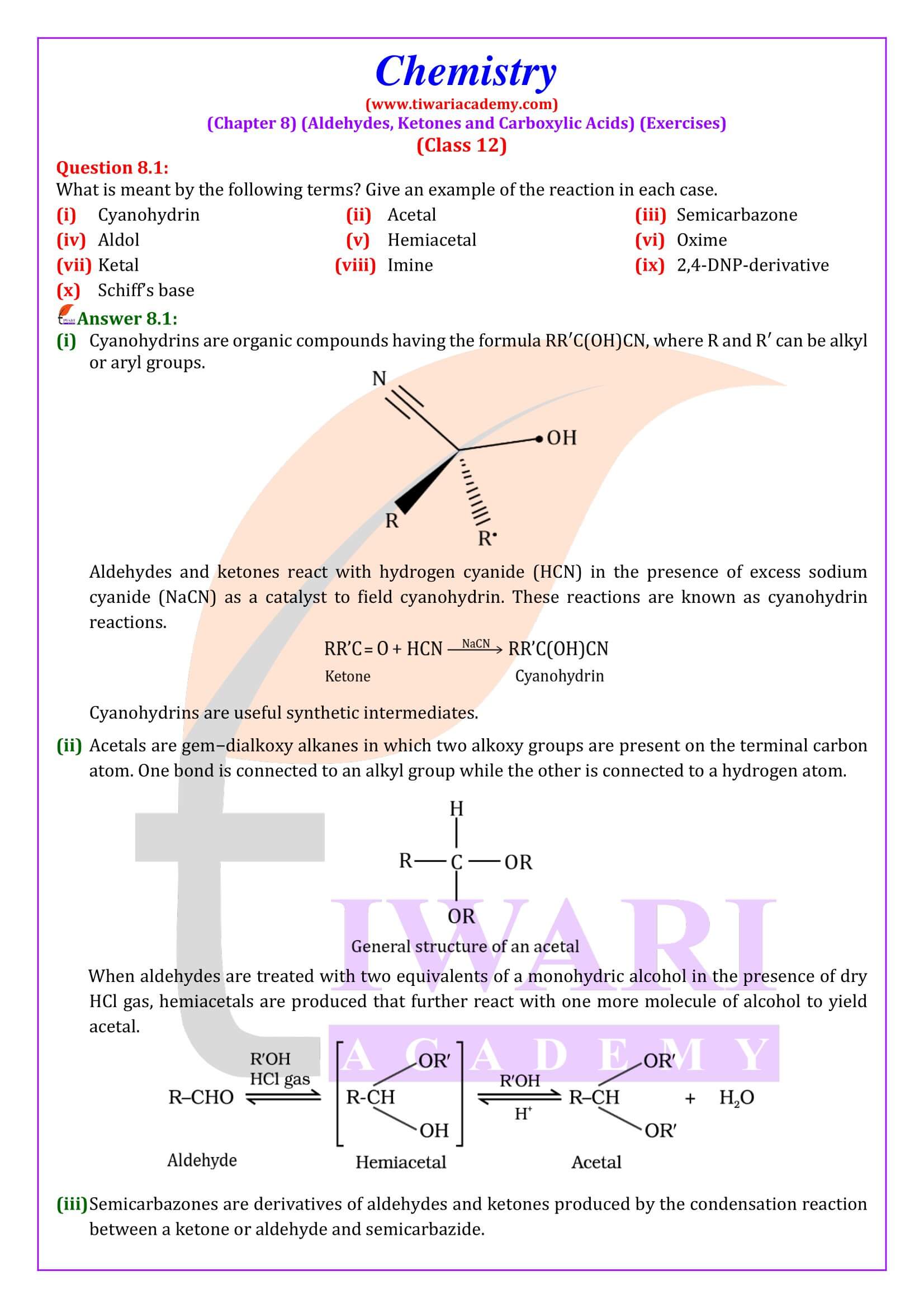
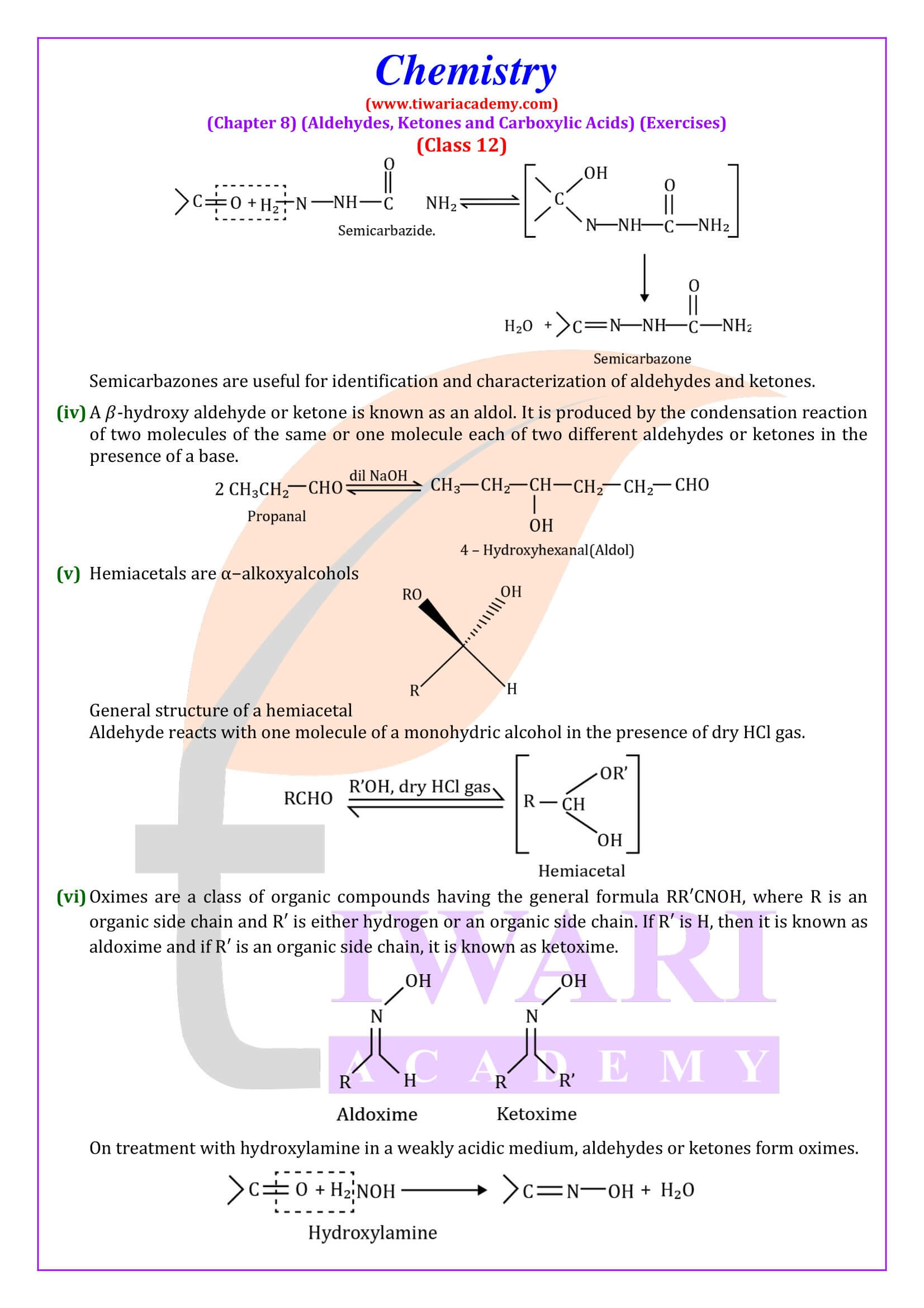
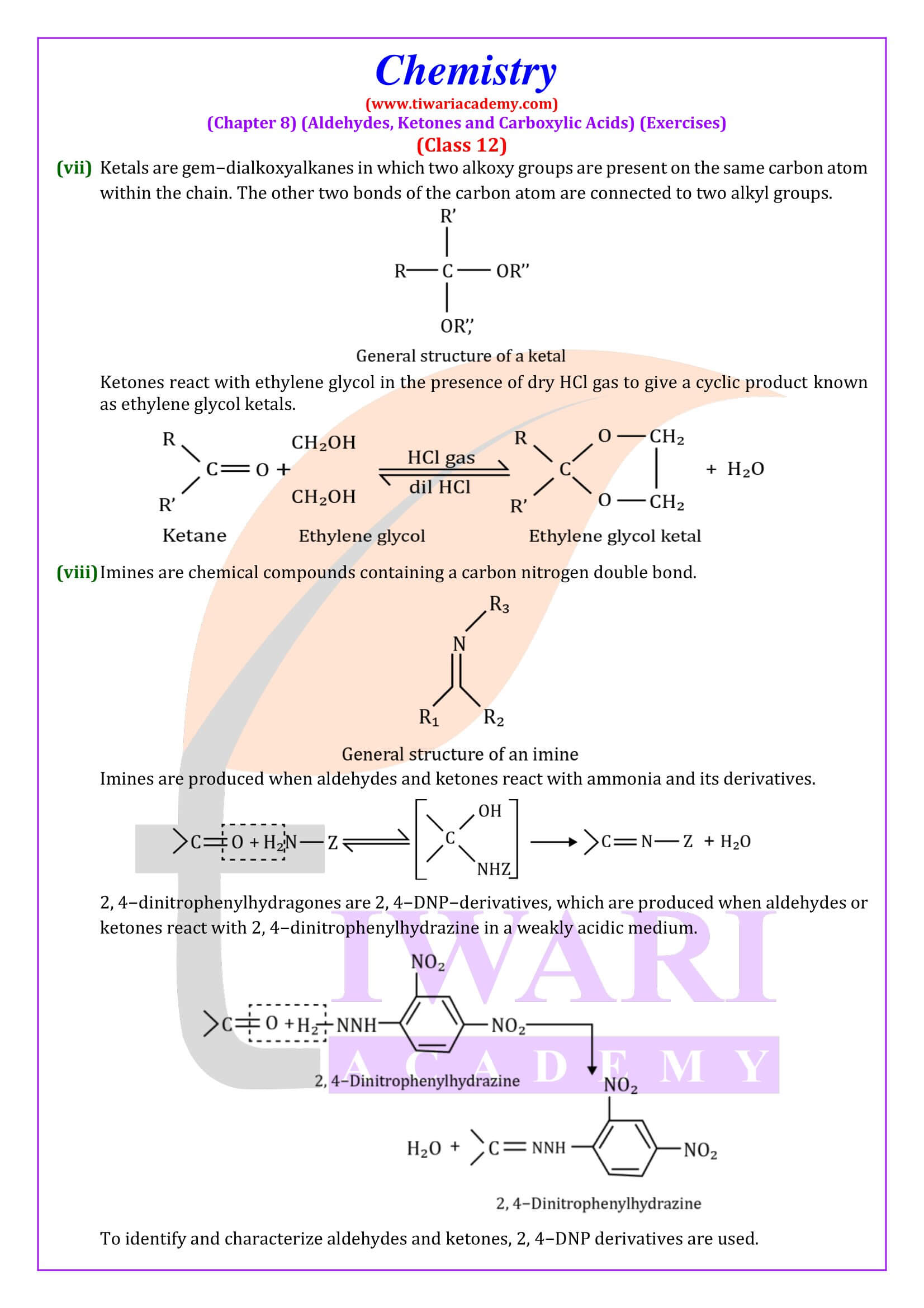
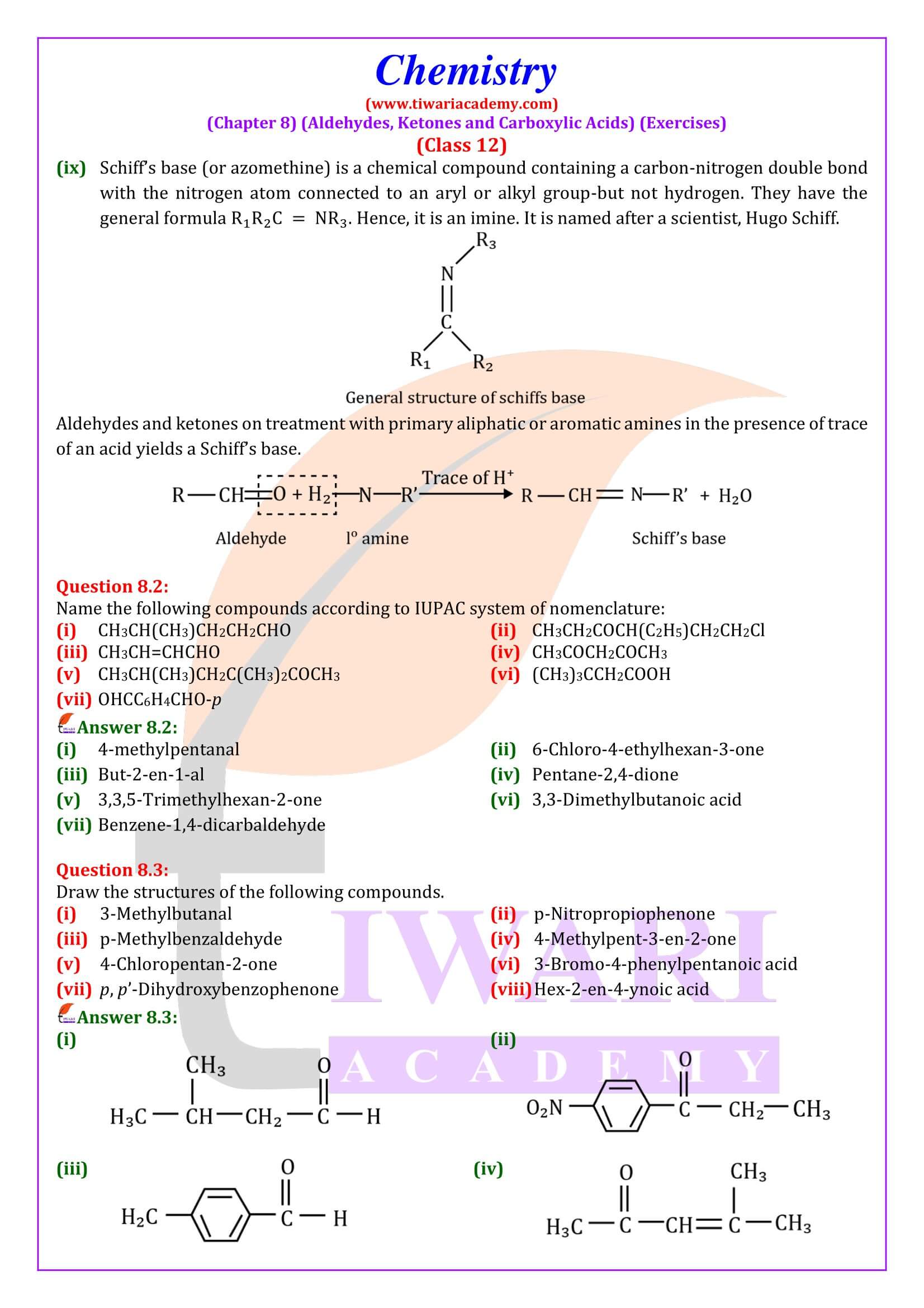
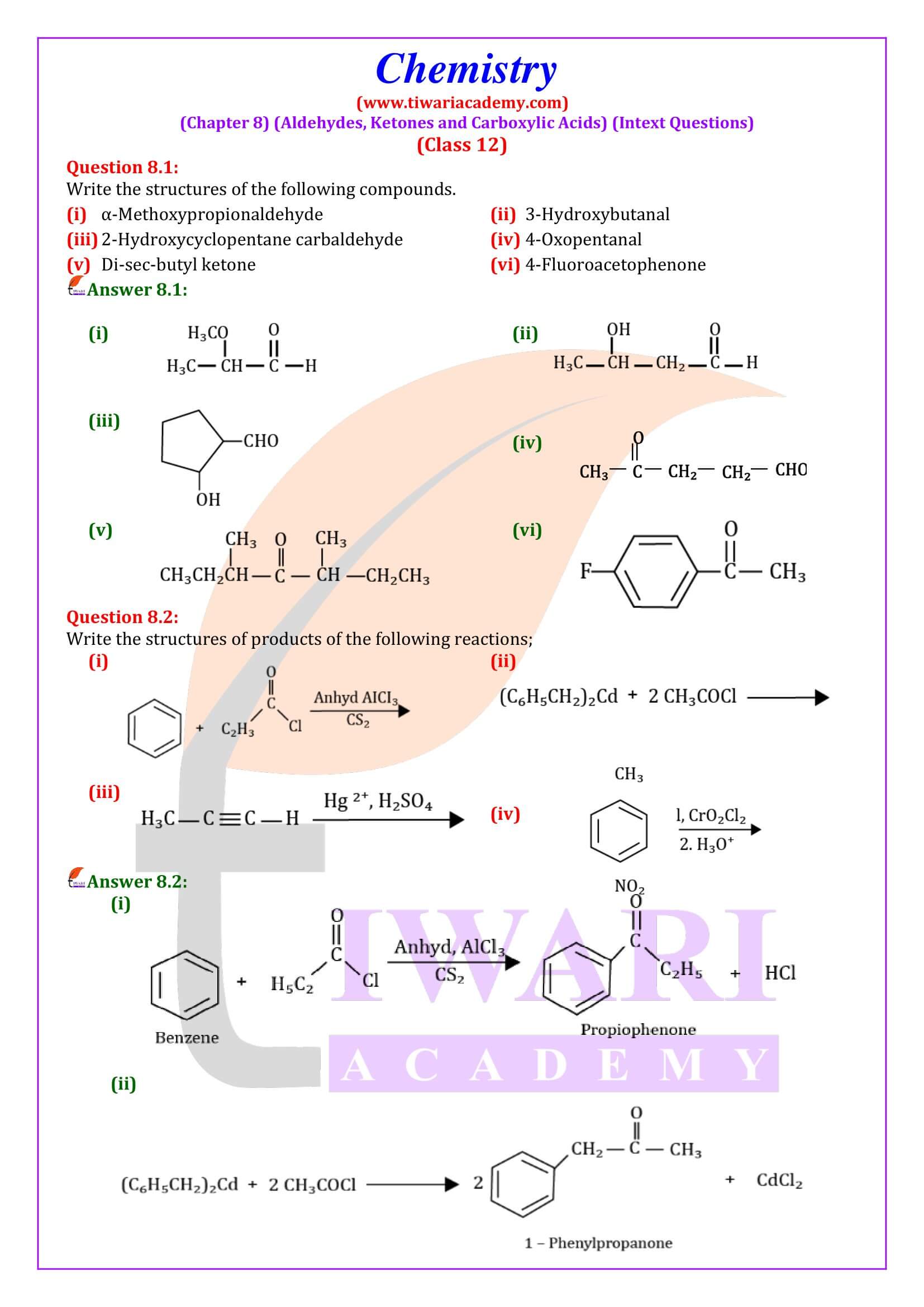
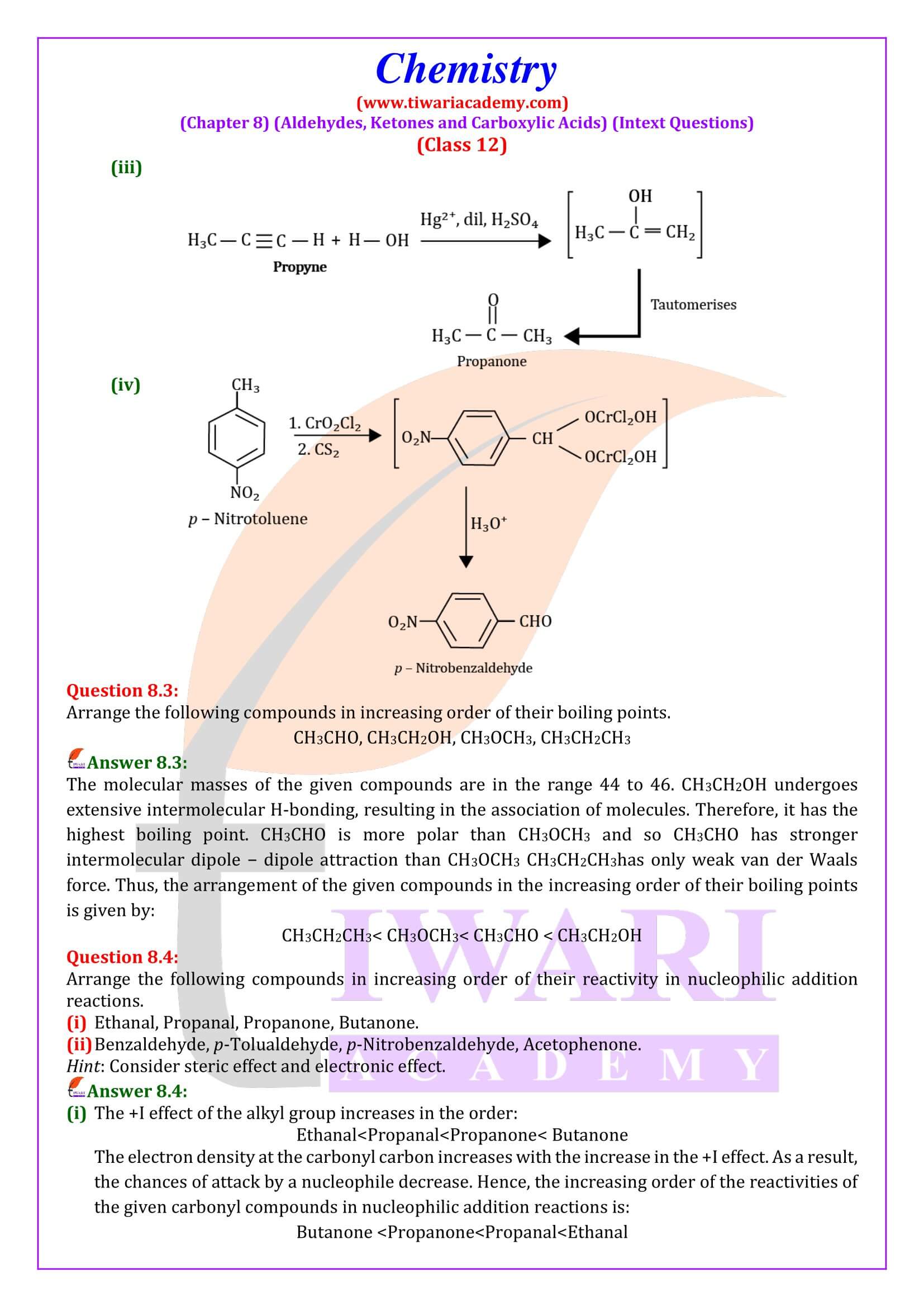
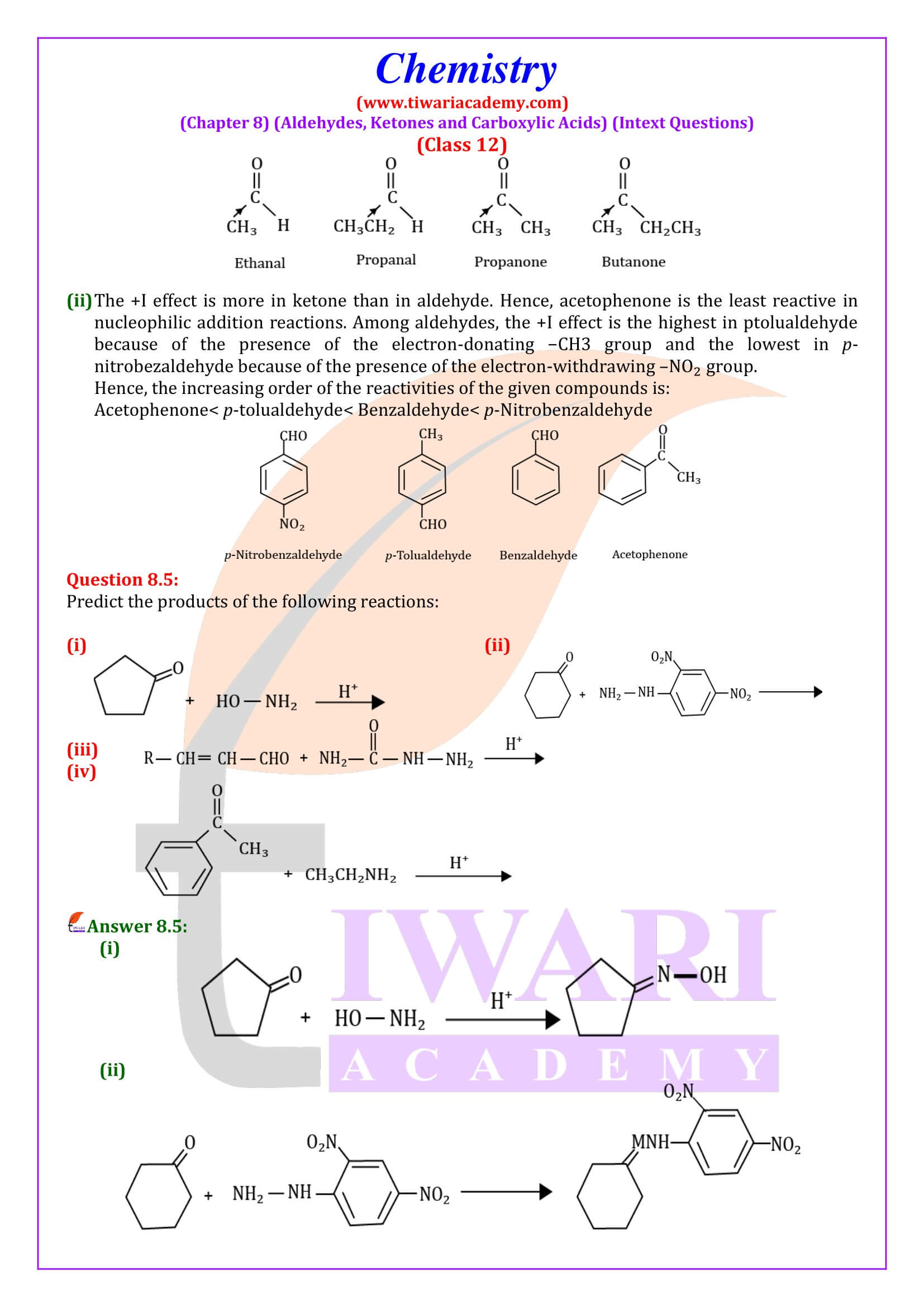
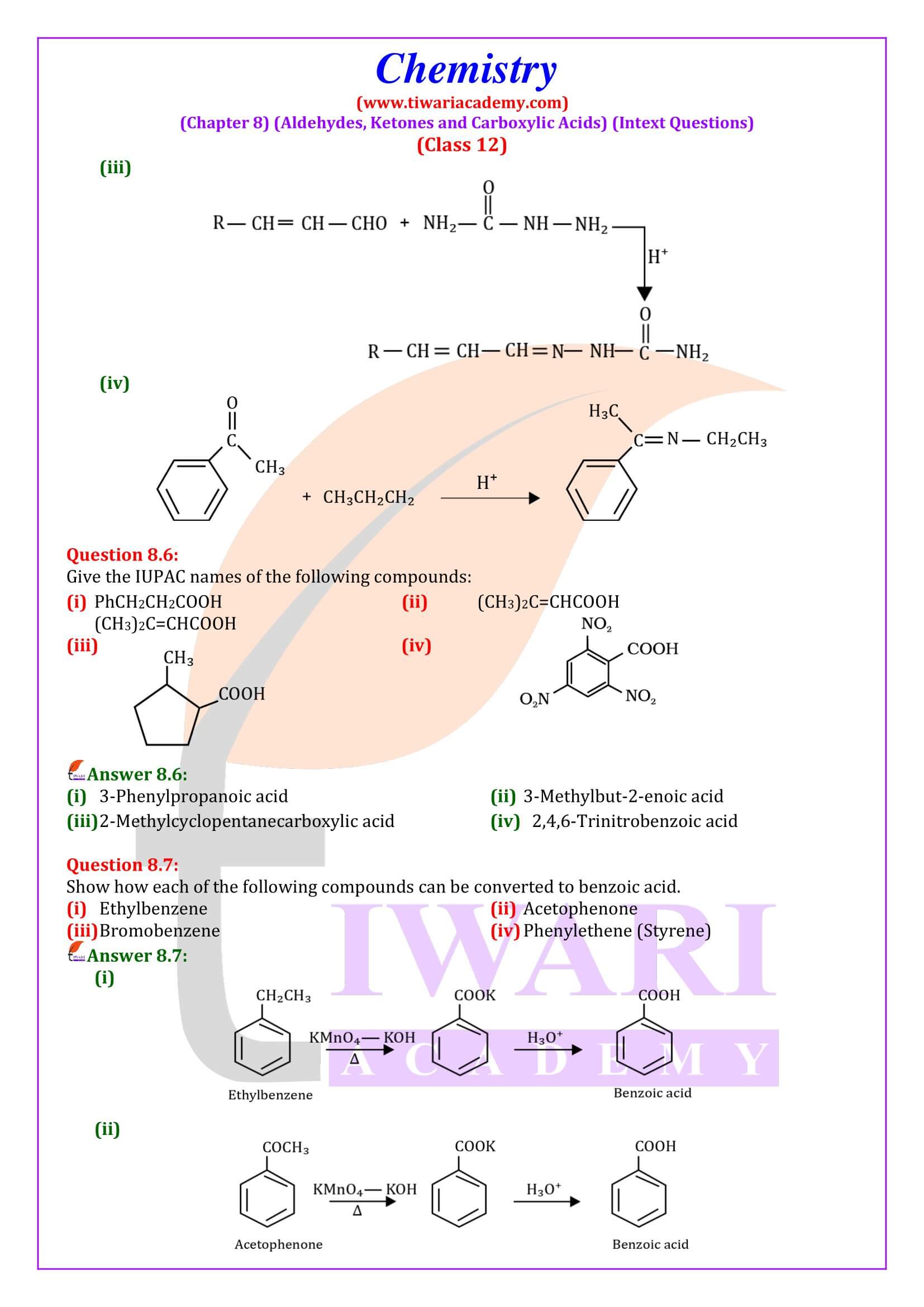
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids in Hindi and English Medium updated for new academic session 2024-25. Get all answers of exercises and intext questions of class 12 Chemistry unit 8 here in simple format.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Question Answers
| Class: 12 | Chemistry |
| Chapter: 8 | Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids |
| Study Material: | Intext and Exercises Solutions |
| Mode of Content: | Images, PDF and Videos |
| Session: | Academic Year 2024-25 |
| Medium: | Hindi and English Medium |
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Aldehydes
Aldehyde, a class of organic compounds in which a carbon atom shares a double bond with an oxygen atom, a single bond with a hydrogen atom, and a single bond with another atom or group of atoms. The double bond between carbon and oxygen is characteristic of all aldehydes and is known as the carbonyl group. Many aldehydes have pleasant odours, and in principle, they are derived from alcohols by dehydrogenation (removal of hydrogen), from which process came the name aldehyde.
Examples of aldehydes: Formaldehyde, Acetaldehyde, Propionaldehyde, Butyraldehyde, Isovaleraldehyde, Benzaldehyde, and Cinnamaldehyde.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 MCQ
Which of the following cannot reduce Fehling’s solution?
Propanone can be prepared from ethyne by
Which is highly soluble in water?
Acetone on heating with ammonia produces
Ketones
A class of organic compounds characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group in which the carbon atom is covalently bonded to an oxygen atom. The remaining two bonds are to other carbon atoms or hydrocarbon radicals.
Examples: the most important ketones are acetone, methylethyl ketone, and cyclohexanone.
12th Chemistry Unit 8 Multiple Choice Questions
Aldehydes other than formaldehyde react with Grignard’s reagent to give addition products which on hydrolysis gives
An alkene C₇H₁₄ on reductive ozonolysis gives an aldehyde with formula C₃H₄O and and a ketone. The ketone is
What is the test to differentiate between penta-2-one and pentan-3-one?
Benzaldehyde can be prepared by the hydrolysis of
Carboxylic Acids
carboxylic acid, any of a class of organic compounds in which a carbon (C) atom is bonded to an oxygen (O) atom by a double bond and to a hydroxyl group (―OH) by a single bond. A fourth bond links the carbon atom to a hydrogen (H) atom or to some other univalent combining group.
Some common examples of carboxylic acids include acetic acid (a component of vinegar) and Formic acid.
Physical Properties
The physical properties of aldehydes and ketones are described as follows.
Methanal is a gas at room temperature. Ethanal is a volatile liquid. Other aldehydes and ketones are liquid or solid at room temperature. The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are higher than hydrocarbons and ethers of comparable molecular masses.
However, the solubility of aldehydes and ketones decreases rapidly on increasing the length of alkyl chain. All aldehydes and ketones are fairly soluble in organic solvents like benzene, ether, methanol, chloroform, etc.
Uses of Aldehydes and Ketones
In chemical industry aldehydes and ketones are used as solvents, starting materials and reagents for the synthesis of other products. Formaldehyde is well known as formalin (40%) solution used to preserve biological specimens and to prepare bakelite (a phenol-formaldehyde resin), urea-formaldehyde glues and other polymeric products.
Acetaldehyde is used primarily as a starting material in the manufacture of acetic acid, ethyl acetate, vinyl acetate, polymers and drugs. Benzaldehyde is used in perfumery and in dye industries. Acetone and ethyl methyl ketone are common industrial solvents. Many aldehydes and ketones, e.g., butyraldehyde, vanillin, acetophenone, camphor, etc. are well known for their odours and flavours.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 Important Questions
How will you distinguish between aldehyde and ketone give one test?
1. Tollen’s Test: Aldehydes give positive Tollen’s test (silver mirror) while ketones do not give any reaction.
2. Fehling’s test: Aliphatic aldehydes on treatment with Fehling’s solution give a reddish brown precipitate (positive result) while aromatic aldehydes and ketones do not.
Why are aldehydes and ketones called carbonyl compounds?
Aldehyde and ketone consist of the divalent unit of carbon and oxygen showing the presence of the carbonyl group. The Carbonyl group is attached to the alkyl or aryl group of the compound. The reactive group in aldehyde and ketone compounds is the carbonyl group.
What is the identification test for aldehyde ketone and carboxylic acid?
Tollens’ test is a qualitative laboratory test used to distinguish between an aldehyde and a ketone, also known as a silver-mirror test.