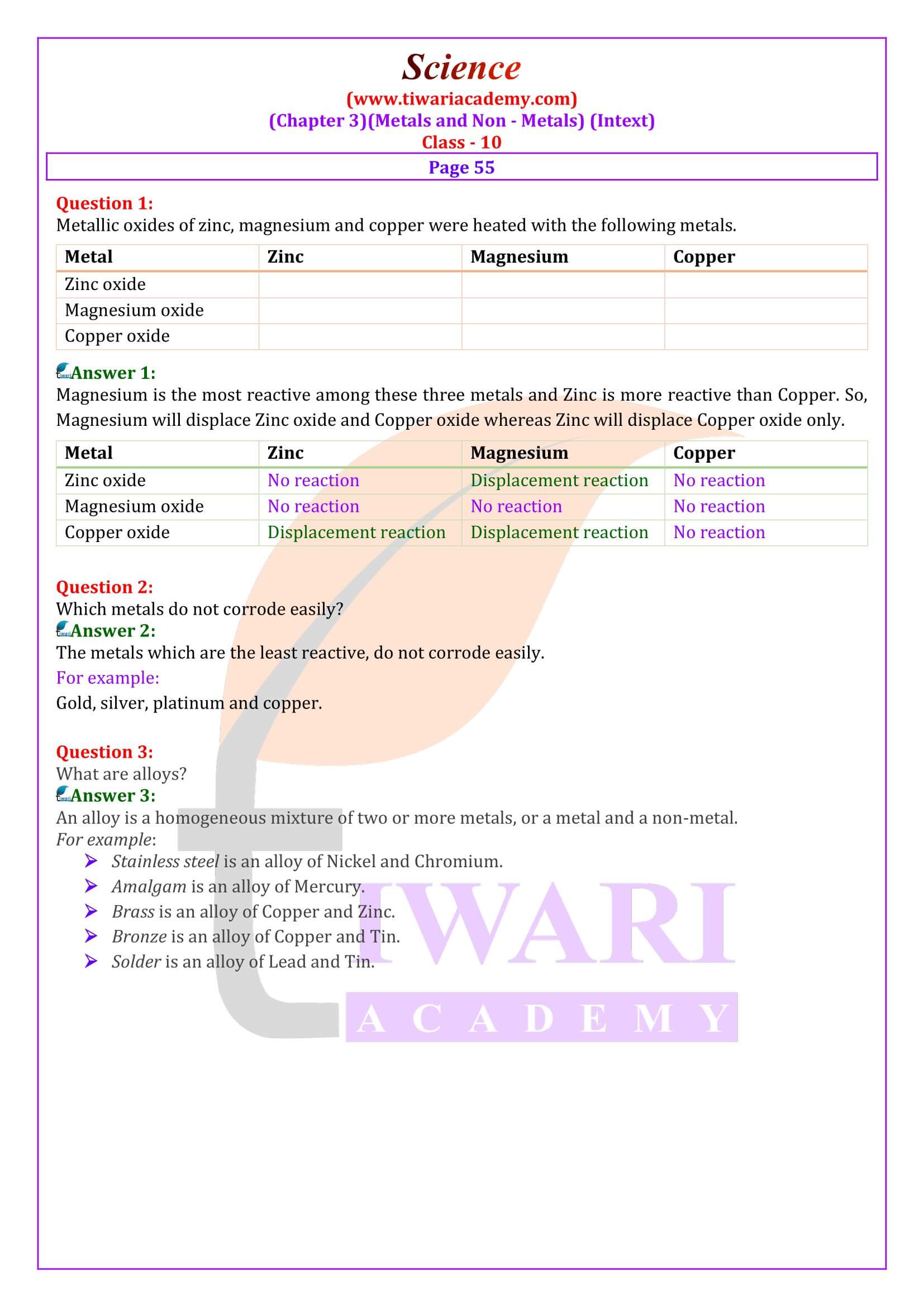
Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Solutions
Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Exercises Solutions
Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Intext Exercises
Class 10 Science Chapter 3 in Hindi Medium
Class 10 Science NCERT Book Download
Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Board Questions
Class 10 Science Chapter 3 MCQ
Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Extra Questions
Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions
Class 10 all Subjects Solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals in Hindi and English Medium updated for board exams 2024-25. The solutions and question answers of chapter 3 class 10 science is based on revised syllabus and new NCERT books issued for CBSE 2024-25 exams. In NCERT Class 10 Science, Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals.
This chapter explores the properties, classification, and various uses of metals and non-metals. Below is an outline of the topics covered in NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 3 introduction to Metals and Non-Metals. Basic definitions of metals and non-metals. Overview of their physical and chemical properties. The concept of corrosion and its causes. Methods to prevent corrosion, include the use of coatings and sacrificial anodes.
| Class: 10 | Science |
| Chapter 3: | Metals and Non-Metals |
| Content: | Exercise and Extra Questions |
| Content Type: | Text and Online Videos |
| Session: | CBSE 2024-25 |
| Medium: | English and Hindi Medium |
Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Solutions in Hindi and English Medium
- Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Exercises
- Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Intext Questions
- Class 10 Science Chapter 3 in Hindi
- Class 10 Science Chapter 3 NCERT Book
- Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Board Questions
- Class 10 Science Chapter 3 MCQ
- Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Extra Questions
- Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 all Subjects Solutions
Physical and Chemical Properties of Metals
Characteristics of metals, such as luster, malleability, ductility, and high electrical conductivity. The relationship between these properties and the atomic structure of metals. Reaction of metals with oxygen (formation of metal oxides). Reaction of metals with water and acids. Explanation of displacement reactions involving metals and their reactivity series.
Sources of metal ores and their extraction processes. Methods of extraction for common metals like iron, copper, and aluminum.

Physical Properties of Non-Metals
The characteristics of non-metals, such as dull appearance, lack of malleability, and poor electrical conductivity. Comparison of non-metallic properties with those of metals. Reaction of non-metals with oxygen (formation of non-metallic oxides). Non-metals as oxidizing agents. Uses of non-metals in various chemical processes. Properties and occurrence of hydrogen. Its role as a non-metal and a non-metallic oxide. Uses of hydrogen. Introduction to the reactivity series of metals and its significance in predicting displacement reactions.
Metals and Non-Metals in Daily Life
Practical applications of metals and non-metals in everyday life and industry. Use of alloys and their advantages. The impact of metals and non-metals on the environment, including issues related to mining and pollution. The role of metals and non-metals in agriculture, including their presence in fertilizers. The use of metals and non-metals in construction and building materials. It’s important to refer to the specific edition of the NCERT textbook you are using for any updates or additional details related to the chapter.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3
Class X Science chapter 3 intext questions given on Page 40 or Page 46 or Page 49 or Page 53 or Page 55 or Exercises in English Medium updated for new session 2024-25. The Hindi Medium version of solutions including Page 45 ke Uttar or Page 51 ke Uttar or Page 54 ke Uttar or Page 59 ke Uttar or Page 61 ke Uttar or Abhyas ke Prashn Uttar are also given to study online or download in PDF format free. NCERT Books and Offline Solutions Apps 2024-25 based on latest CBSE Syllabus are also available to download.
Preparing for NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 3, Metals and Non-Metals, in a better way requires a structured study plan and effective strategies. Here are some steps and tips to help students plan their preparation. Begin by thoroughly understanding the syllabus for Chapter 3. Note down all the topics need to be covered in this chapter. Plan a study schedule that allocates specific time slots for studying this chapter. While reading, take concise notes summarizing important points, formulas, and definitions. Organize your notes for easy reference.
Visual Aids and Practice Numerical Problems
Utilize diagrams, charts, and illustrations in the textbook to better understand the properties and characteristics of metals and non-metals. Class 10 Science chapter 3 include numerical problems related to chemical reactions and properties of metals and non-metals. Practice solving these problems to strengthen your understanding. Explore online resources, such as educational websites like Tiwari Academy and video tutorials, to enhance your understanding of complex topics and experiments related to metals and non-metals.
| Class 10 All Subjects iOS App for iPad & iPhone |

If possible, conduct simple experiments related to metals and non-metals to observe their properties firsthand. Practical experience can deepen your understanding. Create flashcards for key terms, definitions, and chemical reactions. Flashcards are a useful tool for quick revision. Periodically test your knowledge by taking self-assessment quizzes and mock tests related to Chapter 3. Identify areas where you need further practice.
10th Science Chapter 3 Answers in English & Hindi Medium
Solve Previous Year Papers
Practice solving previous year’s question papers to get a sense of the types of questions asked in board exams and improve your time management. Form study groups or discuss concepts with classmates to clarify doubts and reinforce your knowledge through discussions. Don’t hesitate to ask your teacher for clarification if you have doubts or questions about any topic within the chapter. As your exams approach, revise the chapter thoroughly. Focus on your notes, important formulas, and frequently asked questions.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals all intext question answers and chapter end exercises are given below to free download or use online. All NCERT Solution are updated for new academic session based on latest CBSE Syllabus 2024-25.
Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Extra Question Answers
Why are aluminium and copper metals used for making cooking vessels?
Aluminium and copper metals are good conductor of heat. When exposed to air, these develop a layer of oxide. This makes it resistant to further corrosion.
Why is sodium kept immersed in kerosene oil?
Sodium is very reactive. If kept exposed to air, it catches fire.
Distinguish between calcinations and roasting.
Calcination:
(i) The ore is heated is absence of air.
(ii) It is used for carbonate ores.
Roasting:
(i) The ore is heated in the presence of air.
(ii) It is used for sulphide ores.
Ionic compounds have high melting point. Why? Give reason in support your answer.
In iconic compounds, ions are joined together due to powerful electrostatic forces, therefore, considerable energy is required to separate these ions and break the lattice. Thus ionic compounds have high melting points.
Generally, Ionic compounds are hard crystalline solids. Why?
There are solids due to strong force of attraction between oppositely charged ions resulting in the formation of hard crystalline lattice.
What are alloys?
An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals, or a metals and a non-metal. It is prepared by first melting the main metal, and then dissolving the required amount of other metals or non-metals. This mixture is then cooled to form an alloy of a given composition.
What is meant by metallurgy?
Metallurgy involves various processes starting with the treatment of ore to getting metals in the pure form.
Practice Sample Papers
Solve sample papers designed specifically for Class 10 Science. These papers can give you a sense of the exam pattern and help you assess your preparedness. By following a structured study plan, staying organized, and utilizing various learning resources, you can prepare for NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 3 in a better way and perform well in your exams. Tiwari Academy provides resources and support for students preparing for various academic exams, including NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 3, which covers the topic of this chapter.
Questions for Practice
Question 1:
Compare the properties of a typical metal and non-metal on the basis of the following:
(i) nature of oxide formed by them
(ii) conductivity.
Answer :
(i) Metals from basic oxide, e.g., sodium gives a basic oxide, Na2O. Non-metals from acidic oxide, e.g., sulphur gives an acidic oxide, SO2.
(ii) Metals have good conductivity, e.g., copper is a good conductor. Non-metals do not conduct heat or electricity, e.g., sulphur.
Tiwari Academy typically offers detailed NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3. These solutions can help students understand the concepts, solve problems, and gain clarity on topics covered in the chapter. We also provide video lectures or tutorials related to Chapter 3. Video lessons can be a helpful visual aid for students to grasp complex concepts and understand practical experiments. Tiwari Academy often offers a variety of practice questions and exercises related to Chapter 3. These questions can help students test their knowledge, practice problem-solving, and gain confidence in the subject.
Important Questions on 10th Science Chapter 3
Name two metals which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids, and two metals which will not.
Metals that are more reactive than hydrogen displace it from dilute acids. For example: sodium and potassium. Metals that are less reactive than hydrogen do not displace it. For example: copper and silver.
What are the two important ways to prevent the rusting of iron?
Oiling, greasing, or painting: By applying oil, grease, or paint, the surface becomes water proof and the moisture and oxygen present in the air cannot come into direct contact with iron. Hence, rusting is prevented. Galvanisation: An iron article is coated with a layer of zinc metal, which prevents the iron to come in contact with oxygen and moisture. Hence, rusting is prevented.
Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery. Why?
Platinum, gold, and silver are used to make jewellery because they are very lustrous. Also, they are very less reactive and do not corrode easily.
Why are Sodium, potassium and lithium stored under oil?
Sodium, potassium, and lithium are very reactive metals and react very vigorously with air as well as water. Therefore, they are kept immersed in kerosene oil in order to prevent their contact with air and moisture.
Aluminium is a highly reactive metal, yet it is used to make utensils for cooking. Why?
Though aluminium is a highly reactive metal, it is resistant to corrosion. This is because aluminium reacts with oxygen present in air to form a thin layer of aluminium oxide. This oxide layer is very stable and prevents further reaction of aluminium with oxygen. Also, it is light in weight and a good conductor of heat. Hence, it is used to make cooking utensils.
Carbonate and Sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction. Why?
Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction because metals can be easily extracted from their oxides rather than from their carbonates and sulphides.
How is an ore different from a mineral?
Question 2:
“all ores are minerals but all minerals are not ores”. Justify the statement with examples.
Answer 2:
The metals found in nature in combined state are called minerals. If some minerals contain a very high percentage of a particular metal and the metals can be profitably and economically extracted, then it is called an ore.
Atmospheric air always contains moisture. Then, how can you protect iron articles from the affect of atmosphere?
Iron articles can be protected from the effect of atmosphere by painting, oiling and greasing. This gives temporary protection to iron articles. For long time protection, galvanising or chrome plating are quite useful.
Sample Papers and Previous Year Question Papers
The platform provides sample papers and previous year’s question papers for Class 10 Science. Practicing these papers can help students get a feel for the exam pattern and become familiar with the types of questions asked in the board exams. Tiwari Academy offers tips and strategies for effective time management during exam preparation, helping students balance their study schedule with other activities.
NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 3, titled Metals and Non-Metals, is important from an exam perspective for several reasons. Questions related to metals and non-metals are an essential part of the Class 10 Science curriculum and typically carry a significant weightage in the board exams. Devoting sufficient time and effort to this chapter can help students score well in the science paper. This chapter introduces fundamental concepts related to the properties, classification, and chemical behavior of metals and non-metals. A strong understanding of these concepts is crucial as they serve as the foundation for more advanced chemistry topics in higher classes.
What determines the reactivity of metals?
When metals react, they lose electrons to form positive ions. Such metals which can lose electrons easily to form positive ions when reacted with other substances, are reactive metals. On the other hand, if a metal loses electrons less rapidly to form positive ions, it will reacts slowly with other substances. Such a metal will be less reactive. For example, sodium atom is a very reactive metals because it readily loses one electron, forms a positive ion which then combines with other substances. On the other hand, lead atom loses electrons with difficulty to form positive ions, so lead metal is less reactive.
The Chapter 3 of 10th Science includes numerical problems related to chemical reactions and properties of metals and non-metals. These problems assess students’ problem-solving skills and their ability to apply concepts in real-world scenarios. The chapter covers various chemical reactions involving metals, such as reactions with oxygen, water, and acids. Understanding these reactions and being able to balance chemical equations is important for answering questions accurately. Knowledge of the properties and uses of metals and non-metals in daily life and industry is tested in the exams. Students may be asked to explain the practical applications of specific materials.
Questions related to displacement reactions, which are a key concept in this chapter, often appear in the exams. Students need to understand the reactivity series and how it predicts the outcome of displacement reactions. The chapter discusses the environmental impact of various metals and non-metals, including issues related to mining and pollution. These topics are relevant and may be tested in the context of environmental science. Corrosion is a critical concept covered in the chapter 3 of 10th Science.
Questions related to the causes of corrosion, methods of prevention, and the importance of protecting metals may be asked in the exams. The chapter introduces hydrogen gas, its properties, and its uses. Questions related to hydrogen and its significance may be part of the examination. Class 10 Science aims to provide a balanced understanding of various scientific concepts. Knowledge of metals and non-metals is essential to fulfill this objective.
In summary, NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 3, Metals and Non-Metals, is important for board exams because it covers foundational chemistry concepts, practical applications, and environmental considerations. Students should focus on understanding the principles, mastering problem-solving skills, and being able to apply their knowledge to various scenarios to excel in the examination.
Which questions of chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals of grade 10th Science have a chance to come in the board exam?
Chapter 3 (Metals and Non-Metals) of grade 10th Science is important from the exam point of view. Every year questions come from chapter 3 in the exams. There are 28 questions in chapter 3. All the questions of this chapter are significant and can come in the exams. But the most important questions of this chapter that have more chance to come in the board exam are question 1 (page number 40), questions 1, 3, 4 (page number 46), questions 1, 2 (page number 49), question 3 (page number 53), questions 1, 2 (page number 55), and from back exercise questions 1, 6, 7, 8, 9, 12 are important.
Is there any book other than NCERT for chapter 3 of class 10th Science that students can refer to at the time of exams?
Yes, there is a book other than NCERT for chapter 3 of class 10th Science that students can refer to at the exam time. The name of this book is Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur. This book is one of the best books after NCERT. The language of this book is students friendly. Students can easily prepare chapter 3 of class 10th Science from this book.
How much time, students need to do chapter 3 of grade 10th Science?
Students need a maximum of 10-12 days to complete chapter 3 of class 10th Science if they give 1-2 hours per day to this chapter. This time is an approximate time. This time can vary because no students can have the same working speed, efficiency, ability, etc.
Is chapter 3 of 10th Science NCERT easy or tough?
Chapter 3 (Metals and Non-Metals) of class 10th Science is not easy and not tough. It lies in the mid of easy and tough because some part of this chapter is easy, and some part is complex. However, the difficulty level of any topic varies from child to child. So, Chapter 3 (Metals and Non-Metals) of class 10th Science is easy, or tough depends on children also. Some children find it hard, some find it easy, and some find it in the middle of easy and difficult.
What are the main topics of chapter 3 Class 10th Standard Science?
The main topics of chapter 3 (Metals and Non-Metals) of 10th Standard Science are:
- 1. Physical properties of Metals and Non-Metals
- 2. Chemical properties of Metals
- 3. What happens when Metals are burnt in Air?
- 4. What happens when Metals react with Water?
- 5. What happens when Metals react with Acids?
- 6. How do Metals react with Solutions of other Metal Salts?
- 7. The Reactivity Series
- 8. HOW DO METALS AND NON-METALS REA ALS REACT?
- 9. Properties of Ionic Compounds
- 10. OCCURRENCE OF METALS
- 11. Extraction of Metals
- 12. Enrichment of Ores
- 13. Extracting Metals Low in the Activity Series
- 14. Extracting Metals in the Middle of the Activity Series
- 15. Extracting Metals towards the Top of the Activity Series
- 16. Refining of Metals
- 17. Electrolytic Refining
- 18. Corrosion
- 19. Prevention of Corrosion