Question Wise Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Solutions
Class 7 Science Chapter 3 NCERT Answers
Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Hindi Medium
Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Extra Questions
Class 7 Science Chapter 3 MCQ
Class 7 Science NCERT Book Download
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 all Subjects
Get here NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Heat in English Medium and Hindi Medium to download in PDF format updated for Session 2024-25. The question answers of chapter 3 of 7th Science are modified according to new NCERT book issued for 2024-25 exams.
| Class: 7 | Science |
| Chapter 3: | Heat |
| Content: | NCERT Solutions, MCQ, Extra Questions |
| Academic Session: | 2024-25 |
| Medium: | English and Hindi Medium |
Class 7 Science Chapter 3 NCERT Solutions
All the questions are down with complete explanation and in simplified manner. The explanation of chapter with keywords and important topics are also given through videos. Hindi Medium videos and English Medium video are separately given below to use free. NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 3 are also available in Video based on new academic session 2024-25. Offline apps on PLAY STORE based on new NCERT Books are also free to download. Ask your questions or reply to your friend’s questions through Discussion Forum. All the contents of Tiwari Academy website or apps are free to use. No charges or restriction is set to use these solutions and other contents.
Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Answers
NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science Chaper 3 in English
Important Terms to be Covered in Class 7 Science Chapter 3
1. Hot and Cold
In this part of the content focuses on the effects of heat energy in different materials with practical activities which help you to better understanding the concept. In our day to day life, we come across a number of objects. Some of them are hot, and some of them are cold. Tea is hot, and ice is cold. In winter we usually feel cool inside the house. If we come out in the Sun, due to effect of light, we feel warm. In summer, we feel hot even inside the house. How do we know whether an object is hot or cold? By using a reliable device for the measurement of the hotness of an object, is called ‘Thermometer’.
2. Measuring Temperature
In this part of the content introduces the importance of thermometer in our life. Do you know that the thermometer that measures our body temperature is called ‘Doctor’s Thermometer’ or ‘Clinical Thermometer’? And a clinical thermometer consists of a long, narrow, uniform glass tube with a bulb at one end. This bulb contains mercury which is the main source of the measurement. You will also find two types of scale on Clinical thermometer. 35 to 40 degrees in ‘Celsius scale’ and 94 to 108 degrees in ‘Fahrenheit scale’. Do you know the normal temperature of the human body is 37 degrees Celsius, and it is the average body temperature of us? You will be surprised to know that different types of thermometers are used for different purposes. As maximum and minimum thermometer are used for the weather of a day. Clinical thermometer is used for human body temperature. How do we measure the temperature of other objects?
3. Laboratory Thermometer
In this part, we will learn about the process of getting the temperature of different objects. For measuring the temperature of different objects, we use ‘Laboratory thermometer’ for them. The range of a laboratory thermometer is generally from -10 degree Celsius to 110 degrees Celsius. Remember, we do not use a clinical thermometer for measuring the temperature of other objects and also not be use laboratory thermometer for the human body. In both cases, we use a separate device to measure the temperature. We can compare the temperatures of Water from different sources.
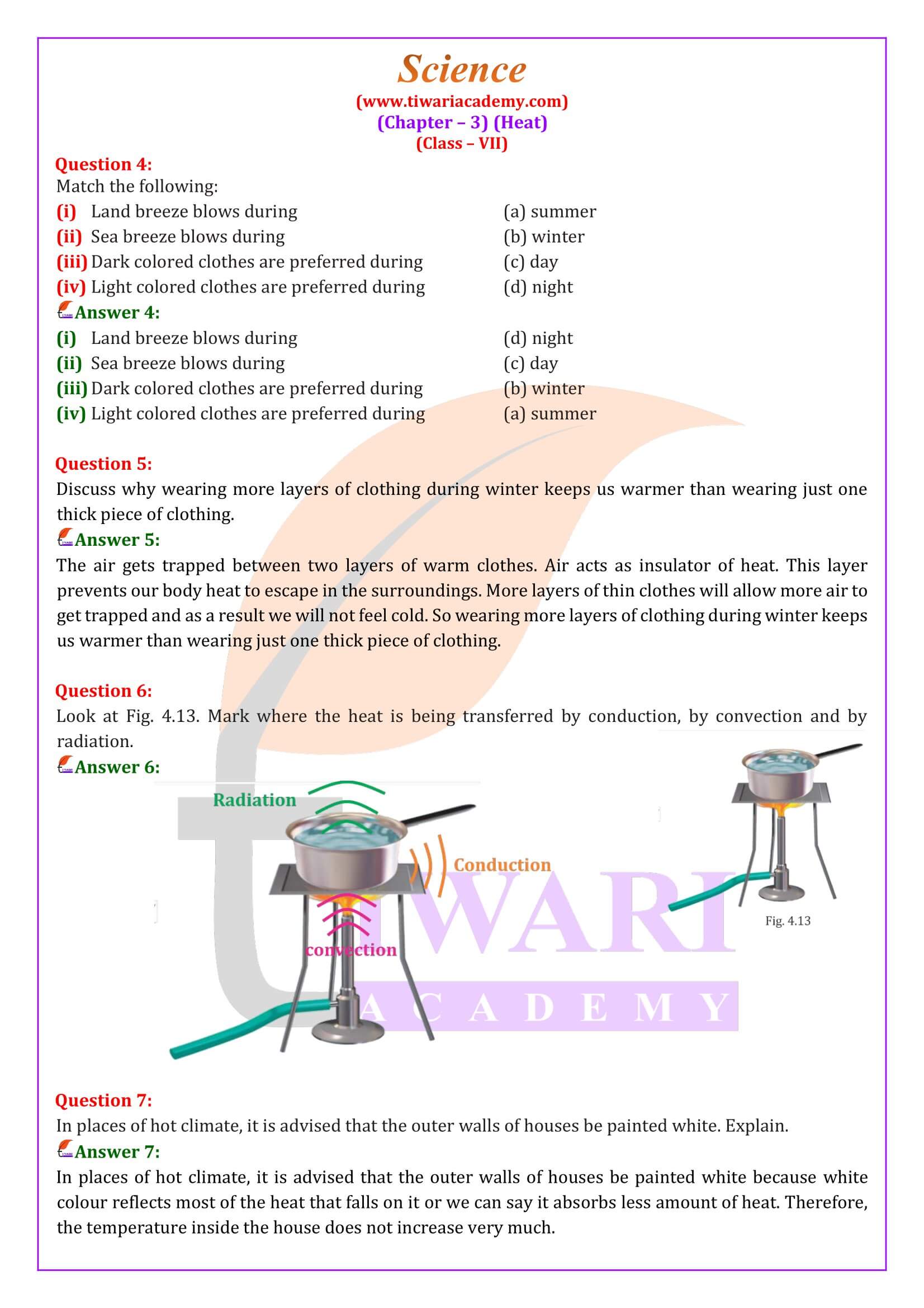
4. Transfer of Heat
In this part of the content helps you to understand the various methods of heat transfer with the help of different practical activities. You might have observed that frying pan becomes hot when kept on a flame. When the pan is removed from the flame, it slowly cools down. Do you know how it happens? Heat is a form of energy which spontaneously transferred from a hotter object to a colder object, called ‘Conduction’. The material which allows heat to pass through them easily is called ‘Conductors’. And those materials which do not pass heat through them are called ‘Insulators’.
5. Convection and Radiation
You will be surprised to know the facts, how water is boiling. When water is heated, the water near the flame gets hot. Hot water rises and cold water moves down towards the source of heat. This water also gets hot, and rises and water from the sides move down again. This process continues until the whole water gets heated. This mode of heat transfer is known as ‘Convection’. When we come out in the sun, we feel warm. It cannot reach us by conduction or convection. Remember, from the sun, the heat comes to us by another process known as ‘Radiation’. The motion of heat by radiation does not require any medium. When we sit in front of a room heater, we get heat by this process.
6. Clothes We Wear in Summer and Winter
You know that in summer we prefer light-coloured clothes and in winter we usually wear dark-coloured clothes. Do you know what the reason behind it is? The dark colour absorbs more heat, and therefore we feel comfortable with dark coloured clothes in winter. And light-coloured clothes reflect most of the light that falls on them and, therefore, we feel more comfortable to wear them in summer. As you know, in the winter we use woollen clothes. Wool is a poor conductor of heat.
Moreover, there is air trapped in between the wool fibres. This air prevents the flow of heat from our body to the cold surroundings. So, we feel warm. Uses of heat energy include but are not limited to: cooking, drying, heating, smoking, baking, water heating, cooling and manufacturing. Besides that, heat from the sun generates our weather patterns and gives energy to the growing green plants that provide the food and oxygen for life on Earth. Thus, the sun is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms.
Important Questions for Practice
1. Paheli and Boojho measured their body temperature. Paheli found hers to be 98.6 °F and Boojho recorded 37°C. Which of the following statement is true?
(a) Paheli has a higher body temperature than Boojho.
(b) Paheli has a lower body temperature than Boojho.
(c) Both have normal body temperature.
(d) Both are suffering from fever.
2. A beggar wrapped himself with a few layers of newspaper on a cold winter night. This helped him to keep himself warm because
(a) friction between the layers of newspaper produces heat.
(b) air trapped between the layers of newspaper is a bad conductor of heat.
(c) newspaper is a conductor of heat.
(d) newspaper is at a higher temperature than the temperature of the surrounding.
3. A marble tile would feel cold as compared to a wooden tile on a winter morning, because the marble tile
(a) is a better conductor of heat than the wooden tile.
(b) is polished while wooden tile is not polished.
(c) reflects more heat than wooden tile.
(d) is a poor conductor of heat than the wooden tile.
4. Shopkeepers selling ice blocks usually cover them with jute sacks. Explain why.
5. Why is it advised not to hold the thermometer by its bulb while reading it?
6. To keep her soup warm Paheli wrapped the container in which it was kept with a woolen cloth. Can she apply the same method to keep a glass of cold drink cool? Give reason for your answer.
7. You may have noticed that a few sharp jerks are given to clinical thermometer before using it. Why is it done so?
8. In a mercury thermometer, the level of mercury rises when its bulb comes in contact with a hot object. What is the reason for this rise in the level of mercury?
Answers of Important Questions
1 (c)
2 (b)
3 (a)
4. They must use some insulating material like, sack, saw dust, newspaper, etc. to cover the ice.
5. If we hold a thermometer by its bulb, the mercury in the bulb will expand due to our body temperature.
6. Yes. Wool is poor conductor of heat.
7. The jerk to the thermometer will allow the mercury in or above the kink to flow into the bulb so that the mercury level is below normal temperature.
8. Mercury expands when heated. Hence, it rises in the capillary tube.
Important NCERT Questions Class 7 Science Chapter 3
Give two examples each of conductors and insulators of heat.
Conductors: Copper, aluminum and iron. Insulators: Wood, water and air.
Fill in the blank: The hotness of an object is determined by its __________.
The hotness of an object is determined by its temperature.
In places of hot climate it is advised that the outer walls of houses be painted white. Explain.
In places of hot climate it is advised that the outer walls of houses be painted white because white colour reflects most of the heat that falls on it or we can say it absorbs less amount of heat. Therefore, the temperature inside the house does not increase very much.