NCERT Solutions for Class 4 Computer Science Chapter 1 Introduction to Computer updated for CBSE session 2025-26. Get here study material for grade 4 computer book chapter 1 with assignments and worksheets with solutions.
Class 4 Computer Science Chapter 1 Introduction to Computer
Introduction to Computer
Charles Babbage was a Professor of Mathematics at Cambridge University. It was his dream to make a machine; which would have an input device, a processing device, an output device and a storage device. Later, this idea was transformed into the development of modern computer. For this reason, he is known as ‘Father of Computer’. The word ‘Computer’ originated from the word ‘Compute’ which means to calculate in English.
Computer is a machine which performs calculations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc. It operates on electricity.
Early Calculating Machines
Calculation was a need from the early days. Some of the early calculating machines are as follows:
Napier’s Bones: In 1616, Sir John Napier made a calculating device, called Napier’s Bones, for addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of numbers.
The device had multiplication tables inscribed on strips of wood or carved bones. The improved form of Napier’s bones was used for performing division and finding square roots.
Pascaline: In 1642, Blaise Pascal invented Pascaline, one of the first mechanical calculators. It consisted of a box with eight movable wheels. It took Pascal two years to develop his machine. With the help of Pascaline, addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of numbers as big as hundreds and thousands could be easily performed.
Difference Engine
Charles Babbage invented a machine called the Difference Engine in the 19th century, to prepare mathematical tables.
He also invented the first general-purpose computer known as the Analytical Engine, which had the same basic elements as the modern computers– input, output and memory devices.
With the advancement in the invention of computers, they were further classified as per the technology they used.
Evolution of Computers
Based on the technology used, computers were further classified as under:
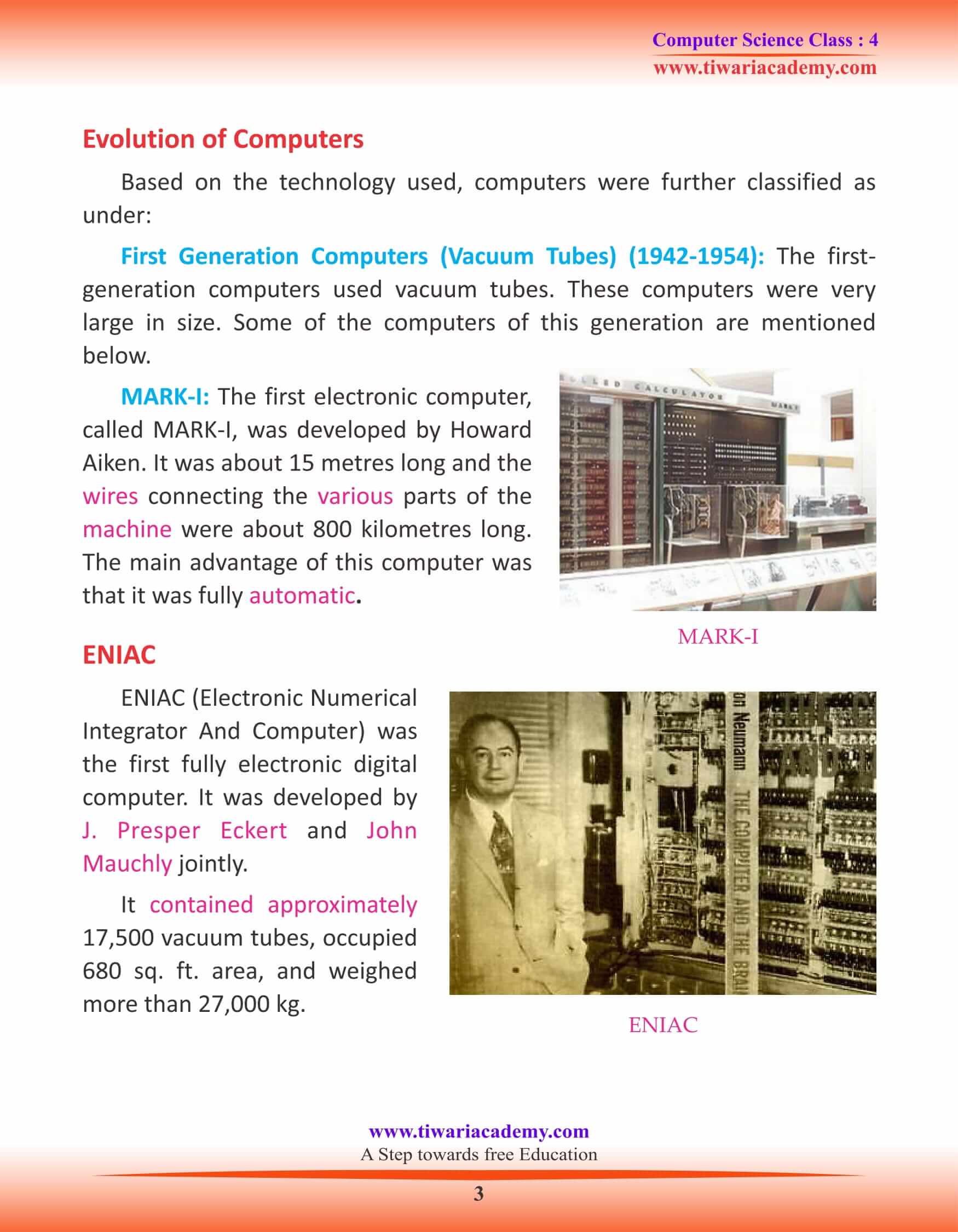
First Generation Computers (Vacuum Tubes) (1942-1954): The first-generation computers used vacuum tubes. These computers were very large in size. Some of the computers of this generation are mentioned below.
MARK-I: The first electronic computer, called MARK-I, was developed by Howard Aiken. It was about 15 metres long and the wires connecting the various parts of the machine were about 800 kilometres long. The main advantage of this computer was that it was fully automatic.
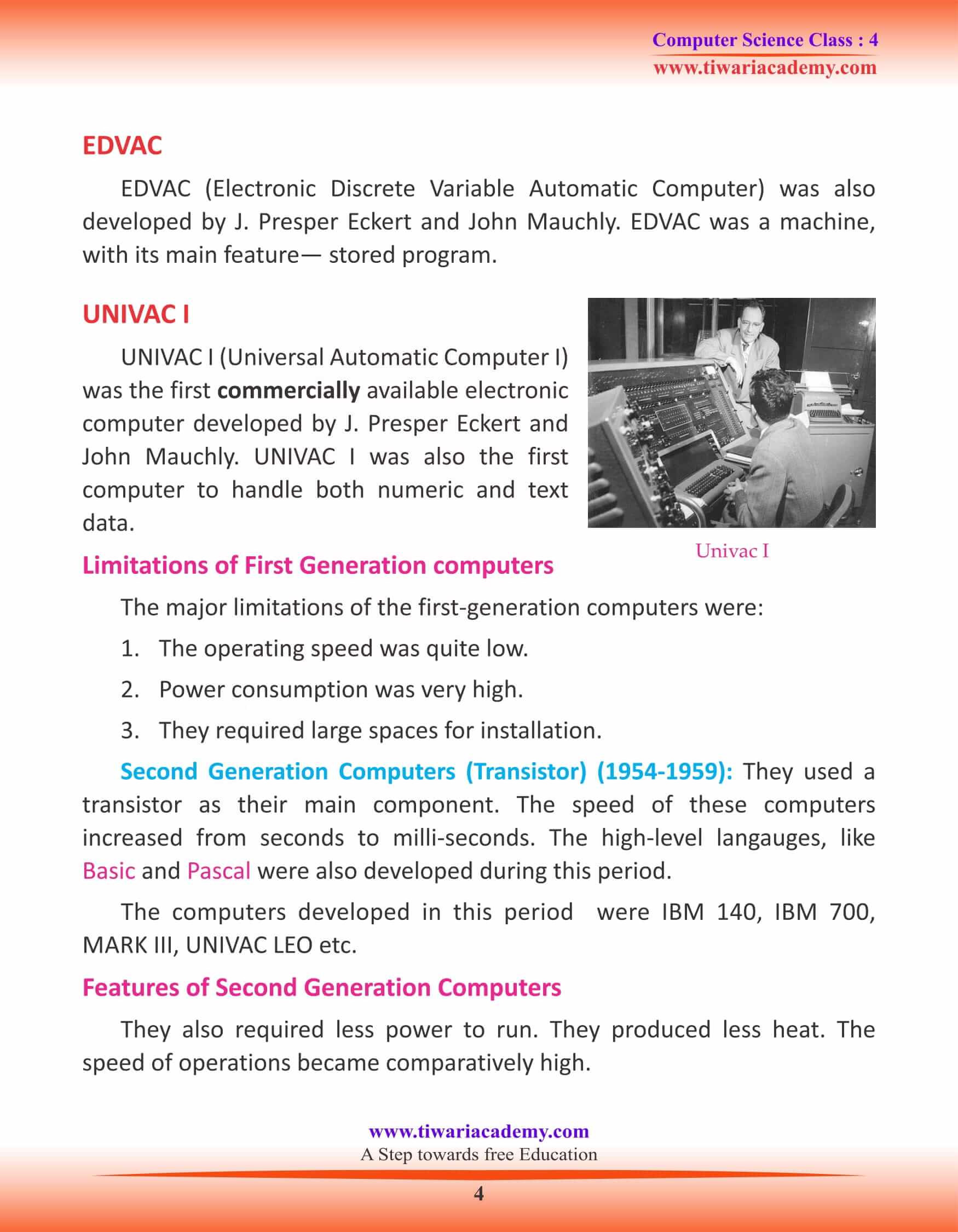
EDVAC
EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer) was also developed by J. Presper Eckert and John Mauchly. EDVAC was a machine, with its main feature— stored program.
UNIVAC I
UNIVAC I (Universal Automatic Computer I) was the first commercially available electronic computer developed by J. Presper Eckert and John Mauchly. UNIVAC I was also the first computer to handle both numeric and text data.
Limitations of First Generation computers
The major limitations of the first-generation computers were:
- The operating speed was quite low.
- Power consumption was very high.
- They required large spaces for installation.
Second Generation Computers (Transistor) (1954-1959)
They used a transistor as their main component. The speed of these computers increased from seconds to milli-seconds. The high-level langauges, like Basic and Pascal were also developed during this period.
The computers developed in this period were IBM 140, IBM 700, MARK III, UNIVAC LEO etc.
Features of Second Generation Computers
They also required less power to run. They produced less heat. The speed of operations became comparatively high.
Third Generation Computers (1959-1971)
With the advancement of technology, around the year 1964, the technology of integrated circuit (IC) came into existence. A single IC (which is a form of electronic circuit) could hold a number of transistors and resistors. These ICs are extremely powerful, fast and small.
Features of Third Generation Computers
The processing speed was reduced from milliseconds to microseconds and further to nanoseconds.
The size of the computer was now comparatively smaller than the previous generations.
The memory was much large as compared to the previous generations.
The languages developed during this period were RPG; ALGOL etc. Computers of third generation are CDC, PDP, IBM-360, HONEY WELL-200, ICL-1900 etc.
Fourth Generation Computers (1971-at present)
The most important electronic device developed during this period was the microprocessor. It led to the development of microcomputers. As the microprocessor chips became smaller and smaller, the computers became more and more compact. These computers need a very small space. These computers could even fit on a desk, so, they are known as desktop computers.
Features of Fourth Generation Computers
They are extremely fast in mathematical calculations as well as in data processing.
They are cheaper in cost as compared to previous generations.
They are more reliable.
They are in the reach of a common man.
The computers of the fourth generation are Intel-4004, Apple, IBM-370, Honey Well-6080.
The different high-level langauges developed during this period are PASCAL, LISP, ADA, SQL etc.
Fifth Generation Computers (Present and Future): In fifth generation computers, the concept of “Artificial Intelligence” (AI) came into existence. These computers may be superior to human beings in terms of calculations, thinking and in decision making. Let us wait for that to happen.
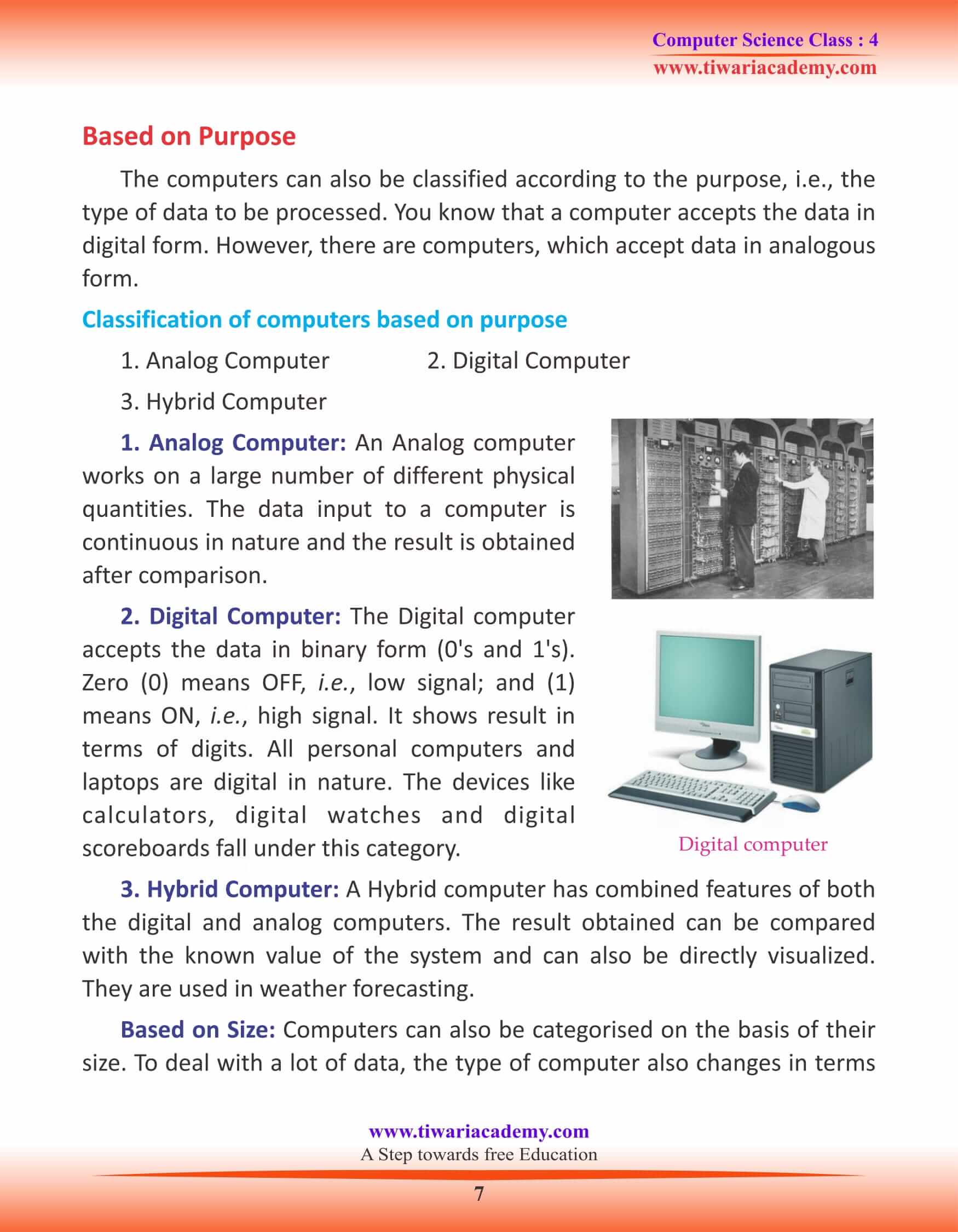
Based on Purpose
The computers can also be classified according to the purpose, i.e., the type of data to be processed. You know that a computer accepts the data in digital form. However, there are computers, which accept data in analogous form.