NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Data Handling in Hindi and English Medium updated and modified for academic year 2025-26. The revised solutions of 3.1 class 7th Maths are given here on the basis of latest NCERT textbooks issued for curriculum 2025-26 based exams.
NCERT Class 7 Maths Exercise 3.1 Solution in Hindi and English Medium
| Class: 7 | Mathematics |
| Chapter: 3 | Exercise: 3.1 |
| Topic Name: | Data Handling |
| Content Type: | Text, Images and Videos |
| Academic Session: | 2025-26 |
| Medium: | Hindi and English Medium |
Class 7 Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1 Solution
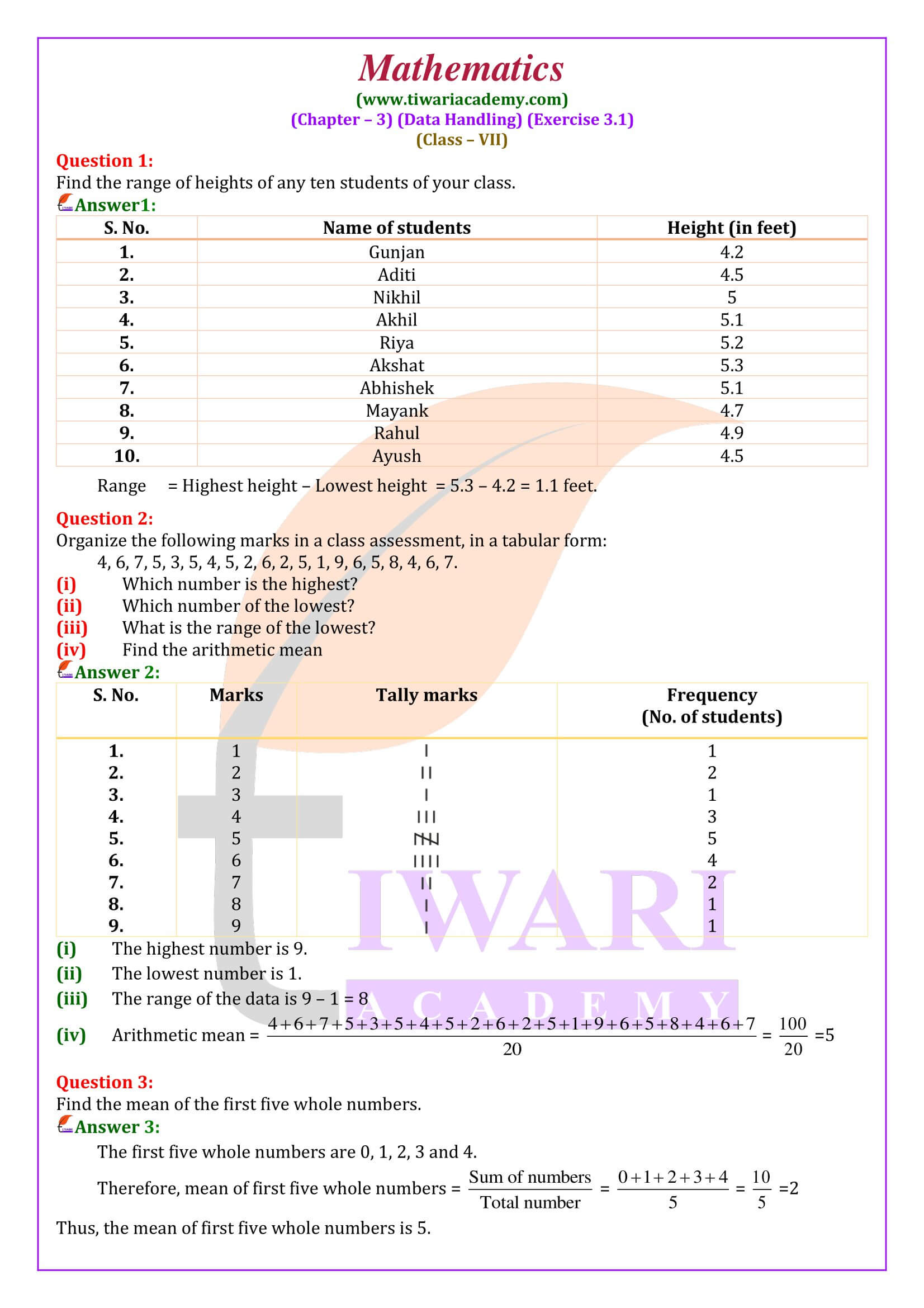
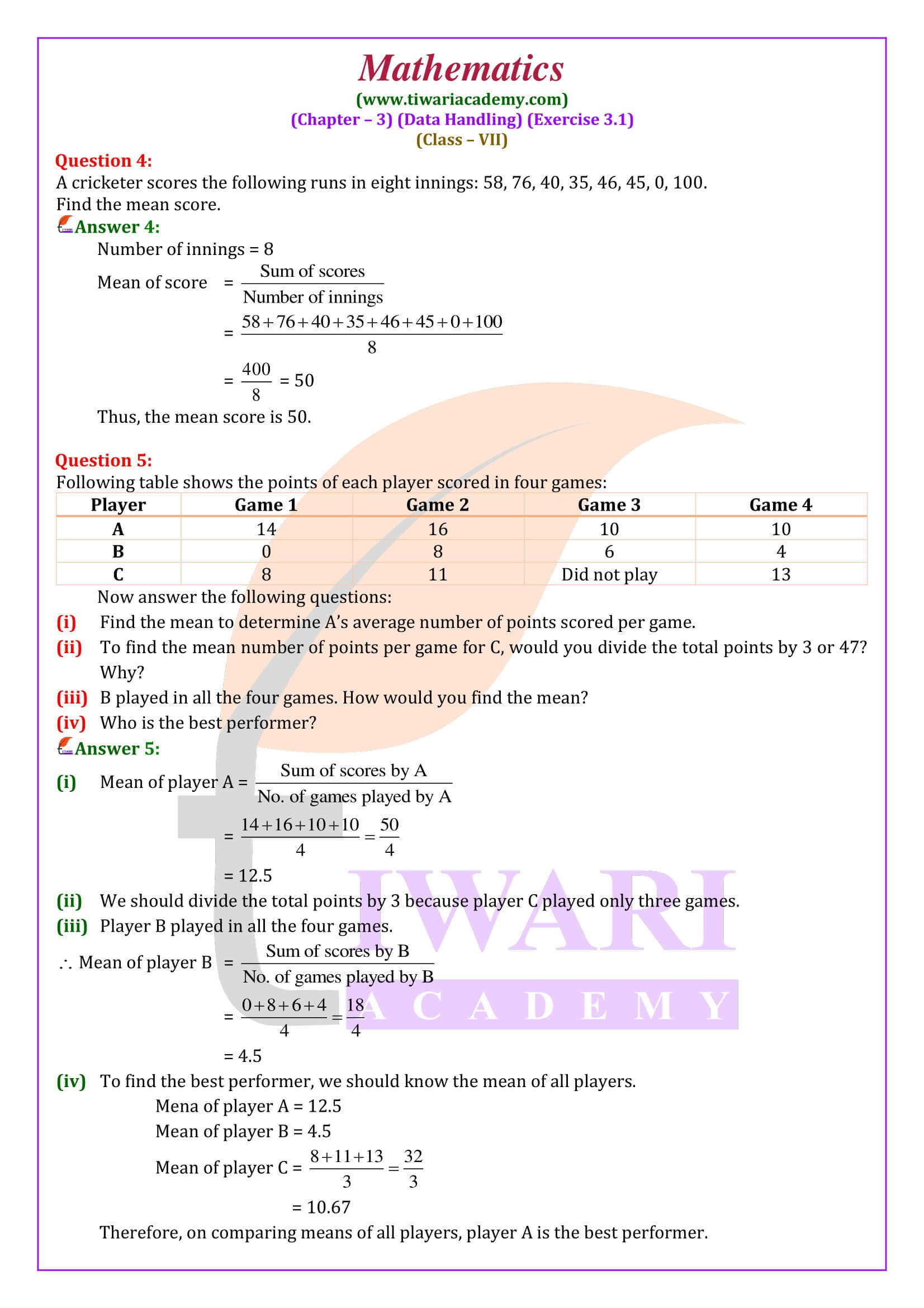
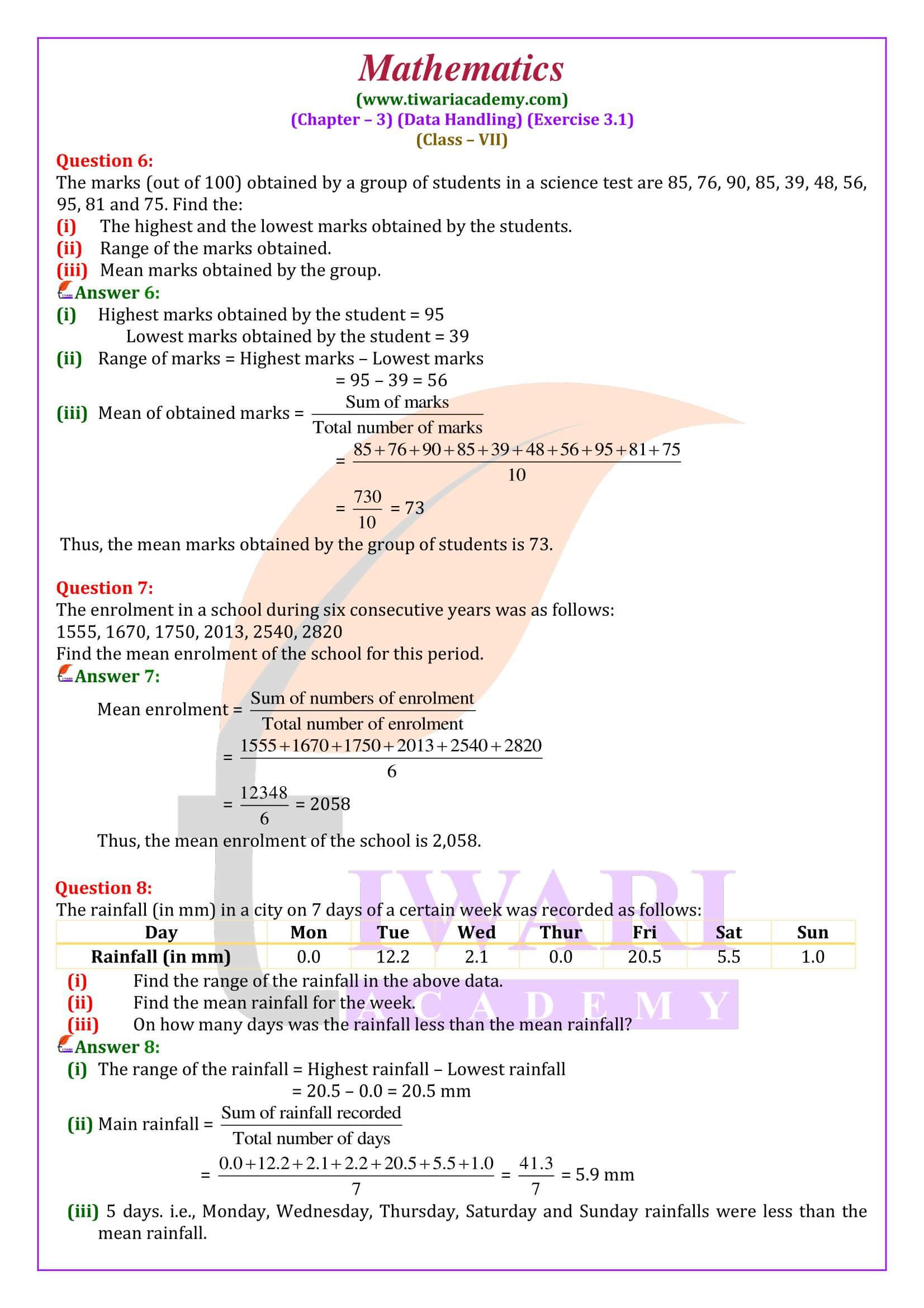
Questions answers are done according to latest CBSE textbooks issued for current year. In class 7 mathematics exercise 3.1 we have to learn how to find range of the given data and how to find mean of the tabular data. All the questions are easy but need more calculation.
Data
A collection of numerical figures giving some particular type of information is called data.
Example:
The heights (in cm) of 11 players in a school are:
155, 148, 161, 144, 159, 152, 147, 163, 156, 150, 165.
We call it the data related to the heights of 11 players in a school.
Raw data
Data obtained in the original form is called raw data. Data given in each of the above examples is a raw data.
Array
Arranging the numerical figures of a data in ascending or descending order is called an array.
Class 7 Maths Exercise 3.1 Extra Questions
Find the mean of the numbers: 7.6, 6.8, 8.5, 9.4, 5.9, 6.4, 9.1 and 4.7.
Sum of the given numbers
= (7.6 + 6.8 + 8.5 + 9.4 + 5.9 + 6.4 + 9.1 + 4.7) = 58.4.
Number of the given numbers = 8.
So, mean = sum of the given numbers/ number of the given numbers
= 58.4/8 = 7.3
Hence, the mean of the given numbers is 7.3.
The following table shows the weights of 12 workers in a factory: Weight (in kg)/ (No. of workers): 60/ 4, 63/ 3, 66/ 2, 69/ 2, 72/ 1 Find the mean weight.
Mean weight = Σ(fi X xi)/ Σfi
Σxifi = 60 x 4 + 63 x 3 + 66 x 2 + 69 x 2 + 72 x 1
= 240 + 189 + 132 + 138 + 72 = 771
Σfi = 4 + 3 + 2 + 2 + 1 = 12
So, Mean weight = Σ(fi X xi)/ Σfi = 771/ 12 = 64.250 kg
Hence, the mean weight is 64.250 kg.
Tabulation of Data
Arranging the data in a systematic form in the form of a table is called tabulation of the data.
Observation
Each numerical figure in a data is called an observation.
Frequency of an observation
The number of times a particular observation occurs is called its frequency.
Class 7 Maths Exercise 3.1 Important Questions
How many types of data handling are there?
Types Of Data: Data Handling In Maths.
Data or observations are classified into mainly two types:
(i) Qualitative data is descriptive information,
(ii) Quantitative data is numerical information.
Furthermore, we can divide quantitative data into two sections, like, continuous data and discrete data.
What does data handling include?
Data handling is the process of ensuring that research data is stored, archived or disposed of in a safe and secure manner during and after the conclusion of a research project. This includes the development of policies and procedures to manage data handled electronically as well as through non-electronic means.
What are the steps of data handling?
Six stages of data processing are:
(i) Data collection: Collecting data is the first step in data processing. …
(ii) Data preparation: Once the data is collected, it then enters the data preparation stage. …
(iii) Data input.
(iv) Processing.
(v) Data output/interpretation.
(vi) Data storage.
Statistics
It is the subject that deals with the collection, presentation, analysis and interpretation of numerical data.
Mean of Ungrouped Data
The mean of some given observations is defined as:
mean = sum of the given observations/number of the given observations
Mean of Tabulated Data
Let the frequencies of n observations x, x, x, …, x be frequencies f, f, f, …, f respectively. 1 2 3 n 1 2 3 n Then, we define:
Mean = (f1 x1 + f2 x2 + … + fn xn)/ (f1 + f2 + … + fn) = Σ(fi X xi)/ Σfi
where Σ (called sigma) is the Greek letter showing summation.
On which topic questions of exercise 3.1 of class 7th Maths are based?
Questions of exercise 3.1 of class 7th Maths are based on the topic named:
1. Collecting Data
2. Organization of Data
3. Representative Values
4. Arithmetic Mean
5. Range
How do students score full marks in exercise 3.1 of class 7th Maths?
Exercise 3.1 of class 7th Maths is very important for the exams. In exercise 3.1, there are 9 questions and 3 examples (Examples 1, 2, 3). All problems of this exercise are important. Students should practice all sums of this exercise to score full marks in exercise 3.1 of grade 7th Maths. Questions 3, 5, 9, and example 3 have more chances to come in the exams compared to other problems of exercise 3.1 of grade 7th Maths.
Is exercise 3.1 of class 7th Maths hard to solve and understand?
Exercise 3.1 of class 7th Maths is not at all hard to solve and understand. Exercise 3.1 is easy. Only 9 questions and 3 examples (Examples 1, 2, 3) are there in this exercise, and all sums of this exercise are nice and easy. Problems of this exercise are straightforward. Students enjoy doing this exercise.
How much time do students need to complete exercise 3.1 of class 7th Maths if students give 1 hour per day to this exercise?
If students give 1 hour per day to exercise 3.1 of grade 7th Maths, they need only 3 days to complete exercise 3.1 of class 7th Maths. The number of days can vary because no students have the same working speed, same capability, etc.