To find the area of a quadrant of a circle with a circumference of 22 cm, first determine the radius of the circle. The circumference C of a circle is given by C = 2πr, where r is the radius. Solving for r, we get r = C/(2π). Substituting C = 22 cm, r becomes approximately 3.5 cm. The area A of a circle is πr², so for our circle, A ≈ 3.14×(3.5)² cm². A quadrant is one-fourth of a circle, so its area is A/4, which is approximately 9.62 cm². This calculation shows how the circumference can be used to find the area of a specific section of a circle.
Let’s discuss in detail
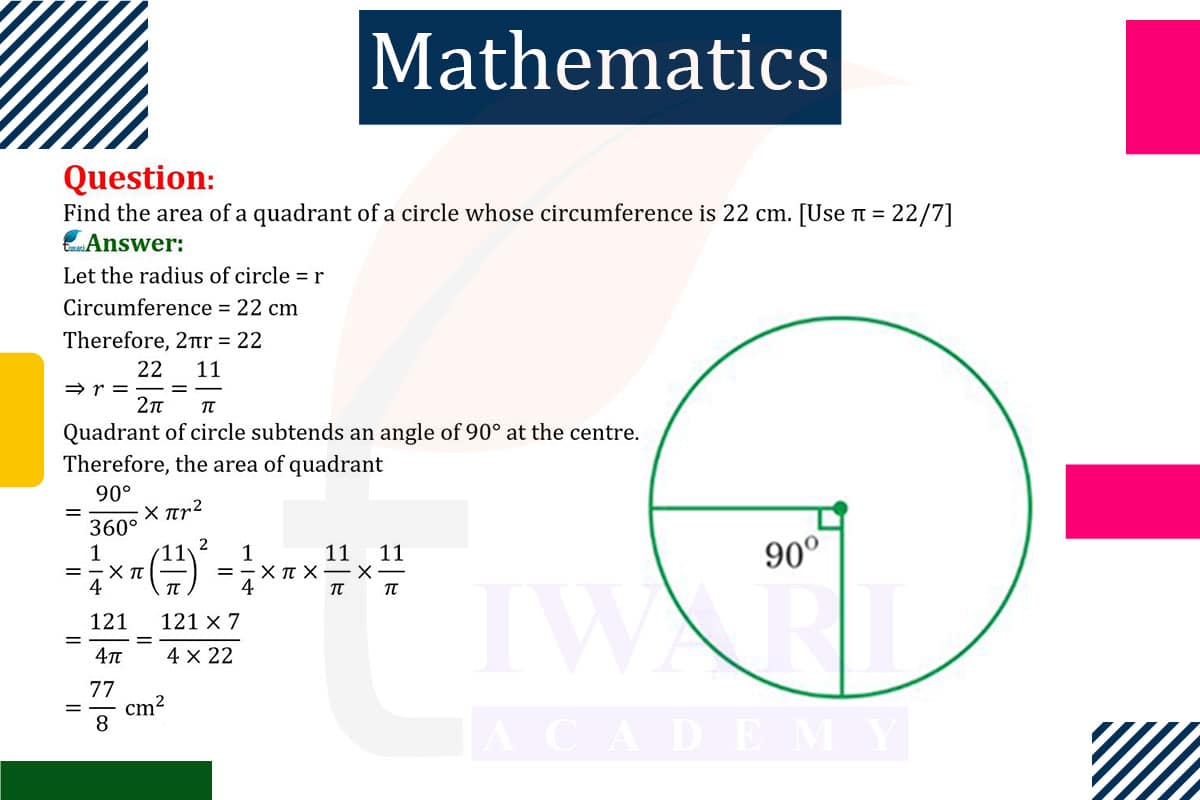
Quadrant Area Calculation
The concept of finding the area of a quadrant of a circle is a fundamental aspect of geometry, especially in understanding the properties of circles. A quadrant is one-fourth of a circle, making it a crucial shape in various mathematical and practical applications. To calculate the area of a quadrant, one must first understand the relationship between the circumference of the entire circle and its radius, as the area of any part of a circle is directly related to its radius. This calculation is not only important in theoretical mathematics but also has practical applications in fields like engineering, architecture, and design.
Understanding the Circle’s Circumference
The circumference of a circle is the total distance around its edge, which is directly proportional to its diameter. The standard formula to calculate the circumference is C = 2πr, where C is the circumference and r is the radius of the circle. The value of π (pi) is approximately 3.14, which is a constant representing the ratio of the circumference of any circle to its diameter. In our scenario, the given circumference of 22 cm will be the starting point to find the radius, which is essential for calculating the area of the quadrant.
Calculating the Radius from Circumference
To find the radius of the circle from its circumference, we rearrange the circumference formula to r = C/(2π). By substituting the given circumference (22 cm) into this formula, we can calculate the radius. This step is crucial because the radius is a key component in determining the area of the circle, and consequently, the area of the quadrant. The radius found from this calculation will be used in the next step to find the area of the entire circle.
Determining the Area of the Circle
Once the radius is known, the next step is to calculate the area of the entire circle using the formula A = πr². This formula is derived from the concept that the area of a circle is proportional to the square of its radius. By plugging in the radius value obtained from the circumference, we can calculate the total area of the circle. This total area is important as it forms the basis for determining the area of the quadrant, which is a fraction of the total area.
Calculating the Area of the Quadrant
A quadrant being one-fourth of a circle, its area is simply one-fourth of the total area of the circle. Therefore, the area of the quadrant is calculated by dividing the total area of the circle by four. This calculation is straightforward but requires accurate computation of the previous steps, particularly ensuring the correct radius is used. The result gives us the area of the quadrant, which is a significant measure in various practical and theoretical applications.
In conclusion, calculating the area of a quadrant of a circle involves finding the radius from the given circumference, determining the area of the whole circle, and then dividing this area by four to find the quadrant’s area. This process highlights the interconnectedness of different geometric properties of a circle. The ability to calculate the area of a quadrant has practical implications in numerous fields, including engineering, design, and everyday problem-solving. It demonstrates the practical utility of geometric principles in real-world scenarios, making it a valuable skill in both academic and professional contexts.
Discuss this question in detail or visit to Class 10 Maths Chapter 11 for all questions.
Questions of 10th Maths Exercise 11.1 in Detail


