NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues in Hindi and English Medium for CBSE session 2024-25. The question answers and explanation of chapter 6 in class 9 science subject is modified according to new NCERT textbooks published for academic session 2024-25.
Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Question Answers
- Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Exercises
- Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Intext Questions
- Class 9 Science Chapter 6 MCQ
- Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Extra Questions
- Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Hindi Medium
- Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Notes in English
- Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Notes in Hindi
- Class 9 Science Chapter 6 NCERT Book
- Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 all Subjects NCERT Solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6
Class IX Science chapter 6 solutions of intext Page 69, Page 74, page 78 and Exercises in English Medium or Page 77 ke Uttar, Page 81 ke Uttar, Page 83 ke Uttar, Page 87 ke Uttar and Abhyaas ke Uttar in Hindi Medium. Download here UP Board Solutions for UP Board High School students in Hindi. NCERT Solutions are free to study online or download in PDF format without any login or password. NCERT Solutions Offline Apps for all subjects of class 9 are given to free download for academic session 2024-25.
| Class: 9 | Science |
| Chapter 6: | Tissues |
| Content: | Intext, Exercise and Extra Questions |
| Content Type: | Text, PDF and Videos Format |
| Session: | CBSE 2024-25 |
| Medium: | Hindi and English Medium |
9th Science Chapter 6 Answers in English and Hindi Medium
Extra Questions on 9th Science Chapter 6
What is a tissue?
Tissue is a group of cells of same kind to perform a particular function.
How are simple tissue different from complex tissue?
Simple tissues are made up of only one type of cells whereas complex tissues are made up of different types of cells.
What is the role of epidermis tissue in the plants?
(i) It is a protective tissue of angiospermic (flowering) plant.
(ii) It is provides protection to the underlying tissues.
(iii) It forms the outer covering of roots, stems, leaves and flowers.
(iv) It prevents entry of micro- organism.
How is carbon fixation takes place in plants?
The process of carbon fixation is done by photosynthesis.
How can we determine age of a tree?
It can be determined by counting annual rings present in the trunk of tree call xylem rings.
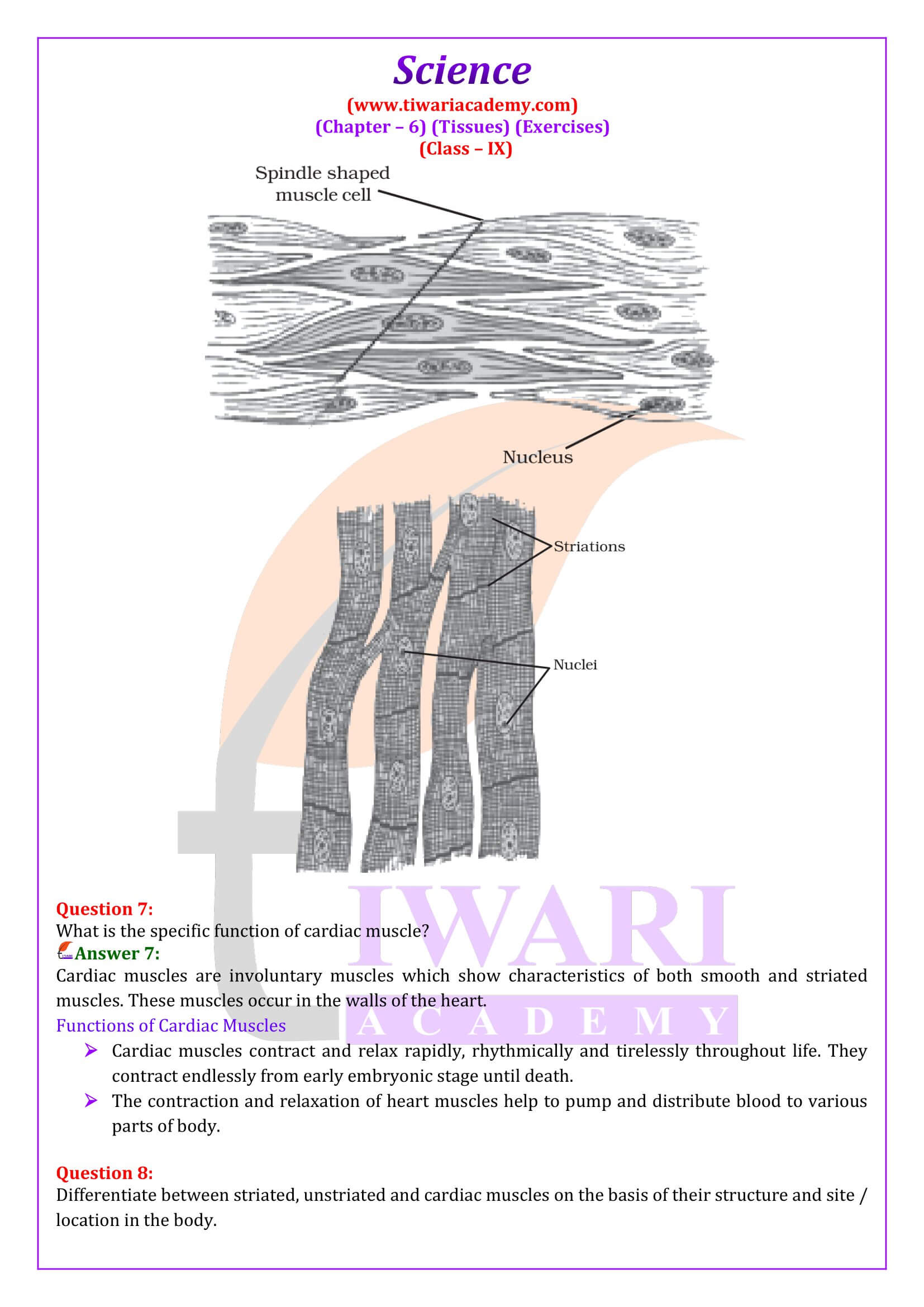
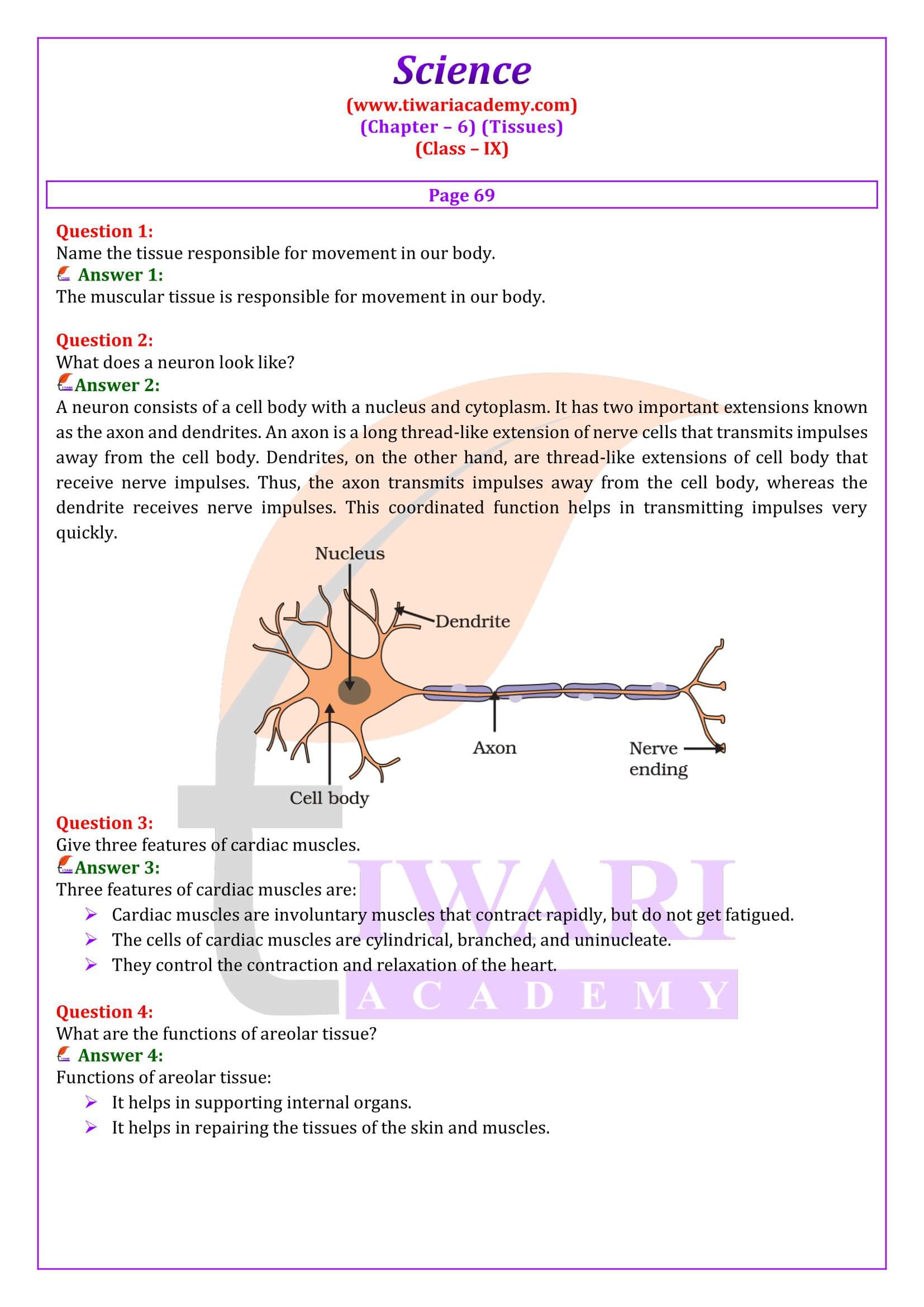
What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Cardiac muscle helps the heart to beat throughout the life with its own contraction and relaxation and involuntary nature.
Girth of stem increases due to which type of meristem?
Lateral Meristem.
What are the function of stomata?
(i) Exchange of gases with atmosphere.
(ii) Transpiration (loss of excess of water) in form of water vapours.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues Intext Questions of all Pages and chapter end exercises question answers in updated form are given below for academic session 2024-25. All the answers are written by experts of Science Subject of High School, if still there is any error, please inform us. Your feedback is the strength of website.
Questions for Practice on 9th Science Chapter 6
Question 1:
(a) Name the plant tissue which is found in the husk of a coconut. Identify the chemical which is responsible for its stiffness.
(b) Give one way in which it differs from parenchymatous cells.
Answer 1:
(a) Sclerenchyma fibres, lignin is responsible for its stiffness.
(b) Scelerenchyma are thick walled dead cells while parenchyma are thin walled living cells.
Question 2:
(a) Name the living component which is common in both the complex permanent tissue found in the plants. What is its function?
(b) Give any two ways in which this tissue differs functionally from each other.
Answer 2:
(a) Parenchyma. It takes part in the storage of nutrients and slows down lateral conduction (water in xylem and nutrients in phloem).
(b) Xylem:
(i) Xylem conducts water and minerals.
(ii) Conduction is unidirectional, upwardly from roots to stem tips and leaves.
Phloem:
(i) Phloem conducts food materials.
(ii) It is bidirectional from leaves to roots and from roots to stem tips.
Important Questions on 9th Science Chapter 6
How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Xylem is a complex tissue. It is made up of following four kinds of cells or elements: (a) Tracheids (b) Vessels (c) Xylem parenchyma (d) Xylem fibres.
How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Simple tissues are made up of one type of cells which coordinate to perform a common function. Complex tissues are made up of more than one type of cells. All these coordinate to perform a common function.
What are the functions of Stomata?
The small pores present in the epidermis of the leaf are stomata. Stomata are enclosed by two kidney shaped cells called guard cells. Functions of Stomata Exchange of gases, particularly CO2 and O2, with atmosphere. Loss of water in the form of vapour during transpiration.
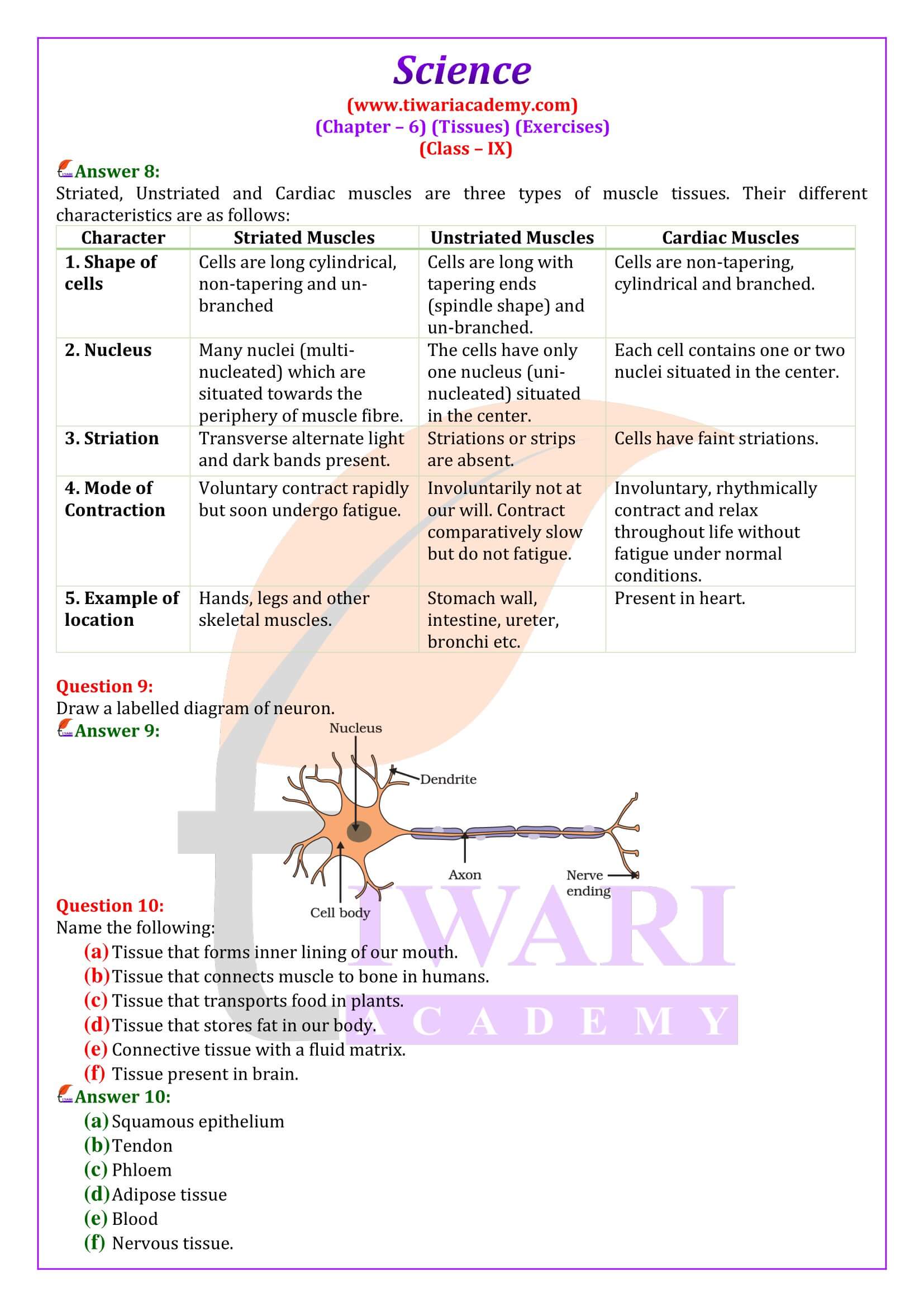
What is the specific function of cardiac muscle?
Cardiac muscles are involuntary muscles which show characteristics of both smooth and striated muscles. These muscles occur in the walls of the heart. Functions of Cardiac Muscles Cardiac muscles contract and relax rapidly, rhythmically and tirelessly throughout life. They contract endlessly from early embryonic stage until death. The contraction and relaxation of heart muscles help to pump and distribute blood to various parts of body.
Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Parenchyma is a simple permanent tissue of angiospermic plants. It is present in cortex and pith of stem and roots. It is also present in mesophyll of leaves. When it contains chlorophyll, it is called Chlorenchyma, found in green leaves.
What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Epidermis is a protective tissue of angiospermic plants. It provides protections to underlying tissues. Epidermis forms outer covering of various plant organs such as roots, stem, leaves, and flowers and remains in direct contact with the environment. Any substance whether solid, liquid or gas can enter into the plant or move outside only after passing through this layer. Epidermis helps in absorption, secretion, gaseous exchange and transpiration. It helps in preventing the entry of pathogens.
How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
The cork cells are dead cells and do not have any intercellular spaces. The cell wall of the cork cells are coated with suberin (a waxy substance). Suberin makes these cells impermeable to water and gases. Cork is protective in function; it protects underlying tissues from desiccation, infection and mechanical injury.