NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Magnetic Effect of Electric Current in Hindi and English Medium for session 2025-26. Get here the revised question answers of chapter 12 class 10th science based on syllabus and new textbooks for CBSE 2025-26.
Prepare Class 10 Science for Exam
Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Solutions
Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Exercises Solutions
Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Intext Exercises
Class 10 Science Chapter 12 MCQ
Class 10 Science Chapter 12 in Hindi Medium
Class 10 Science Book Download in PDF
Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Board Questions
Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Extra Questions
| Class: 10 | Science |
| Chapter 12: | Magnetic Effect of Electric Current |
| Content: | Exercise and Intext Answers |
| Content Mode: | Online Text, PDF and Videos |
| Session: | CBSE 2025-26 |
| Medium: | English and Hindi Medium |
NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current explores various aspects of magnetism and its relationship with electric current. The main topics covered in Chapter 12 are introduction to Magnetism, and basics of magnetism, and the properties of magnets. Magnetic poles (north and south) and magnetic field lines. Magnetic field due to a current-carrying conductor, Investigating the magnetic field pattern around a straight conductor. Magnetic field lines around a bar magnet, examining the magnetic field lines around a bar magnet and their properties and defining magnetic field lines and their significance.
Magnetic Field due to a Current through a Straight Conductor
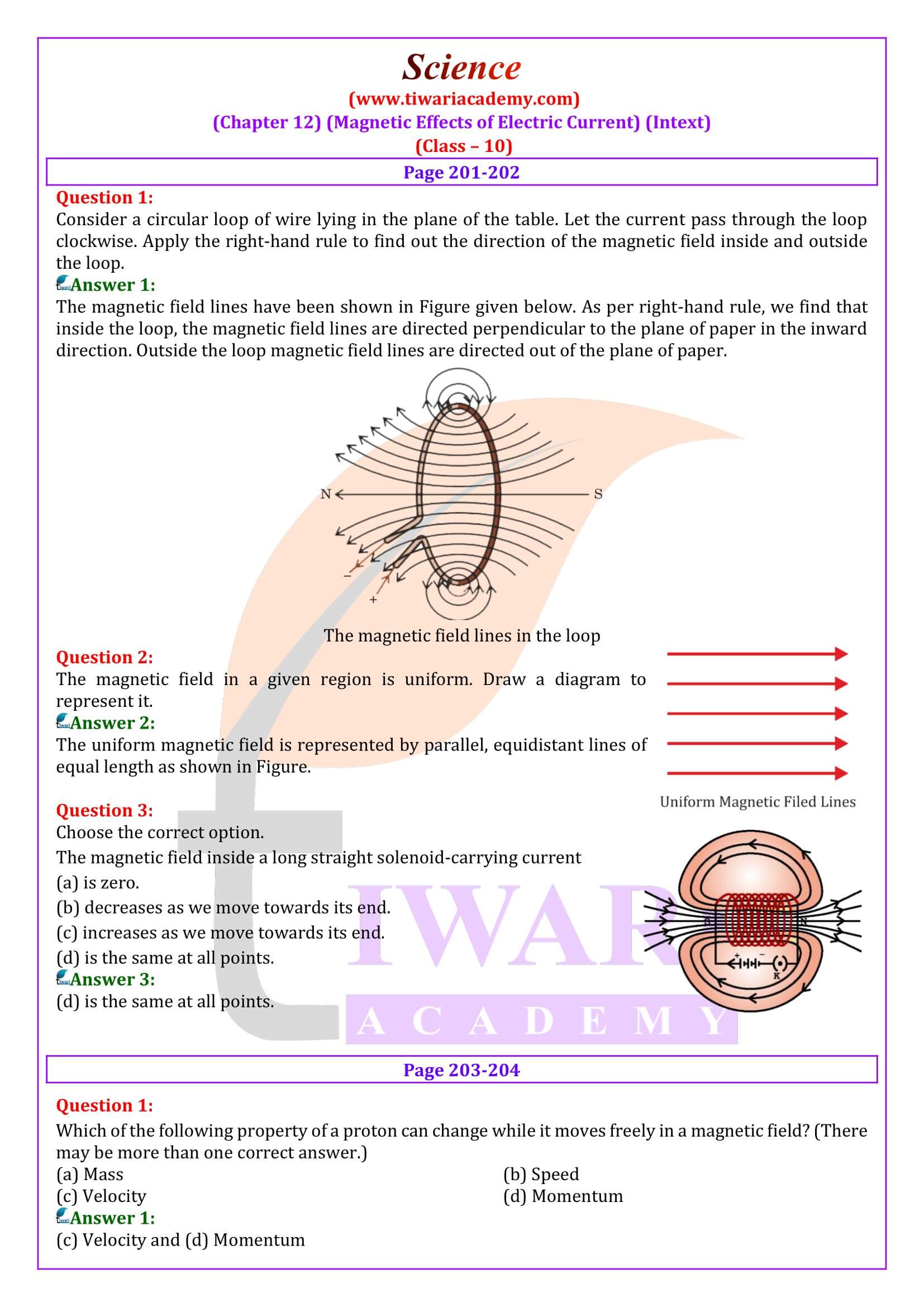
Understanding how the direction of the magnetic field depends on the direction of current flow in a straight conductor. Introduction to the right-hand thumb rule for determining the direction of the magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor. Magnetic Field due to a current through a circular loop, and exploring the magnetic field pattern around a circular loop carrying electric current, understanding the direction of the magnetic field lines within and outside the loop.
Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Answers in Hindi and English Medium
Magnetic Field due to a Current through a Solenoid
Understanding the magnetic field produced by a solenoid (a long coil of wire) when an electric current flows through it. Investigating the properties of the magnetic field inside a solenoid. Exploring the magnetic force experienced by a current-carrying conductor when placed in a magnetic field. Understanding the factors affecting the magnitude and direction of the force. Introduction to the working principle of an electric motor. Understanding how the interaction between magnetic fields and current in a coil results in rotational motion.
Electromagnetic Induction
Basics of electromagnetic induction and Faraday’s experiments. Understanding how a change in magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) in a coil. Electric generator, and introduction to the working principle of an electric generator. Understanding how electromagnetic induction is used to generate electric current. Domestic electric circuits, overview of domestic electric circuits and safety precautions. Understanding the use of fuses and circuit breakers. Electric power and electric energy, and calculation of electric power and electrical energy consumed by electrical appliances. Understanding the unit of electrical energy, the kilowatt-hour (kWh).
Preparing for NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current requires a structured approach and a focus on understanding the fundamental concepts related to magnetism and its connection with electric current. Here’s a strategy to help you prepare effectively. Read the chapter thoroughly, begin by reading the entire chapter from your NCERT textbook. Pay attention to definitions, explanations, and examples provided. Make concise notes while reading the chapter. Summarize key points, definitions, and formulas. Highlight important terms and concepts.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12
Class X Science chapter 12 intext questions on Page 224, Page 228, Page 229, Page 231, Page 233, Page 236, Page 237, Page 238 and Exercises are given. 10th Science Chapter 12 solutions are in English Medium PDF file format updated for academic session 2025-26 for UP Board, MP Board as well as those boards who are following CBSE Syllabus. Hindi Medium question answers in Hindi Medium are also given to view online or in PDF file format.
Focus on understanding the fundamental concepts such as magnetic field, magnetic field lines, and the relationship between electricity and magnetism. Right-hand thumb rule, familiarize yourself with the right-hand thumb rule for determining the direction of the magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor. Force on a current-carrying conductor, and understand the concept of the magnetic force experienced by a current-carrying conductor when placed in a magnetic field. Learn how to calculate the magnitude and direction of this force.
Electric Motors and Generators
Study the working principles of electric motors and generators. Understand how the interaction between magnetic fields and current results in motion or electricity generation. Electromagnetic induction, learn about electromagnetic induction and how a change in magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) in a coil. Understand the components and safety precautions in domestic electric circuits. Learn about the use of fuses and circuit breakers.
Practice solving numerical problems related to the magnetic effects of electric current, magnetic forces, and electromagnetic induction. Pay attention to units and use the appropriate formulas. Study and practice drawing diagrams to visualize magnetic field patterns and the operation of electric motors and generators. Real-life applications, relate the concepts in the chapter to real-life applications, such as how electric motors power appliances and how generators produce electricity.
Solve the exercise questions and examples given in your textbook. Practice questions related to magnetic effects, force calculations, and electromagnetic induction. Use online simulations and visual aids to better understand magnetic phenomena and their effects. Regularly revise your notes, diagrams, and important concepts from the chapter. Take practice tests or solve previous years’ board exam questions related to this chapter.
Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Extra Question Answer
State the law of magnetic poles.
Law Of Magnetic Poles: It states that like poles repel while unlike poles of magnets attracts each other. Thus, two N-poles repels, two S-poles repel while N-pole attracts S-pole.
Give some basic properties of magnets.
Some basic properties of magnets are as follows:
(i) Attractive property: a magnet attracts small pieces of iron, cobalt, nickel, etc.
(ii) Directive property: a freely suspended magnet aligns itself nearly in the north-south direction.
(iii) Law of magnetic poles: Like magnetic poles repel and unlike magnetic poles attract each other.
(iv)Magnetic poles exist in pairs: If we break a magnet into two pieces, we always get two small dipoles magnets. It is not possible to obtain an isolated N-pole or S-pole.
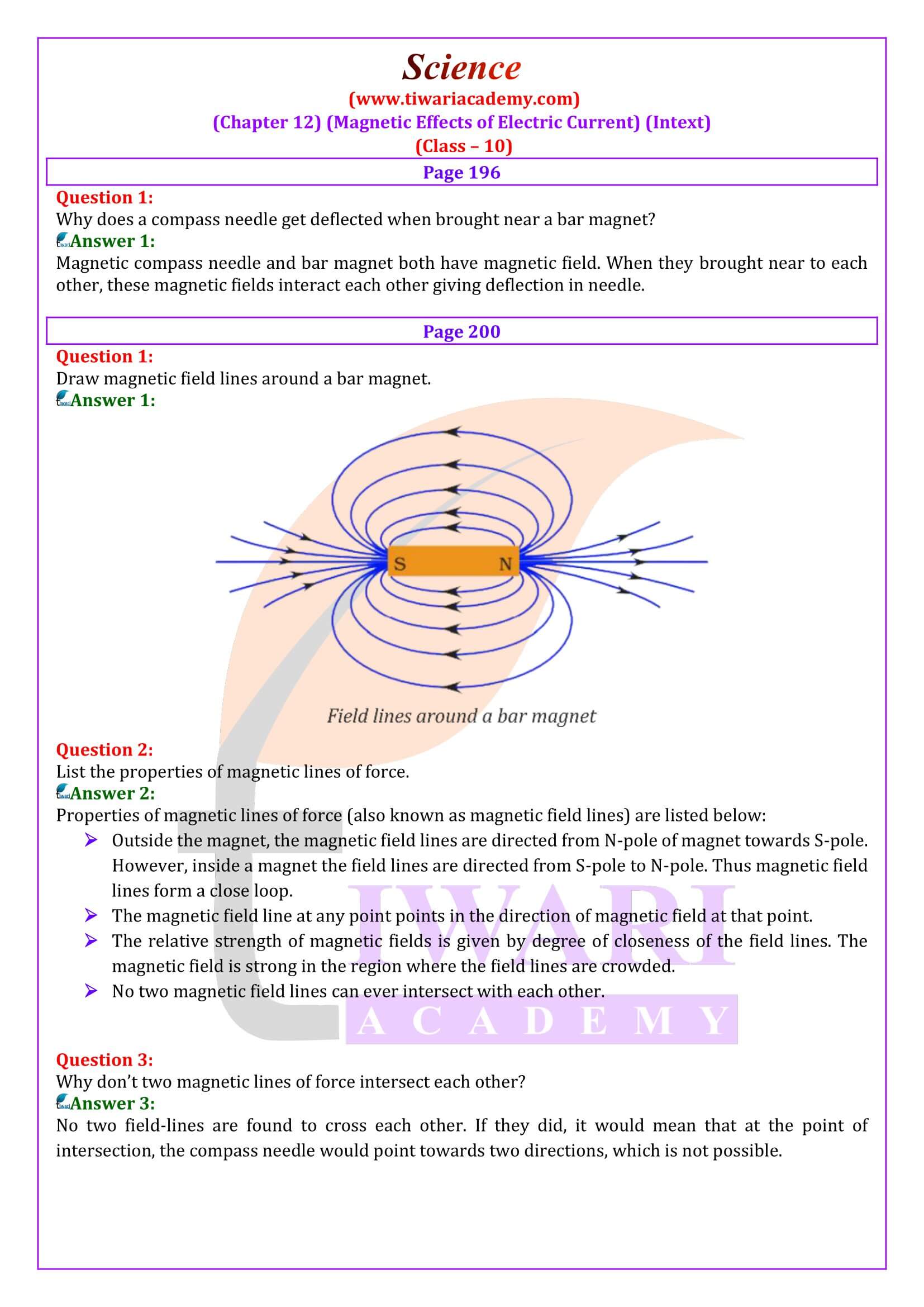
What are magnetic lines of force? Give their important properties.
Magnetic lines of force:
A magnetic line of force may be defined as the curve the tangent to which at any point gives the direction of the magnetic field at that point. It may also be defined as the path along with a free north pole tends to move.
Properties of line of force:
(i) These are closed curves which start in air from N-pole and end at the S-pole and then return to the N-pole through the interior of the magnet.
(ii) No two magnetic lines of force can interest each other.
(iii) They start from and end on the surface of the magnet normally.
(iv)The lines of force have a tendency to contract lengthwise and expand sidewise. This explains attraction between unlike poles and repulsion between like poles.
(v) The relative closeness of the lines of force gives a measure of the strength of the magnetic field which is maximum at the poles.
Mention some important uses of magnets in everyday life.
Uses of magnets:
(i) Magnets are used in radio and stereo speakers.
(ii) They are used in video and audio cassette tapes, on the hard discs and floppies for computers.
(iii) They are used in almirah and refrigerator doors to snap them closed.
(iv) In children’s toys.
(v) In medicine, the magnetic resonance image (MRI) scanners expose the inner parts of the patient’s body for detailed examination by doctors.
What are magnetic field lines? How is the direction of a magnetic field at a point determined?
A magnetic field line may be defined as the path along with a unit north pole tends to move. The direction of magnetic field is determined by placing a small compass needle. The direction of deflection of N-pole of the compass needle gives the direction of the magnetic field at that point.
Why does a current-carrying conductor experience a force in a magnetic field?
We know that an electric current flowing through a conductor produces a magnetic field. This field exerts a force on a magnet placed near the conductor. In accordance with Newton’s Third law, the magnets must also exerts an equal and opposite force on the current carrying conductor. Thus a magnetic field exerts a force on a current-carrying conductor. Such a force was first suggested and demonstrated experimentally by French Scientist Andre Marie Ampere in 1820.
In what way can the magnitude of the induced current be increased?
The magnitude of the induced current can be decreased by rapidly increasing or decreasing the number of magnetic field lines passing through a closed coil.
What is the function of an earth wire? Why is it necessary to earth the metallic appliances?
Earthing: Earthing of an electrical appliance means connecting the metallic body of the high powered appliance (electric iron, toaster, refrigerator, oven, etc.,) to the earth through the earth wire in the domestic circuit. The earth wire has green insulation cover and is connected to a metal plate deep in the earth near the house and hence it is at zero potential.
Function and importance of earthing: If, by chance, the live wire touches the metallic body of the electrical appliance, its current flows to the earth through the earth wire, which provides a low resistance conducting path for the current. Thus, the earth wire (or earthing) is used as a safety measure which ensures any leakage of current to the metallic body of the appliance keeps its potential equal to that of the earth (zero volt) and the user may not get a severe electric shock.
Download the best NCERT Solutions Apps Free to download for offline use. Important Questions related to Chapter 12 of class 10 Science and previous years board questions are also given with solutions and proper answers. UP Board Students are also using NCERT Books, use UP Board Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12 in Hindi Medium from here.
If you have any doubts or find certain concepts challenging, don’t hesitate to seek help from your teacher or classmates. Maintain a positive attitude and stay confident in understanding and applying the concepts. By following these steps and deeply understanding the concepts, you can prepare effectively for NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current. Practical applications and numerical problems are key aspects of this chapter, so practicing both is essential for success.
Tiwari Academy is a valuable online resource to assist students in their preparation for NCERT 10th Science Chapter 12 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current. Here’s how Tiwari Academy helps students in their preparation. Tiwari Academy provides detailed solutions to the exercises and questions found in the NCERT textbook for Chapter 12. These solutions help students understand the correct approach to solving problems and verify their answers. Additional. It often offers supplementary practice questions and exercises that go beyond what’s provided in the NCERT textbook. These extra questions allow students to practice and reinforce their understanding of the chapter.
10th Science Chapter 12 Answers in English & Hindi Medium
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Physics Chapter 12 Magnetic Effect of Electric Current all question answers updated for new academic session. Download in PDF format or use it online without downloading free. Download NCERT Solutions for class 10 all other subjects in Hindi and English medium.
Tiwari Academy provides comprehensive explanatory notes and study materials that simplify complex concepts in Chapter 12. These materials can be beneficial for students who need additional explanations and examples. Tiwari Academy website offers video tutorials on various topics. These videos can help students visualize and understand challenging concepts more effectively. It includes interactive simulations and animations related to the concepts in Chapter 12. These tools can make learning more effective and help students grasp abstract ideas related to magnetism and electricity.
Tiwari Academy is a useful supplementary resource for students preparing for NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 12, Magnetic Effects of Electric Current. It provides additional practice, explanations, and interactive tools to support their learning and help them perform well in their exams.
NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 12, Magnetic Effects of Electric Current, is of significant importance from the examination point of view for several reasons. Chapters in the NCERT syllabus are designed to carry weightage in board exams. Chapter 12, like other chapters, contributes to your overall score in the science subject. This chapter covers fundamental concepts related to magnetism and its relationship with electric current. A strong grasp of these concepts is essential for understanding more advanced topics in physics.
Questions for Practice
Question 1:
In a household circuit, why are all the distribution circuit kept in parallel? OR What are the advantages of connecting different electrical appliances in parallel? Mention any three advantages.
Answer 1:
It has the following advantages:
(i) If one line is overloaded, the fuse in this circuit only will be blown off, other distribution lines are protected.
(ii) There is a constant potential difference across each line.
(iii) If more lines are added in the circuit, it makes no difference to the other lines as p.d. is maintained at a constant value.
Questions related to magnetic fields, magnetic forces, electromagnetic induction, and calculations involving electric current are commonly included in board exams. Numerical problem-solving skills are crucial for this chapter. Understanding the working principles of electric motors and generators is a key aspect of this chapter. Questions assess your knowledge of these devices and their applications. Familiarity with the right-hand thumb rule for determining the direction of the magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor is important. Questions ask you to apply this rule to solve problems.
Important Questions on 10th Science Chapter 12
List three sources of magnetic fields.
Three methods of producing magnetic field are as follows: Magnetic field can be produced by placing a permanent bar magnet or a horse-shoe magnet at the place, where magnetic field is required. Magnetic field is produced around a current-carrying straight conductor or a current carrying circular coil. A very good method to produce magnetic field is due to flow of current in a solenoid.
When is the force experienced by a current–carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field largest?
The force experienced by a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field is largest when the current-carrying conductor is placed in a direction perpendicular to that of magnetic field.
Name some devices in which electric motors are used.
Electric motors are used in all such devices where we want to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy so as to drive that machine. In our houses, electric motors are being fitted in electric fans, coolers, air conditioners, mixer grinders, washing machines, refrigerators, juicers, computers etc. In factories, motors are used in almost all machines.
A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is (i) pushed into the coil, (ii) withdrawn from inside the coil, (iii) held stationary inside the coil?
A current induces in a solenoid if a bar magnet is moved relative to it. This is the principle of electromagnetic induction. (i) When a bar magnet is pushed into a coil of insulated copper wire, a current is induced momentarily in the coil. As a result, the needle of the galvanometer deflects momentarily in a particular direction. (ii) When the bar magnet is withdrawn from inside the coil of the insulated copper wire, a current is again induced momentarily in the coil in the opposite direction. As a result, the needle of the galvanometer deflects momentarily in the opposite direction. (iii) When a bar magnet is held stationary inside the coil, no current will be induced in the coil. Hence, galvanometer will show no deflection.
Two circular coils A and B are placed closed to each other. If the current in the coil A is changed, will some current be induced in the coil B? Give reason.
Yes, a current is induced in the coil B. When the current in the coil A is changed, the magnetic field associated with it also changes. As coil B is placed close to A, hence magnetic field lines around this coil also change. Due to change in magnetic field lines associated with coil B, an induced current is also induced in it.
When does an electric short circuit occur?
If either the insulation of wires used in an electrical circuit is damaged or there is a fault in the appliance, live wire and neutral wire may come in direct contact. As a result, the current in the circuit abruptly rises and short-circuiting occurs.
What is the function of an earth wire? Why is it necessary to earth metallic appliances?
The metallic body of electric appliances is connected to the earth by means of earth wire so that any leakage of electric current is transferred to the ground. This prevents any electric shock to the user. That is why earthing of the electrical appliances is necessary.
Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet?
Magnetic compass needle and bar magnet both have magnetic field. When they brought near to each other, these magnetic fields interact each other giving deflection in needle.
Why don’t two magnetic lines of force intersect each other?
No two field-lines are found to cross each other. If they did, it would mean that at the point of intersection, the compass needle would point towards two directions, which is not possible.
What is Fleming’s left-hand rule?
According to Fleming’s left-hand rule, stretch the thumb, forefinger and middle finger of your left hand such that they are mutually perpendicular. If the first finger points in the direction of magnetic field and the second finger in the direction of current, then the thumb will point in the direction of motion or the force acting on the conductor.
What is the principle of an electric motor?
The working principle of an electric motor is based on the magnetic effect of current. A current-carrying loop experiences a force and rotates when placed in a magnetic field. The direction of rotation of the loop is given by the Fleming’s left-hand rule.
What is the role of the split ring in an electric motor?
The split ring in the electric motor acts as a commutator. The commutator reverses the direction of current flowing through the coil after each half rotation of the coil. Due to this reversal of the current, the coil continues to rotate in the same direction.
What is the principle of an electric generator?
An electric generator is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When a rectangular coil is rotated in a uniform magnetic field, an induced voltage is generated between the ends of the coil.
Name some sources of direct current.
Some sources of direct current are a cell, a battery and a D.C. generator.
Which sources produce alternating current?
A.C. generator and invertors (used in house for emergency power supply) produces alternating current.
What precaution should be taken to avoid the overloading of domestic electric circuits?
The precautions that should be taken to avoid the overloading of domestic circuits are as follows: Too many appliances should not be connected to a single socket. Too many appliances should not be used at the same time. Faulty appliances should not be connected in the circuit. Fuse should be connected in the circuit.
Electromagnetic Induction
Questions related to Faraday’s experiments and electromagnetic induction are often included. Understanding how a change in magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) in a coil is crucial. This chapter discusses the practical applications of magnetic effects, such as electric motors and generators. Questions related to these applications and their significance in real-life scenarios are important. The chapter emphasizes problem-solving and analytical skills, which are valuable not only for exams but also for developing critical thinking abilities.
Question 2:
State Oersted observation. OR How can it be shown that a magnetic field exist around a wire through which a direct electric current is passing?
Answer 2:
An magnetic needle brought close to a straight current carrying wire aligns itself perpendicular to the wire, reversing the direction of current reverses the direction of deflection. This shows that the current carrying wire is associated with a magnetic field.
Questions from Board Papers
Question 1:
Explain the meaning of the term electromagnetic induction. In what factors does the value of induced current produced in a circuit depend? Name and state the rule used for determination of direction of induced current. State one practical application of this phenomenon in everyday life.
Answer 1:
(i) The term electromagnetic induction means including electricity by magnetism. Whenever, the magnetic flux linked with a closed circuit changes, an induced potential and hence an induced current is set up in it. This phenomenon is called electromagnetic induction.
(ii) The value of current induced in a circuit depends on the rate of change of magnetic flux linked with the closed circuit.
(iii) Fleming’s right hand rule is used to find the direction of induced current.
(iv) Electric generator is an important practical application based on electromagnetic induction.
Question 2:
What are direct and alternating currents? OR What is difference between direct current and alternating current?
Answer 2:
Direct Current: A direct current is that current which flows with constant magnitude in the same direction.
Alternating Current: An alternating current is that current whose magnitude changes continuously with time and whose direction reverses after equal intervals of time.
Some questions require applying the knowledge of magnetic effects to real-world situations or scenarios, testing your ability to connect theoretical knowledge with practical situations. In conclusion, NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 12, Magnetic Effects of Electric Current, is indeed important from the examination point of view. It covers fundamental concepts related to magnetism and electricity, practical applications, and numerical problem-solving skills. A good score in this chapter contributes to your overall performance in the science subject. Therefore, it is advisable to dedicate sufficient time and effort to prepare effectively for this chapter.
Which questions of chapter 12 of class 10th Science are expected for the board exams?
Chapter 12 of class 10th Science has 39 questions (21 questions are in between chapter 12 and 18 questions are in the back exercise of chapter 12). All the questions of this chapter are important for the exams and can come in the board exam. Students should practice all questions of this chapter to score full marks in this chapter in the board exam.
Can students complete chapter 12 of class 10th Science in 2 days?
No, students can’t complete chapter 12 of class 10th Science in 2 days. Students require at least 10-15 days to complete chapter 12 of class 10th Science if they give at least 1-2 hours per day to this chapter. This time also depends on student’s working speed, efficiency, capability, and many other factors.
Which topics will students learn in chapter 12 of class 10th Science for exams?
In chapter 12 of class 10th Science, students will learn:
- Magnetic field and field lines
- Magnetic field due to a current-carrying conductor
- Magnetic field due to a current through a straight conductor
- Right-hand thumb rule.
- Magnetic field due to a current through a circular loop.
- Magnetic field due to a current in a solenoid.
- Force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field.
- Electric motor
- Electromagnetic induction
- Electric generator
- Domestic electric circuits.
Is chapter 12 of class 10th Science easy?
Chapter 12 of class 10th Science is not easy and not tough. It lies in the mid of simple and tough. However, the difficulty level of any chapter varies from child to child. So, chapter 12 of class 10th Science is easy, or tough depends on children also. Some children find it hard, some find it easy, and some find it in the middle of easy and hard.
Are there any important activity in chapter 12 (Magnetic Effects of Electric Current) of grade 10th Science?
There are nine activities in chapter 12 (Magnetic Effects of Electric Current) of grade 10th Science. All the activities are nice, interesting, and logical. These activities help students to understand the chapter easily and practically. Also, these activities help the teachers to teach chapter easily to the students. Students enjoy doing these activities in school.