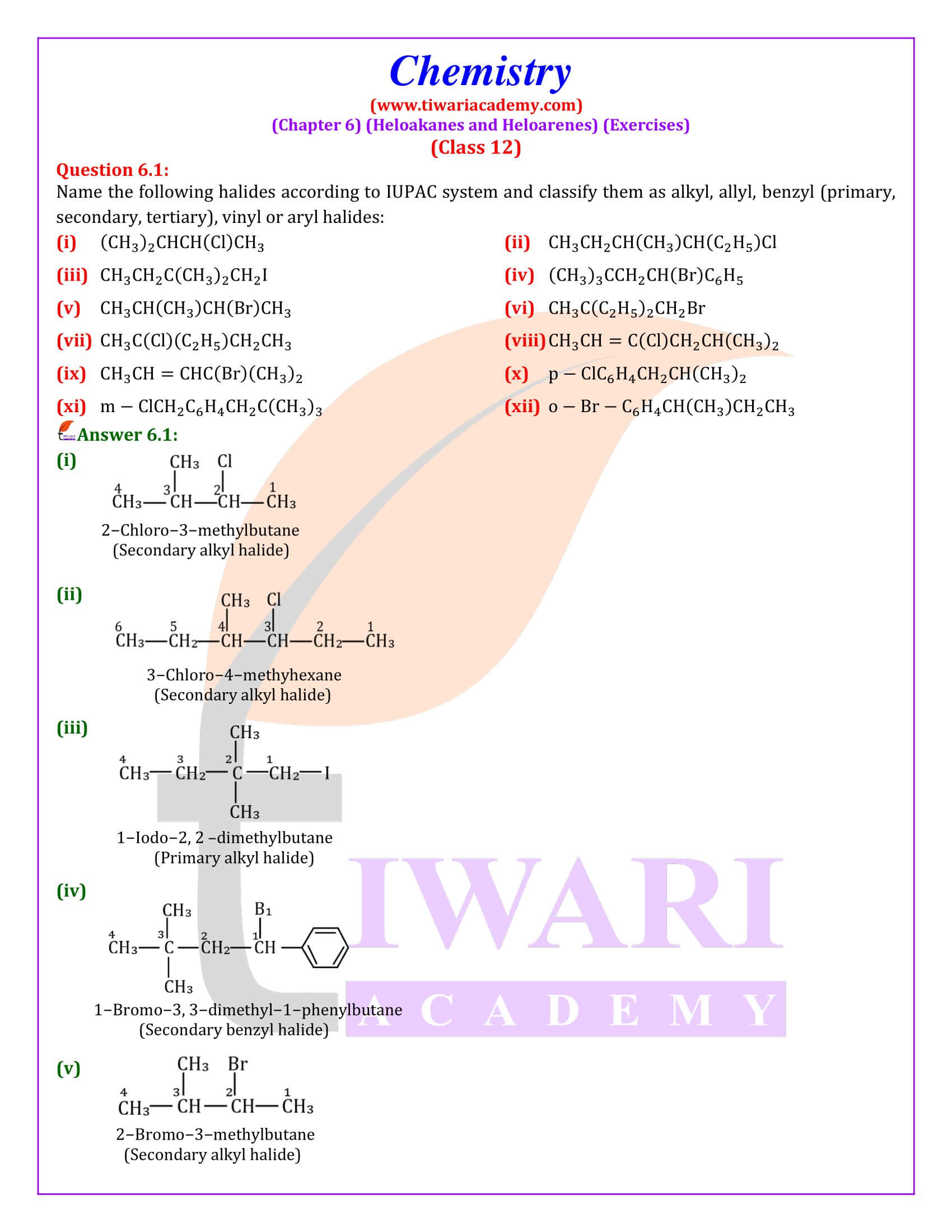
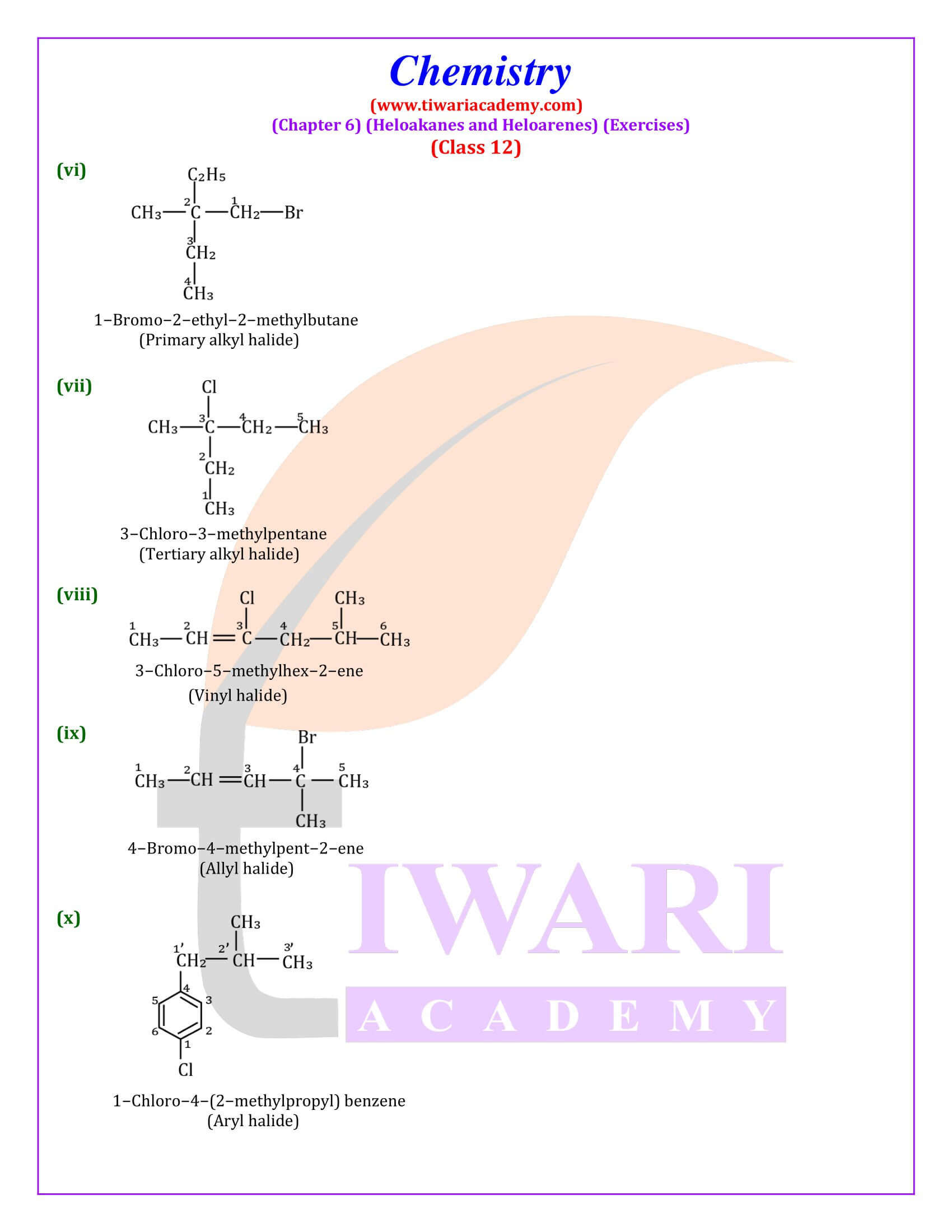
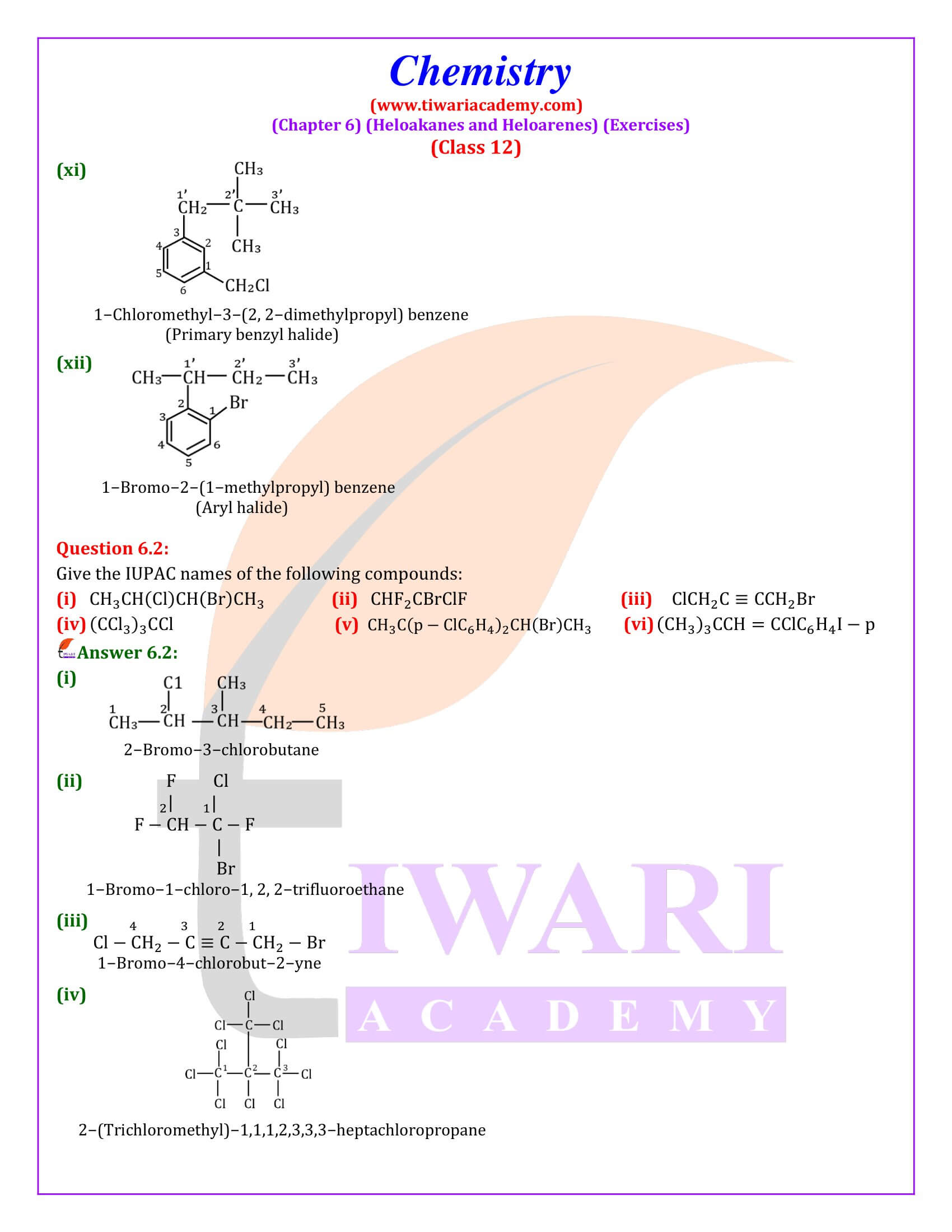
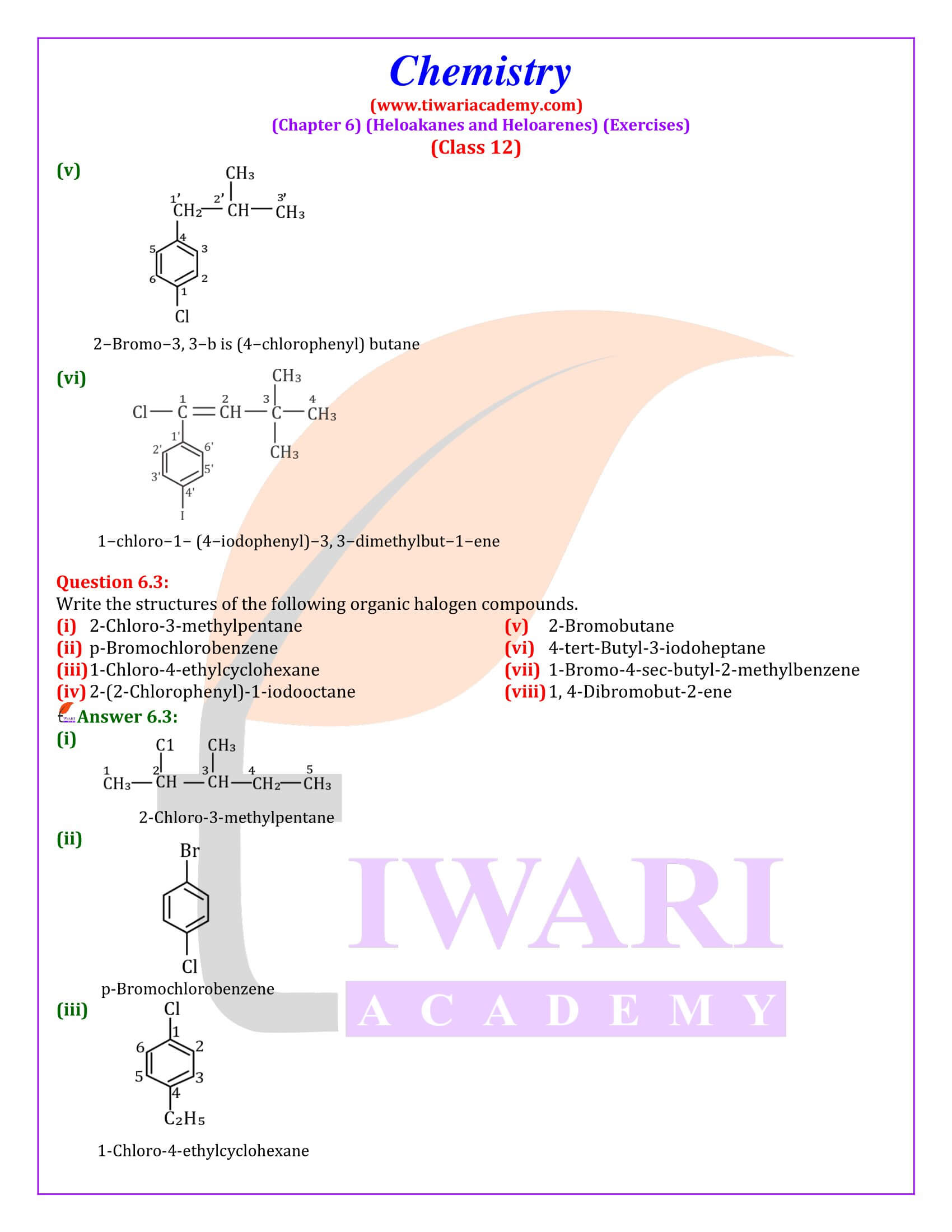
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes with intext and exercises question answers with MCQ for session 2025-26. Class 12 Chemistry unit 6 solutions are given here in Hindi and English Medium format free to access online.
Important Viva Questions for 12th Chemistry
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question Answers
| Class: 12 | Chemistry |
| Chapter: 6 | Haloalkanes and Haloarenes |
| Content: | Study Material and Exercises Solutions |
| Content Format: | Images, PDF, Text and Videos |
| Session: | Academic Year 2025-26 |
| Medium: | English and Hindi Medium |
Haloalkane Compounds
Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula “RX” where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I).
Some Haloalkane compounds are given below with their chemical formula and common name:
| Chemical formula | IUPAC Name | Common Name |
|---|---|---|
| CH₃—Cl | Chloromethane | Methyl chloride |
| CH₃—Br | Bromomethane | Methyl bromide |
| CH₃—I | Iodomethane | Methyliodide |
| F—CH₂—F | Difluoromethane | Methylene fluoride |
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 MCQ
Alkene gives which of the following reactions?
Which of the following is a primary halide?
Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN 1 mechanism?
Halogenation of alkenes is
Haloarenes
Haloarenes are hydrocarbons containing aromatic alkane with one or more hydrogen atom/s replaced by halogens.Examples of haloarenes are chlorobenzene, bromobenzene, iodobenzene, 2-Chlorotoluene etc.
Classification
Haloalkanes and haloarenes may be classified as follows:
1. On the Basis of Number of Halogen Atoms
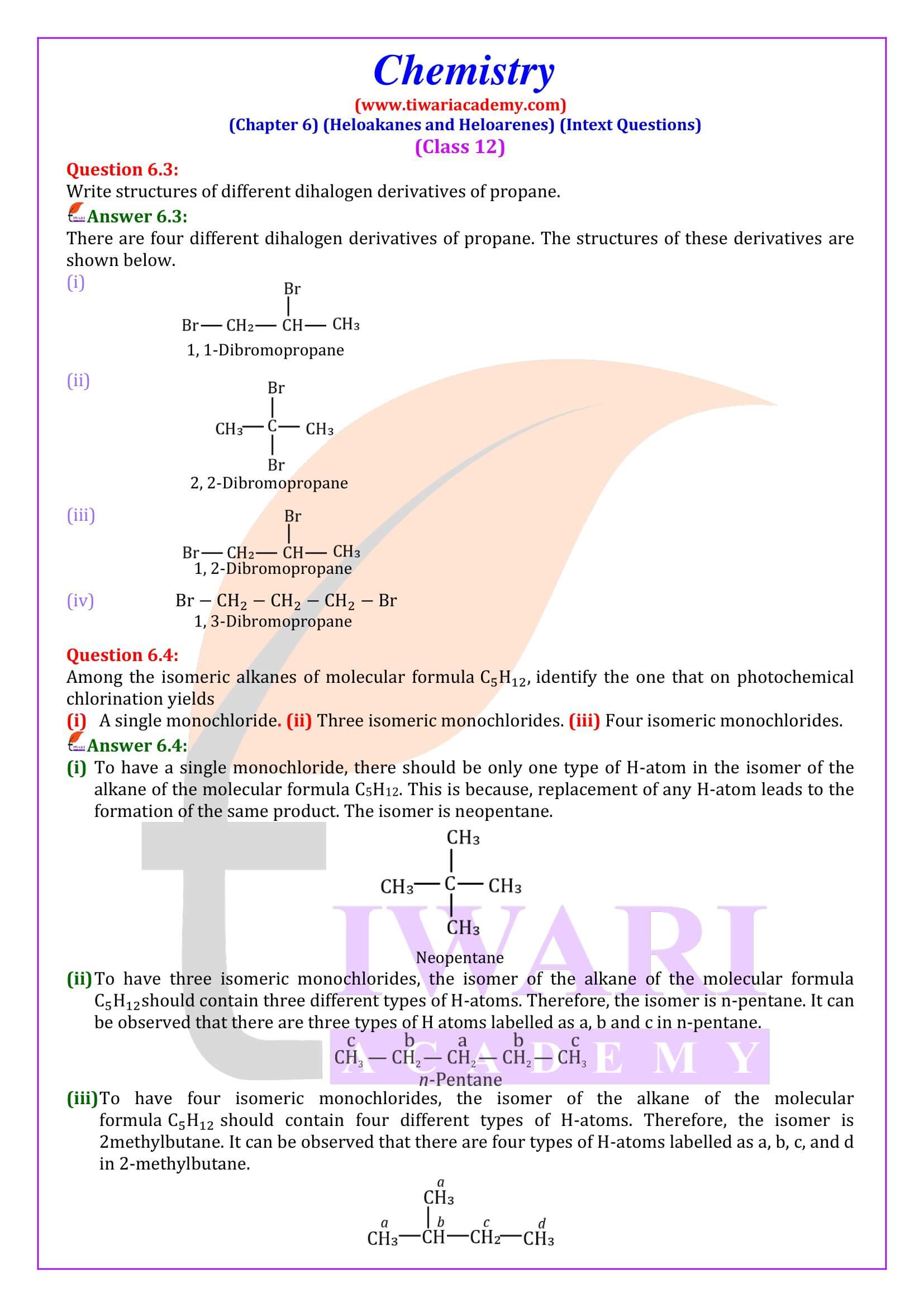
These may be classified as mono, di, or polyhalogen (tri-, tetra-, etc.) compounds depending on whether they contain one, two or more halogen atoms in their structures C₂H₅X, C₂ H₄ X₂, C₃H₅X₃, etc.
Monohalocompounds may further be classified according to the hybridisation of the carbon atom to which the halogen is bonded, as discussed below.
Compounds Containing sp³ C—X Bond (X= F, Cl, Br, I)
- (A) Alkyl halides or haloalkanes (R—X)
- (B) Allylic halides
- (C) Benzylic halides
12th Chemistry Unit 6 Multiple Choice Questions
Criteria for purity of organic solid is
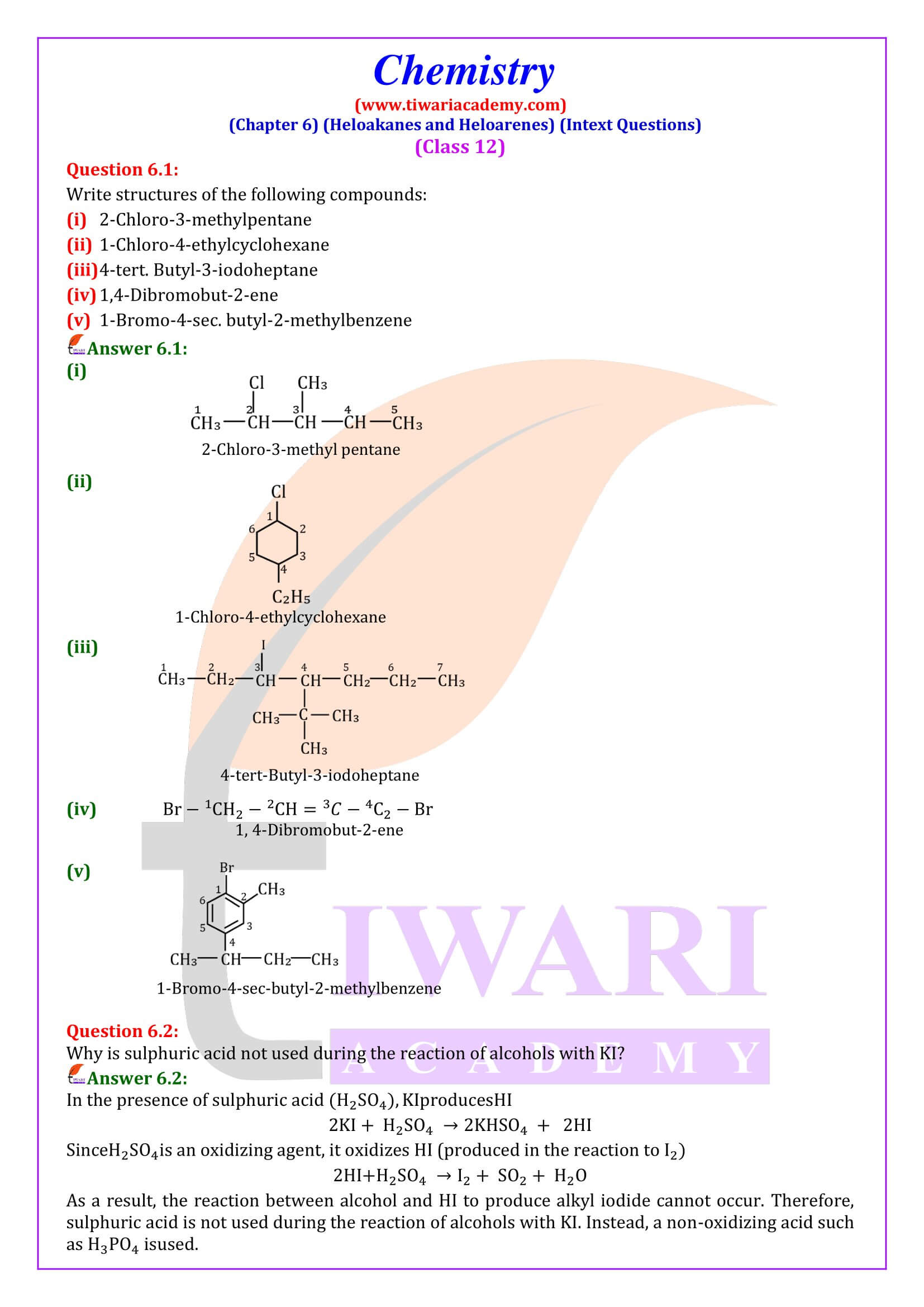
How many structural isomers are possible for a compound with molecular formula C₃H₇Cl?
The synthesis of alkyl fluoride is best accomplished by
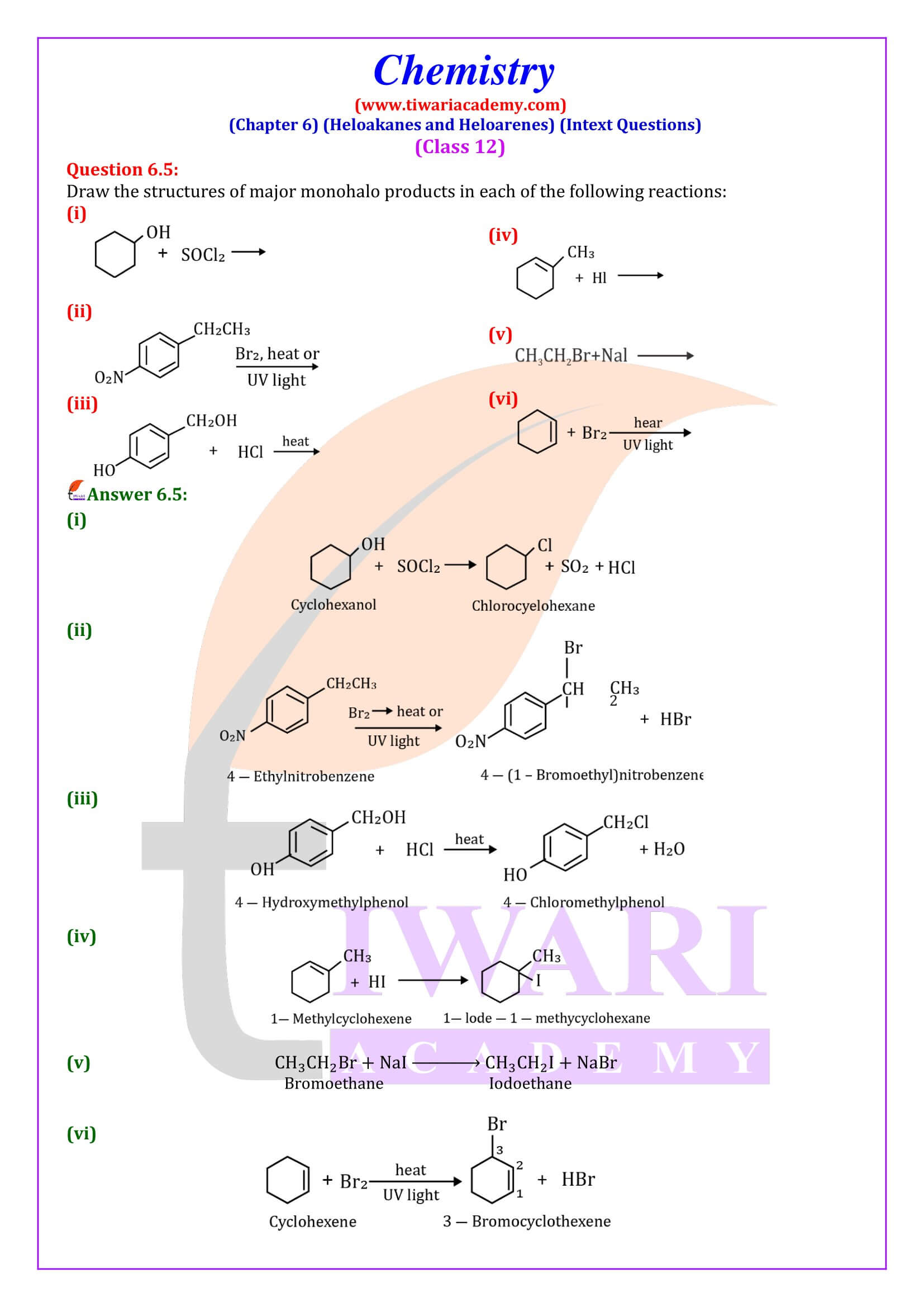
Which of the following compounds can yield only one monochlorinafed product upon free radical chlorination?
Compounds Containing sp² C—X Bond
This class includes:
(A) Vinylic halides
(B) Aryl halides
Physical Properties
Alkyl halides are colourless when pure. However, bromides and iodides develop colour when exposed to light. Many volatile halogen compounds have sweet smell.
Melting and boiling points
Methyl chloride, methyl bromide, ethyl chloride and some chlorofluoromethanes are gases at room temperature. Higher members
are liquids or solids. The boiling points of isomeric haloalkanes decrease with increase in branching. For example, 2-bromo-2- methylpropane has the lowest boiling point among the three isomers.
Density and Solubility
Density
Bromo, iodo and polychloro derivatives of hydrocarbons are heavier than water. The density increases with increase in number of carbon atoms, halogen atoms and atomic mass of the halogen atoms.
Solubility
The haloalkanes are very slightly soluble in water. In order to dissolve haloalkane in water, energy is required to overcome the attractions between the haloalkane molecules and break the hydrogen bonds between water molecules.
Chemical Reactions
The reactions of haloalkanes may be divided into the following categories:
- Nucleophilic substitution
- Elimination reactions
- Reaction with metals.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 Important Questions
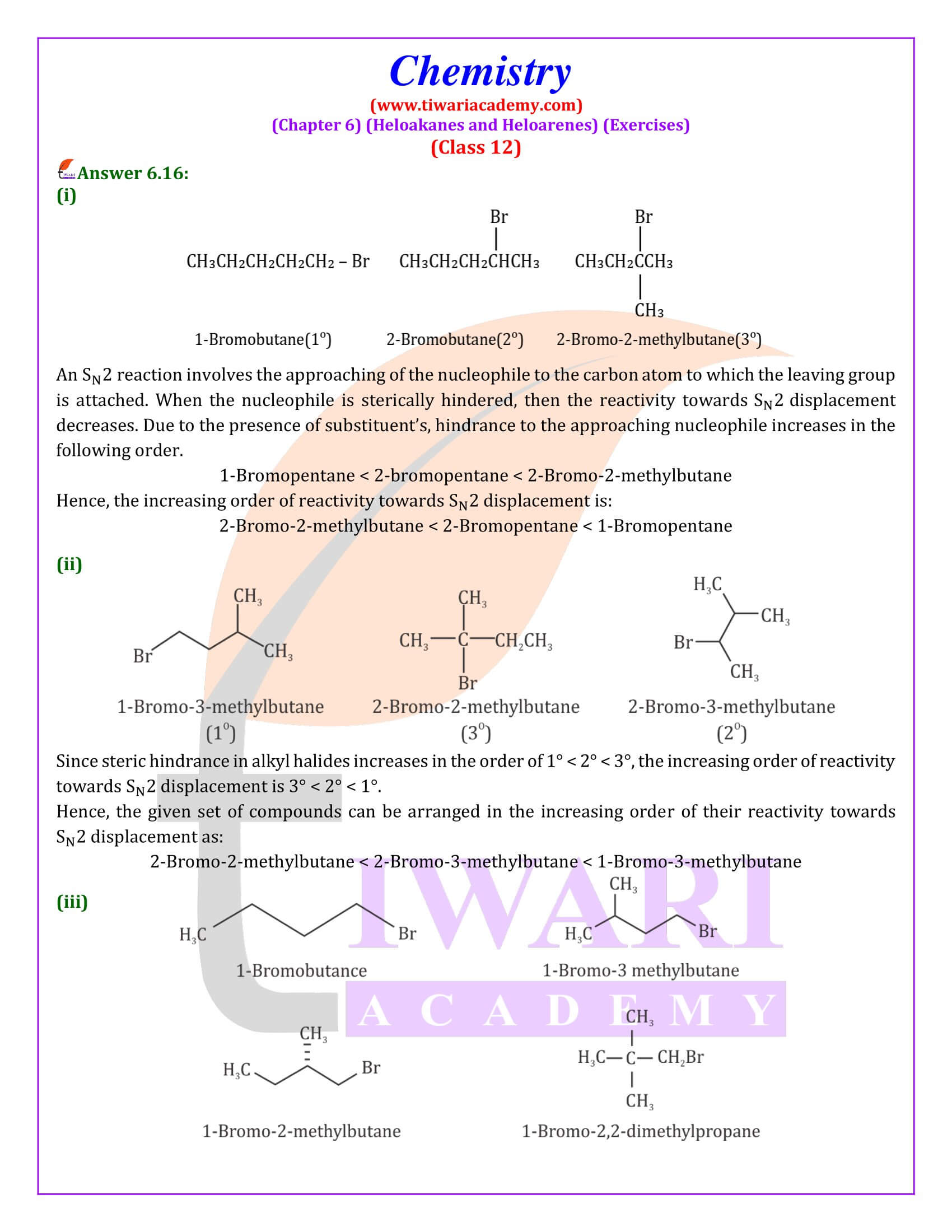
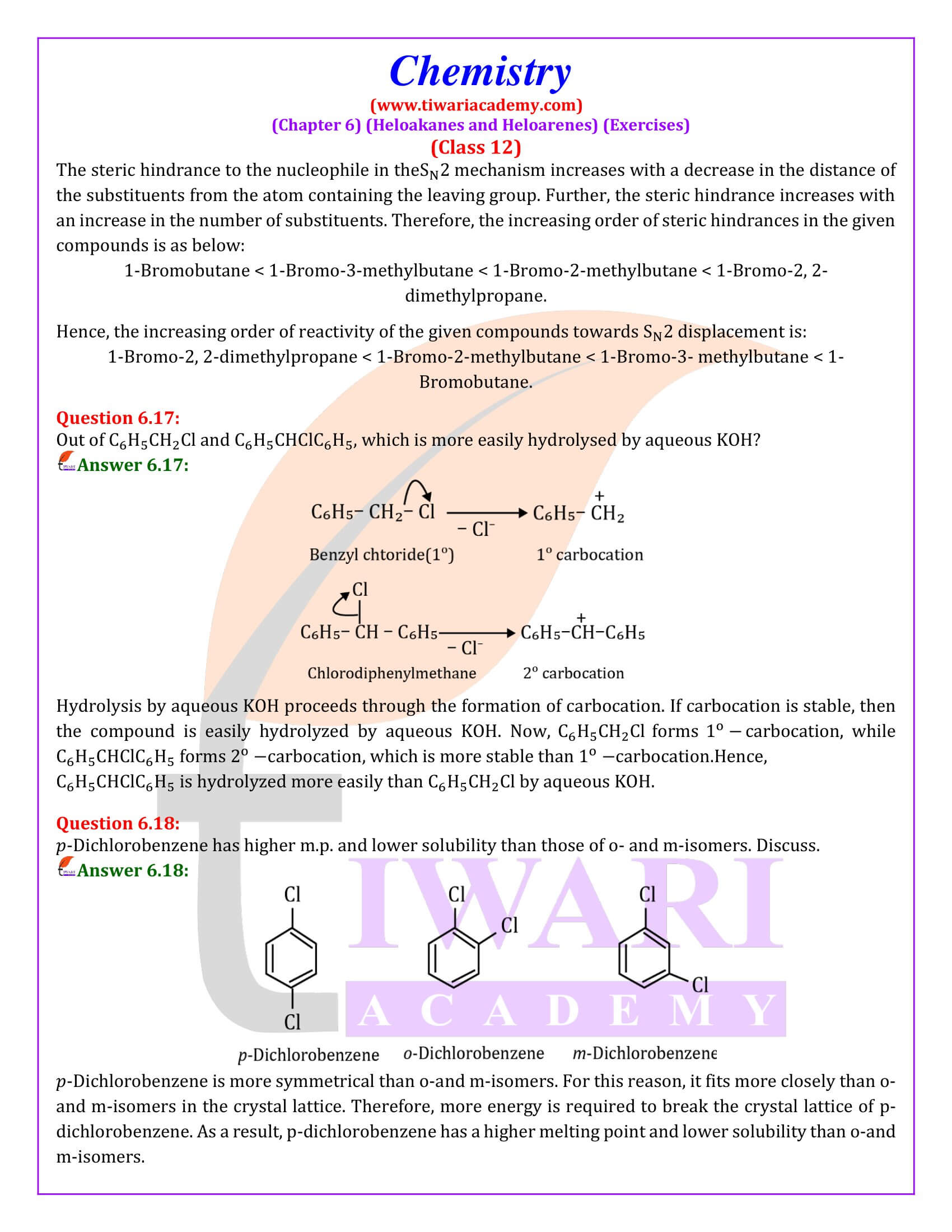
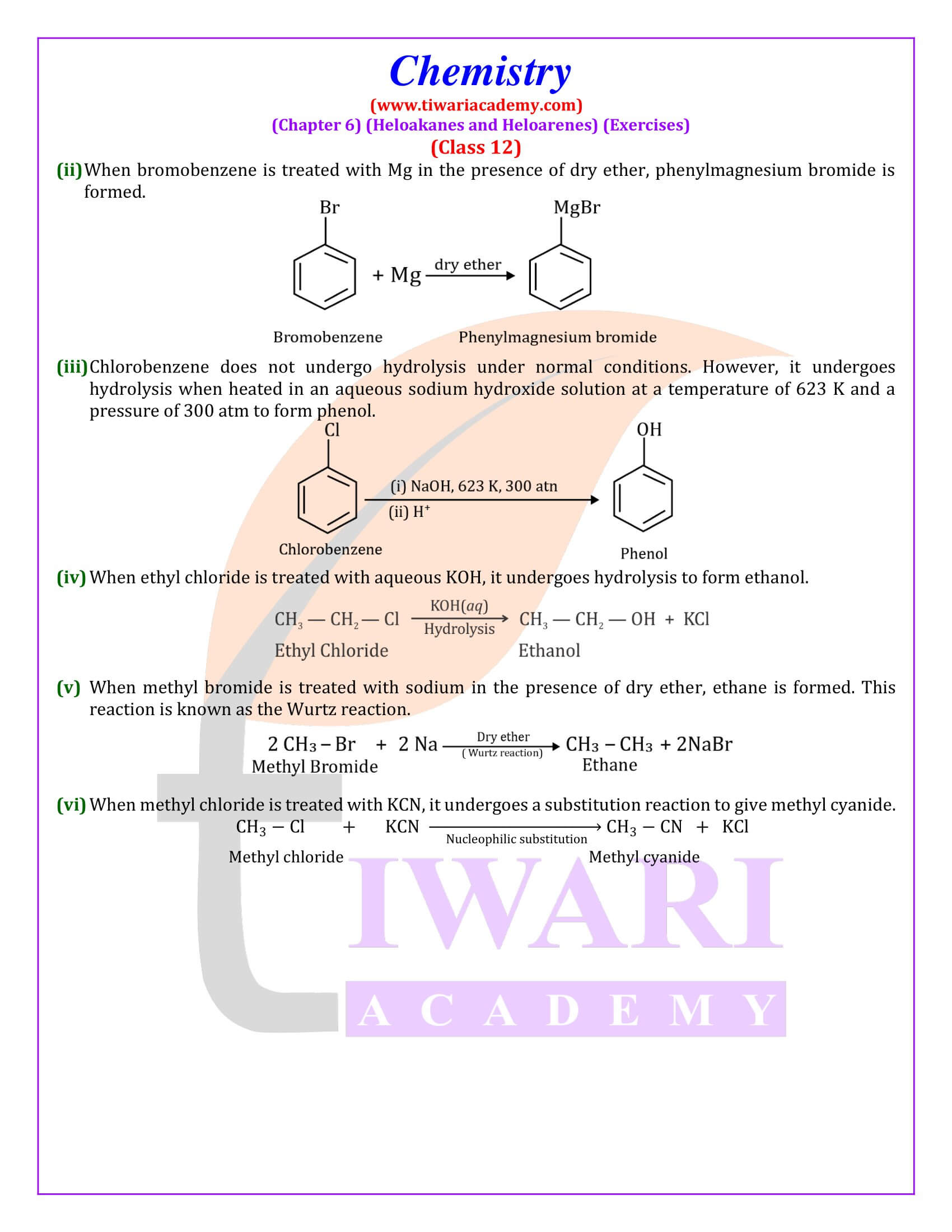
Out of chlorobenzene and benzyl chloride, which one gets easily hydrolysed by aqueous NaOH and why?
Benzyl chloride; Due to resonance, stable benzyl carbocation is formed.
Give reasons for the following:
(i) Benzyl chloride is highly reactive towards the SN₁ reaction.
(ii) 2-bromobutane is optically active but 1-bromobutane is optically inactive.
(iii) Electrophilic reactions in haloarenes occur slowly.
Answer:
(i) Benzyl carbonadon is stabilized by resonance.
(ii) 2-Bromobutane is chiral, therefore, optically active, whereas 1 -chlorobutane is not chiral, therefore optically inactive.
(iii) It is due to —I effect of halogens, it deactivates benzene ring towards electrophilic substitution reactions.
What is the difference between alkyl and aryl group?
Aryl group is a simple aromatic compound where one hydrogen atom is removed from the ring, allowing it to get attached to a carbon chain. The main difference between alkyl and aryl is that alkyl group has no aromatic ring whereas aryl group has an aromatic ring.