NCERT Solutions for Class 4 Maths Mela Chapter 13 The Transport Museum for Session 2025-26 Exams. It provides clear, step-by-step explanations of all questions based on multiplication, division, patterns and real-life transport situations. These solutions follow the latest NCERT syllabus and help students understand concepts like times tables, multiples of 10 and 100, word problems and logical thinking. Written in simple language, they are ideal for exam preparation, homework help and building strong mathematical foundations in an engaging way effectively.
Class 4 Maths Mela Chapter 13 MCQ
Class 4 Math Magic Chapter 13 MCQ
Chapter 13 Fields and Fences Solutions
Key Concepts Covered in Class 4 Maths Mela Chapter 13
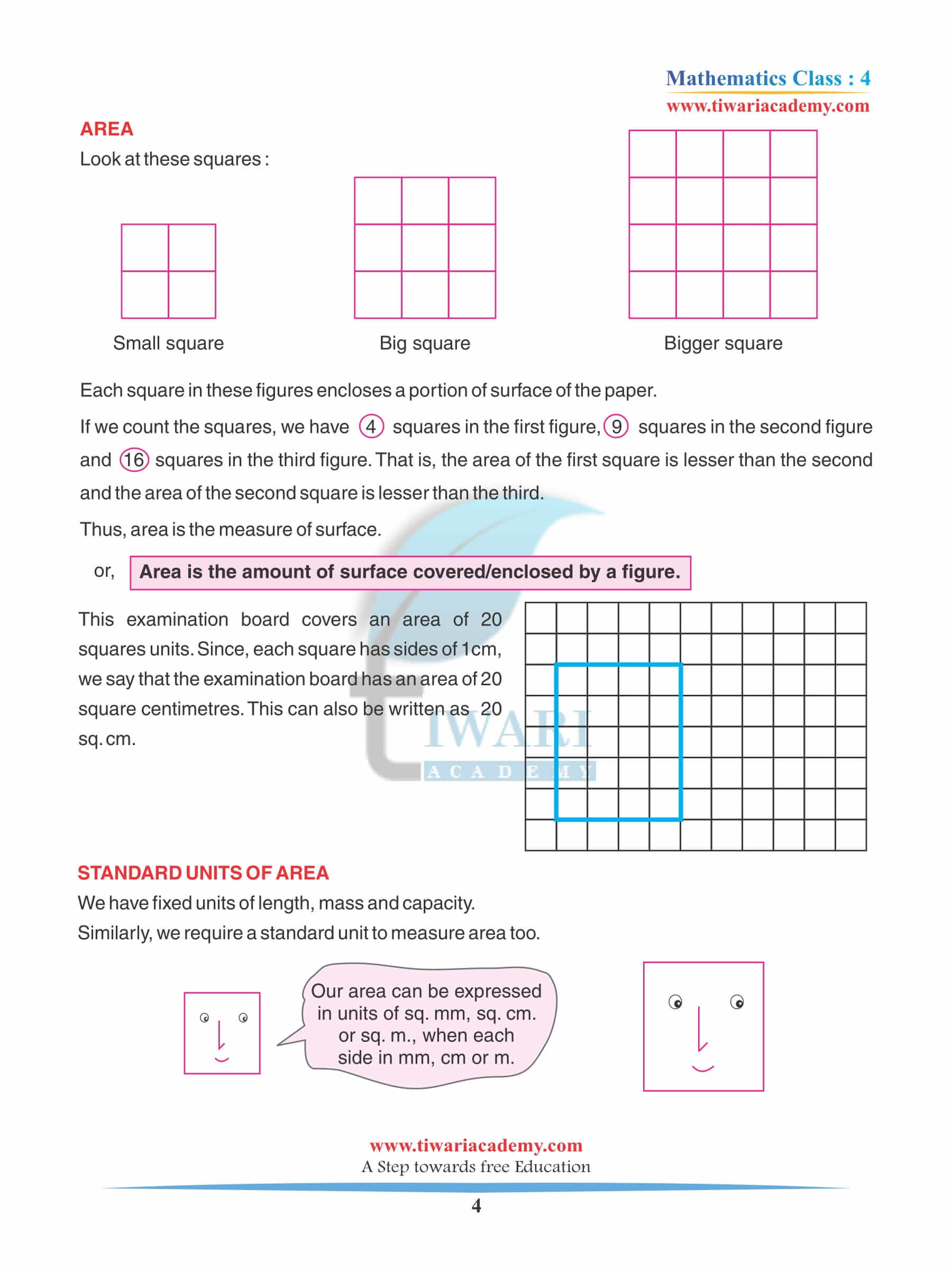
Page 184
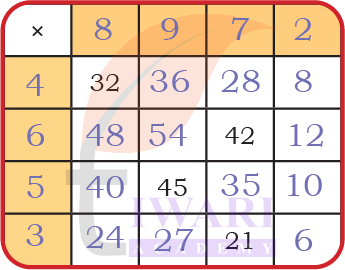
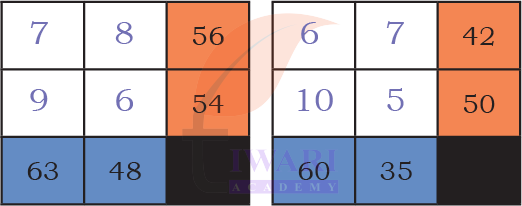
Mystery Matrix
1. Fill the yellow boxes with 1-digit numbers (multiplicands and multipliers) such that you get the products in white boxes.
Fill the remaining white boxes with appropriate products.

Answer:
The product of the numbers in each row is given in the orange boxes. The product of the numbers in each column is given in the blue boxes. Identify appropriate numbers to fill the blank boxes.
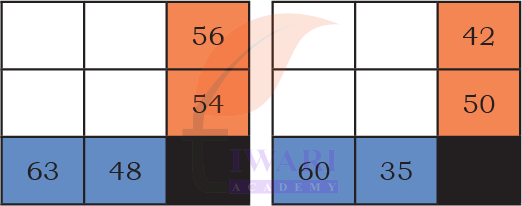
Answer:
Times-10
Match each problem with the appropriate pictorial representation and write the answer.

Answer:
Page 185
Constructing Tables
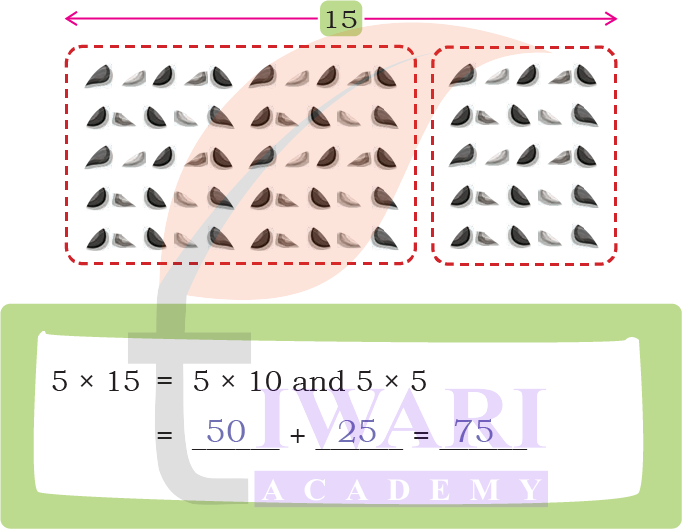
How many pebbles are there in this arrangement?
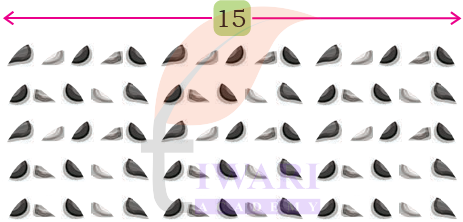
Answer:
This is a 5 × 15 arrangement so total pebbles are 75 pebbles.
This is a 5 × 15 arrangement. There is an easy way to find this product by splitting the arrangement.

Answer:
Recall the times-tables that we created in Grade 3. Now construct a times-15 table. You may use the arrangement given below and split the columns into 10 and 5 for ease of counting, as shown on the previous page.
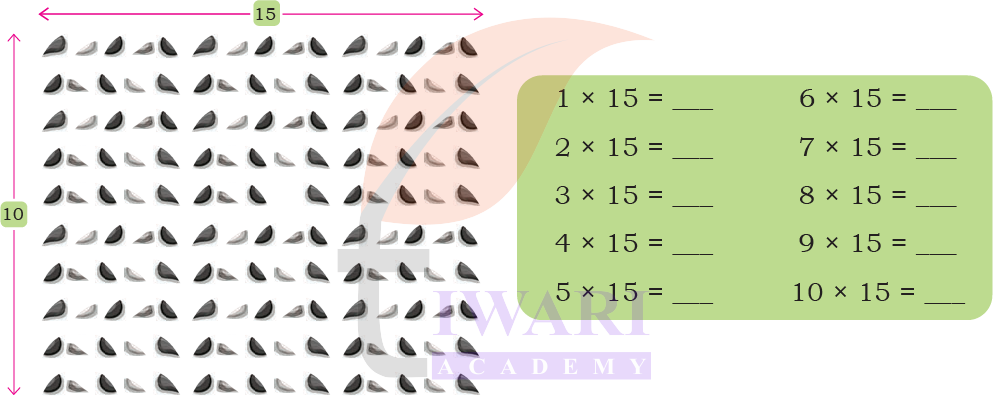
Answer:

1. What pattern do you see in this table?
Answer:
► The ones digit follows a pattern of 5-0-5-0-5-0-5-0-5-0
► Each product increases by 15 as we move down the table
► The tens digit increases by 1 when the ones digit is 0, and stays the same when the ones digit is 5.
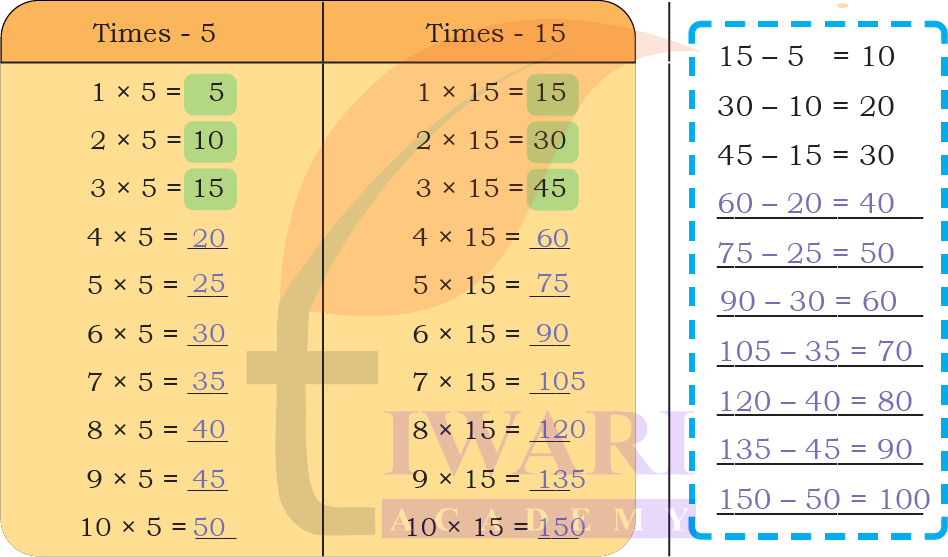
2. Compare the times of 15 table with the times 5 table. What similarities and difference do you notice?
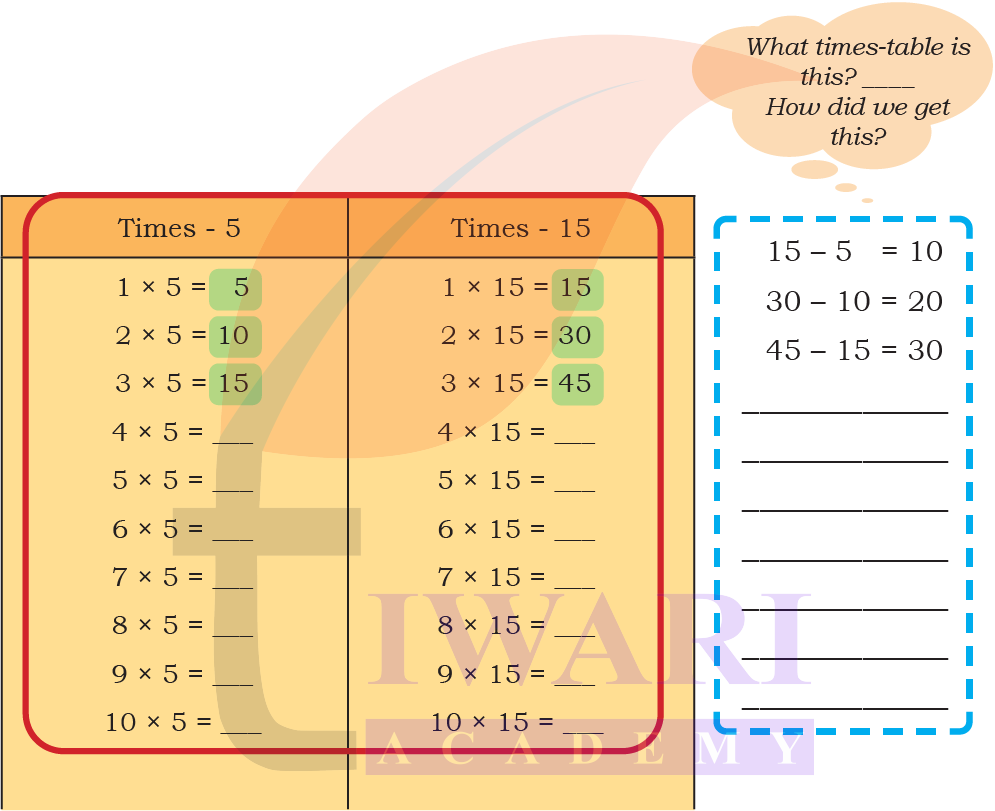
Answer:
► Each answer in the times-15 table is exactly 3 times the corresponding answer in the times-5 table.
► Both tables have a pattern in the ones digit (5-0-5-0…)
The times-15 table grows three times faster than the times-5 table.
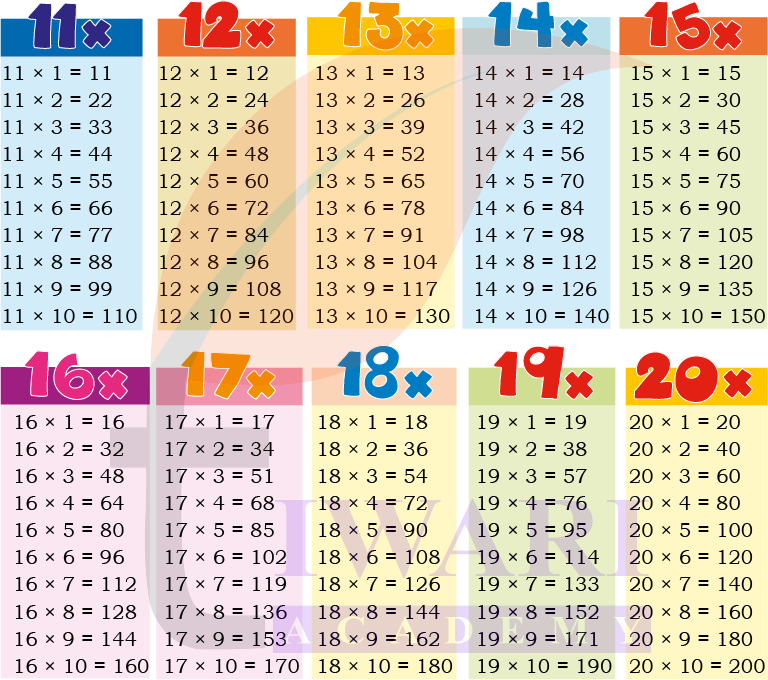
3. Construct other times-table for number from 11 to 20, as you did for 15.
Answer:
4. As you compared the times-5 table with the times-15 table, compare the times-1 table with the times-11 table, the times-2 table with the times-12 table, and so on. Share your observations.
Answer:
► Times-1 table and Times-11 table
In the times-1 table, the answer is always the same as the number we multiply. Nothing changes.
But in the times-11 table, each answer becomes a two-digit number where both digits are the same (11, 22, 33, 44, …).
We can also notice that every answer in the times-11 table is 11 more than the corresponding times-1 answer.
So, the times-11 table feels like the times-1 table with 10 extra added each time.
► Times-2 table and Times-12 table
The times-2 table gives answers by doubling numbers.
The times-12 table can be made easily by adding the times-10 table to the times-2 table.
This means every answer in the times-12 table is the times-2 answer plus ten more groups of the same number.
So, the pattern is times-12 = times-10 + times-2.
► Times-3 table and Times-13 table
The times-3 table counts in jumps of 3.
The times-13 table can be formed by adding the times-10 table to the times-3 table.
So each answer in the times-13 table is 10 more groups added to the times-3 answer.
This shows the same pattern again:
times-13 = times-10 + times-3.
► Same pattern continues for all pairs
Times-4 matches with times-14, times-5 with times-15, and so on.
In every case, the bigger table is formed by adding the times-10 table to the smaller one.
Final Observation:
► All tables from 11 to 20 are closely connected to the tables from 1 to 10.
► They are not new tables — they are just old tables plus ten more each time.
► This makes learning bigger tables easier, faster and less confusing.
Page 188
We have seen how to calculate 3 × 14 and 6 × 14 by splitting and doubling. Can we construct the times-14 table by splitting and doubling? Try!
Answer:
Constructing the times-14 table by splitting and doubling
1 × 14 = 1 × 7 + 1 × 7 = 7 + 7 = 14
2 × 14 = 2 × 7 + 2 × 7 = 14 + 14 = 28
3 × 14 = 3 × 7 + 3 × 7 = 21 + 21 = 42
4 × 14 = 4 × 7 + 4 × 7 = 28 + 28 = 56
5 × 14 = 5 × 7 + 5 × 7 = 35 + 35 = 70
6 × 14 = 6 × 7 + 6 × 7 = 42 + 42 = 84
7 × 14 = 7 × 7 + 7 × 7 = 49 + 49 = 98
8 × 14 = 8 × 7 + 8 × 7 = 56 + 56 = 112
9 × 14 = 9 × 7 + 9 × 7 = 63 + 63 = 126
10 × 14 = 10 × 7 + 10 × 7 = 70 + 70 = 140
What other times-tables can be constructed by splitting into equal groups and doubling? Give examples.
Answer:
Other times-tables that can be constructed by splitting into equal groups and doubling. This method works for even numbers.
Examples:
Times-20 table
1 × 20 = 1 × 10 + 1 × 10 = 10 + 10 = 20
2 × 20 = 2 × 10 + 2 × 10 = 20 + 20 = 40
3 × 20 = 3 × 10 + 3 × 10 = 30 + 30 = 60
Times-16 table
1 × 16 = 1 × 8 + 1 × 8 = 8 + 8 = 16
2 × 16 = 2 × 8 + 2 × 8 = 16 + 16 = 32
3 × 16 = 3 × 8 + 3 × 8 = 24 + 24 = 48
Times-12 table
1 × 12 = 1 × 6 + 1 × 6 = 6 + 6 = 12
2 × 12 = 2 × 6 + 2 × 6 = 12 + 12 = 24
3 × 12 = 3 × 6 + 3 × 6 = 18 + 18 = 36
Times-18 table
1 × 18 = 1 × 9 + 1 × 9 = 9 + 9 = 18
2 × 18 = 2 × 9 + 2 × 9 = 18 + 18 = 36
3 × 18 = 3 × 9 + 3 × 9 = 27 + 27 = 54
Times-tables of even numbers such as 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, etc., can be easily constructed by splitting the number into two equal parts and then doubling.
Page 188
Multiples of 10
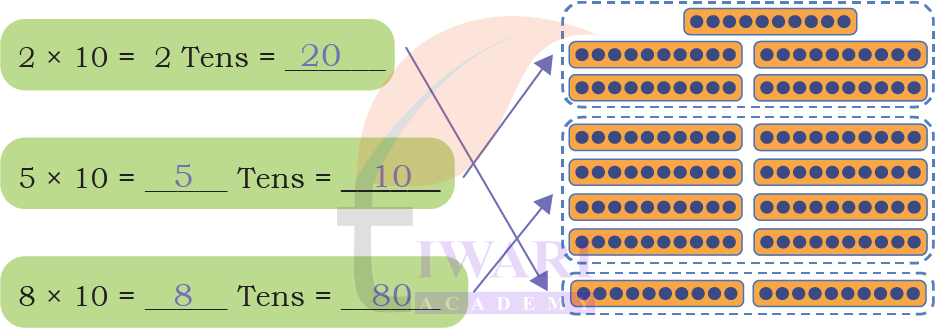
Find the answers to the following:
a) 15 × 10 = _____ Tens = _____
b) 16 × 10 = _____ Tens = _____
c) 19 × 10 = _____ Tens = _____
d) 20 × 10 = _____ Tens = _____
Answer:
a) 15 × 10 = 15 Tens = 150
b) 16 × 10 = 16 Tens = 160
c) 19 × 10 = 19 Tens = 190
d) 20 × 10 = 20 Tens = 200.
Page 188
10 × 10 = ____ 2 times (i.e., double of) 10 × 10 = ____
Discuss in grade what happens when we take several groups of 10.
Answer:
10 × 10 = 100
2 times (double of) 10 × 10 = 200
When we take several groups of 10, the numbers become bigger very fast.
Each group of 10 is called one ten. Adding more tens adds a zero at the end.
That is why multiplying by 10 is easy.
Page 189
Now think and answer the following problems.
30 × 10 = _____
40 × 10 = _____
70 × 10 = _____
50 × 10 = _____
60 × 10 = _____
80 × 10 = _____
Answer:
► 30 × 10 = 30 Tens
= 10 Tens + 20 Tens
= 100 + 200
= 300
► 40 × 10 = 40 Tens
= 10 Tens + 30 Tens
= 100 + 300
= 400
► 50 × 10 = 50 Tens
= 10 Tens + 40 Tens
= 100 + 400
= 500
► 60 × 10 = 60 Tens
= 10 Tens + 50 Tens
= 100 + 500
= 600
► 70 × 10 = 70 Tens
= 10 Tens + 60 Tens
= 100 + 600
= 700
► 80 × 10 = 80 Tens
= 10 Tens + 70 Tens
= 100 + 700
= 800.
Page 189
Answer the following questions. Share your thoughts.
a) 21 × 10 = _____
b) 42 × 10 = _____
c) 65 × 10 = _____
d) 38 × 10 = _____
e) 53 × 10 = _____
f) 87 × 10 = _____
Answer:
a) 21 × 10 = 21 Tens
= 20 Tens + 1 Ten
= 200 + 10
= 210
b) 42 × 10 = 42 Tens
= 40 Tens + 2 Tens
= 400 + 20
= 420
c) 65 × 10 = 65 Tens
= 60 Tens + 5 Tens
= 600 + 50
= 650
d) 38 × 10 = 38 Tens
= 30 Tens + 8 Tens
= 300 + 80
= 380
e) 53 × 10 = 53 Tens
= 50 Tens + 3 Tens
= 500 + 30
= 530
f) 87 × 10 = 87 Tens
= 80 Tens + 7 Tens
= 800 + 70
= 870.
Page 190
Solve the following problems. Share your thoughts.
24 × 40 = _______
50 × 60 = _______
13 × 30 = _______
43 × 60 = _______
70 × 80 = _______
Answer:
► 24 × 40
= 24 × (4 Tens)
= (24 × 4) Tens
= 96 Tens
= 960
► 50 × 60
= (5 Tens) × (6 Tens)
= (5 × 6) × 100
= 30 × 100
= 3000
► 13 × 30
= 13 × (3 Tens)
= (13 × 3) Tens
= 39 Tens
= 390
► 43 × 60
= 43 × (6 Tens)
= (43 × 6) Tens
= 258 Tens
= 2580
► 70 × 80
= (7 Tens) × (8 Tens)
= (7 × 8) × 100
= 56 × 100
= 5600
When we multiply numbers ending in zero, we first multiply the non-zero numbers. Then we add the zeros at the end. More tens mean bigger numbers.
Page 192
Let Us Solve
Also, identify remainder (if any) in the division problems.
a) 25 × 34
Answer:
25 × 34
= (20 + 5) × (30 + 4)
= 20 × 30 + 20 × 4 + 5 × 30 + 5 × 4
= 600 + 80 + 150 + 20
= 850
b) 16 × 43
Answer:
16 × 43
= (10 + 6) × (40 + 3)
= 10 × 40 + 10 × 3 + 6 × 40 + 6 × 3
= 400 + 30 + 240 + 18
= 688
c) 68 × 12
Answer:
68 × 12
= (60 + 8) × (10 + 2)
= 60 × 10 + 60 × 2 + 8 × 10 + 8 × 2
= 600 + 120 + 80 + 16
= 816
d) 39 × 13
Answer:
39 × 13
= (30 + 9) × (10 + 3)
= 30 × 10 + 30 × 3 + 9 × 10 + 9 × 3
= 300 + 90 + 90 + 27
= 507
e) 125 ÷ 15
Answer:
125 ÷ 15 = 8 + remainder 5.
f) 94 ÷ 11
Answer:
94 ÷ 11 = 8 + remainder 6.
g) 440 ÷ 22
Answer:
440 ÷ 22 = 20
h) 508 ÷ 18
Answer:
508 ÷ 18 = 28 + remainder 4.
Page 192
Multiples of 100
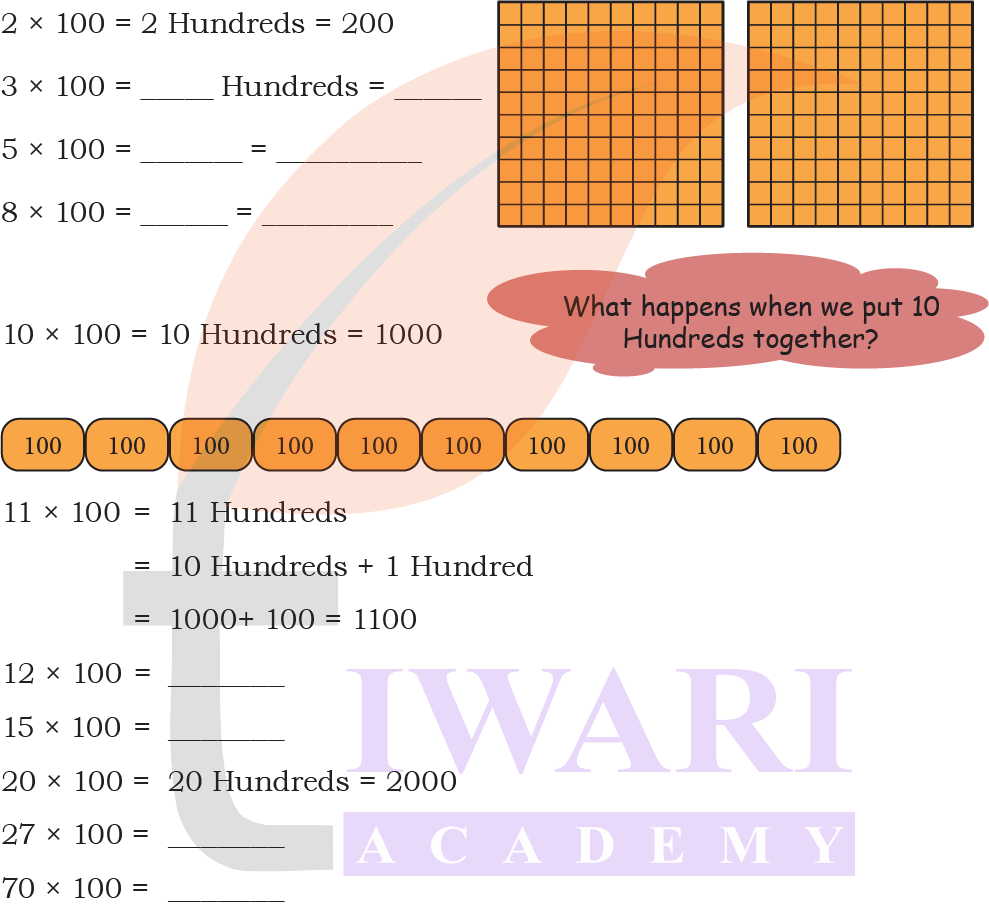
Answer:
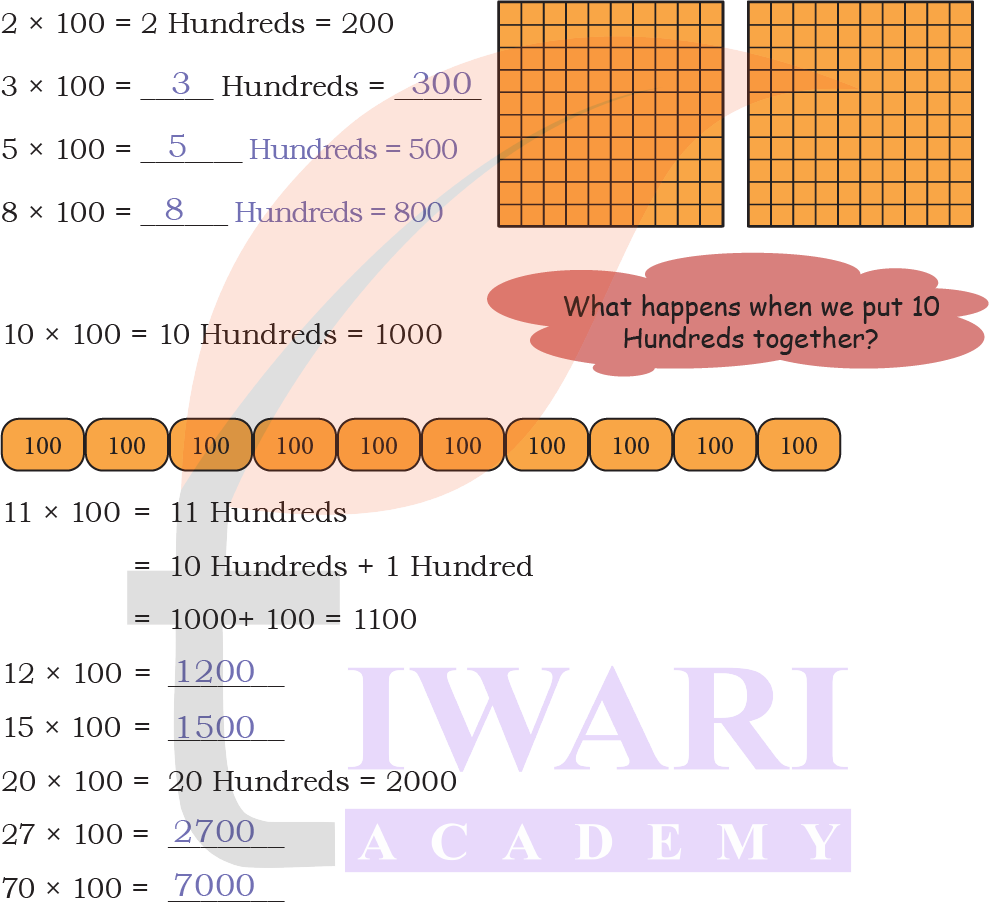
Page 193
Now answer the following questions. Share your thoughts.

Answer:

Division with and without Remainders in Class 4 Maths Mela Chapter 13
Page 194
Share what you notice about the answers to these problems.
11 × 100 = ______
22 × 100 = ______
11 × 200 = ______
22 × 200 = ______
Answer:
► 11 × 100
11 × 100 = 11 × 1 Hundreds
= 11 Hundreds
= 1100
► 22 × 100
11 × 200 = 11 × 2 Hundreds
= 22 Hundreds
= 2200
► 11 × 200
11 × 200 = 10 × 200 and 1 × 200
= 2000 + 200 = 2200
► 22 × 200
= 20 × 200 and 2 × 200
= 4000 + 400
= 4400
We notice about the answers that multiplying by 100 gives answers in Hundreds. Multiplying by 200 is double the hundreds compared to multiplying by 100. Splitting numbers into tens and ones (or hundreds) makes multiplication easier. The answers increase proportionally with the number of hundreds or with doubling.
Page 194
Answer the following questions. Share your thoughts.

Answer:
Multiplying by hundreds is just counting hundreds. Splitting big numbers into smaller groups (like 5 × 500 = 25 Hundreds) makes calculations easier. The more hundreds we multiply, the bigger the answer. This method works for any number of hundreds or multiples of 100.

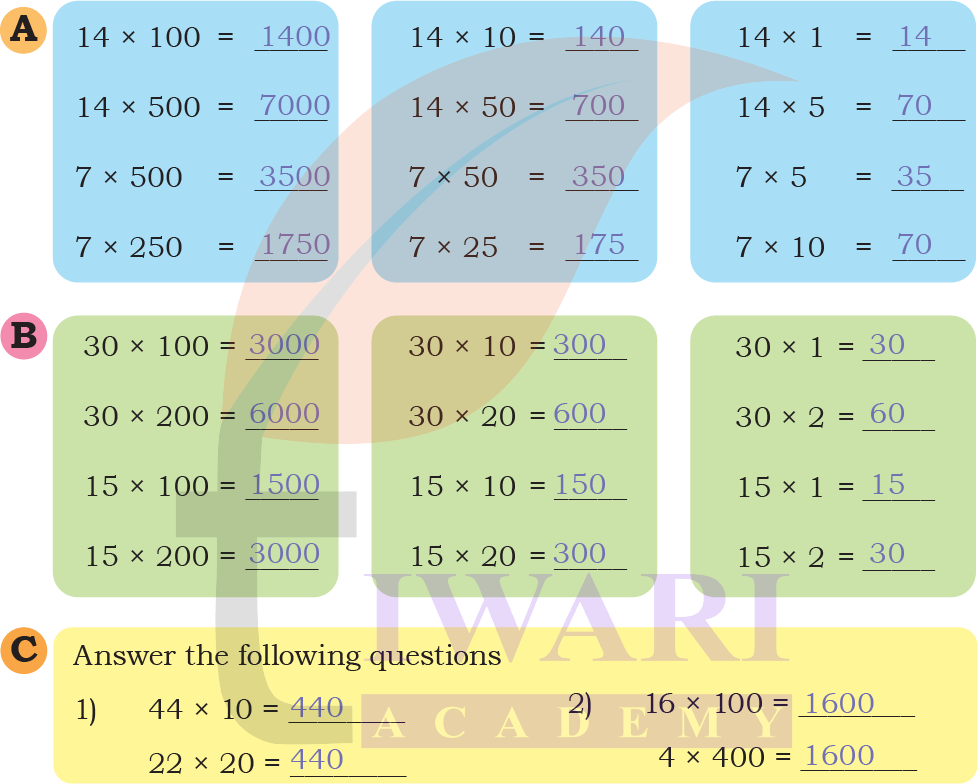
Find the answers in Set A. Examine the relationship between the problems answers in Set A carefully. Then use this understanding to find the answers in Set B.
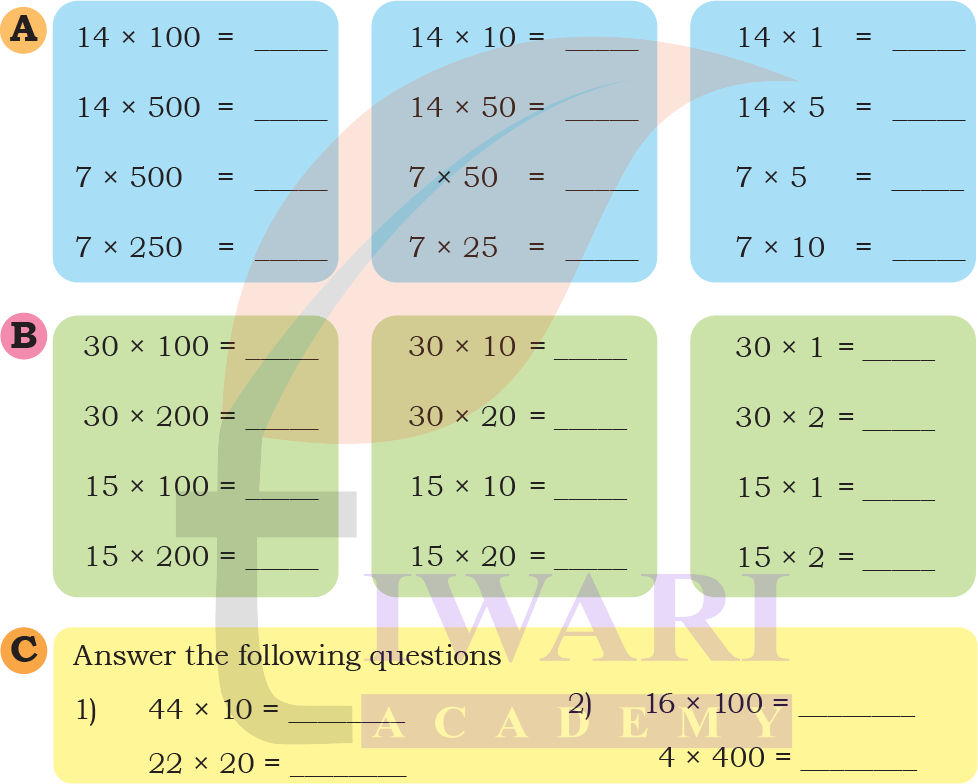
Answer:
Page 197
Let Us Solve
Also, identify remainder (if any) in the division problems.
a) 237 × 28
Answer:
237 × 28
= 200 × 20 + 200 × 8 + 30 × 20 + 30 × 8 + 7 × 20 + 7 × 8
= 4000 + 1600 + 600 + 240 + 140 + 56
= 6636
b) 140 × 16
Answer:
140 × 16
= 100 × 10 + 100 × 6 + 40 × 10 + 40 × 6 + 0 × 16
= 1000 + 600 + 400 + 240 + 0
= 2240
c) 389 × 57
Answer:
389 × 57
= 300 × 50 + 300 × 7 + 80 × 50 + 80 × 7 + 9 × 50 + 9 × 7
= 22173
d) 807 ÷ 24
Answer:
807 ÷ 24 = 33 + remainder 15.
e) 692 ÷ 33
Answer:
692 ÷ 33 = 20 + remainder 32.
f) 996 ÷ 45
Answer:
996 ÷ 45 = 22 + remainder 6.
Page 197
Dividing by 10 and 100
A farmer packs his rice in sacks of 10 kg each.
a) If he has 60 kg of rice, how many sacks does he need?
b) If he has 600 kg of rice, how many sacks does he need?

Answer:

Page 198
Find the answers to the following questions. Share your thoughts in grade.
40 ÷ 10 = ____
4 ÷ 2 = ____
400 ÷ 2 = ____
400 ÷ 10 = ____
40 ÷ 20 = ____
400 ÷ 20 = ____
400 ÷ 100 = ____
400 ÷ 200 = ____
Answer:
40 ÷ 10 = 4
4 ÷ 2 = 2
400 ÷ 2 = 200
400 ÷ 10 = 40
40 ÷ 20 = 2
400 ÷ 20 = 20
400 ÷ 100 = 4
400 ÷ 200 = 2
400 ÷ 200 = 2
Thoughts: When we divide, we are finding how many equal groups we can make.
Dividing by 10 or 100 makes the number smaller because we are making bigger groups. When the divisor is larger, the answer is smaller. Removing zeros helps in division (for example, 400 ÷ 10 = 40). If the number is divided by half, the answer becomes double (400 ÷ 2 = 200).
Page 198
Think and answer. Write the division statement in each case.
1. Manku the monkey sees 870 bananas in the market. Each bunch has 10 bananas. How many bunches are there in the market?
Answer:
Total number of bananas = 870
Numberof bananas in one bunch = 10
So, the number of bunches = 870 ÷ 10 = 87
Hence, there are 87 bunches of bananas in the market.
2. Rukhma Bi wants to distribute 1000/- equally among her 10 grandchildren on the occasion of Eid. How much money will each of them get?
Answer:
Total money = ₹ 1000
Number of grandchildren = 10
Money for each of them = 1000 ÷ 10 = 100
So, each grandchild will get ₹ 100.
Page 198
Let Us Solve
1. The oldest long-distance train of the Indian Railways is the Punjab Mail which ran between Mumbai and Peshawar. Its first journey was on 12 October 1912. Do you know how many coaches it had on its first journey? It had 6 coaches: 3 carrying 96 passengers and 3 for goods.
a) How many people travelled in each coach on the first journey?
b) This train has been running for 106 years now. It runs between Mumbai, Maharashtra and Ferozepur, Punjab. It has 24 coaches. Each coach can carry 72 passengers. How many people can travel on this train?
Answer:
Given that on its first journey, Punjab Mail had 6 coaches.
3 coaches carried 96 passengers (total) and 3 coaches were for goods.
a) Total passengers = 96
Number of passenger coaches = 3
Number of passenger in each coach = 96 ÷ 3 = 32
So, 32 people travelled in each coach.
b) As per present situation:
Number of coaches = 24
Passengers per coach = 72
Total passengers = 24 × 72
= 24 × (70 + 2)
= (24 × 70) + (24 × 2)
= 1680 + 48
= 1728
So, 1728 people can travel on this train.
2. Amala and her 35 classmates, along with 6 teachers, are going on a school trip to Goa. They are using the double-decker “hop on hop off” sightseeing bus to explore the city.
a) 2 people can sit on every seat of the bus. There are 15 seats in the lower deck and 10 in the upper deck. How many seats will they need to occupy? Are there enough seats for everyone?
b) Find the total cost of the tickets for all children.
c) What is the cost of the tickets for all teachers?

Answer:
Amala + 35 classmates = 36 children
Number of teachers = 6
So, total people = 36 + 6 = 42
a) Lower deck seats = 15
Upper deck seats = 10
Total seats = 25
Each seat can accommodate 2 people.
Total people that can sit = 25 × 2 = 50
People going = 42
Seats needed = 42 ÷ 2 = 21 seats
Yes, there are enough seats for everyone, because the bus can seat 50 people.
b) Cost for one child = ₹359
Total cost for all children = 36 × 359
= (30 × 359) + (6 × 359)
= 10,770 + 2,154
= ₹12,924
Total cost for all children = ₹12,924
c) Cost for one teacher = ₹899
Total cost for all teachers = 6 × 899
= 6 × (900 − 1)
= 5,400 − 6
= ₹5,394
So, the total cost for all teachers is ₹5,394.
3. Kedar works in a brick kiln.
a) The kiln makes 125 bricks in a day. How many bricks can be made in a month?
b) Each brick is sold in the market for ₹9. How much money can they earn in a month?
Answer:
a)The kiln makes 125 bricks in one day.
Assuming 1 month = 30 days:
Number of bricks for the month = 125 × 30 = 3750
So, 3750 bricks can be made in a month.
b) Earning from one brick = ₹9
So, earning from 3750 bricks = 3750 × 9 = 33,750
Hence, they can earn ₹ 33,750 in a month.
4. Chilika lake in Odisha is the largest saltwater lake in India. It is famous for the Irrawaddy dolphins. Boats can be hired to go see the dolphins. The trip from Puri includes a bus ride followed by a boat ride. Eight people will be going on the trip.
A bus ticket from Puri to Satapada costs ₹60.
A two-hour boat ride for 8 people costs ₹1200.
How much money do we need to spend on each person?
Answer:
Number of people = 8
Bus ticket (per person) = ₹60
So, total cost for 8 people = 8 × 60 = ₹480
Boat ride cost (for 8 people) = ₹1200
Total trip cost = Bus cost + Boat cost = 480 + 1200 = ₹1680
Now, the cost per person: 1680 ÷ 8 = ₹210
So, each person needs to spend ₹210.
5. Find the multiplication and division sentences below. Shade the sentences. How many can you find? Some are done for you.
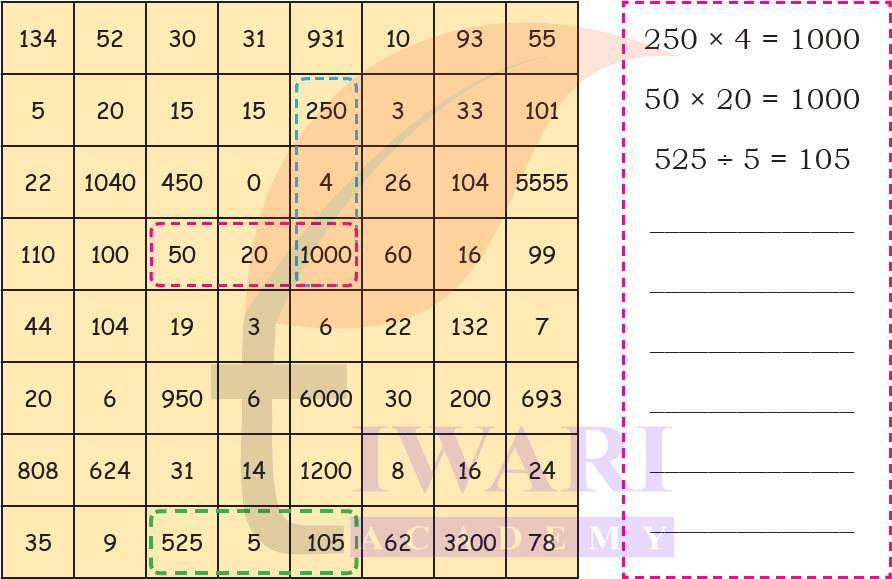
Answer:
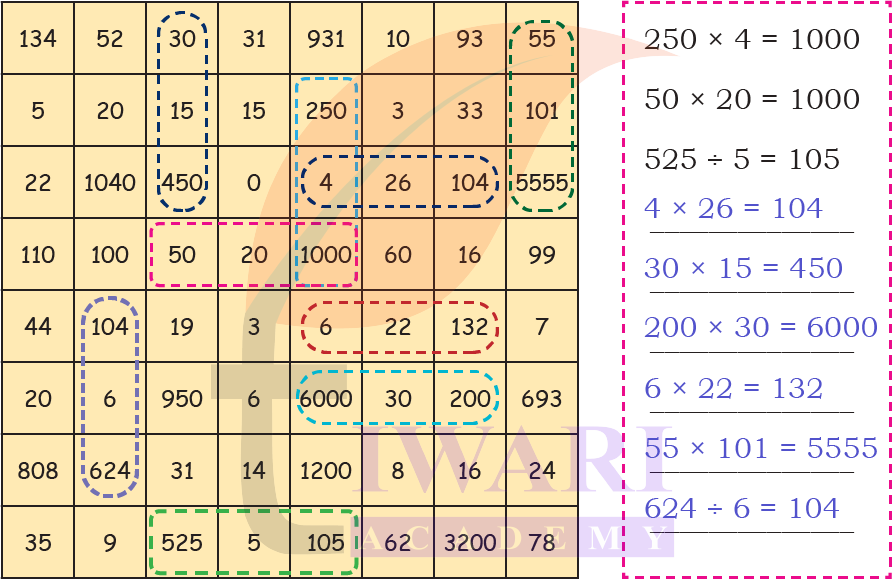
6. Solve
a) 35 × 76
Answer:
35 × 76
= 35 × (70 + 6)
= 35 × 70 + 35 × 6
= 2450 + 210
= 2660
b) 267 × 38
Answer:
267 × 38
= 267 × (30 + 8)
= 267 × 30 + 267 × 8
= 8010 + 2136
= 10,146
c) 498 × 9
Answer:
498 × 9
= (500 − 2) × 9
= 500 × 9 − 2 × 9
= 4500 − 18
= 4482
d) 89 × 42
Answer:
89 × 42
= 89 × (40 + 2)
= 89 × 40 + 89 × 2
= 3560 + 178
= 3738
e) 55 × 23
Answer:
55 × 23
= 55 × (20 + 3)
= 55 × 20 + 55 × 3
= 1100 + 165
= 1265
f) 345 × 17
Answer:
345 × 17
= 345 × (10 + 7)
= 345 × 10 + 345 × 7
= 3450 + 2415
= 5865
g) 66 × 22
Answer:
66 × 22
= 66 × (20 + 2)
= 66 × 20 + 66 × 2
= 1320 + 132
= 1452
h) 704 × 11
Answer:
704 × 11
= 704 × (10 + 1)
= 704 × 10 + 704 × 1
= 7040 + 704
= 7744
i) 319 × 26
Answer:
319 × 26
= 319 × (20 + 6)
= 319 × 20 + 319 × 6
= 6380 + 1914
= 8294
j) 459 ÷ 3
Answer:
459 ÷ 3 = 153
k) 774 ÷ 18
Answer:
k) 774 ÷ 18 = 43
l) 864 ÷ 26
Answer:
l) 864 ÷ 26 = 33 remainder 6.
m) 304 ÷ 12
Answer:
304 ÷ 12 = 25 remainder 4.
n) 670 ÷ 9
Answer:
670 ÷ 9 = 74 remainder 4.
o) 584 ÷ 25
Answer:
584 ÷ 25 = 23 remainder 9.
p) 900 ÷ 15
Answer:
900 ÷ 15 = 60
q) 658 ÷ 32
Answer:
658 ÷ 32 = 20 remainder 18.
r) 974 ÷ 9
Answer:
974 ÷ 9 = 108 remainder 2.
Page 201
Chinnu’s Coins
1. Five friends plan to visit an amusement park nearby. Each of them use different notes and coins to buy the ticket. The cost of the ticket is ₹750.
• Bujji has brought all notes of ₹200.
• And Munna has brought all notes of ₹50.
• Whereas Balu has brought all notes of ₹20.
• And guess what, Chinnu has all coins of ₹5.
• And Sansu has all coins of ₹2.

a) Find out how many notes/coins each child has to bring to buy the ticket.
Answer:
Given: Cost of one ticket = ₹750
Each friend uses only one type of note or coin.
► Bujji (₹200 notes): ₹750 ÷ 200
200 × 3 = 600
200 × 4 = 800 (more than 750)
So Bujji gives 4 notes of ₹200 (= ₹800)
► Munna (₹50 notes)
₹750 ÷ 50
50 × 15 = 750
So Munna gives 15 notes of ₹50
► Balu (₹20 notes)
₹750 ÷ 20
20 × 37 = 740
20 × 38 = 760 (more than 750)
So Balu gives 38 notes of ₹20 (= ₹760)
► Chinnu (₹5 coins)
₹750 ÷ 5 = 150
So Chinnu gives 150 coins of ₹5
► Sansu (₹2 coins)
₹750 ÷ 2 = 375
So Sansu gives 375 coins of ₹2.
b) Which of these children will not receive any change from the cashier?
Answer:
Only Munna gives exactly ₹750 (15 × 50 = 750).
So Munna will not receive any change.
All others give more than ₹750, so they will get change back.
c) How long would the cashier take to count Chinnu’s coins?
Answer:
Chinnu gives 150 coins of ₹5.
Counting coins takes more time than counting notes because:
Coins are small.
They must be counted one by one.
So, the cashier will take a long time to count Chinnu’s coins compared to the notes used by others.
2. Observe the following multiplications. The answers have been provided.
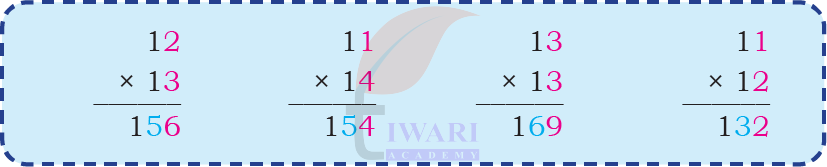
In each case, do you see any pattern in the two numbers and their product? (Hint: Look at the coloured digits!)
For what other multiplication problems will this pattern hold?
Find 5 such examples.
Answer:
Multiplication patterns:
12 × 13 = 156
11 × 14 = 154
13 × 13 = 169
11 × 12 = 132
Pattern:
When the digits in one number increase by 1 and the other decrease by 1, the product remains the same or very close.
Other examples:
21 × 14 = 294
20 × 15 = 300
19 × 16 = 304
18 × 17 = 306
22 × 13 = 286.
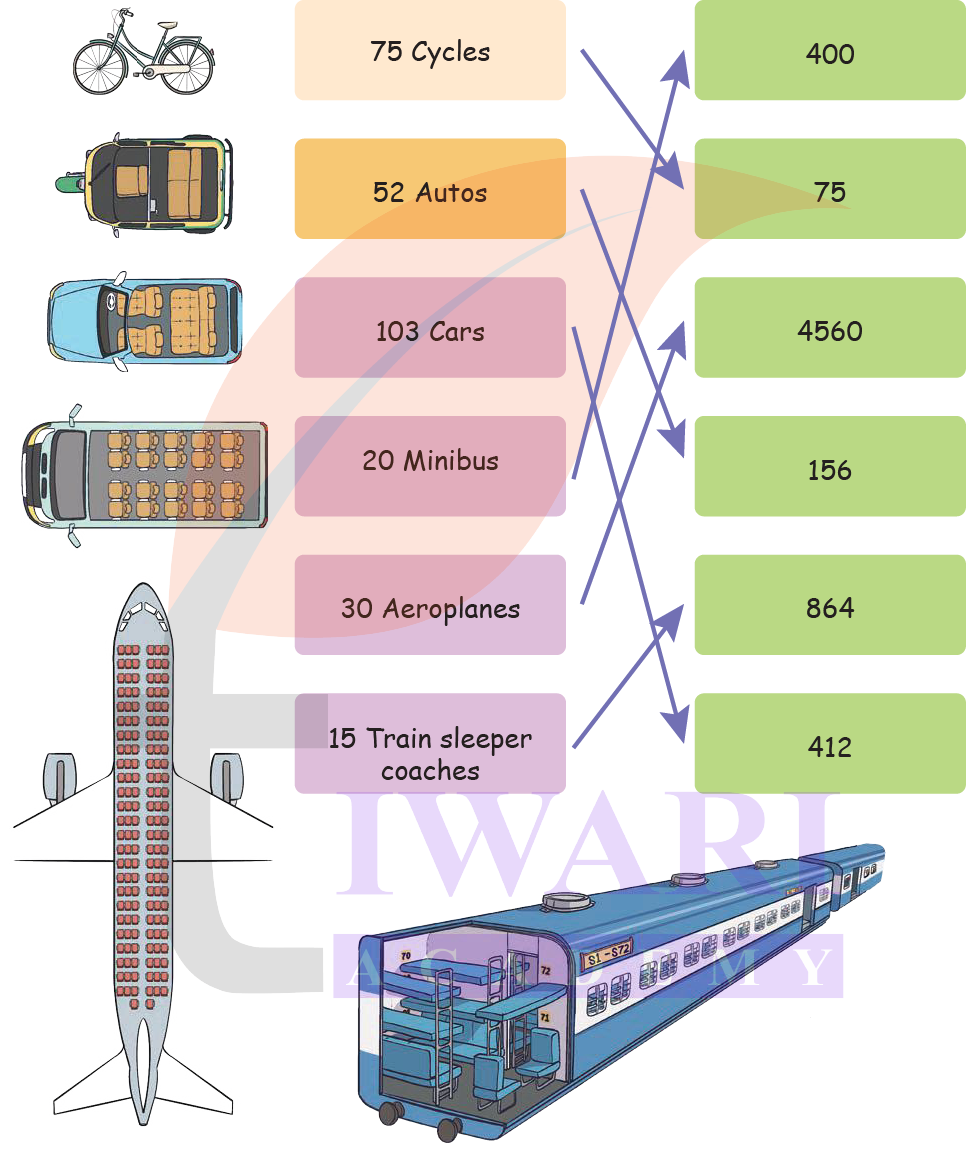
3. Assume each vechicle is travelling with full capacity. How many people can travel in each of these vehicles? Match them up.
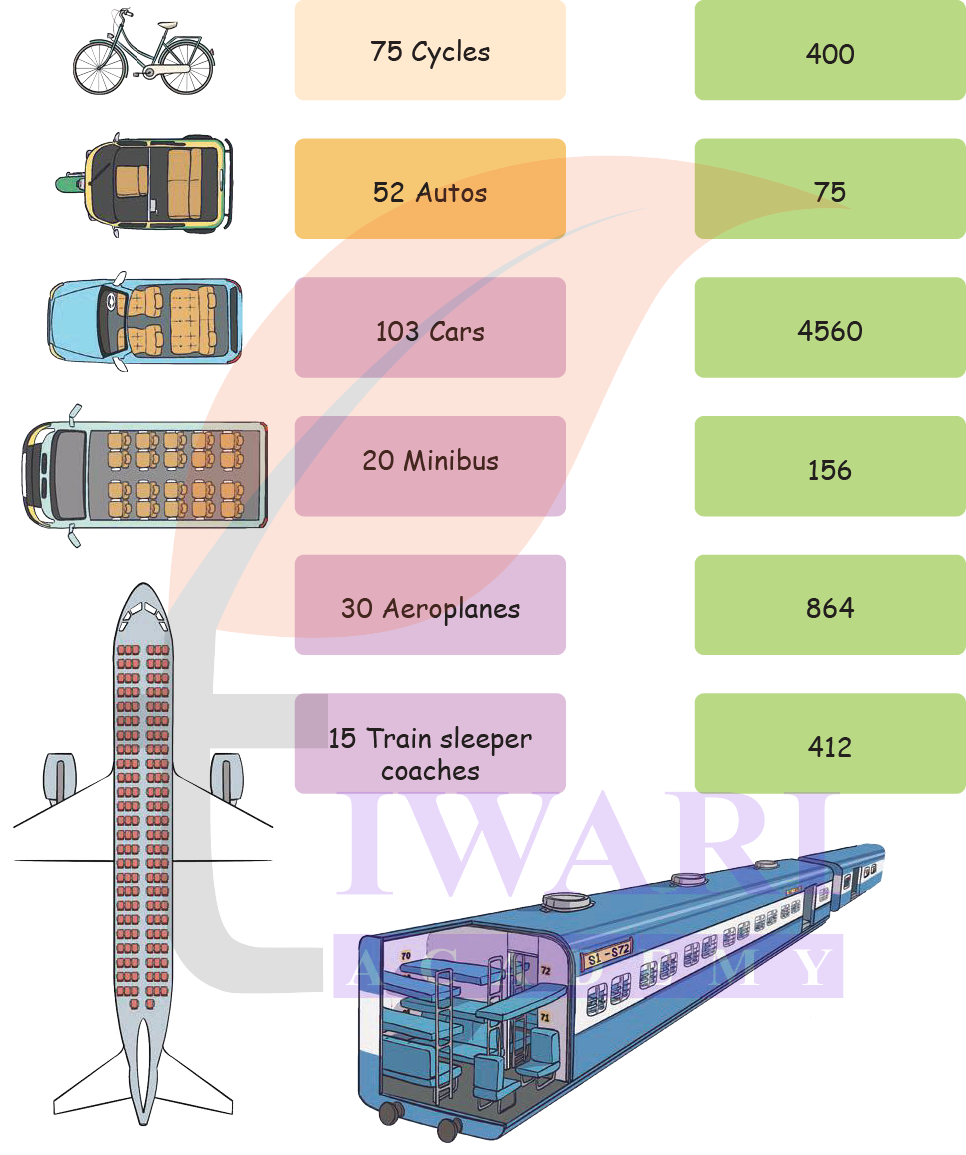
Answer:
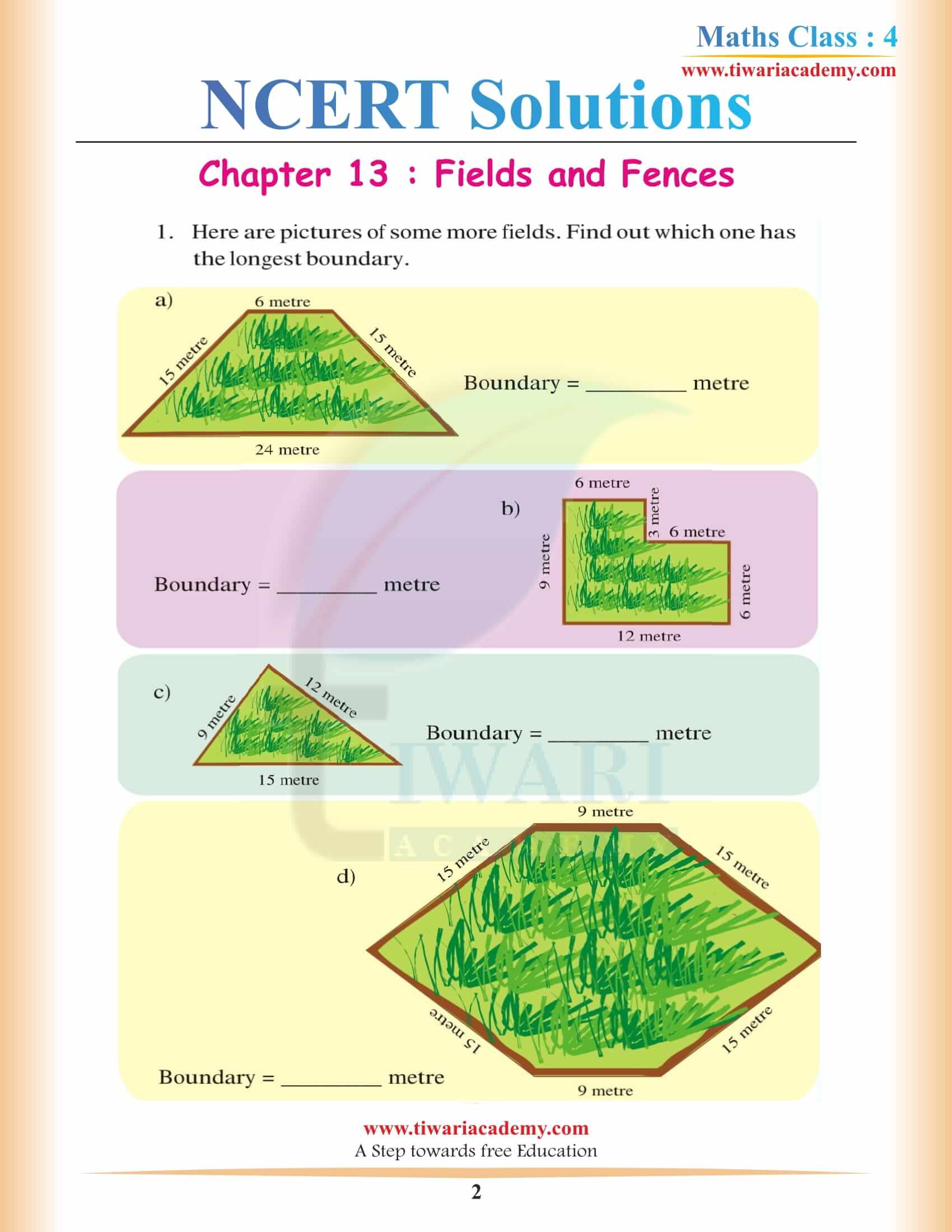
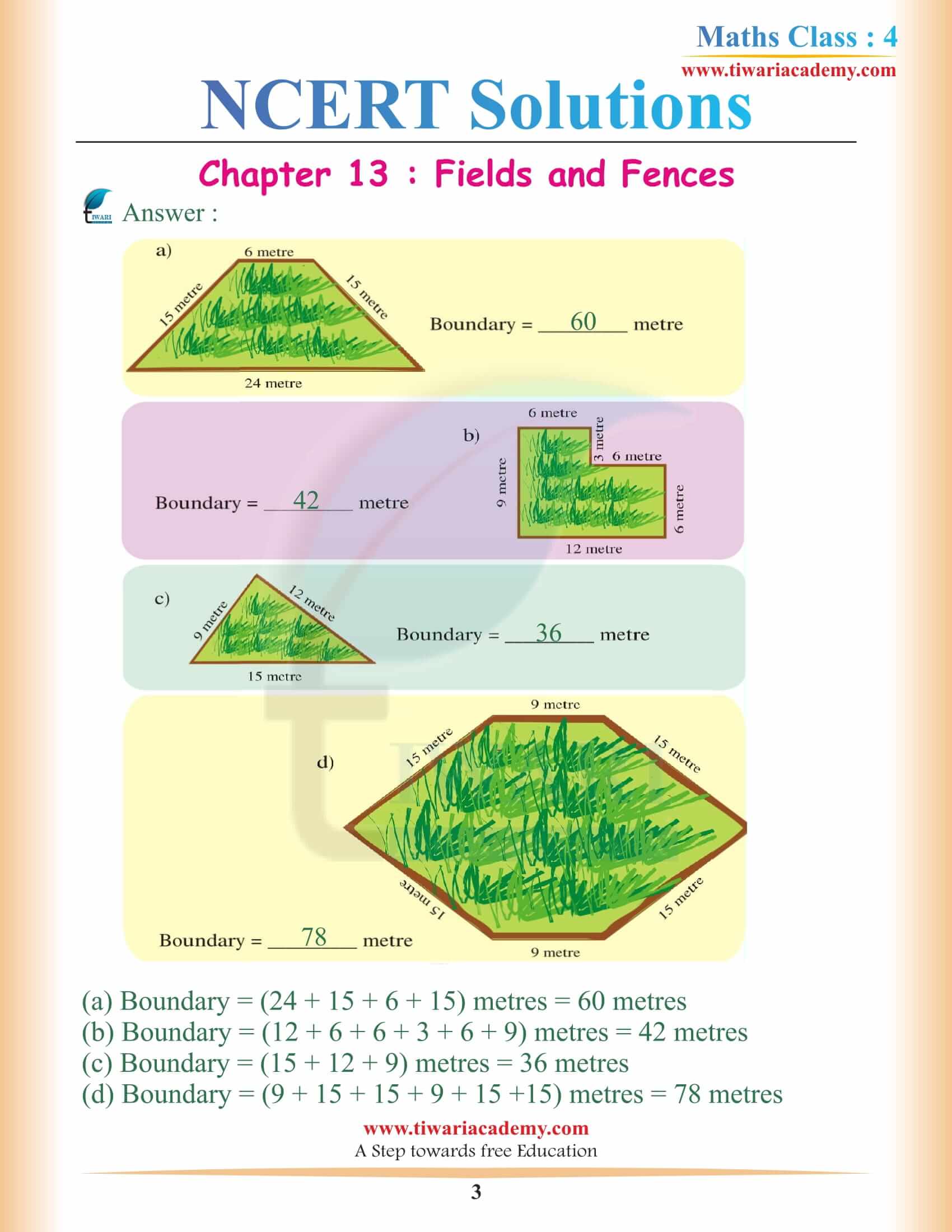
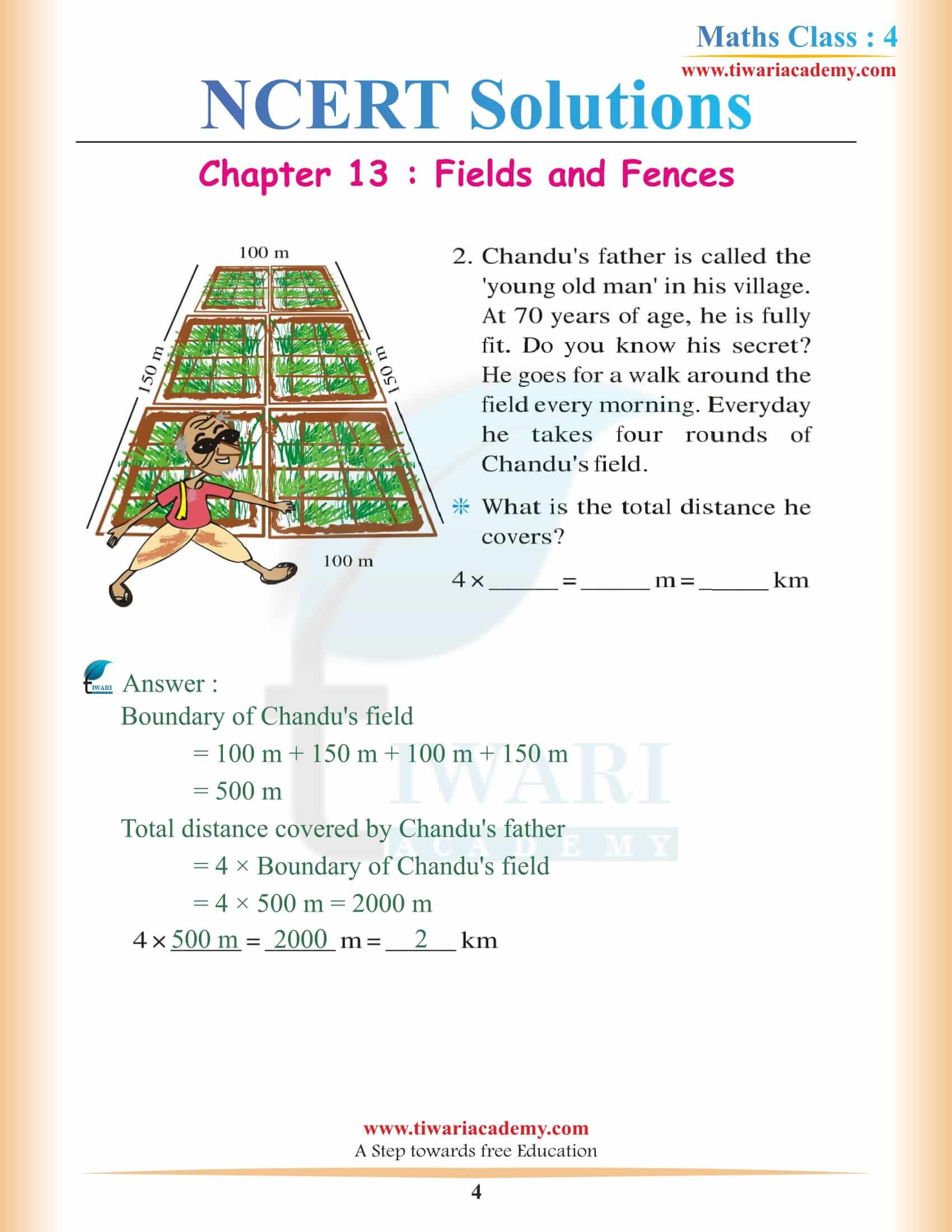
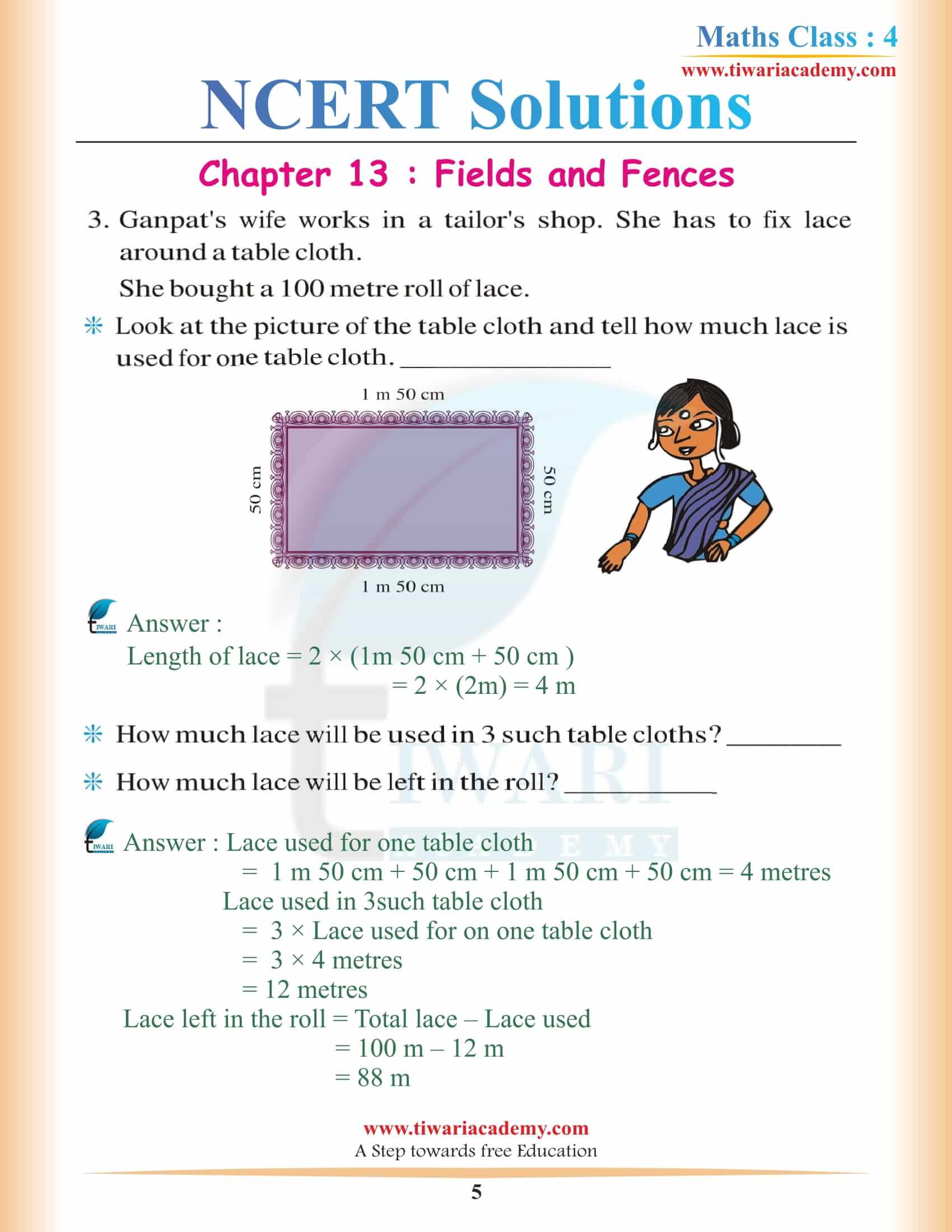
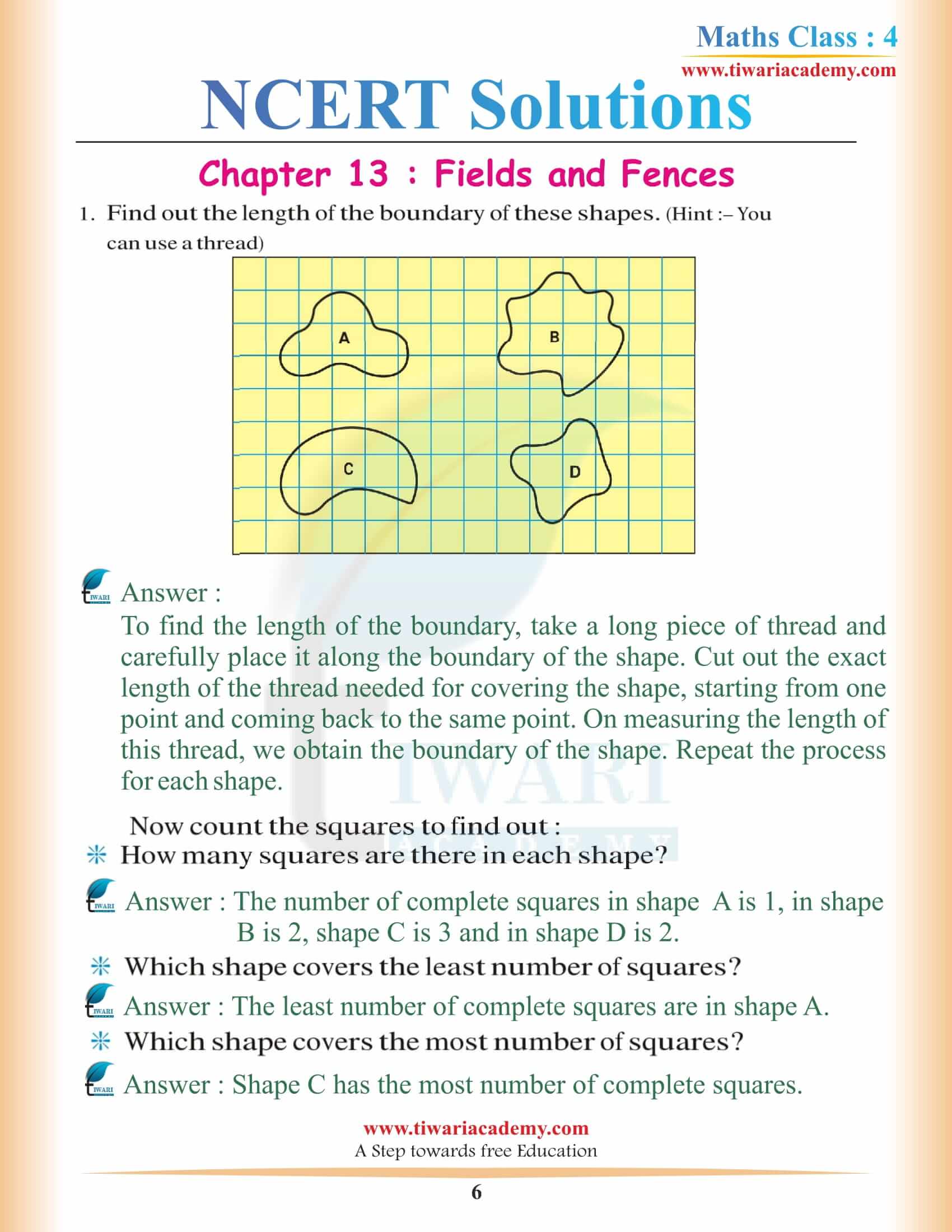
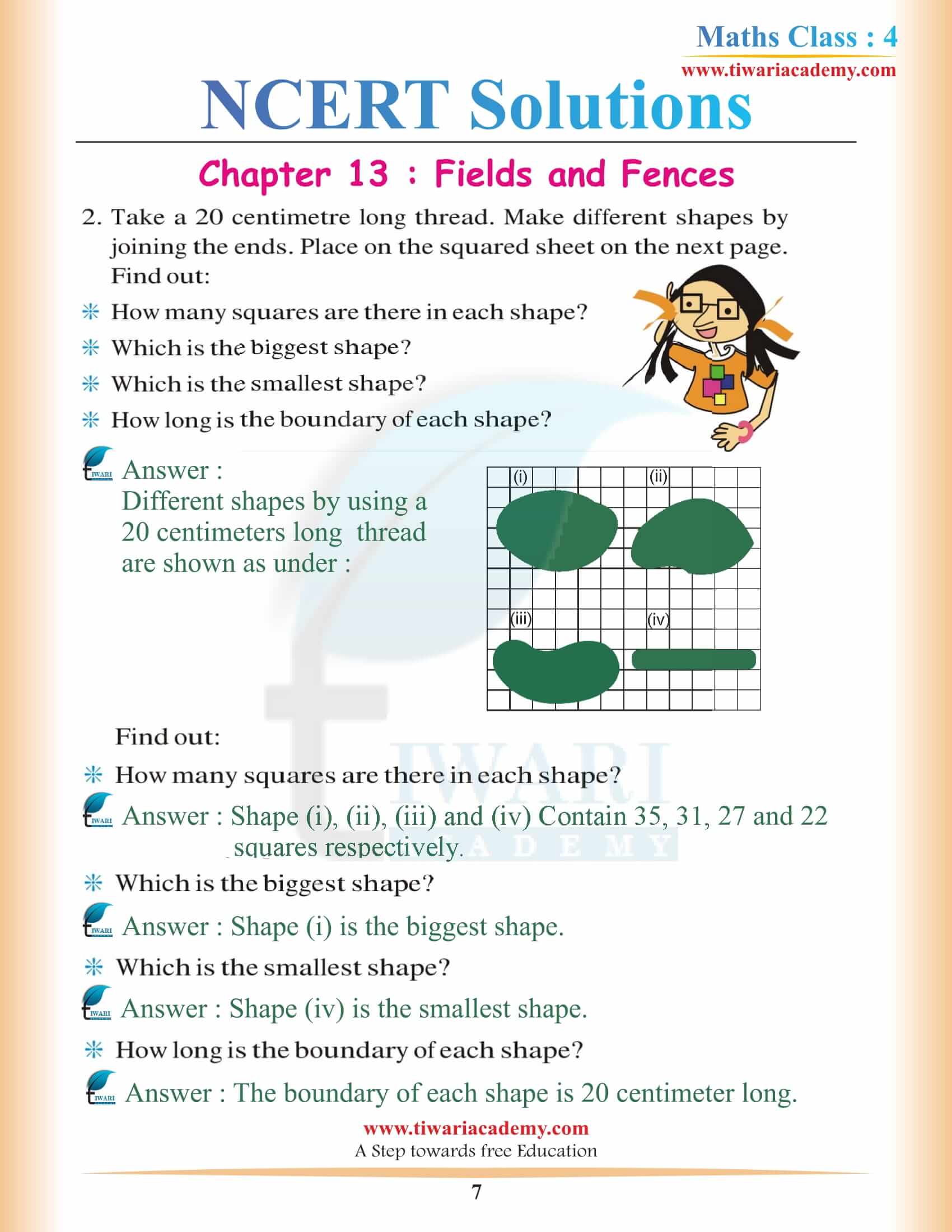
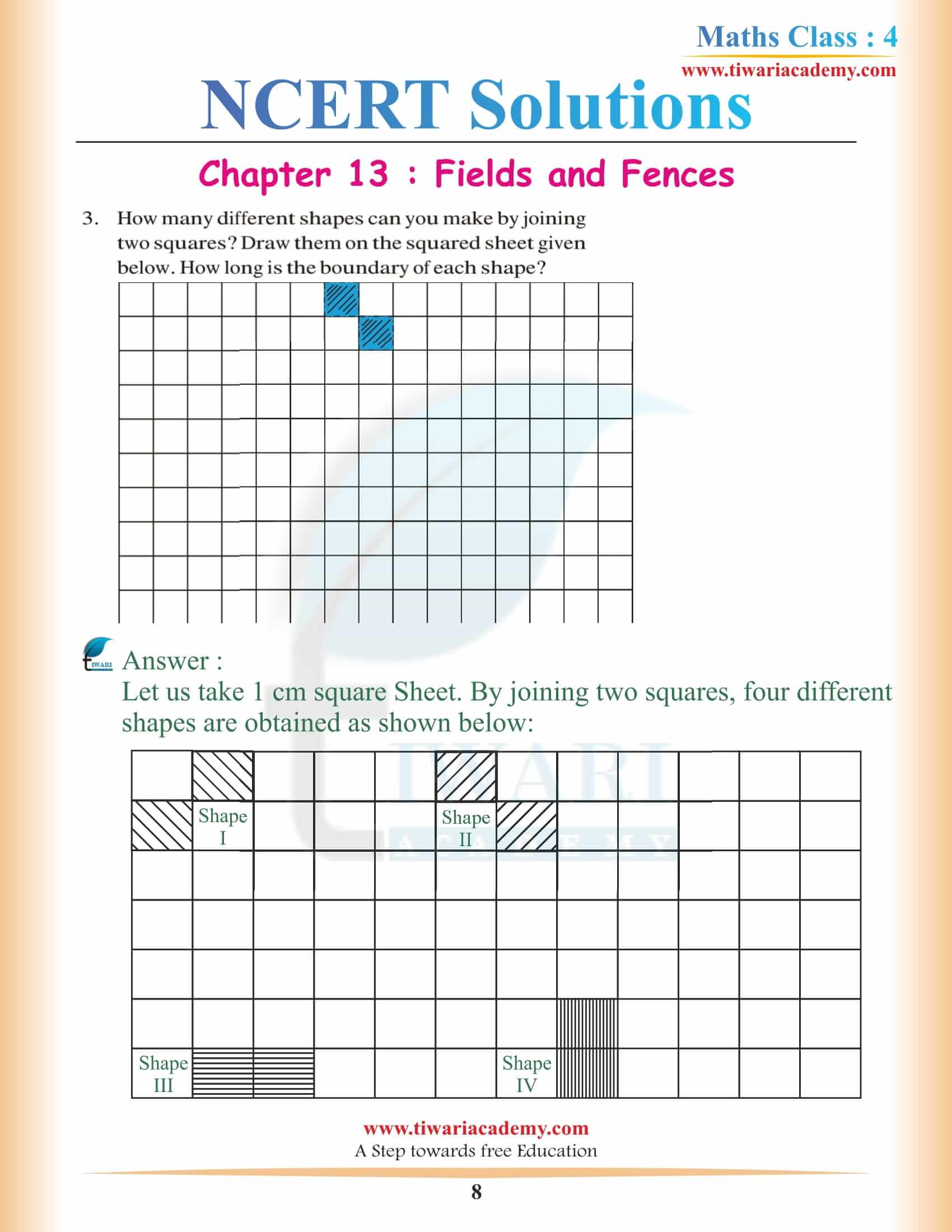
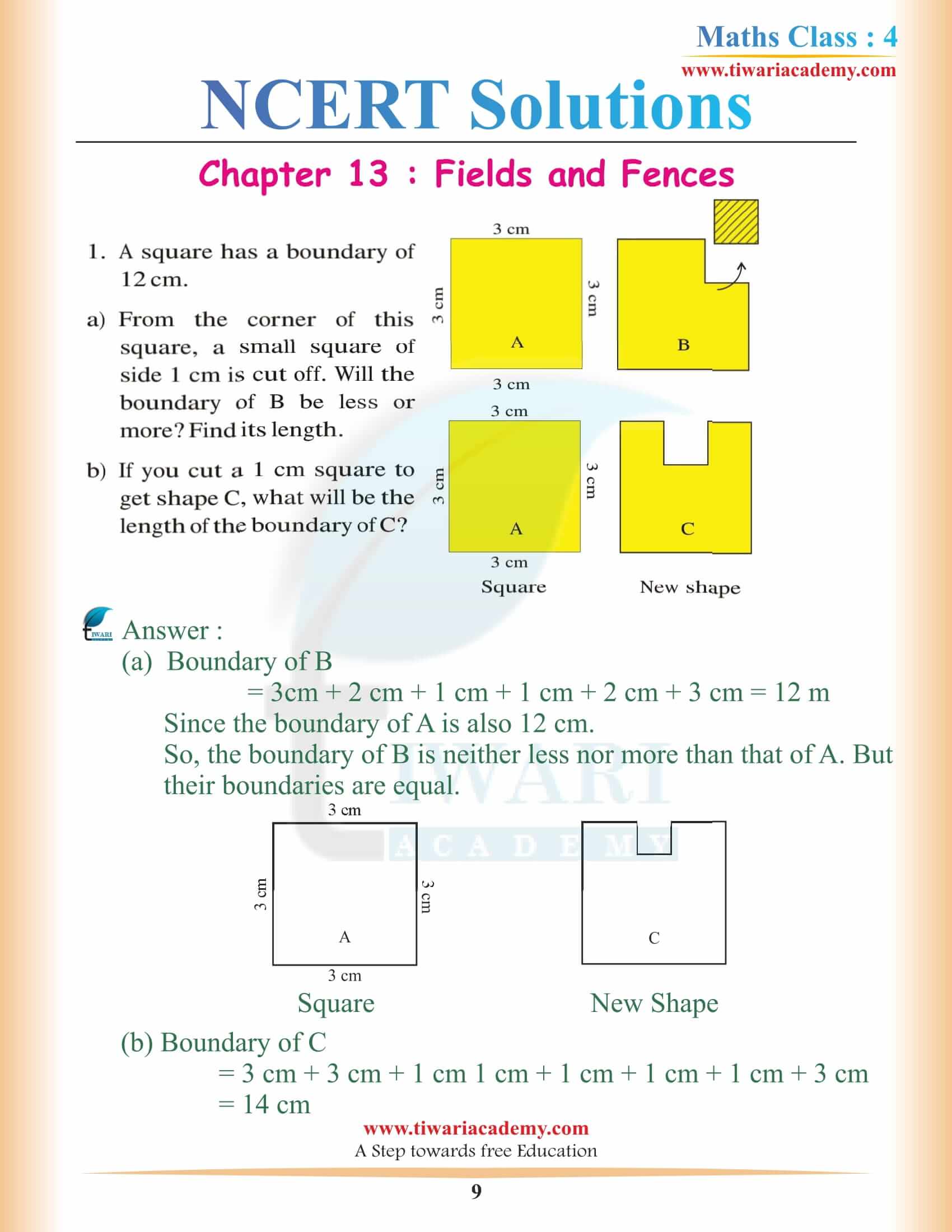
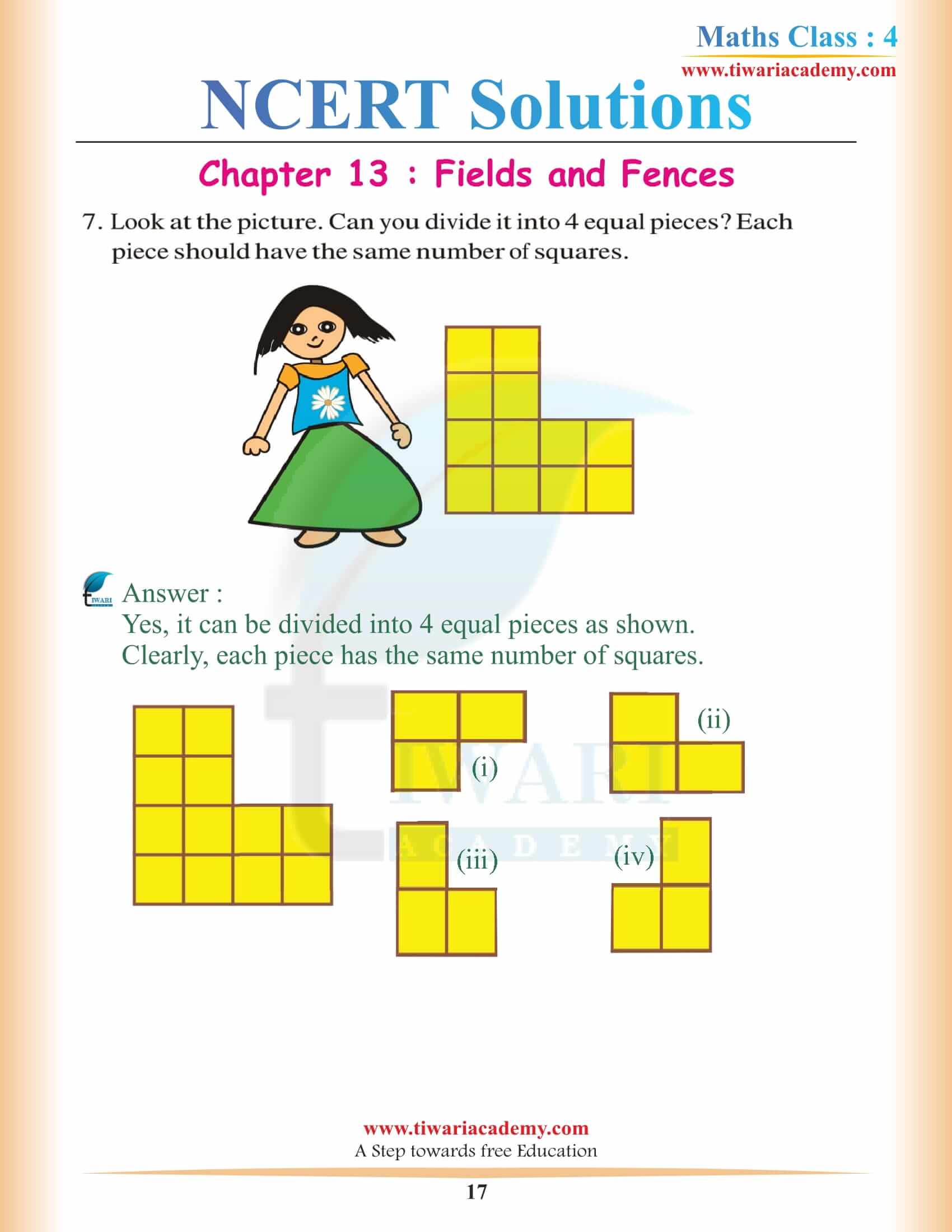
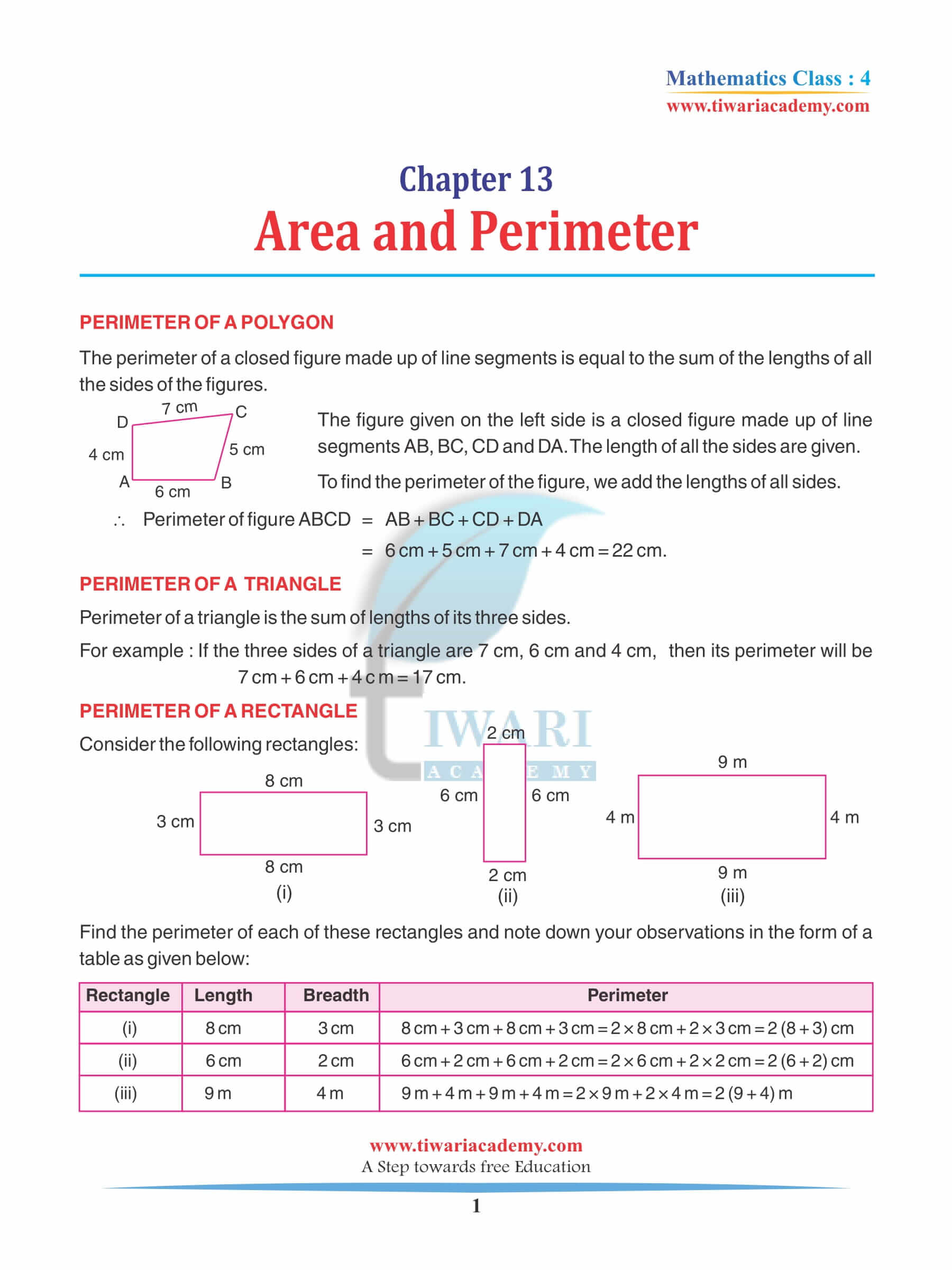
NCERT Solutions for Class 4 Maths Chapter 13 Fields and Fences
Class 4 NCERT Maths Chapter 13 Use of Fencing
Have you ever visited any farm, where farmers do the farming to grow various things like potatoes and many cabbages and lots of many things? If not have you seen any flower beds that are covered with the fence in order to keep them protected from the people who broke the trees and animals who can harm the trees.
Have you ever tried to think the area that is covered with the fence is not straight and then how they have still used the fence to cover it, is it really that important to cover the tree with the fence because everyone loves to get a flower?
4th Mathematics Textbook Chapter 13 Measurement of Fencing
This chapter will teach you how they can manage to measure the area. And it is important to know how they can measure the area because not only for fencing the bigger lands in farming that required them to be protected and this knowledge is required in such areas.
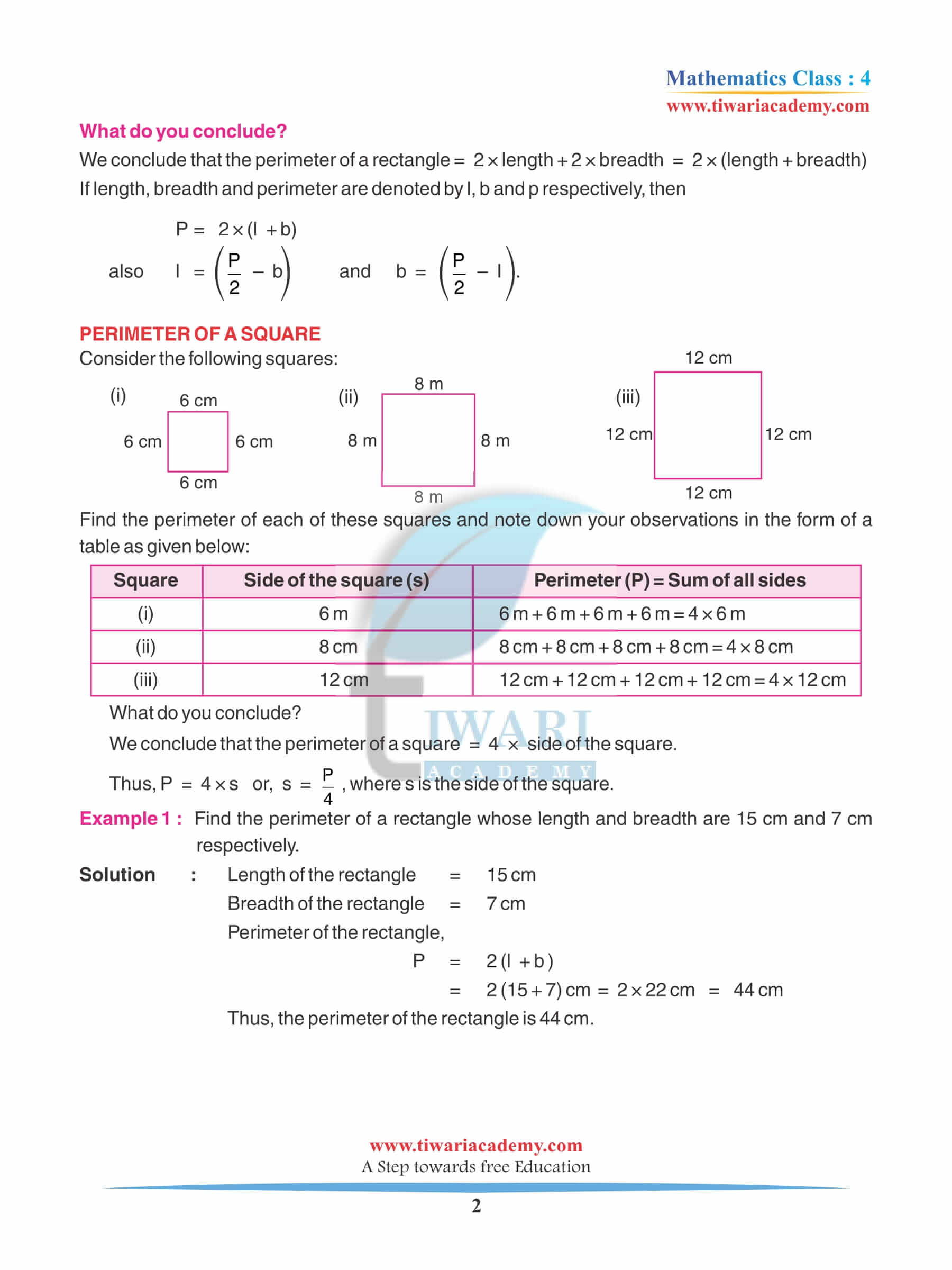
Class 4 NCERT Maths Book Chapter 13 Idea of Fencing
Now, imagine you have done such hard work to grow a rose in a plant and your little sibling goes and plucks it without your consent and now your hard work went in vain. Now you have to wait for a long time till it grows again but this time you hide it somewhere only you know and can enjoy the beauty of flower. The same idea goes to farming and with the help of such ideas.
This chapter will make you understand the shapes and addition methods so that you can solve the problems given in the chapter. Several such questions will make you utilize your knowledge of shapes and addition to get to answer that is required not only that you have to open your mindset to picture the farm in your mind.
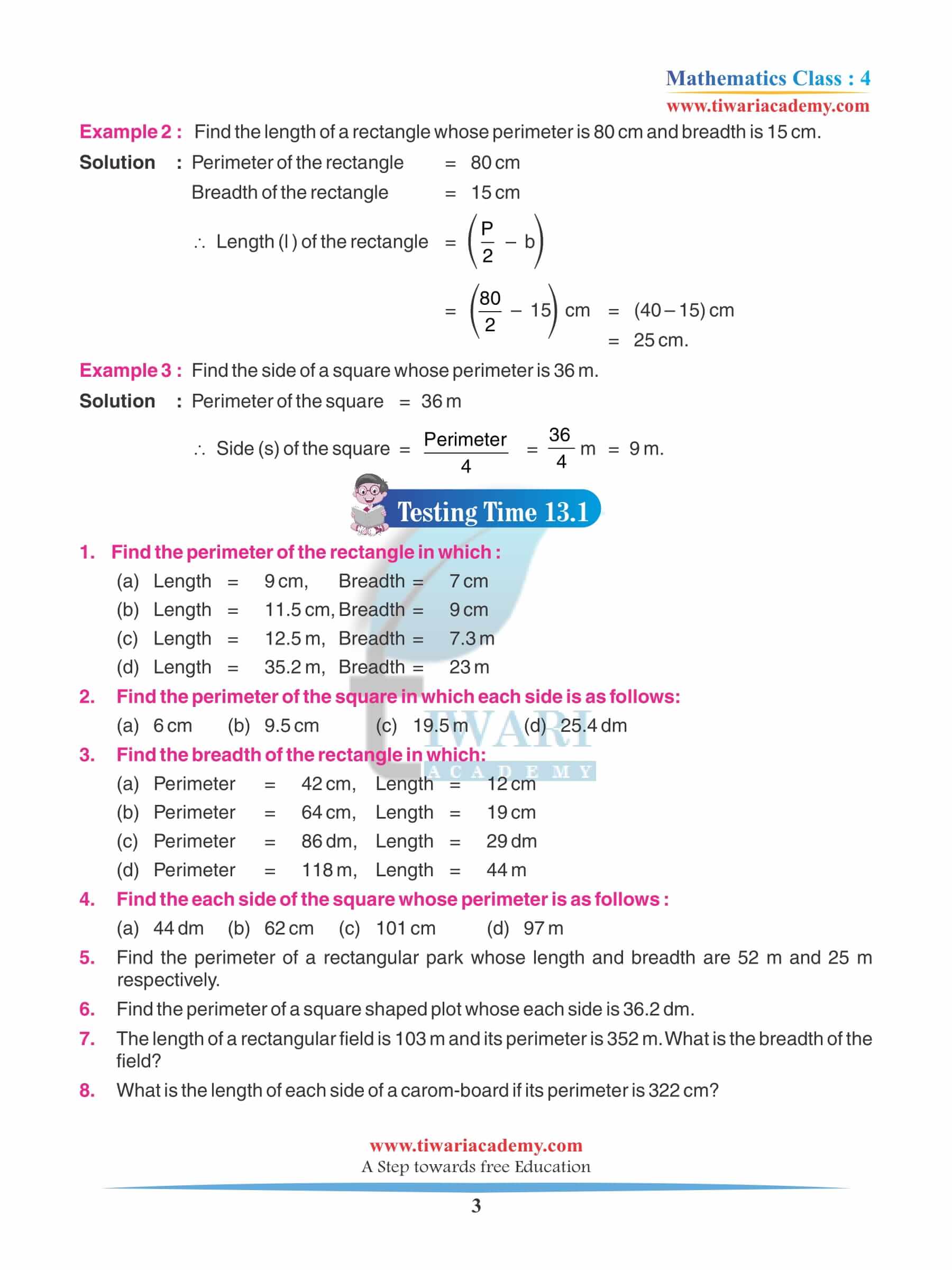
4th Standard NCERT Maths Chapter 13 Activity
Once you completely understand the fundamentals of this chapter you are suggested to get the Practice time to use the fundamentals that you have learned in this chapter to solve more questions and make sure that you have learned facts and now you won’t forget that easily. That is one of the reasons practice is been suggested to complete as it is an important part to cover.
Class 4 Maths Mela Chapter 13 Transport Museum – FAQs
What is Class 4 Maths Mela Chapter 13 The Transport Museum about?
Class 4 Maths Mela Chapter 13 The Transport Museum is designed to help students understand multiplication and division through real-life transport-related examples. The chapter takes children on a learning journey through buses, trains, aeroplanes, boats and museums to explain mathematical ideas in a relatable way. It introduces times tables from 11 to 20, multiplication by 10, 20, 50, 100 and division with and without remainders. Instead of rote learning, students are encouraged to observe patterns, split numbers and use logical reasoning. This chapter helps students see mathematics as a useful life skill rather than just a classroom subject.
How do NCERT Solutions help in understanding Class 4 Maths Mela Chapter 13?
NCERT Solutions for Class 4 Maths Mela Chapter 13 provide step-by-step explanations that make complex-looking problems simple and easy to understand. Each solution follows the exact method suggested in the textbook, such as splitting numbers, doubling, grouping and repeated subtraction. This helps students understand why a method works, not just how to get the answer. The solutions are written in clear, child-friendly language, making them ideal for self-study. Parents and teachers can also use these solutions to guide children effectively. Regular use of NCERT Solutions builds strong conceptual clarity and boosts confidence in solving mathematics problems independently.
Why are times tables comparisons important in Class 4 Maths Mela Chapter 13?
In Class 4 Maths Mela Chapter 13, comparing times tables such as times-2 with times-12 or times-5 with times-15 helps students identify patterns in multiplication. This approach shows children that higher tables are not entirely new but are built using simpler tables they already know. For example, times-12 can be understood as times-10 plus times-2. This method reduces the need for memorisation and encourages logical thinking. By recognising these relationships, students develop better number sense and mental math skills. Such comparisons make learning multiplication easier, faster and more enjoyable for young learners.
What types of word problems are covered in Class 4 Maths Mela Chapter 13?
Class 4 Maths Mela Chapter 13 includes a wide range of word problems based on real-life situations related to transport and travel. These problems involve calculating seating capacity in buses and trains, counting passengers, finding the total number of people travelling and dividing groups evenly. The chapter also includes money-related problems such as buying tickets using different notes and coins. Some questions involve division with remainders, helping students understand situations where exact sharing is not possible. These word problems improve comprehension skills, logical reasoning and the ability to apply math concepts in everyday situations.
How can students prepare for exams using Class 4 Maths Mela Chapter 13 solutions?
Students can prepare effectively for exams by practising NCERT Solutions for Class 4 Maths Mela Chapter 13 regularly. Since exam questions are directly based on the NCERT textbook, these solutions help students understand the correct methods and presentation of answers. Step-by-step explanations ensure that students do not miss important calculation steps. Practising word problems improves accuracy and confidence. Students can also revise tables, division methods and patterns quickly using these solutions before tests. Overall, consistent practice with NCERT Solutions ensures strong preparation, better performance and reduced exam stress.
What skills does Class 4 Maths Mela Chapter 13 help develop in students?
Class 4 Maths Mela Chapter 13 helps develop multiple important skills in young learners. It strengthens logical thinking by encouraging students to split numbers and observe patterns. Problem-solving skills are improved through real-life word problems. The chapter also enhances mental math, estimation and understanding of large numbers. Reading and comprehension skills improve as students interpret story-based questions carefully. Most importantly, the chapter builds confidence in mathematics by showing students that even large calculations can be solved using simple ideas. These skills form a strong foundation for advanced math concepts in higher classes.