NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Coordination Compounds and their examples in Hindi and English Medium prepared for new session 2025-26. Class 12 Chemistry unit 5 intext and exercises answers are useful for CBSE as well as State board students.
Practical Viva Questions for Class 12 Chemistry
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5
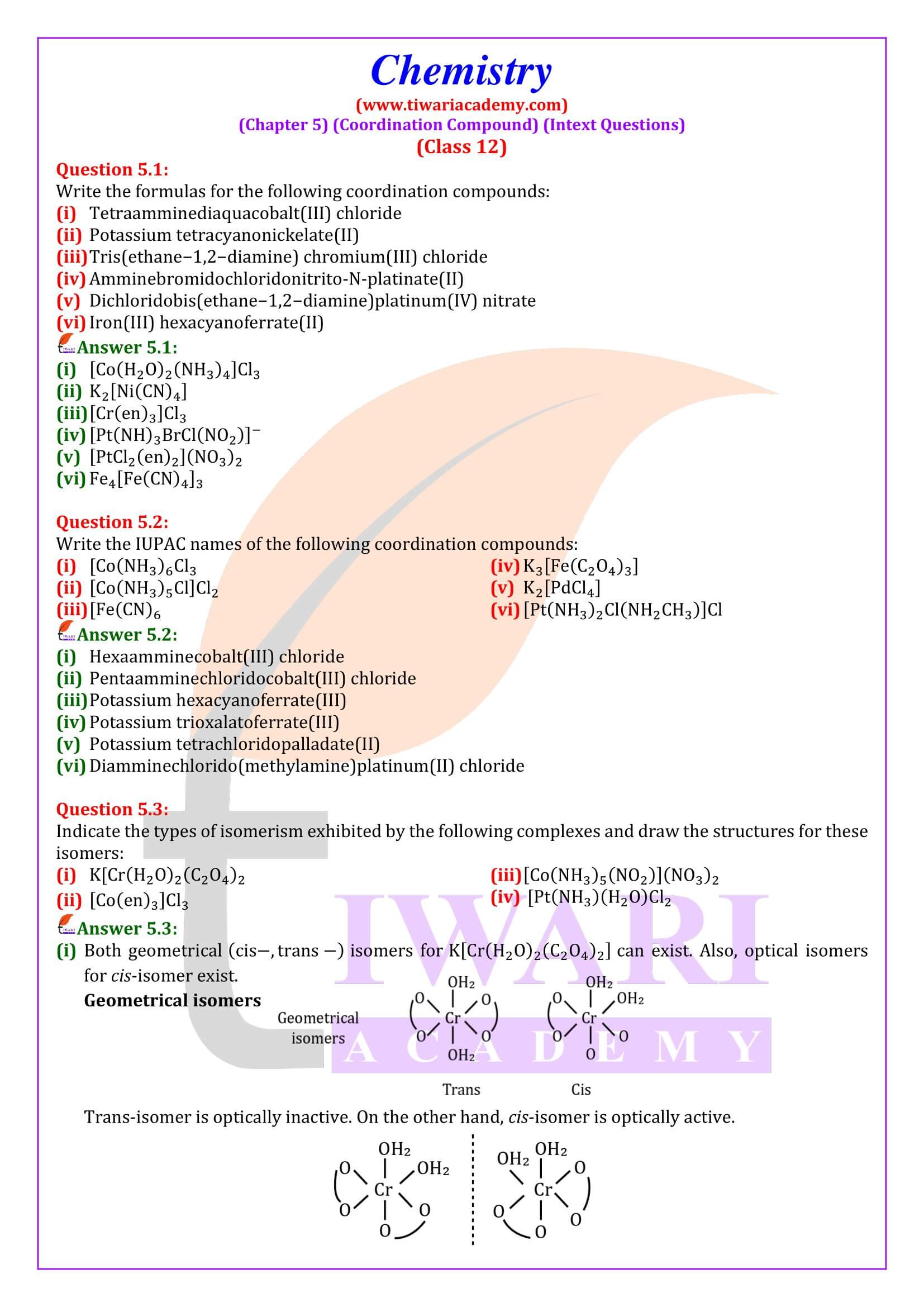
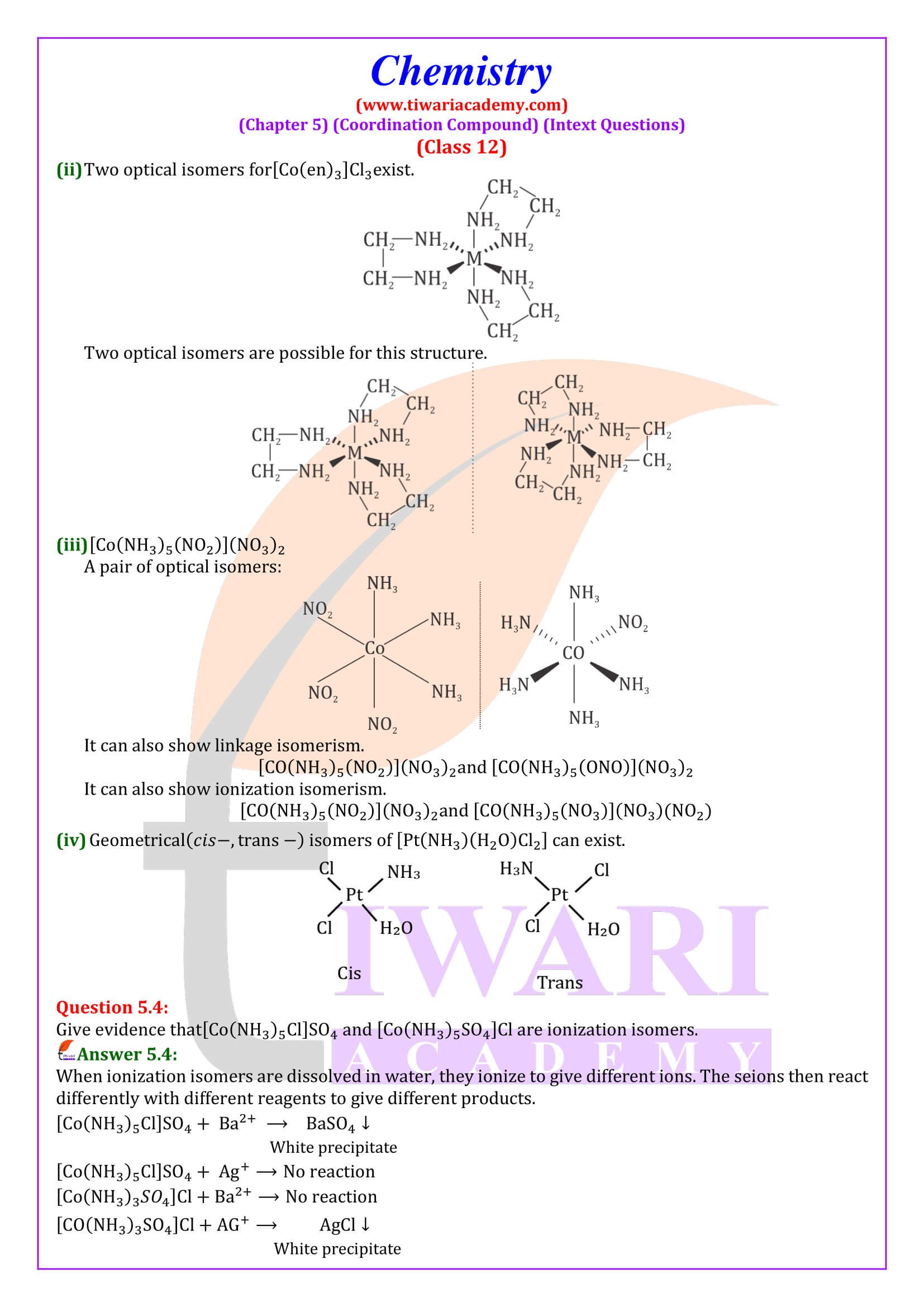
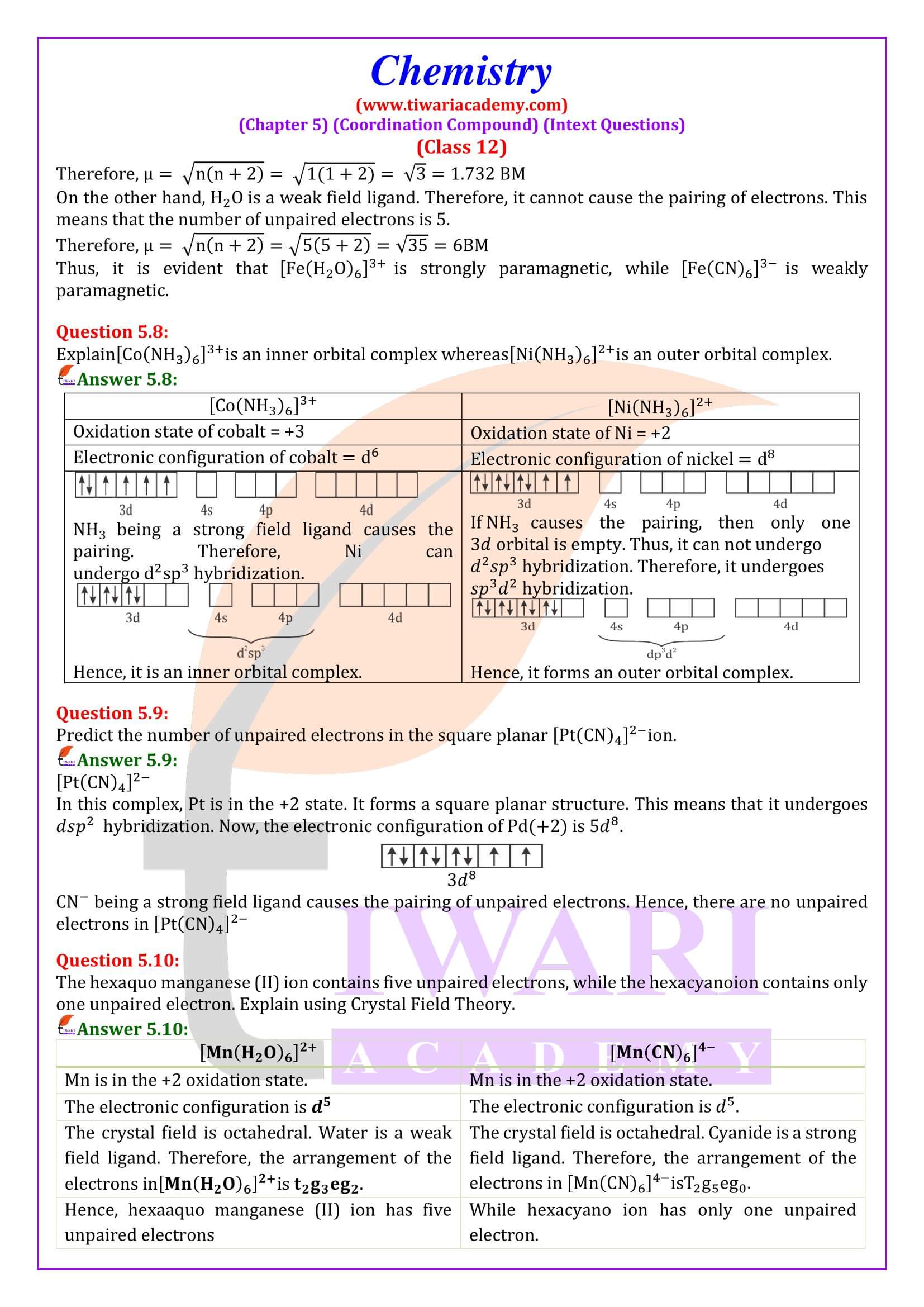
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Coordination Compounds Question Answers
| Class: 12 | Chemistry |
| Chapter: 5 | Coordination Compounds |
| Content: | Exercises and Intext Questions |
| Mode of Content: | Images, Videos and Online Text |
| Session: | Academic Year 2025-26 |
| Medium: | Hindi and English Medium |
Coordination Compounds
Coordination compounds are compounds in which a central metal atom or ion is linked to a number of ions or neutral molecules by coordinate bonds or which contain complex ions.
Examples: K₄[Fe(CN)₆]; [ Cu(NH₃)₄]SO₄; Ni(CO)₄.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 MCQ
According to Werner’s theory of coordination compounds
Which of the following compounds has tetrahedral geometry?
Which of the following ligands form a chelate?
Facial and meridional isomerism will be shown by
Werner’s Theory of Coordination Compounds
Werner in 1898, propounded his theory of coordination compounds. The main postulates are:
- In coordination compounds metals show two types of linkages (valences)-primary and secondary.
- The primary valences are normally ionisable and are satisfied by negative ions.
- The secondary valences are non ionisable. These are satisfied by neutral molecules or negative ions. The secondary valence is equal to the coordination number and is fixed for a metal.
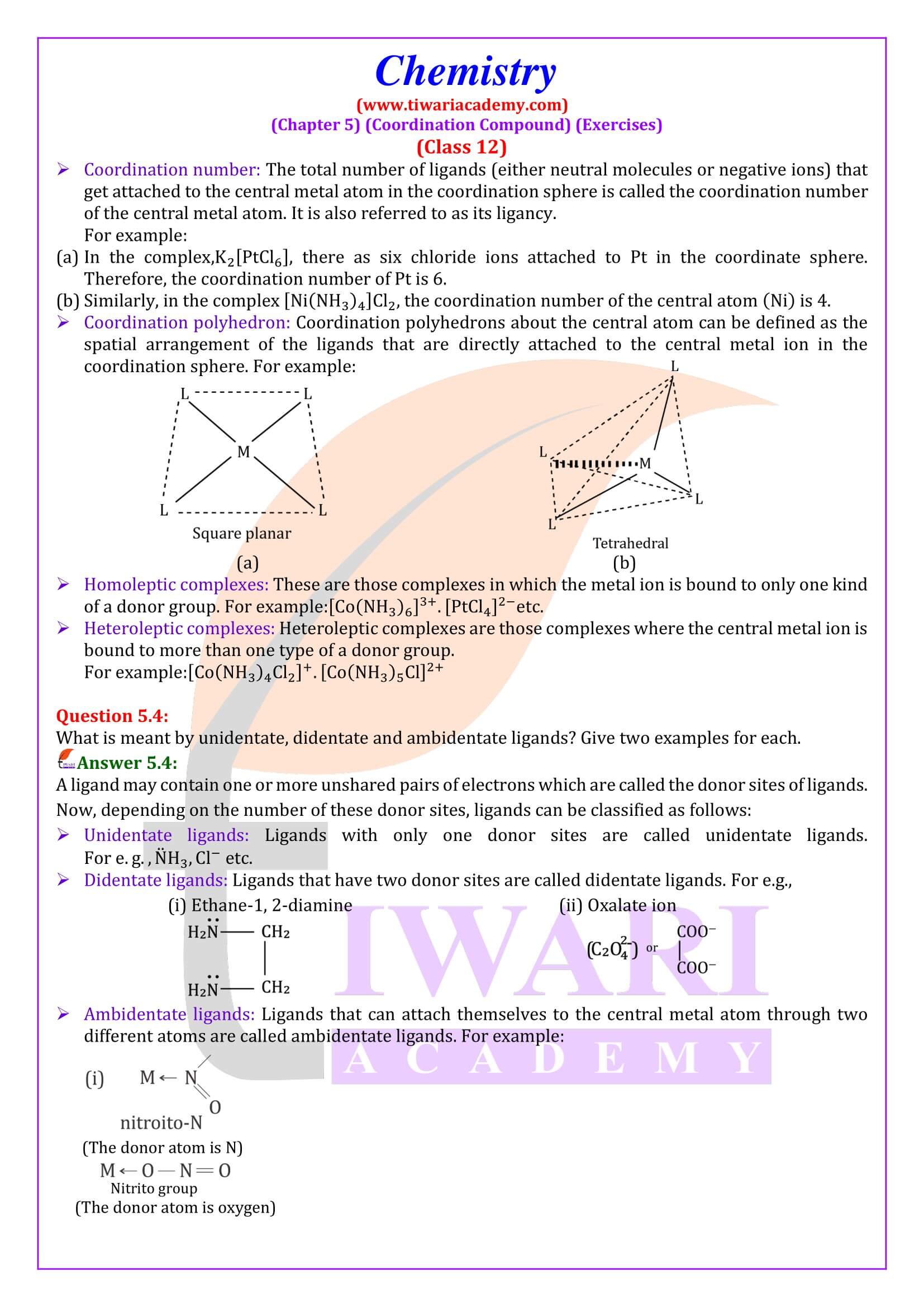
- The ions/groups bound by the secondary linkages to the metal have characteristic spatial arrangements corresponding to different coordination numbers.
In modern formulations, such spatial arrangements are called coordination polyhedra. The species within the square bracket are coordination entities or complexes and the ions outside the square bracket are called counter ions.
12th Chemistry Unit 5 Multiple Choice Questions
The co-ordination number of cobalt in the complex [Co(en)2Br₂]Cl₂ is
Which metal is present in vitamin B₁₂ cyanocobalamin?
According to Lewis, the ligands are
A chelating agent has two or more than two donor atoms to bind to a single metal ion. Which of the following is not a chelating agent?
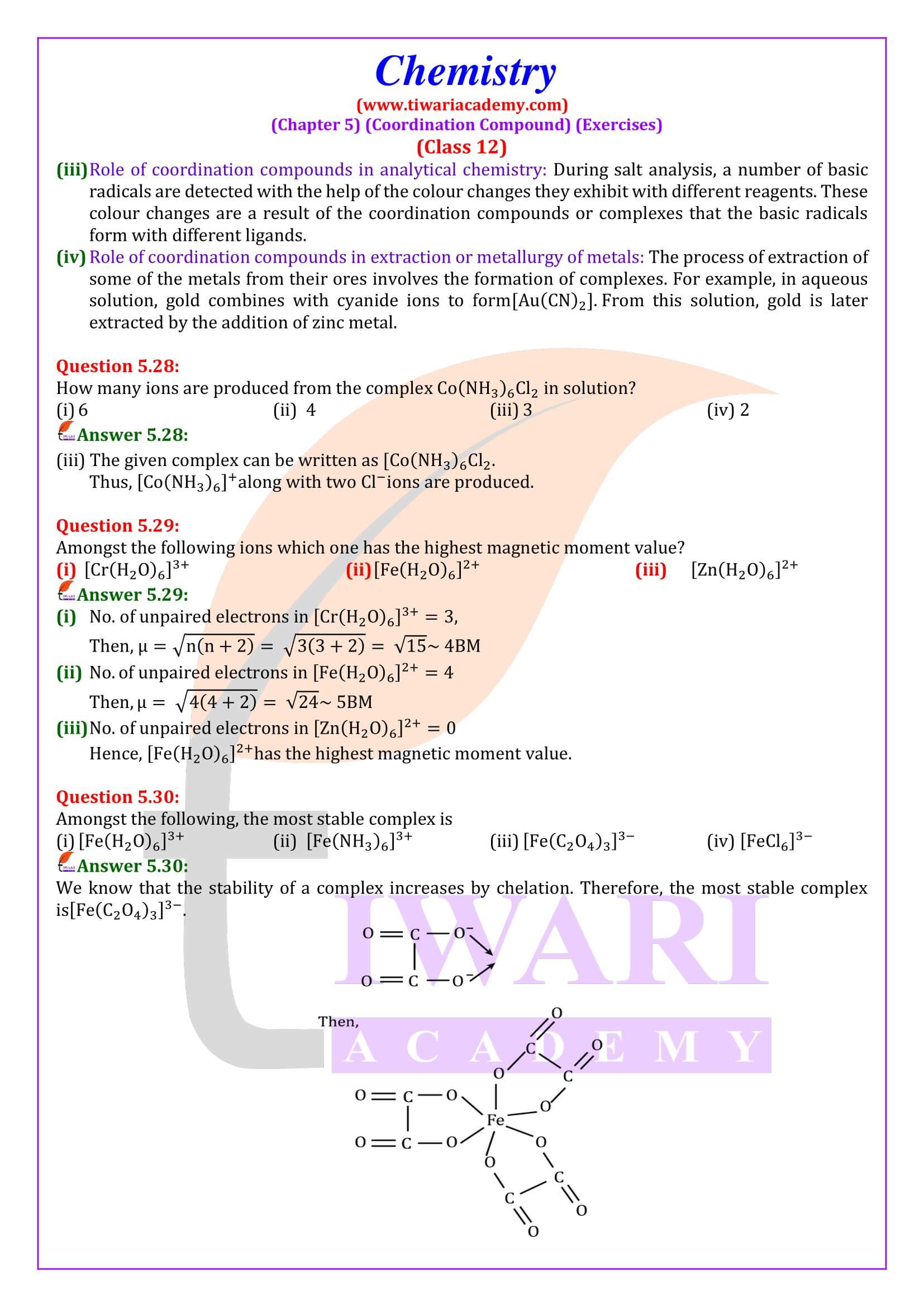
Difference between a double salt and a complex
Both double salts as well as complexes are formed by the combination of two or more stable compounds in stoichiometric ratio. However, they differ in the fact that double salts such as carnallite, KCl.MgCl₂.6H₂O, Mohr’s salt, FeSO₄.(NH₄)2SO₄.6H₂O, potash alum, KAl(SO₄)₂.12H₂O, etc. dissociate into simple ions completely when dissolved in water. However, complex ions such as [Fe(CN)6]₄⁻ of K₄[Fe(CN)6] do not dissociate into Fe²⁺ and CN⁻ ions.
Nomenclature of Coordination Compounds
Nomenclature is important in Coordination Chemistry because of the need to have an unambiguous method of describing formulas and writing systematic names, particularly when dealing with isomers. The formulas and names adopted for coordination entities are based on the recommendations of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry.
Bonding in Coordination Compounds
Many approaches have been put forth to explain the nature of bonding in coordination compounds viz. Valence Bond Theory (VBT), Crystal Field Theory (CFT), Ligand Field Theory (LFT) and Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT). According to this theory, the metal atom or ion under the influence of ligands can use its (n-1)d, ns, np or ns, np, nd orbitals for hybridization to yield a set of equivalent orbitals of definite geometry such as octahedral, tetrahedral, square planar and so on. These hybridised orbitals are allowed to overlap with ligand orbitals that can donate electron pairs for bonding.
Importance and Applications of Coordination Compounds
The coordination compounds are of great importance. These compounds are widely present in the mineral, plant and animal worlds and are known to play many important functions in the area of analytical chemistry, metallurgy, biological systems, industry and medicine.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Important Questions
What are coordination compounds give two examples?
A chemical compound in which the central ion or atom (or the coordination centre) is bound to a set number of atoms, molecules, or ions is called a coordination entity. Some examples of such coordination entities include [CoCl₃(NH₃)₃], and [Fe(CN)₆]⁴⁻.
What are the applications of coordination compounds Class 12?
Applications of coordination compounds
(i) They are used in estimation of hardness of water as calcium and, magnesium ions form complexes with EDTA.
(ii) It is used in estimation and detection of metal ions.
(iii) It is used in Extraction of metals.
(iv) It is used in medicines like cis platin is used in treatment of cancer.
Why are tetrahedral complexes high spin?
It is because of small splitting energy gap, electrons are not forced to pair, therefore, there are large number of unpaired electrons, i.e. high spin.