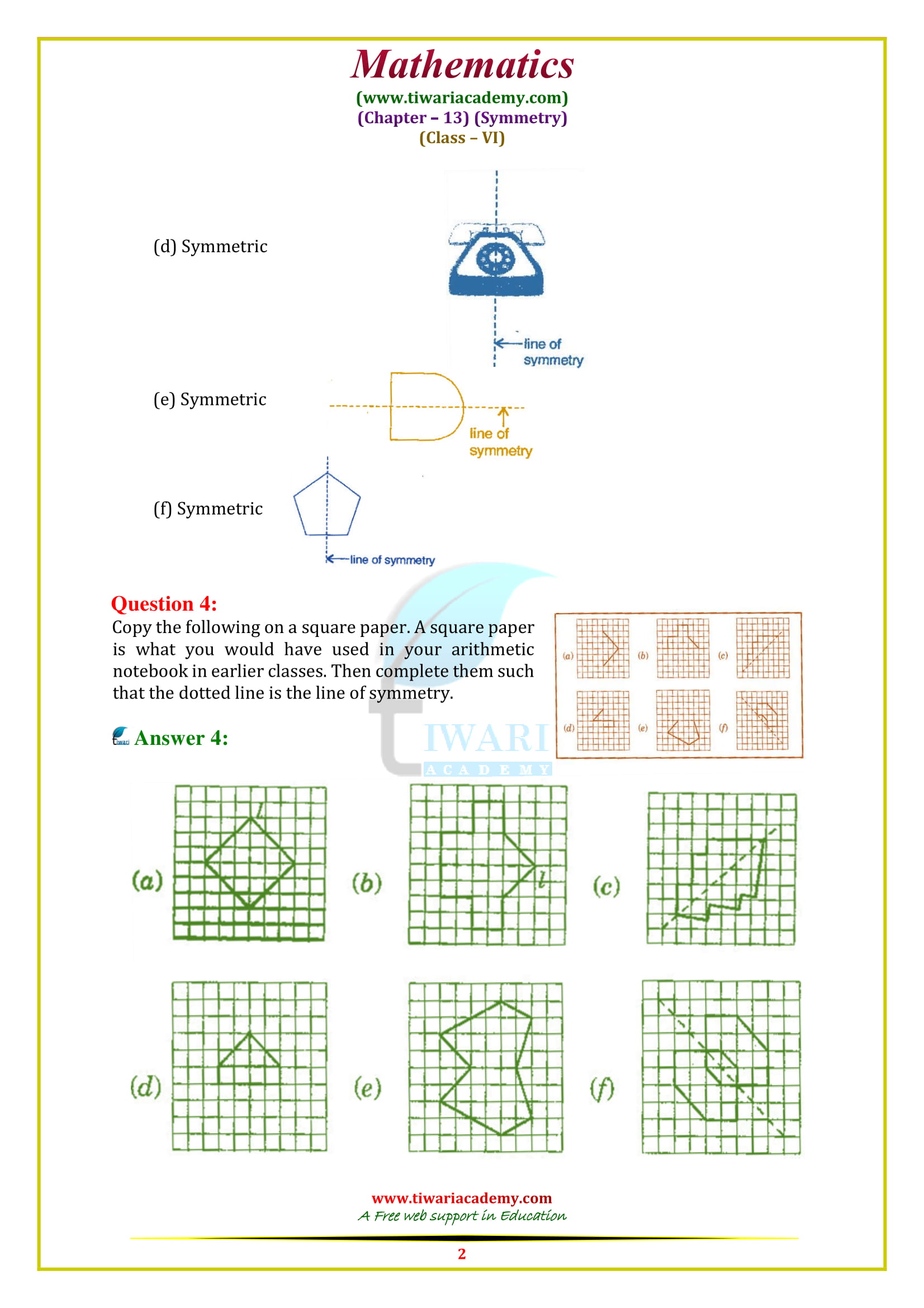
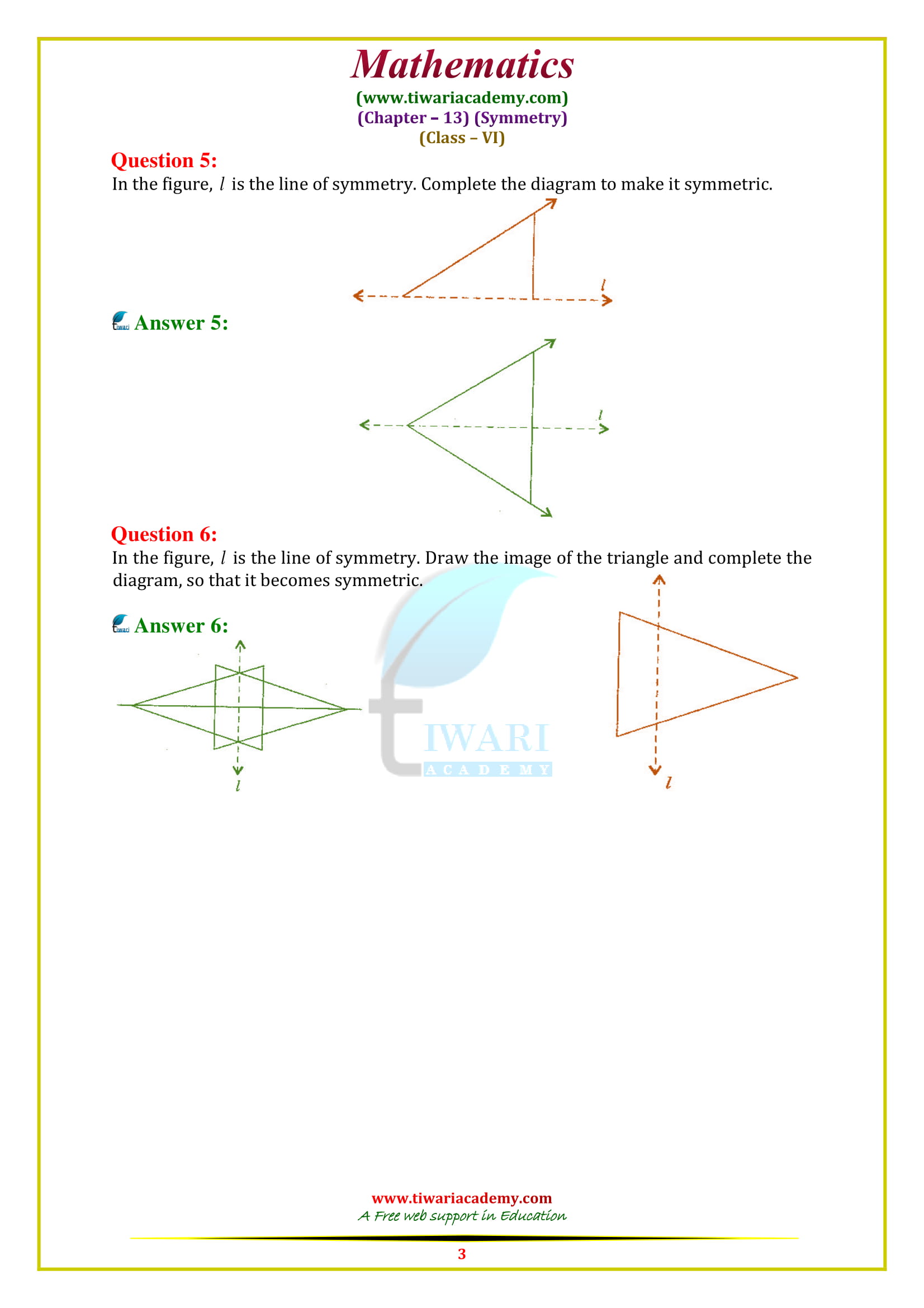
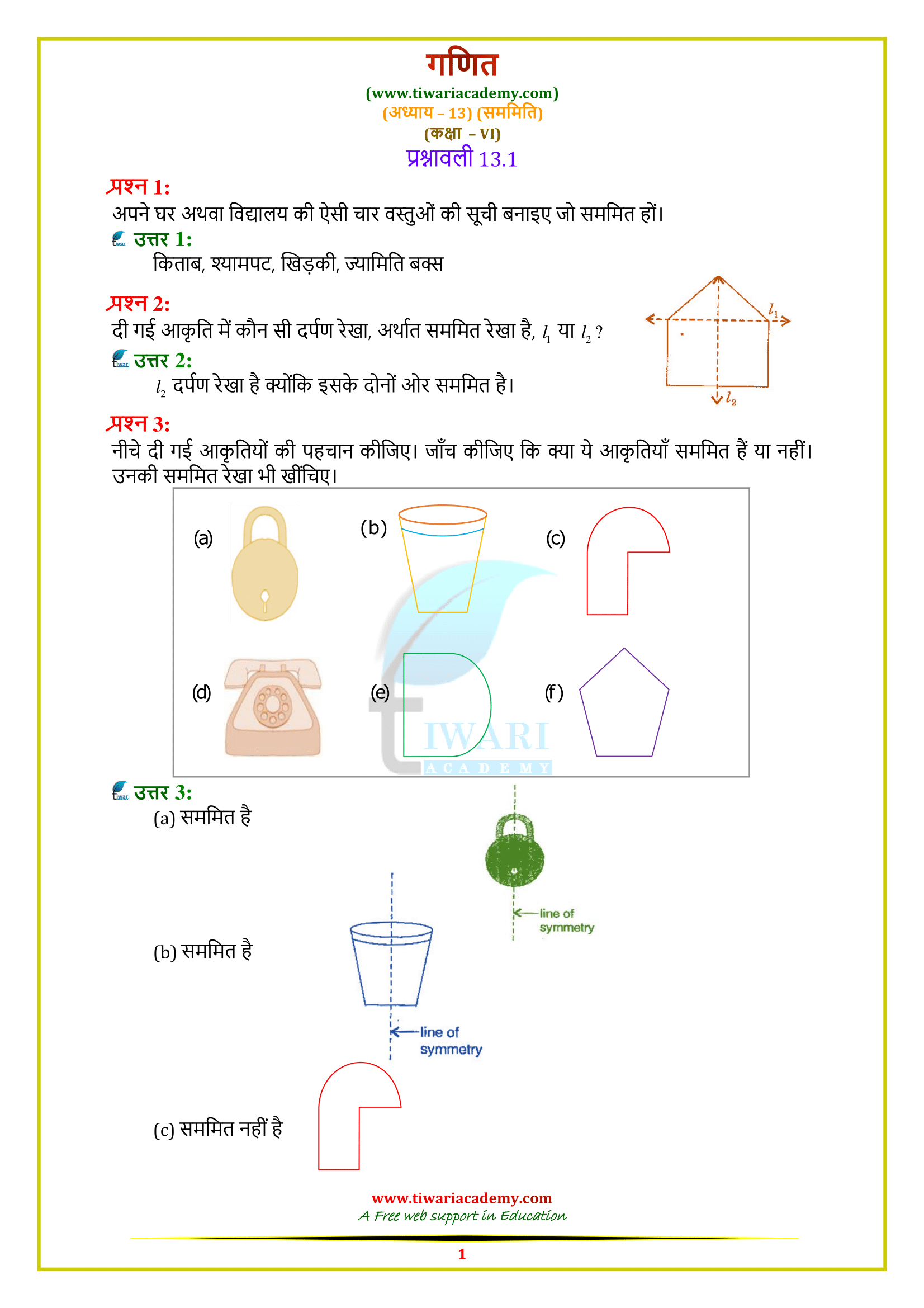
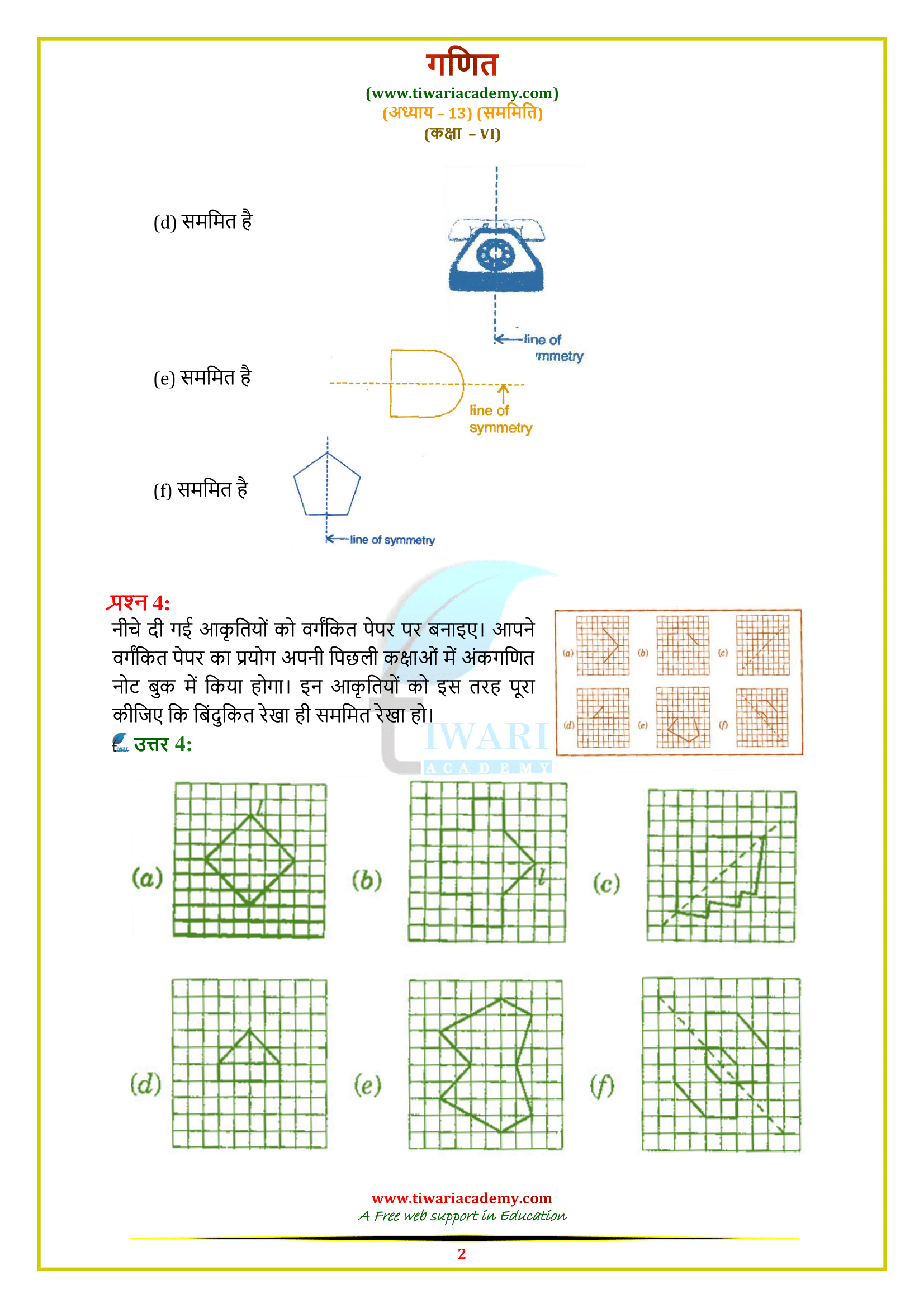
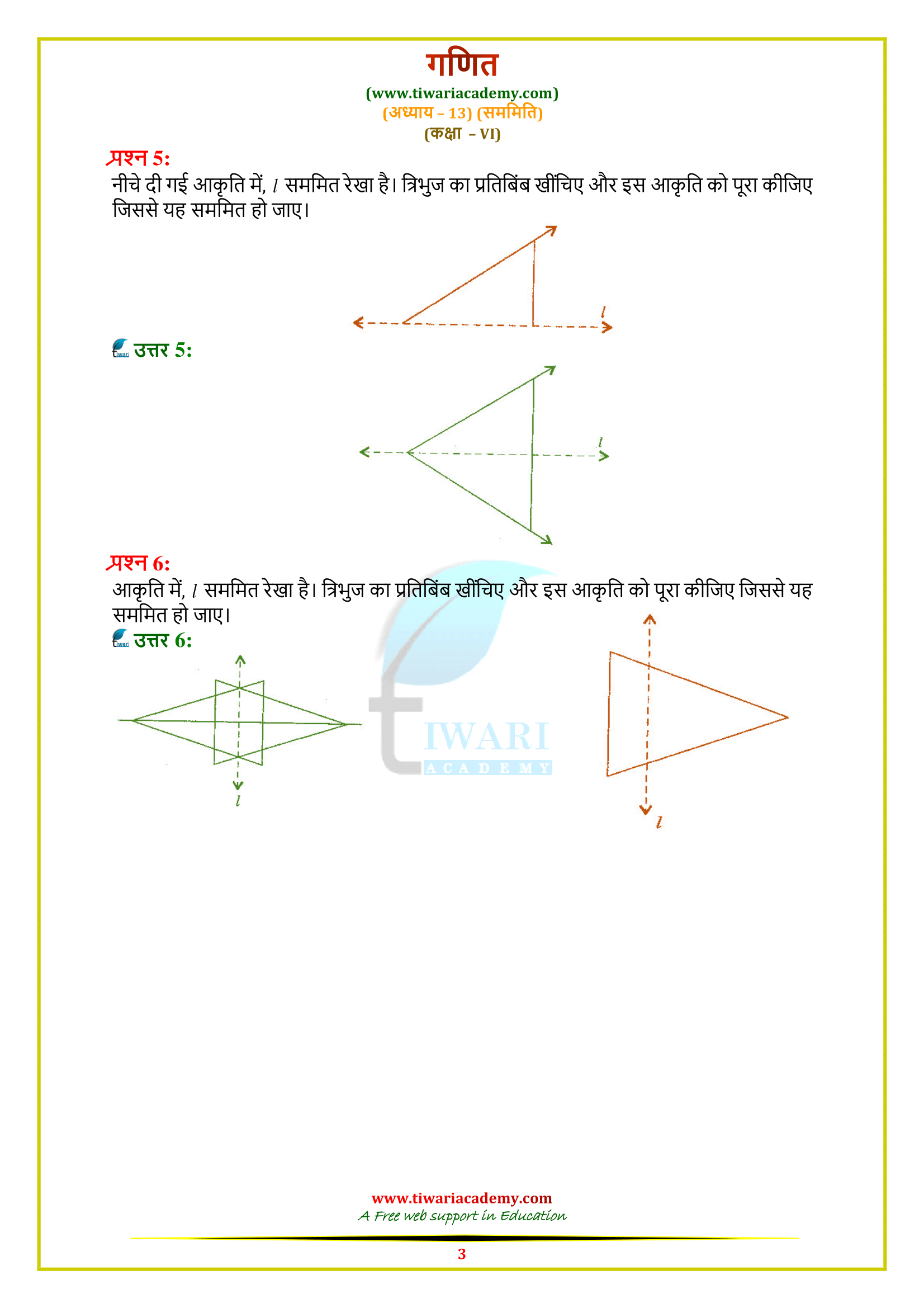
Class 6 Maths Chapter 13 Exercise 13.1 Solution
Class VI Mathematics textbook by NCERT (https://ncert.nic.in/) chapter 13 Ex. 13.1 solutions topic Symmetry in Hindi and English Medium updated for CBSE board and state board students. Along with the PDF solutions, the video solutions are also given to help the students. For the Maths practice in class 6, exercise 13.1 contains the questions related to symmetric figures and based on the concept of line of symmetry. Questions are easy but tricky for a student of standard 6.
| Class: 6 | Mathematics |
| Chapter: 13 | Exercise: 13.1 |
| Chapter topic: | Symmetry |
| Content: | NCERT Book’s Solutions |
| Medium: | Hindi and English Medium |
Class 6 Maths Chapter 13 Exercise 13.1 Solution in Videos
Symmetry
In Mathematics, the meaning of symmetry is that one shape is exactly like the other shape when it is moved, rotated, or flipped.
Note: If a line divides a given figure into two identical halves, then we say that the given figure is symmetrical about that line and the line is called the axis of symmetry or line of symmetry.
For example, two congruent triangles are symmetric.
Which shape has only one line of symmetry?
A kite has one line of symmetry.
Symmetrical Figures with Two Lines of Symmetry
Let us take a rectangular sheet of paper (like a postcard). Fold it once length-wise, so that one half fits exactly over the other half. Clearly, this fold line is the line of symmetry. Now open it up and again fold it once breadth-wise, in the same way. The second fold line is also a line of symmetry. Thus, a rectangle has two lines of symmetry.
Each of the following letters from English alphabet has two lines of symmetry. They are symmetrical about the dotted lines.
H, I, O, X
Class 6 Maths Exercise 13.1 Important Questions
Which letters have more than 2 lines of symmetry?
M has one line of symmetry, and H, I, and O have 2 lines of symmetry.
How is symmetry used in everyday life?
Real-life examples of symmetry
Reflection of trees in clear water and reflection of mountains in a lake. Wings of most butterflies are identical on the left and right sides. Some human faces are the same on the left and right side. People can also have a symmetrical mustache.
How many types of symmetry are there?
There are three types of symmetry: reflection (bilateral), rotational (radial), and translational symmetry.
What are the 3 lines of symmetry?
The division of triangles into scalene, isosceles, and equilateral can be thought of in terms of lines of symmetry. A scalene triangle is a triangle with no lines of symmetry while an isosceles triangle has at least one line of symmetry and an equilateral triangle has three lines of symmetry.
Why do we need symmetry?
Symmetry is a fundamental part of geometry, nature, and shapes. It creates patterns that help us organize our world conceptually. We see symmetry every day but often don’t realize it. People use concepts of symmetry, including translations, rotations, reflections, and tessellations as part of their careers.
Figures with More Than Two Lines of Symmetry
Let us take a square piece of paper. Fold it into half vertically and then fold it again into half horizontally. Open out the folds. You will get two lines of symmetry, one horizontal and one vertical. Now, fold the paper into half along a diagonal. Open it and fold it into half along the other diagonal. Open out the fold. Now you will get two more lines of symmetry one along each diagonal. Thus, a square has four lines of symmetry as shown below.
Are there any questions in exercise 13.1 of 6th standard Maths that are most important?
Exercise 13.1 of 6th standard Maths has 6 questions in all. Out of these 6 questions, three questions of exercise 13.1 of 6th standard Maths are most important. These most important questions are questions 3, 4, and 6.
Does exercise 13.1 Class 6 Maths take less time to be solved?
Yes, exercise 13.1 of 6th standard Maths is short. Only 6 questions are there in exercise 13.1 of grade 6th Maths and no example. Teachers need at most 2 lectures to finish exercise 13.1 of 6th-grade Maths. This time also depends on the teacher’s working speed, and efficiency.
Is exercise 13.1 of 6th standard Maths easy or complicated?
Exercise 13.1 of 6th standard Maths is quite easy. This exercise has 6 sums. All questions of this exercise are straightforward, nice, and logical. Students, who like drawing, enjoy solving the questions of exercise 13.1 of 6th class Maths.
Which question is the best question of exercise 13.1 of Class 6 Maths?
Question 6 is the best question of exercise 13.1 of 6th standard Maths. This question is a little tricky. This question requires higher-order thinking skills. This question helps to increase the thinking power of students.